Antioxidants 2023, 12(2), 448; https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox12020448 - 10 Feb 2023
Cited by 2 | Viewed by 3302
Abstract
Reduced glutathione (GSH) and ascorbic acid (AA) are the two most abundant low-molecular-weight antioxidants in mammalian tissues. GclmKO knockout mice lack the gene encoding the modifier subunit of the rate-limiting enzyme in GSH biosynthesis; GclmKO mice exhibit 10–40% of normal tissue
[...] Read more.
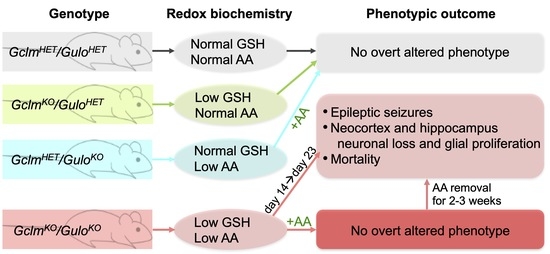
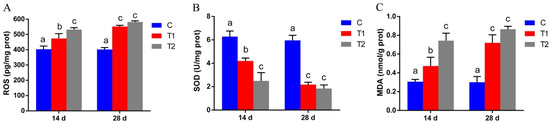
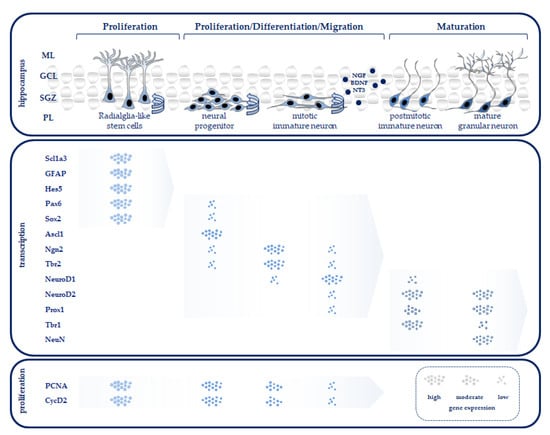
Reduced glutathione (GSH) and ascorbic acid (AA) are the two most abundant low-molecular-weight antioxidants in mammalian tissues. GclmKO knockout mice lack the gene encoding the modifier subunit of the rate-limiting enzyme in GSH biosynthesis; GclmKO mice exhibit 10–40% of normal tissue GSH levels and show no overt phenotype. GuloKO knockout mice, lacking a functional Gulo gene encoding L-gulono-γ-lactone oxidase, cannot synthesize AA and depend on dietary ascorbic acid for survival. To elucidate functional crosstalk between GSH and AA in vivo, we generated the GclmKO/GuloKO double-knockout (DKO) mouse. DKO mice exhibited spontaneous epileptic seizures, proceeding to death between postnatal day (PND)14 and PND23. Histologically, DKO mice displayed neuronal loss and glial proliferation in the neocortex and hippocampus. Epileptic seizures and brain pathology in young DKO mice could be prevented with AA supplementation in drinking water (1 g/L). Remarkably, in AA-rescued adult DKO mice, the removal of AA supplementation for 2–3 weeks resulted in similar, but more severe, neocortex and hippocampal pathology and seizures, with death occurring between 12 and 21 days later. These results provide direct evidence for an indispensable, yet underappreciated, role for the interplay between GSH and AA in normal brain function and neuronal health. We speculate that the functional crosstalk between GSH and AA plays an important role in regulating glutamatergic neurotransmission and in protecting against excitotoxicity-induced brain damage.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Topic Antioxidants and Oxidative Stress in Brain Health)
►
Show Figures