1
NIT-O2S, UTBM, University Bourgogne Franche-Comté, 90010 Belfort, France
2
CIAD, UTBM, University Bourgogne Franche-Comté, 90010 Belfort, France
Appl. Sci. 2023, 13(8), 5035; https://doi.org/10.3390/app13085035 - 17 Apr 2023
Cited by 9 | Viewed by 2980
Abstract
Currently, road transport constitutes a considerable proportion of global fossil fuel consumption, as well as CO2 and pollutant emissions. To mitigate transportation energy consumption, two primary approaches have emerged: the large-scale adoption of Hybrid Electric Vehicles (HEVs) and Plug-In Electric Vehicles (PHEVs),
[...] Read more.
Currently, road transport constitutes a considerable proportion of global fossil fuel consumption, as well as CO2 and pollutant emissions. To mitigate transportation energy consumption, two primary approaches have emerged: the large-scale adoption of Hybrid Electric Vehicles (HEVs) and Plug-In Electric Vehicles (PHEVs), as well as the implementation of eco-driving strategies, which present an immediate and low-cost solution. In this context, this paper provides a comprehensive review of these two technologies and their integration for connected HEV/PHEVs. We summarize the framework of recent approaches to incorporate fusion road information in single-vehicle and multi-vehicle scenarios, respectively, wherein we compare their advantages, their disadvantages, and their effectiveness in reducing energy consumption. Additionally, we reflect on the future development directions of cooperative optimization in EMS and eco-driving strategies from various perspectives. This comprehensive review underscores the importance and potential impact of these approaches in addressing environmental challenges in transportation systems, thereby offering useful insights for new researchers and practitioners in this area.
Full article
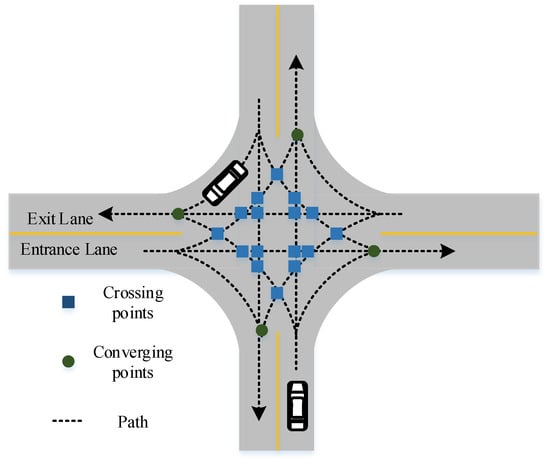
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Traffic Planning and Control at Urban Intersections)
▼
Show Figures