1
Mineral and Energy Economy Research Institute, Polish Academy of Sciences, 7A Wybickiego St., 31-261 Cracow, Poland
2
Faculty of Electrical Engineering, Warsaw University of Technology, 1 Politechniki Sq., 00-661 Warsaw, Poland
3
Veolia Energia Polska S.A., 2 Puławska St., 02-556 Warsaw, Poland
Appl. Sci. 2023, 13(7), 4258; https://doi.org/10.3390/app13074258 - 27 Mar 2023
Cited by 16 | Viewed by 4543
Abstract
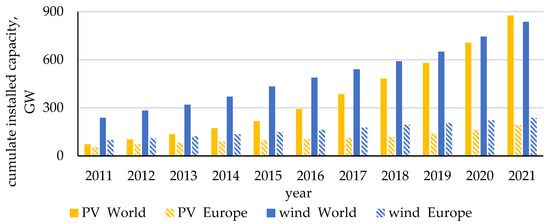
Wind power is the leader in electricity production among the standing RES technologies, both in Poland and in Europe/World. In Poland, so far there are only onshore wind turbines. Their dynamic increase in installed capacity has been observed, especially between 2011 and 2017.
[...] Read more.
Wind power is the leader in electricity production among the standing RES technologies, both in Poland and in Europe/World. In Poland, so far there are only onshore wind turbines. Their dynamic increase in installed capacity has been observed, especially between 2011 and 2017. This study analyzed the impact of offshore wind energy on the ability of the Polish power system to meet power demands. For this purpose, methods of statistical analysis (of existing onshore and planned offshore technologies) for the determination of wind turbine productivity based on wind speed components data from the ERA5 service were used. For onshore wind turbines, the value of the capacity factor CF(P) in Poland was 25.5% in 2021 and 30.1% in 2022. As a result of the simulation, it was calculated that for the planned offshore wind farms, the capacity factor CF(B) would be 55.6% under 2022 wind speed conditions. The 2022 peak load demands in the Polish system were also analyzed. The quantitative impact of installing 6 GW of offshore wind turbine capacity on the national power system was also identified.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Wind Energy: Current Trends, Implementations and Future Developments)
▼
Show Figures