1
REQUIMTE/LAQV, Instituto Superior de Engenharia do Porto, Instituto Politécnico do Porto, Rua Dr. António Bernardino de Almeida, 431, 4249-015 Porto, Portugal
2
Department of Materials and Ceramic Engineering, CICECO, University of Aveiro, 3810-193 Aveiro, Portugal
3
Betão Liz Grupo Cimpor, Av. Alm. Gago Coutinho CB, 2725-079 Algueirão-Mem Martins, Portugal
4
REQUIMTE/LAQV, Faculdade de Ciências e Tecnologia (FCT), Universidade Nova de Lisboa (UNL), 2829-516 Caparica, Portugal
Appl. Sci. 2023, 13(7), 4513; https://doi.org/10.3390/app13074513 - 2 Apr 2023
Cited by 8 | Viewed by 2313
Abstract
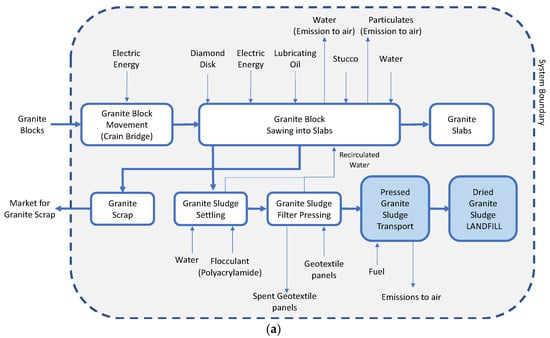
The granite sludge (GS) produced during block sawing can be exploited as alternative raw material in ceramic and concrete industries. Based on the case study of a Portuguese granite processing plant, this work analysed, by experimental tests and Environmental and Cost Life Cycle
[...] Read more.
The granite sludge (GS) produced during block sawing can be exploited as alternative raw material in ceramic and concrete industries. Based on the case study of a Portuguese granite processing plant, this work analysed, by experimental tests and Environmental and Cost Life Cycle analyses, the feasibility of GS valorisation as a substitute (i) for feldspar in a ceramic paste and (ii) fine–medium inert filler in structural concrete. The results demonstrated that both the valorisation pathways are more advantageous than GS landfilling. Due to granulometric, mineralogical composition and shrinkage, GS can substitute feldspar in sandstone tiles or tableware products, although its tinting effect can limit noble whitish ceramic applications. In structural concrete mixes, 5% w/w GS instead of fine inert filler reduces the compressive strength and increases the water:cement ratio. The GS generates lower environmental impacts as a substitute for inert filler than as a substitute for feldspar in most of the impact categories analysed, even though the latter valorisation pathway provides higher benefits in Climate Change and the Depletion of Fossil resources, Water, and Ozone. If no monetary value is recognised for GS valorisation by the market, the sustainability of GS life cycle cost decreases when compared to its landfilling.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Solid Waste Management in a Life Cycle Analysis Perspective)
▼
Show Figures