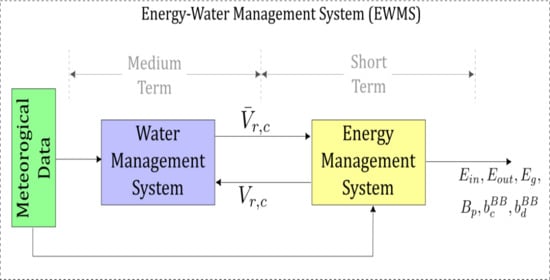
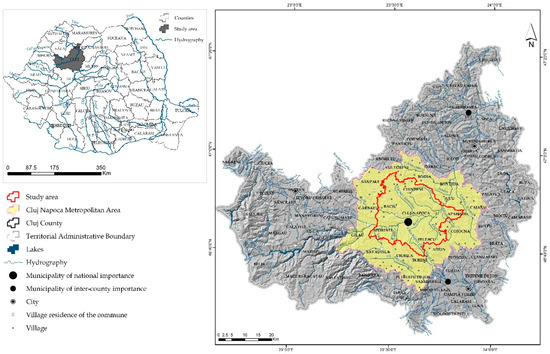
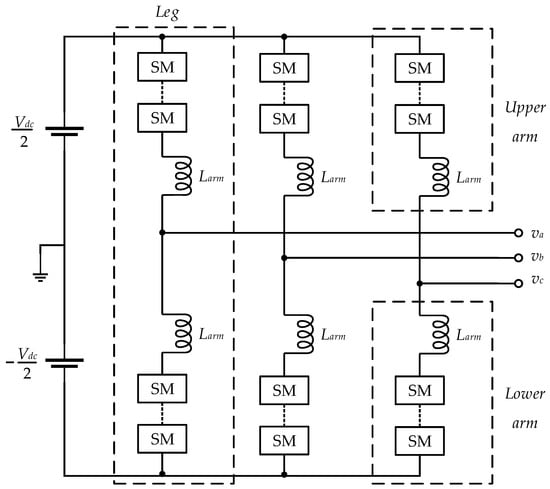
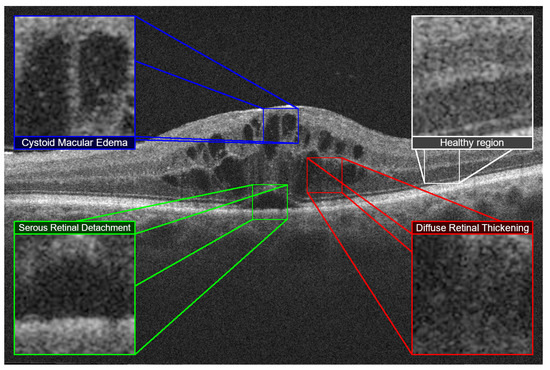
Appl. Sci. 2020, 10(21), 7724; https://doi.org/10.3390/app10217724 - 31 Oct 2020
Cited by 5 | Viewed by 3555
Abstract
In order to improve the electrochemical properties of poly(ethylene oxide), a well-known-solid polymer electrolyte, by adding zwitterion molecules, the synthesis of a new zwitterion (ZN) having imidazolium cation and sulfonyl(trifluoromethane sulfonyl)imide anion is investigated. The addition of different amounts of ZN
[...] Read more.
In order to improve the electrochemical properties of poly(ethylene oxide), a well-known-solid polymer electrolyte, by adding zwitterion molecules, the synthesis of a new zwitterion (ZN) having imidazolium cation and sulfonyl(trifluoromethane sulfonyl)imide anion is investigated. The addition of different amounts of ZN to the mixture of lithium bis(trifluoromethane sulfonyl)imide (LiTFSI) and poly(ethylene glycol)dimethyl ether (PEGDM) of 1000 g mol−1 does not significantly affect the transition temperature of PEGDM but causes a slight decrease in ionic conductivity of the electrolyte mixtures. However, even with the presence of only 0.05 mole fraction of ZN, the anodic stability of LiTFSI/PEGDM based electrolytes is improved to over 4.5 V vs. Li+/Li at 25 °C. This makes the new synthesized zwitterion a promising electrolyte’s additive for high voltage batteries.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Ionic Liquids: Properties and Applications)
►
Show Figures