Microorganisms 2021, 9(2), 254; https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms9020254 - 27 Jan 2021
Cited by 32 | Viewed by 7088
Abstract
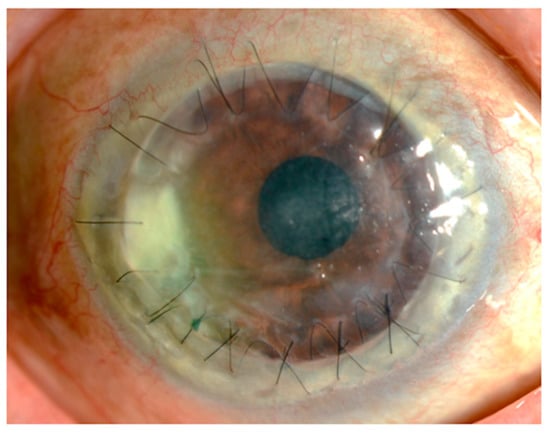
Corynebacterium species are commonly found in the conjunctiva of healthy adults and are recognized as non-pathogenic bacteria. In recent years, however, Corynebacterium species have been reported to be potentially pathogenic in various tissues. We investigated Corynebacterium species on the ocular surface and reviewed
[...] Read more.
Corynebacterium species are commonly found in the conjunctiva of healthy adults and are recognized as non-pathogenic bacteria. In recent years, however, Corynebacterium species have been reported to be potentially pathogenic in various tissues. We investigated Corynebacterium species on the ocular surface and reviewed various species of Corynebacterium in terms of their antimicrobial susceptibility and the underlying molecular resistance mechanisms. We identified a risk for Corynebacterium-related ocular infections in patients with poor immunity, such as patients with diabetes or long-term users of topical steroids, and in those with corneal epithelial damage due to trauma, contact lens wear, lagophthalmos, and trichiasis. The predominant strain in the conjunctiva was C. macginleyi, and the species associated with keratitis and conjunctivitis were C. macginleyi, C. propinquum, C. mastitidis, C. pseudodiphtheriticum, C. accolens, C. striatum, C. xerosis, and C. bovis. Overall, Corynebacterium species present on the ocular surface were resistant to quinolones, whereas those in the nasal cavity were more susceptible. The prevalence of fluoroquinolone-resistant Corynebacterium has not changed in the past 10 years; however, Corynebacterium species remain susceptible to third-generation cephems. In conclusion, the use of third-generation cephems should be a reasonable and pragmatic approach for treatment of ocular infections caused by Corynebacterium species.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Genetics and Physiology of Corynebacteria)
►
Show Figures