Quercus litseoides, an endangered montane cloud forest species, is endemic to southern China. To understand the genomic features, phylogenetic relationships, and molecular evolution of
Q. litseoides, the complete chloroplast (cp) genome was analyzed and compared in
Quercus section
Cyclobalanopsis. The
[...] Read more.
Quercus litseoides, an endangered montane cloud forest species, is endemic to southern China. To understand the genomic features, phylogenetic relationships, and molecular evolution of
Q. litseoides, the complete chloroplast (cp) genome was analyzed and compared in
Quercus section
Cyclobalanopsis. The cp genome of
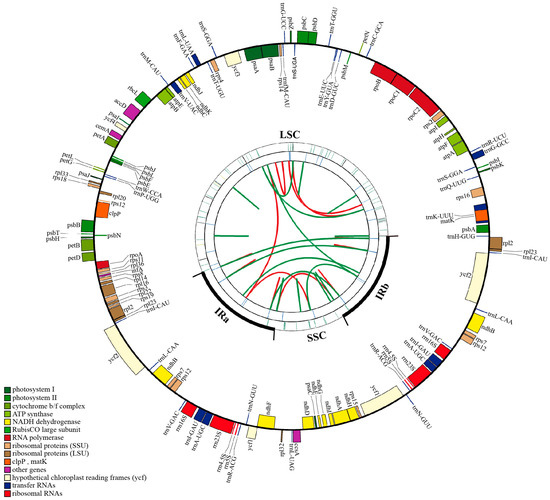
Q. litseoides was 160,782 bp in length, with an overall guanine and cytosine (GC) content of 36.9%. It contained 131 genes, including 86 protein-coding genes, eight ribosomal RNA genes, and 37 transfer RNA genes. A total of 165 simple sequence repeats (SSRs) and 48 long sequence repeats with A/T bias were identified in the
Q. litseoides cp genome, which were mainly distributed in the large single copy region (LSC) and intergenic spacer regions. The
Q. litseoides cp genome was similar in size, gene composition, and linearity of the structural region to those of
Quercus species. The non-coding regions were more divergent than the coding regions, and the LSC region and small single copy region (SSC) were more divergent than the inverted repeat regions (IRs). Among the 13 divergent regions, 11 were in the LSC region, and only two were in the SSC region. Moreover, the coding sequence (CDS) of the six protein-coding genes (
rps12,
matK,
atpF,
rpoC2,
rpoC1, and
ndhK) were subjected to positive selection pressure when pairwise comparison of 16 species of
Quercus section
Cyclobalanopsis. A close relationship between
Q. litseoides and
Quercus edithiae was found in the phylogenetic analysis of cp genomes. Our study provided highly effective molecular markers for subsequent phylogenetic analysis, species identification, and biogeographic analysis of
Quercus.
Full article