Polymers 2022, 14(6), 1195; https://doi.org/10.3390/polym14061195 - 16 Mar 2022
Cited by 6 | Viewed by 3247
Abstract
The design of nanocomposites with the potential for drug delivery is a topic of great interest. In this work, the synthesis of nanocomposites of poly(methacrylic acid) (PMAA) grafted onto carbon nanotubes (CNTs) functionalized with poly(amidoamine) (PAMAM) dendrimer by semicontinuous heterophase polymerization SHP,
[...] Read more.
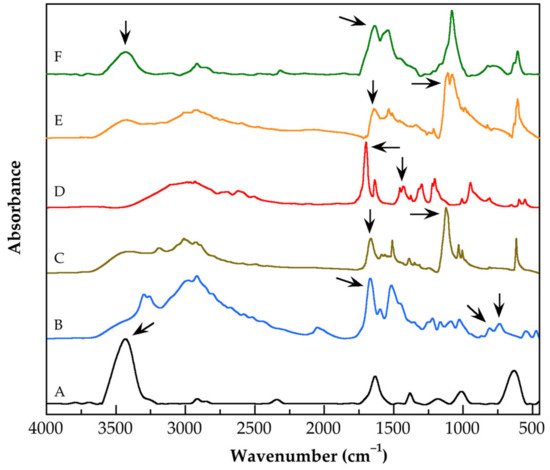
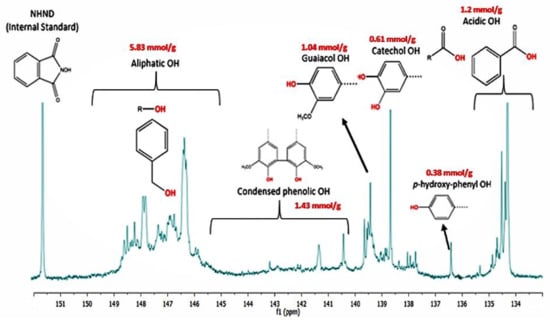
The design of nanocomposites with the potential for drug delivery is a topic of great interest. In this work, the synthesis of nanocomposites of poly(methacrylic acid) (PMAA) grafted onto carbon nanotubes (CNTs) functionalized with poly(amidoamine) (PAMAM) dendrimer by semicontinuous heterophase polymerization SHP, at three different methacrylic acid (MAA) dosing rates, is reported. SHP is a polymerization technique poorly used to prepare nanocomposites containing CNTs and has the potential to produce more ordered alkyl methacrylic polymer chains, which could favor the obtaining of a homogenous nanocomposite. For the nanocomposites synthesized, a lowest addition rate monomer-starved condition was reached. Analysis by X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS), and thermogravimetric analysis (TGA) demonstrate that functionalized CNTs are grafted onto the PMAA matrix. The ability of prepared nanocomposites to deliver hydrocortisone was evaluated by ultraviolet-visible spectroscopy (UV-Vis). The hydrocortisone release profiles of pure PMAA and of their nanocomposites prepared at the lowest monomer fed rate were fitted with Higuchi and Korsmeyer–Peppas models, successfully. Functionalized CNTs have a crucial role to induce an effective release of hydrocortisone from the prepared nanocomposites.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Functional Polymers for Drug Delivery System)
►
Show Figures