1
Faculty of Management, AGH University of Science and Technology, 30-067 Cracow, Poland
2
Mineral and Energy Economy Research Institute, Polish Academy of Sciences, 31-261 Cracow, Poland
Sustainability 2020, 12(14), 5634; https://doi.org/10.3390/su12145634 - 13 Jul 2020
Cited by 11 | Viewed by 4352
Abstract
One of the priority lines of action in Poland is to increase energy production from renewable energy sources (RESs). Based on the “Poland’s national energy and climate plan for the years 2021–2030”, Poland aims to achieve 21%–23% of RES share in gross final
[...] Read more.
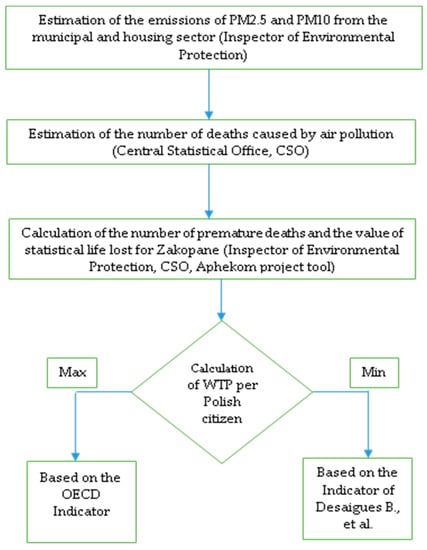
One of the priority lines of action in Poland is to increase energy production from renewable energy sources (RESs). Based on the “Poland’s national energy and climate plan for the years 2021–2030”, Poland aims to achieve 21%–23% of RES share in gross final energy consumption by 2030. While coal is still the most important source of energy, new technological and organisational solutions for increasing RESs are being tested and implemented. Therefore, the creation of energy clusters based on the idea of urban and industrial symbiosis was first proposed by the Ministry of Energy in 2016. To date, there are 66 clusters in different regions in Poland, but only a few of them are active and innovative. One of them is located in the city of Zakopane, a mountain resort, which attracts about 3 million tourists annually and has developed the wide-ranging use of geothermal sources for energy supply and recreation. The paper aims to analyse the impact of the creation of energy clusters on the city’s development, including economic, social, and environmental aspects. The “willingness to pay” (WTP) method was used to calculate the impact of air pollution on Zakopane and to compare it with the Polish average to estimate the significance of the transformation to RESs in this tourist city. The results from the studies are as follows: health cost per capita in Zakopane is between 252.07 and 921.30 euro. The investigations presented can be the basis for recommendations in strategic documents in the field of regional development and environmental protection, especially on the use and promotion of urban symbiosis for increasing use of RESs.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Life Cycle Thinking and Industrial Symbiosis: Challenges for A Sustainable Growth)
▼
Show Figures