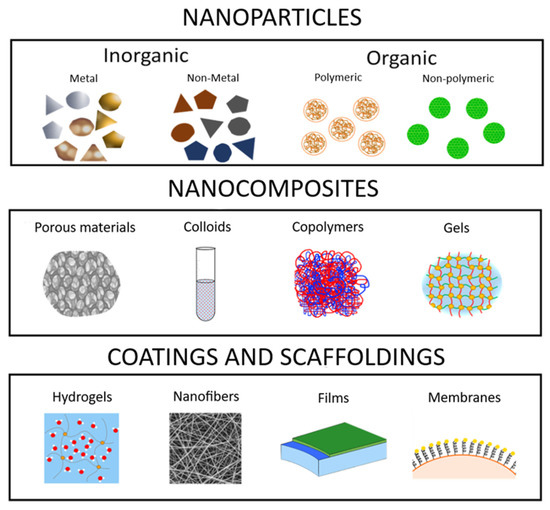
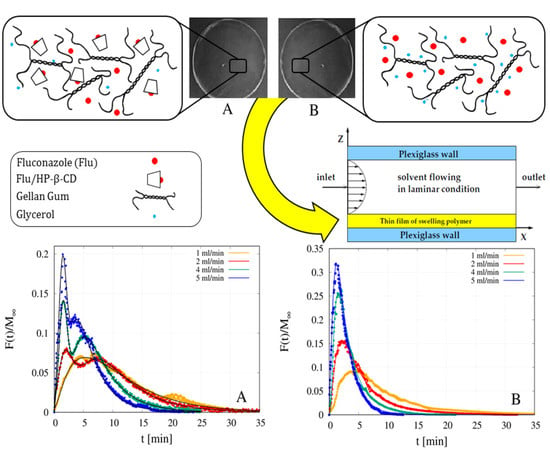
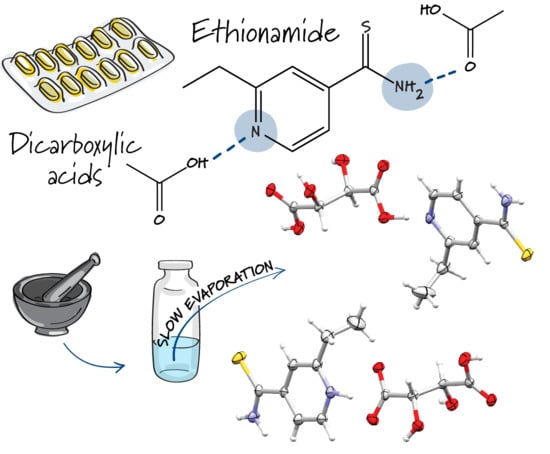
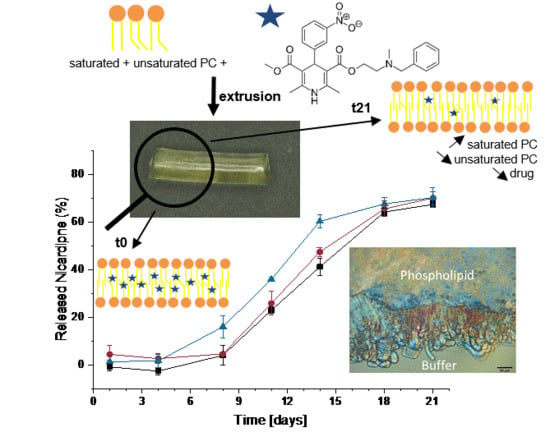
Pharmaceutics 2020, 12(9), 829; https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics12090829 - 31 Aug 2020
Viewed by 2019
Abstract
In their article, Casiraghi, A. et al. describe a few relevant methods to assess the quality of a pharmaceutical preparation of oral viscous budesonide, intended to be swallowed, and treat the esophagus in eosinophilic esophagitis patients. They choose the following methods for this
[...] Read more.
In their article, Casiraghi, A. et al. describe a few relevant methods to assess the quality of a pharmaceutical preparation of oral viscous budesonide, intended to be swallowed, and treat the esophagus in eosinophilic esophagitis patients. They choose the following methods for this purpose: rheological properties, syringeability, mucoadhesiveness, and in vitro penetration of budesonide in porcine esophageal tissue. At the end of the article, they concluded that the best formulation of oral viscous budesonide was the one already being used in hospitals, based on xanthan gum. In their article, the authors did not emphasize that this specific formula was developed by the compounding pharmacist Eyal Zur from Israel and was published eight years before, as part of an article in the International Journal of Pharmaceutical Compounding. The purpose of this comment is to give the appropriate credit to the pharmacist who first developed and published this well designed formulation.
Full article