Materials 2022, 15(19), 6754; https://doi.org/10.3390/ma15196754 - 29 Sep 2022
Cited by 9 | Viewed by 1978
Abstract
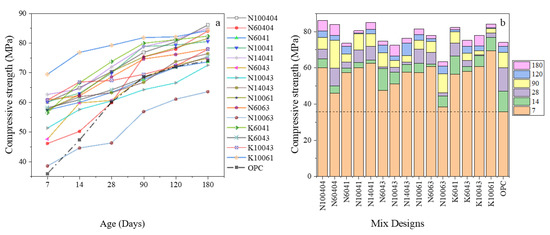
Long-term deterioration and durability concerns in harsh environments with acidic attacks are considered as the weaknesses of ordinary Portland cement (OPC) concrete. Although the performance of alkali-activated slag concrete (AASC) has been reported to be superior in acidic environments, there is a poor
[...] Read more.
Long-term deterioration and durability concerns in harsh environments with acidic attacks are considered as the weaknesses of ordinary Portland cement (OPC) concrete. Although the performance of alkali-activated slag concrete (AASC) has been reported to be superior in acidic environments, there is a poor understanding regarding the impacts of diverse mix design parameters on AASC durability in an acidic environment. This research aims to understand the impact of mix design parameters on the durability of AASC in the sulfuric acid (H2SO4) environment with pH = 3. The type of alkaline solution, the molarity of alkaline solutions, the weight ratio of alkaline solutions to slag, and the weight ratio of NaOH to Na2SiO3 are mix design parameters investigated in this study. The compressive strength reduction and weight loss were monitored from early ages up to 180 days. Moreover, an OPC concrete sample was produced as a reference.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Geopolymers and Alkali-Activated Materials: Synthesis, Characterization, and Applications)
►
Show Figures