Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17(6), 2108; https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph17062108 - 22 Mar 2020
Cited by 36 | Viewed by 7226
Abstract
Background: This study aimed to investigate the associations between individual factors, electronic health (eHealth) literacy, dietary behaviors, and exercise habits in college students, as well as the moderating effect of gender on the above target behaviors. Methods: A pen-and-paper questionnaire with a stratified
[...] Read more.
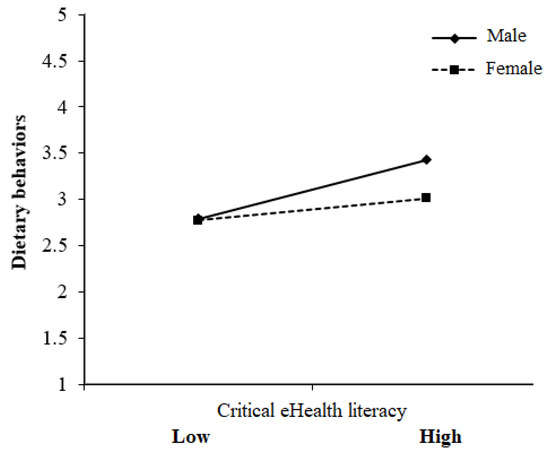
Background: This study aimed to investigate the associations between individual factors, electronic health (eHealth) literacy, dietary behaviors, and exercise habits in college students, as well as the moderating effect of gender on the above target behaviors. Methods: A pen-and-paper questionnaire with a stratified sampling method was used to collect data, and at least 100 students from each stratum were determined to be used for the official sample in this study. Finally, 674 students completed the survey. Results and Conclusions: Chi-square test results demonstrated that genders had dissimilar dietary supplement use and subjective health status. Further analyses indicated females had a higher likelihood of taking dietary supplements and poorer subjective health statuses. The t-test results indicated that the functional eHealth literacy, dietary behaviors, and exercise habits of genders were different, and the mean scores showed that males had higher functional eHealth literacy, healthier dietary behaviors, and higher exercise involvement than females. Regression analyses showed that students who were male, took dietary supplements, placed the utmost importance on health, and had high critical eHealth literacy tended to possess healthy dietary behaviors. Students who were male and had good subjective health statuses tended to have higher exercise involvement. Specifically, the critical eHealth literacy changed dietary behaviors less effectively for women than for men, and the subjective health status changed exercise habits less effectively for women than for men. Therefore, when designing the diet and exercise intervention programs, gender-specific programs rather than generic programs should be given priority to develop.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Collection Health Behaviors, Risk Factors, NCDs and Health Promotion)
►
Show Figures