1
Department of Chemistry, Faculty of Applied Sciences, Umm Al-Qura University, Makkah 21955, Saudi Arabia
2
Department of Clinical Laboratory Sciences, College of Applied Medical Sciences, Taif University, P.O. Box 11099, Taif 21944, Saudi Arabia
3
Department of Chemistry, College of Science, United Arab Emirates University, Al Ain P.O. Box 15551, United Arab Emirates
4
Department of Chemistry, Faculty of Science, Assiut University, Assiut 71516, Egypt
Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24(5), 5003; https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24055003 - 5 Mar 2023
Cited by 6 | Viewed by 3415
Abstract
Norovirus (HNoV) is a leading cause of gastroenteritis globally, and there are currently no treatment options or vaccines available to combat it. RNA-dependent RNA polymerase (RdRp), one of the viral proteins that direct viral replication, is a feasible target for therapeutic development. Despite
[...] Read more.
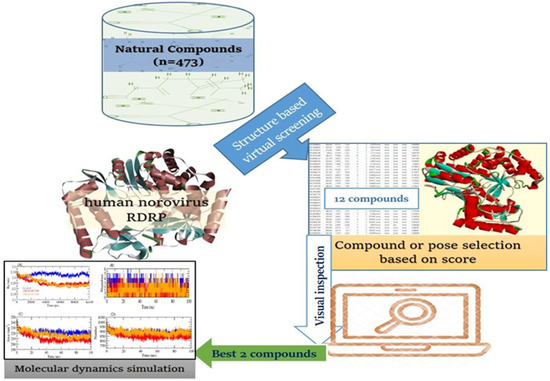
Norovirus (HNoV) is a leading cause of gastroenteritis globally, and there are currently no treatment options or vaccines available to combat it. RNA-dependent RNA polymerase (RdRp), one of the viral proteins that direct viral replication, is a feasible target for therapeutic development. Despite the discovery of a small number of HNoV RdRp inhibitors, the majority of them have been found to possess a little effect on viral replication, owing to low cell penetrability and drug-likeness. Therefore, antiviral agents that target RdRp are in high demand. For this purpose, we used in silico screening of a library of 473 natural compounds targeting the RdRp active site. The top two compounds, ZINC66112069 and ZINC69481850, were chosen based on their binding energy (BE), physicochemical and drug-likeness properties, and molecular interactions. ZINC66112069 and ZINC69481850 interacted with key residues of RdRp with BEs of −9.7, and −9.4 kcal/mol, respectively, while the positive control had a BE of −9.0 kcal/mol with RdRp. In addition, hits interacted with key residues of RdRp and shared several residues with the PPNDS, the positive control. Furthermore, the docked complexes showed good stability during the molecular dynamic simulation of 100 ns. ZINC66112069 and ZINC69481850 could be proven as potential inhibitors of the HNoV RdRp in future antiviral medication development investigations.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Protein Structure and Function in Microorganisms)
▼
Show Figures