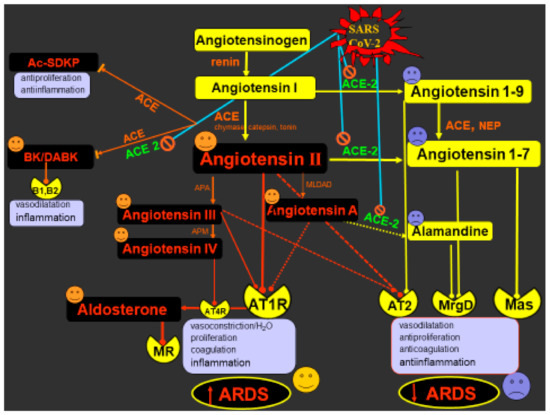
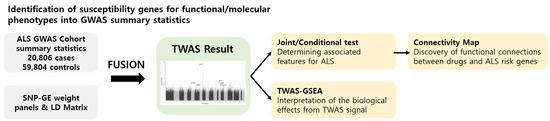
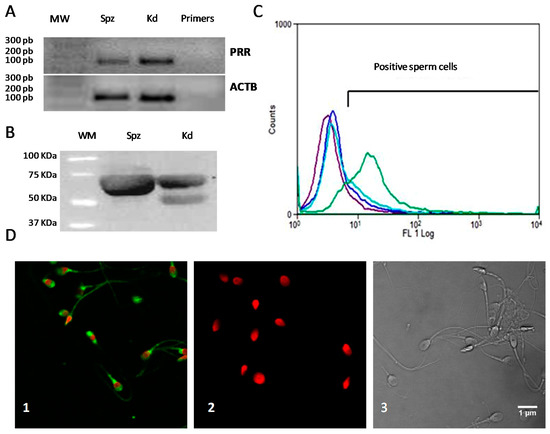
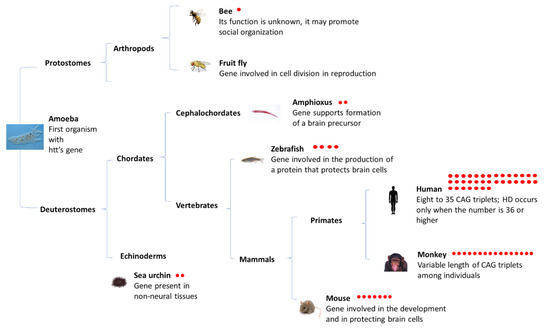
Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22(6), 3228; https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22063228 - 22 Mar 2021
Cited by 8 | Viewed by 3345
Abstract
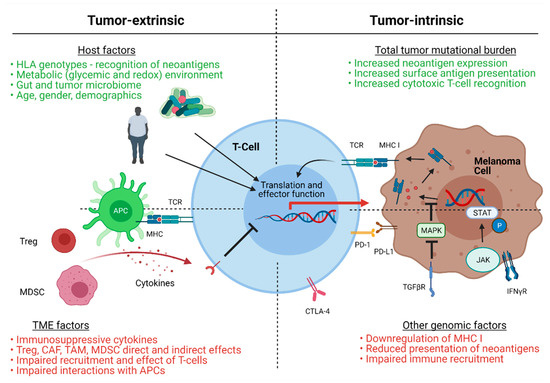
Metastatic melanoma remains the deadliest form of skin cancer. Immune checkpoint inhibition (ICI) immunotherapy has defined a new age in melanoma treatment, but responses remain inconsistent and some patients develop treatment resistance. The myriad of newly developed small molecular (SM) inhibitors of specific
[...] Read more.
Metastatic melanoma remains the deadliest form of skin cancer. Immune checkpoint inhibition (ICI) immunotherapy has defined a new age in melanoma treatment, but responses remain inconsistent and some patients develop treatment resistance. The myriad of newly developed small molecular (SM) inhibitors of specific effector targets now affords a plethora of opportunities to increase therapeutic responses, even in resistant melanoma. In this review, we will discuss the multitude of SM classes currently under investigation, current and prospective clinical combinations of ICI and SM therapies, and their potential for synergism in melanoma eradication based on established mechanisms of immunotherapy resistance.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Precision Oncology in Melanoma Progression)
►
Show Figures