- Article
Braking Energy Recovery Control Strategy Based on Instantaneous Response and Dynamic Weight Optimization
- Lulu Cai,
- Pengxiang Yan and
- Xiaopeng Yang
- + 5 authors
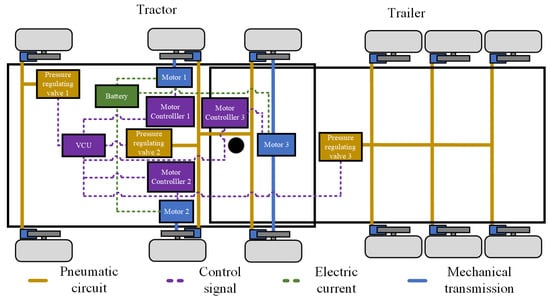
Multi-axle electric heavy-duty trucks face significant challenges in maintaining braking stability and achieving real-time control during regenerative braking due to their large mass and complex inter-axle coupling dynamics. To address these issues, this paper proposes an improved model predictive control (IMPC) strategy that enhances computational efficiency and control responsiveness through an instantaneous response mechanism. The approach integrates a first-order error attenuation term within the MPC framework and employs an extended Kalman filter to estimate tire–road friction in real time, enabling adaptive adjustment between energy recovery and stability objectives under varying road conditions. A control barrier function constraint is further introduced to ensure smooth and safe regenerative braking. Simulation results demonstrate improved energy recovery efficiency and faster convergence, while real-vehicle tests confirm that the IMPC maintains superior real-time performance and adaptability under complex operating conditions, reducing average computation time by approximately 14% compared with conventional MPC and showing strong potential for practical deployment.
19 December 2025