Journal Description
BioTech
BioTech
- formerly High-Throughput - is an international, peer-reviewed, open access journal on biotechnology, published quarterly online by MDPI.
- Open Access— free for readers, with article processing charges (APC) paid by authors or their institutions.
- High Visibility: indexed within ESCI (Web of Science), Scopus, PubMed, PMC, Inspec, CAPlus / SciFinder, and other databases.
- Rapid Publication: manuscripts are peer-reviewed and a first decision is provided to authors approximately 26.1 days after submission; acceptance to publication is undertaken in 2.6 days (median values for papers published in this journal in the second half of 2024).
- Recognition of Reviewers: reviewers who provide timely, thorough peer-review reports receive vouchers entitling them to a discount on the APC of their next publication in any MDPI journal, in appreciation of the work done.
Impact Factor:
2.7 (2023)
Latest Articles
Anti-Inflammatory Function Analysis of Lacticaseibacillus rhamnosus CP-1 Strain Based on Whole-Genome Sequencing
BioTech 2025, 14(2), 47; https://doi.org/10.3390/biotech14020047 (registering DOI) - 7 Jun 2025
Abstract
Lacticaseibacillus rhamnosus (L. rhamnosus) is a safe probiotic with no side effects, providing benefits such as gut microbiota regulation and immune enhancement, making it highly valuable with strong potential. However, strains from different sources have unique traits, and whole-genome sequencing (WGS)
[...] Read more.
Lacticaseibacillus rhamnosus (L. rhamnosus) is a safe probiotic with no side effects, providing benefits such as gut microbiota regulation and immune enhancement, making it highly valuable with strong potential. However, strains from different sources have unique traits, and whole-genome sequencing (WGS) helps analyse these differences. In this study, we used WGS to examine L. rhamnosus strains from mice with fish oil-treated smoking-induced pneumonia to better understand their biological functions and explore possible anti-inflammatory mechanisms. Methods: We isolated a strain, Lacticaseibacillus rhamnosus CP-1 (L. rhamnosus CP-1), from mice intestines where fish oil alleviated smoking-induced pneumonia. Identification of probiotic-related genes by WGS and characterised the strain’s probiotic properties. Results: L. rhamnosus CP-1 has a single circular chromosome (2,989,570 bp, 46.76% GC content) and no plasmids. COG, GO, and KEGG databases revealed genes linked to carbohydrate metabolism. The CAZy database identified GH25 lysozyme and PL8 polysaccharide lyase genes. KEGG highlighted an antimicrobial peptide ABC transporter permease, while TCDB noted the ABC-type antimicrobial peptide transporter (the main active transport component). KEGG also showed 10 genes for terpenoid skeleton biosynthesis and 5 for keto-glycan unit biosynthesis. Additionally, L. rhamnosus CP-1 carries metabolic regulators and bacteriocin-related genes. Conclusions: Whole-genome sequencing analysis revealed that L. rhamnosus CP-1 has carbohydrate utilisation and potential anti-inflammatory effects at the molecular level. Potential functional genes include carbohydrate transport and hydrolase, antimicrobial peptide ABC transporter and its osmotic enzyme components, bacteriocin immune protein, terpenoid skeleton, and keto-glycan synthesis.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Computational Biology)
►
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
In Vitro Antioxidant Potential, Antidiabetic Activities, and GC–MS Analysis of Lipid Extracts of Chlorella Microalgae
by
Somruthai Kaeoboon, Rattanaporn Songserm, Rungcharn Suksungworn, Sutsawat Duangsrisai and Nuttha Sanevas
BioTech 2025, 14(2), 46; https://doi.org/10.3390/biotech14020046 - 6 Jun 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Microalgae represent promising biotechnological platforms for bioactive compound production with pharmaceutical applications. This study investigated the phytochemical composition and biological activities of lipid extracts from three Chlorella species to evaluate their potential as antioxidant and antidiabetic sources. Lipid extraction using chloroform–methanol (2:1) followed
[...] Read more.
Microalgae represent promising biotechnological platforms for bioactive compound production with pharmaceutical applications. This study investigated the phytochemical composition and biological activities of lipid extracts from three Chlorella species to evaluate their potential as antioxidant and antidiabetic sources. Lipid extraction using chloroform–methanol (2:1) followed by GC–MS analysis revealed distinct compound distributions: 29 compounds in C. ellipsoidea, 33 in C. sorokiniana, and 19 in C. vulgaris. Major bioactive compounds included 2-hexanol, 1,3,6-heptatriene, 4-(2,3-dimethyl-2-cyclopenten-1-yl)-4-methylpentanal, n-hexadecanoic acid, and octadecanoic acid. Biological activity screening encompassed antioxidant assessment through DPPH• and •NO radical scavenging assays and FRAP analysis, while antidiabetic potential was evaluated using α-glucosidase and α-amylase inhibition assays. C. sorokiniana exhibited superior bioactivity with the highest antioxidant capacity (DPPH• IC50 = 329.03 ± 4.30 µg/mL; •NO IC50 = 435.53 ± 10.20 µg/mL; FRAP = 94.74 ± 5.72 mg TE/g) and strongest enzyme inhibition (α-glucosidase IC50 = 752.75 ± 57.95 µg/mL; α-amylase IC50 = 3458.50 ± 104.01 µg/mL). This is the first report on C. sorokiniana strain KU.B2′s biological properties and phytochemical profile. These findings establish C. sorokiniana as a valuable biotechnological platform for pharmaceutical bioactive compound development.
Full article
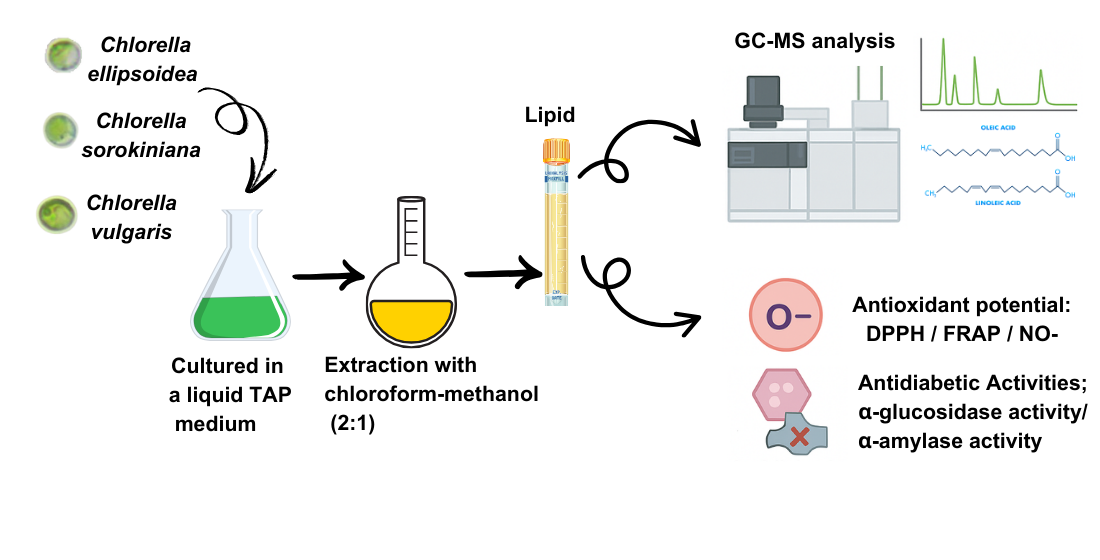
Graphical abstract
Open AccessArticle
Green-Synthesized Silver Nanoparticles (AgNPs) Enhance In Vitro Multiplication and Rooting of Strawberries (Fragaria × ananassa Duchesne)
by
José Luis Aguirre-Noyola, Marco A. Ramírez-Mosqueda, Jorge David Cadena-Zamudio, José Humberto Caamal-Velázquez, Esmeralda J. Cruz-Gutiérrez and Alma Armenta-Medina
BioTech 2025, 14(2), 45; https://doi.org/10.3390/biotech14020045 - 6 Jun 2025
Abstract
Nanobiotechnology applications in plant tissue culture have improved the development and physiology of explants, resulting in plants with high genetic homogeneity and phytosanitary quality. Silver nanoparticles (AgNPs) are well-known for their microbicidal properties, but their biochemical effects on plants require further exploration. In
[...] Read more.
Nanobiotechnology applications in plant tissue culture have improved the development and physiology of explants, resulting in plants with high genetic homogeneity and phytosanitary quality. Silver nanoparticles (AgNPs) are well-known for their microbicidal properties, but their biochemical effects on plants require further exploration. In this work, green-synthesized AgNPs were evaluated in strawberry in vitro culture, photosynthetic pigment production, and acclimatization. AgNPs produced by Lysinibacillus fusiformis were characterized. Strawberry explants were grown in vitro on MS medium with 0, 100, 200, and 300 mg L−1 AgNPs at 24 ± 2 °C and a photoperiod of 16:8 h light/dark. Shoot height and number, number of leaves, number of roots, and root length were evaluated, and chlorophyll (a, b, and total) was quantified. Rooted shoots were acclimatized ex vitro on substrates containing 0 and 200 mg L−1 AgNPs. The results showed that low AgNPs concentrations had a positive impact on shoot multiplication, development, and rooting, but at higher concentrations, the effects decayed. However, chlorophyll production improved with increasing AgNP concentration. Shoots treated with AgNPs showed higher ex vitro survival. Our study has direct implications for the profitability and sustainability of commercial strawberry production.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Industry, Agriculture and Food Biotechnology)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Spatial and Temporal Aspects of Fungicide Resistance in Venturia inaequalis (Apple Scab) Populations in Northern Germany
by
Roland W. S. Weber, Rebekka Busch and Johanna Wesche
BioTech 2025, 14(2), 44; https://doi.org/10.3390/biotech14020044 - 5 Jun 2025
Abstract
Venturia inaequalis, the cause of apple scab, readily develops resistance to fungicides with specific modes of action. Knowledge of the spatial and temporal pattern of resistance development is therefore relevant to fruit producers and their consultants. In the Lower Elbe region of
[...] Read more.
Venturia inaequalis, the cause of apple scab, readily develops resistance to fungicides with specific modes of action. Knowledge of the spatial and temporal pattern of resistance development is therefore relevant to fruit producers and their consultants. In the Lower Elbe region of Northern Germany, a two-year survey based on a conidial germination test was conducted, examining fungicide resistance in 35 orchards under Integrated Pest Management (IPM), 16 orchards of susceptible cultivars as well as a further 12 orchards of scab-resistant (Vf) cultivars under organic management, and 34 abandoned or unmanaged sites. No evidence of resistance to SDHI compounds (fluopyram, fluxapyroxad) was found after >5 yr of their regular use. Resistance to anilinopyrimidines (cyprodinil, pyrimethanil) had disappeared 15 yr after its widespread occurrence. Isolates from a few IPM orchards showed a reduced sensitivity to dodine. Double resistance to the MBC compound thiophanate-methyl and the QoI trifloxystrobin was rare in V. inaequalis strains that had achieved breakage of Vf-resistance, but very common (>50%) on scab-susceptible cultivars in IPM, organic and abandoned orchards in the ‘Altes Land’ core area of the Lower Elbe region, and in IPM orchards in the periphery. We conclude that resistance to QoI and MBC fungicides is persistent even decades after their last use, and that the core area harbours a uniform population adapted to intensive crop protection, whereas isolated orchards in the periphery are colonised by discrete populations of V. inaequalis.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Industry, Agriculture and Food Biotechnology)
►▼
Show Figures
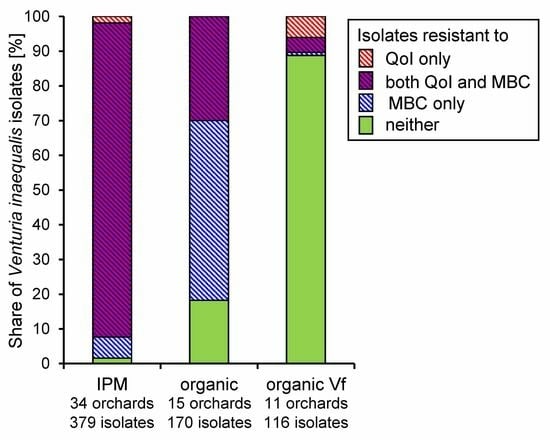
Graphical abstract
Open AccessArticle
Interaction Between Rumen Microbiota and Epithelial Mitochondrial Dynamics in Tibetan Sheep: Elucidating the Mechanism of Rumen Epithelial Energy Metabolism
by
Ying Xu, Yuzhu Sha, Xiaowei Chen, Qianling Chen, Xiu Liu, Yanyu He, Wei Huang, Yapeng He and Xu Gao
BioTech 2025, 14(2), 43; https://doi.org/10.3390/biotech14020043 - 5 Jun 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Investigating the functional interactions between rumen microbial fermentation and epithelial mitochondrial dynamics/energy metabolism in Tibetan sheep at different altitudes, this study examined ultrastructural changes in rumen epithelial tissues, expression levels of mitochondrial dynamics-related genes (fusion: Mfn1, Mfn2, OPA1, Mic60;
[...] Read more.
Investigating the functional interactions between rumen microbial fermentation and epithelial mitochondrial dynamics/energy metabolism in Tibetan sheep at different altitudes, this study examined ultrastructural changes in rumen epithelial tissues, expression levels of mitochondrial dynamics-related genes (fusion: Mfn1, Mfn2, OPA1, Mic60; fission: Drp1, Fis1, MFF), and ketogenesis pathway genes (HMGS2, HMGCL) in Tibetan sheep raised at three altitudes (TS 2500m, TS 3500m, TS 4500m). Correlation analysis was performed between rumen microbiota/metabolites and mitochondrial energy metabolism. Results: Ultrastructural variations were observed across altitudes. With increasing altitude, keratinized layer became more compact; desmosome connections between granular layer cells increased; mitochondrial quantity and distribution in spinous and basal layers increased. Mitochondrial dynamics regulation: Fission genes (FIS1, DRP1, MFF) showed significantly higher expression at TS 4500m (p < 0.01); fusion genes (Mfn1, OPA1) exhibited altitude-dependent upregulation. Energy metabolism markers: Pyruvate (PA) decreased significantly at TS 3500m/TS 4500m (p < 0.01); citrate (CA) increased with altitude; NAD+ peaked at TS 3500m but decreased significantly at TS 4500m (p < 0.01); Complex II (SDH) and Complex IV (CO) activities decreased at TS 4500m (p < 0.01). Ketogenesis pathway: β-hydroxybutyrate increased significantly with altitude (p < 0.01); acetoacetate peaked at TS 2500 m/TS 4500 m; HMGCS2 expression exceeded HMGCL, showing altitude-dependent upregulation at TS 4500m (p < 0.01). Microbiome–metabolism correlations: Butyrivibrio_2 and Fibrobacter negatively correlated with Mic60 (p < 0.01); Ruminococcaceae_NK4A214_Group positively correlated with Mfn1/OPA1 (p < 0.05); WGCNA identified 17 metabolite modules, with MEturquoise module positively correlated with DRP1/Mfn2/MFF (p < 0.05). Conclusion: Altitude-induced ultrastructural adaptations in rumen epithelium correlate with mitochondrial dynamics stability and ketogenesis upregulation. Mitochondrial fission predominates at extreme altitudes, while microbiota–metabolite interactions suggest compensatory energy regulation mechanisms.
Full article
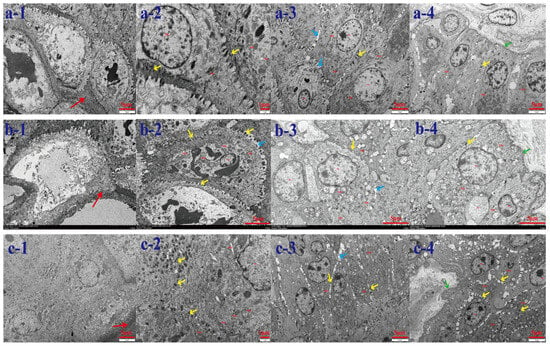
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Genomic Characterization of Linezolid-Resistant Clostridioides difficile Harboring cfr Variants
by
Aikaterini Panou, Andigoni Malousi and Melina Kachrimanidou
BioTech 2025, 14(2), 42; https://doi.org/10.3390/biotech14020042 - 31 May 2025
Abstract
The emergence of antimicrobial resistance (AMR) in Clostridium difficile (C. difficile), particularly to last-line antibiotics such as linezolid, represents a critical challenge in clinical settings. This study investigates the genomic epidemiology of linezolid-resistant C. difficile, focusing on the distribution and
[...] Read more.
The emergence of antimicrobial resistance (AMR) in Clostridium difficile (C. difficile), particularly to last-line antibiotics such as linezolid, represents a critical challenge in clinical settings. This study investigates the genomic epidemiology of linezolid-resistant C. difficile, focusing on the distribution and mutational patterns of the chloramphenicol–florfenicol resistance (cfr) gene and its association with multidrug resistance. We analyzed 514 clinical isolates (354 from NCBI Pathogen Detection, 160 from EnteroBase), revealing distinct prevalence patterns among cfr subtypes: cfr(C) was dominant (156/354 NCBI strains; 101/160 EnteroBase strains), whereas cfr(B) frequently harbored missense mutations (p.R247K, p.V294I, and less commonly p.A334T). The cfr(E) subtype was exclusively identified in ribotype 027 (RT027) strains. Notably, cfr(C) exhibited a strong association with RT017, correlating with a conserved 99 bp genomic deletion. Phylogenetic analysis linked cfr-carriage to predominant sequence types (ST1 in NCBI strains, ST37 in EnteroBase isolates). Furthermore, the co-occurrence of cfr with additional AMR genes conferred resistance to macrolides (erythromycin, azithromycin) and tetracyclines, indicating a convergent evolution toward multidrug resistance. These findings underscore the interplay between cfr mutations, hypervirulent ribotypes, and AMR dissemination, necessitating enhanced surveillance to mitigate the spread of resistant C. difficile lineages.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue BioTech: 5th Anniversary)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessReview
Spirulina as a Key Ingredient in the Evolution of Eco-Friendly Cosmetics
by
Sergiana dos Passos Ramos, Monize Bürck, Stephanie Fabrícia Francisco da Costa, Marcelo Assis and Anna Rafaela Cavalcante Braga
BioTech 2025, 14(2), 41; https://doi.org/10.3390/biotech14020041 - 30 May 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Limnospira spp., commercially known as spirulina, is widely recognized for its remarkable benefits due to its rich composition of bioactive compounds like phycobiliproteins, carotenoids, and phenolic compounds. These natural bioactive compounds not only serve as colorants but also offer potent antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, immunomodulatory,
[...] Read more.
Limnospira spp., commercially known as spirulina, is widely recognized for its remarkable benefits due to its rich composition of bioactive compounds like phycobiliproteins, carotenoids, and phenolic compounds. These natural bioactive compounds not only serve as colorants but also offer potent antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, immunomodulatory, anticancer, antimicrobial, and anti-aging properties. As a result, spirulina and its components are increasingly used in cosmetic formulations to promote skin hydration, reduce wrinkles, and protect against UV radiation damage. Its bioactive components enhance fibroblast growth, boost collagen production, and prevent premature skin aging by inhibiting enzymes responsible for elastin degradation. Additionally, spirulina-based cosmetics have demonstrated wound-healing properties without genotoxic effects, with formulations containing C-phycocyanin particularly effective in shielding skin cells from UV-induced apoptosis. Despite these well-established benefits, there remains significant potential for the cosmetic industry to harness spirulina’s capabilities further. Research into the molecular mechanisms underlying its bioactive compounds in cosmetic formulations is still in its early stages, offering many opportunities for innovation. Emerging fields of biotechnology, such as nanotechnology and biocosmetics, could enhance the stability, efficacy, and delivery of spirulina-based ingredients, unlocking new possibilities for skin protection and rejuvenation. Furthermore, its proven biological properties align perfectly with the increasing consumer demand for safe, sustainable, and nature-inspired skincare solutions.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessReview
Broomrapes in Major Mediterranean Crops: From Management Strategies to Novel Approaches for Next-Generation Control
by
Demosthenis Chachalis, Eleni Tani, Aliki Kapazoglou, Maria Gerakari, Angeliki Petraki, Francisco Pérez-Alfocea, Purificación A. Martínez-Melgarejo, Markus Albert, Khalil Khamassi and Mohamed Kharrat
BioTech 2025, 14(2), 40; https://doi.org/10.3390/biotech14020040 - 25 May 2025
Abstract
Broomrapes (Orobanche and Phelipanche spp.) are parasitic weeds that significantly impact the productivity of major crops in the Mediterranean region, like tomato (Solanum spp.) and faba bean (Vicia faba) species. This review article extensively discusses management strategies to control
[...] Read more.
Broomrapes (Orobanche and Phelipanche spp.) are parasitic weeds that significantly impact the productivity of major crops in the Mediterranean region, like tomato (Solanum spp.) and faba bean (Vicia faba) species. This review article extensively discusses management strategies to control broomrapes, which range from preventive measures to curative approaches. Additionally, it includes meaningful information on the intricate molecular mechanisms underlying the broomrape–host interaction, focusing on the host recognition of parasitic plant molecular patterns and the hormonal crosstalk that regulates the establishment of parasitism. Moreover, this article highlights the potential of breeding for resistance in cultivated crops, such as tomato and faba bean, as a sustainable, long-term solution to combat broomrape infestation. This review serves as a valuable resource for both researchers and farmers, offering insights for developing, implementing, and adapting effective and environmentally sustainable management practices for broomrape in Mediterranean agricultural systems.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue BioTech: 5th Anniversary)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessEssay
The Origins and Proliferation of Unfounded Comparisons Regarding the Safety of Mifepristone
by
Cameron Louttit
BioTech 2025, 14(2), 39; https://doi.org/10.3390/biotech14020039 - 24 May 2025
Abstract
As part of the substantial public discourse surrounding the distribution and use of mifepristone, which is used with misoprostol to facilitate drug-induced abortions, claims comparing the safety of this regimen to that of common pharmaceuticals have emerged and proliferated. Offered in forums ranging
[...] Read more.
As part of the substantial public discourse surrounding the distribution and use of mifepristone, which is used with misoprostol to facilitate drug-induced abortions, claims comparing the safety of this regimen to that of common pharmaceuticals have emerged and proliferated. Offered in forums ranging from social media to the Supreme Court, these claims have so gained public acceptance that they are now echoed without scrutiny and, at times, reference. Yet the simplistic slogan that “mifepristone is safer than Tylenol”, though easily disseminated, defies both an intuitive understanding of how we evaluate drug safety and our norms and regulations for doing so. Indeed, if such an assertion was attributable to the manufacturer, it would precipitate a reprimand by the FDA given the lack of specific, controlled, and head-to-head evidence rightly required for its support. To the extent that these claims persist, however, including among the outputs of medical societies, abortion centers, clinical researchers, and government officials, and to the extent that they aim to inform both individual and public decision-making, it is critical that the evidence offered for their support be thoroughly explored. Such examination reveals these claims to be wholly unfounded, offering deficient and disingenuous representations of safety for any of the drugs compared.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Biotechnology Regulation)
Open AccessArticle
Strategy for the Construction of SARS-CoV-2 S and N Recombinant Proteins and Their Immunogenicity Evaluation
by
Paulo Henrique Guilherme Borges, Barbara Gregio, Helena Tiemi Suzukawa, Gislaine Silva-Rodrigues, Emanuella de Castro Andreassa, Isabela Madeira de Castro, Guilherme Bartolomeu-Gonçalves, Emerson José Venancio, Phileno Pinge-Filho, Viviane Monteiro Góes, Celso Vataru Nakamura, Eliandro Reis Tavares, Tatiana de Arruda Campos Brasil de Souza, Sueli Fumie Yamada-Ogatta and Lucy Megumi Yamauchi
BioTech 2025, 14(2), 38; https://doi.org/10.3390/biotech14020038 - 23 May 2025
Abstract
This study reports the construction, expression, and purification of synthetic SARS-CoV-2 spike (S) and nucleoprotein (N) containing immunodominant epitopes. The pET28aS_epit construct included epitopes 287–317, 402, 507, 524–598, and 601–640, while the pET28aN_epit construct included residues 42–62, 153–172, and 355–401. Commercial sequences of
[...] Read more.
This study reports the construction, expression, and purification of synthetic SARS-CoV-2 spike (S) and nucleoprotein (N) containing immunodominant epitopes. The pET28aS_epit construct included epitopes 287–317, 402, 507, 524–598, and 601–640, while the pET28aN_epit construct included residues 42–62, 153–172, and 355–401. Commercial sequences of both proteins were used as controls. The four constructs were expressed using the Escherichia coli BL21(DE3) star strain at 37 °C. The results show that the S protein constructs were insoluble, unlike the N protein constructs. Both recombinant proteins induced immune responses in mice and were recognized by antibodies present in sera from COVID-19-positive and/or SARS-CoV-2-vaccinated humans. No significant differences in immune recognition were observed between our constructs and the commercially available proteins. In conclusion, S_epit and N_epit could be promising starting points for the development of new strategies based on immunological reactions for the control of SARS-CoV-2 infections.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Computational Biology)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Exploring Genetic Diversity and Population Structure of Australian Passion Fruit Germplasm
by
Xinhang Sun, Peter Bundock, Patrick Mason, Pragya Dhakal Poudel, Rajeev Varshney, Bruce Topp and Mobashwer Alam
BioTech 2025, 14(2), 37; https://doi.org/10.3390/biotech14020037 - 16 May 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Evaluating the genetic variability of germplasms is essential for enhancing and developing superior cultivars. However, there is limited information on cultivated germplasm diversity for Australian passion fruit breeding programs. The genetic diversity of Australian passion fruit (Passiflora spp.), including 94 rootstocks and
[...] Read more.
Evaluating the genetic variability of germplasms is essential for enhancing and developing superior cultivars. However, there is limited information on cultivated germplasm diversity for Australian passion fruit breeding programs. The genetic diversity of Australian passion fruit (Passiflora spp.), including 94 rootstocks and 95 scions, was evaluated to support breeding programs aimed at enhancing productivity, fruit quality, and overall crop resilience. Rootstocks were genotyped using high-density 24k Diversity Arrays Technology (DArT)-based single-nucleotide polymorphism (SNP) markers, while genetic characterization of scions was conducted using eight simple sequence repeat (SSR) markers. The resulting genetic relationships revealed significant variation within rootstock populations. Bayesian cluster analysis in STRUCTURE showed that the rootstock population was divided into six distinct genetic groups, whereas only two subpopulations were identified among the scion accessions. SNP-based genotyping further highlighted the allelic diversity of Australian rootstocks, suggesting a rich reservoir of genetic traits for rootstock improvement. These findings underscore the importance of preserving and utilizing genetic diversity in Australian passion fruit germplasm to drive the development of superior cultivars with enhanced adaptability and performance under diverse environmental conditions.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Bioremediation Potential of a Non-Axenic Cyanobacterium Synechococcus sp. for Municipal Wastewater Treatment in the Peruvian Amazon: Growth Kinetics, Ammonium Removal, and Biochemical Characterization Within a Circular Bioeconomy Framework
by
Remy G. Cabezudo, Juan C. Castro, Carlos G. Castro, Hicler N. Rodriguez, Gabriela L. García, Paul M. Vizcarra, Carmen Ruiz-Huamán and Marianela Cobos
BioTech 2025, 14(2), 36; https://doi.org/10.3390/biotech14020036 - 13 May 2025
Abstract
Effective wastewater management is critical for mitigating environmental and health impacts in ecologically sensitive regions like the Peruvian Amazon, where rapid urbanization has led to increased discharge of nutrient-rich effluents into freshwater systems. Conventional treatment methods often fail to address nutrient imbalances while
[...] Read more.
Effective wastewater management is critical for mitigating environmental and health impacts in ecologically sensitive regions like the Peruvian Amazon, where rapid urbanization has led to increased discharge of nutrient-rich effluents into freshwater systems. Conventional treatment methods often fail to address nutrient imbalances while generating secondary pollutants. This study aims to evaluate the bioremediation potential of a non-axenic cyanobacterium, Synechococcus sp., isolated from the Amazon Basin, for municipal wastewater treatment within a circular bioeconomy framework. The strain was cultivated in different concentrations of municipal wastewater (25%, 50%, 75%, 100%) from Moronacocha Lake in the Peruvian Amazon to assess growth kinetics, ammonium removal efficiency, and biochemical composition. The cyanobacterium exhibited optimal performance in 25% wastewater, achieving the highest specific growth rate (22.8 × 10−2 μ·day−1) and biomass increase (393.2%), exceeding even the standard BG-11 medium. This treatment also demonstrated exceptional ammonium removal efficiency (95.4%) and enhanced phycocyanin production (33.6 μg/mg, 56% higher than the control). As wastewater concentration increased, both growth parameters and removal efficiency progressively declined. Biochemical analysis revealed that higher wastewater concentrations resulted in decreased protein content and increased lipid accumulation in the biomass. These findings demonstrate the dual potential of Synechococcus sp. for effective wastewater remediation and production of valuable biomass with modifiable biochemical characteristics, offering a sustainable approach for wastewater management in the Peruvian Amazon region.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Topic Sustainable Water Purification Technologies for Multiple Applications)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Comparative Potential of Chitinase and Chitosanase from the Strain Bacillus thuringiensis B-387 for the Production of Antifungal Chitosan Oligomers
by
Gleb Aktuganov, Alexander Lobov, Nailya Galimzianova, Elena Gilvanova, Lyudmila Kuzmina, Polina Milman, Alena Ryabova, Alexander Melentiev, Sergey Chetverikov, Sergey Starikov and Sergey Lopatin
BioTech 2025, 14(2), 35; https://doi.org/10.3390/biotech14020035 - 8 May 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
The depolymerization of chitosan using chitinolytic enzymes is one of the most promising approaches for the production of bioactive soluble chitooligosaccharides (COS) due to its high specificity, environmental safety, mild reaction conditions, and potential for development. However, the comparative efficacy of bacterial chitinases
[...] Read more.
The depolymerization of chitosan using chitinolytic enzymes is one of the most promising approaches for the production of bioactive soluble chitooligosaccharides (COS) due to its high specificity, environmental safety, mild reaction conditions, and potential for development. However, the comparative efficacy of bacterial chitinases and chitosanases in terms of yield, solubility, and antimicrobial activity of produced COS remains understudied. In this work, chitinase (73 kDa) and chitosanase (40 kDa) from the strain Bacillus thuringiensis B-387 (Bt-387) were purified using various chromatographic techniques and compared by their action on chitosan (DD 85%). The molecular mass and structure of generated COS was determined using TLC, LC-ESI-MS, HP-SEC, and C13-NMR techniques. Chitosanase converted the polymer more rapidly to short COS (GlcN2-GlcN4), than chitinase, and was more specific in its action on mixed bonds between GlcN and GlcNAc. Chitosanase needed a noticeably shorter incubation time and enzyme–substrate ratio than chitinase for production of larger oligomeric molecules (Mw 2.4–66.5 and 15.4–77.7 kDa, respectively) during controlled depolymerization of chitosan. Moreover, chitosanase-generated oligomers demonstrate better solubility and a higher antifungal activity in vitro against the tested plant pathogenic fungi. These features, as well as the high enzyme production and its simplified purification protocol, make chitosanase B-387 more suitable for the production of antifungal chitooligomers than chitinase.
Full article

Graphical abstract
Open AccessArticle
Combined Effect of Spent Mushroom Substrate and Agro-Industrial Residues on Pleurotus columbinus Production and Intra-Cellular Polysaccharide Synthesis
by
Marianna Dedousi, Chrysavgi Gardeli, Seraphim Papanikolaou and Panagiota Diamantopoulou
BioTech 2025, 14(2), 34; https://doi.org/10.3390/biotech14020034 - 2 May 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Spent mushroom substrate (SMS), spent coffee grounds from espresso production (SCG), faba bean harvest residues (FBR), pistachio shells (PS) wheat straw (WS) (control) agro-industrial waste were combined in different ratios, with or without supplements (wheat bran, soybean flour), to create novel substrates for
[...] Read more.
Spent mushroom substrate (SMS), spent coffee grounds from espresso production (SCG), faba bean harvest residues (FBR), pistachio shells (PS) wheat straw (WS) (control) agro-industrial waste were combined in different ratios, with or without supplements (wheat bran, soybean flour), to create novel substrates for Pleurotus columbinus growth. The impact of the substrates on the mycelial growth rate (Kr), biomass production, laccase, total cellulases and carbohydrate synthesis, along with the C and N consumption by P. columbinus, were examined in fully colonized substrates. The incubation period, earliness and biological efficiency (B.E.) (%) were also determined. Then, the intracellular polysaccharide (ICP) contents of the P. columbinus produced mushrooms were evaluated in the most promising substrates. P. columbinus was grown successfully in a wide range of C/N ratios of substrates and the fastest Kr (7.6 mm/d) was detected on the 70 SMS-30 FBR, without supplements, whereas substrates consisting of SCG enhanced biomass production (700.0–803.7 mg/g d.w.). SMS and PS or SCG led to the shortest incubation and earliness period of P. columbinus. The C content was reduced and the N content was substantially increased in all the colonized substrates. The 70 SMS-30 FBR and 80 SMS considerably enhanced the laccase production (up to 59,933.4 U/g d.w.) and substrates consisting of PS promoted total cellulases activities. Greater amounts of carbohydrates (3.8–17.4 mg/g d.w.) than that in the control were recorded for all the substrates. The combination of SMS and SCG or WS led to the highest B.E. values (59.3–87.1%) and ICP amounts (34.7–45.9%, w/w), regardless of the supplement addition. These findings support the effective utilization of agro-industrial waste in P. columbinus cultivation, producing high-value-added compounds and supporting mushroom growth.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Innovations in Proteomic Technologies and Artificial Neural Networks: Unlocking Milk Origin Identification
by
Achilleas Karamoutsios, Emmanouil D. Oikonomou, Chrysoula (Chrysa) Voidarou, Lampros Hatzizisis, Konstantina Fotou, Konstantina Nikolaou, Evangelia Gouva, Evangelia Gkiza, Nikolaos Giannakeas, Ioannis Skoufos and Athina Tzora
BioTech 2025, 14(2), 33; https://doi.org/10.3390/biotech14020033 - 28 Apr 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Milk’s biological origin determination, including its adulteration and authenticity, presents serious limitations, highlighting the need for innovative advanced solutions. The utilisation of proteomic technologies combined with personalised algorithms creates great potential for a more comprehensive approach to analysing milk samples effectively. The current
[...] Read more.
Milk’s biological origin determination, including its adulteration and authenticity, presents serious limitations, highlighting the need for innovative advanced solutions. The utilisation of proteomic technologies combined with personalised algorithms creates great potential for a more comprehensive approach to analysing milk samples effectively. The current study presents an innovative approach utilising proteomics and neural networks to classify and distinguish bovine, ovine and caprine milk samples by employing advanced machine learning techniques; we developed a precise and reliable model capable of distinguishing the unique mass spectral signatures associated with each species. Our dataset includes a diverse range of mass spectra collected from milk samples after MALDI-TOF MS (Matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization-time of flight mass spectrometry) analysis, which were used to train, validate, and test the neural network model. The results indicate a high level of accuracy in species identification, underscoring the model’s potential applications in dairy product authentication, quality assurance, and food safety. The current research offers a significant contribution to agricultural science, providing a cutting-edge method for species-specific classification through mass spectrometry. The dataset comprises 648, 1554, and 2392 spectra, represented by 16,018, 38,394, and 55,055 eight-dimensional vectors from bovine, caprine, and ovine milk, respectively.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Production of Multifunctional Hydrolysates from the Lupinus mutabilis Protein Using a Micrococcus sp. PC7 Protease
by
Keyla Sofía Llontop-Bernabé, Arturo Intiquilla, Carlos Ramirez-Veliz, Marco Santos, Karim Jiménez-Aliaga, Amparo Iris Zavaleta, Samuel Paterson and Blanca Hernández-Ledesma
BioTech 2025, 14(2), 32; https://doi.org/10.3390/biotech14020032 - 27 Apr 2025
Abstract
The growing demand for functional foods has driven the search for bioactive compounds derived from plant proteins. Lupinus mutabilis “Tarwi”, a legume native to the Peruvian Andes, stands out for its high protein content and potential as a source of bioactive peptides (BPs).
[...] Read more.
The growing demand for functional foods has driven the search for bioactive compounds derived from plant proteins. Lupinus mutabilis “Tarwi”, a legume native to the Peruvian Andes, stands out for its high protein content and potential as a source of bioactive peptides (BPs). In this study, the functionality of the proteins contained in the albumin fraction (AF) isolated by tangential ultrafiltration (TFF) was investigated by using the OmicsBox software. The identified proteins were functionally classified into three groups: cellular component (35.57%), molecular function (33.45%), and biological process (30.97%). The isolated AF was hydrolysed with the native protease PC7 (HAP), optimizing the E/S ratio and time parameters. Additionally, sequential hydrolysis of the PC7 protease and alcalase (HAPA) was performed. In vitro multifunctionality assays, HAP and HAPA demonstrated the ability to scavenge radicals (ABTS and ORAC) and inhibit angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE)-I and dipeptidyl peptidase IV (DPP-IV). The findings of this study highlight the potential of L. mutabilis albumin hydrolysate as a multifunctional ingredient for functional foods aimed at managing chronic conditions associated with oxidative stress, hypertension, and/or metabolic disorders.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Natural Antioxidants: Determination in Food and Nutraceuticals and Implications on Human Health)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Vaginal Microbiota Patterns Associated with Yeast Infection in Mexican Women, a Pilot Study
by
Janet Pineda-Díaz, Carolina Miranda-Brito, Carmen Josefina Juárez-Castelán, Alberto Piña-Escobedo, Noemí del Socorro Lázaro-Pérez, Alejandra de la Cruz-Munguía, Daniela Ramírez-Sánchez, Yuliana Gómez-Meraz, Juan Manuel Vélez-Ixta and Jaime García-Mena
BioTech 2025, 14(2), 31; https://doi.org/10.3390/biotech14020031 - 26 Apr 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Recurrent vulvovaginal candidiasis (RVVC) is a common condition that affects women of reproductive age. The etiology of RVVC remains largely unknown, but it is believed to be associated with changes in vaginal microbiota composition. This study investigates the vaginal microbiota in 57 women
[...] Read more.
Recurrent vulvovaginal candidiasis (RVVC) is a common condition that affects women of reproductive age. The etiology of RVVC remains largely unknown, but it is believed to be associated with changes in vaginal microbiota composition. This study investigates the vaginal microbiota in 57 women with RVVC and 38 healthy controls. Bacterial DNA was analyzed using high-throughput 16S rRNA gene sequencing, and Candida and Saccharomyces species were determined by PCR. RVVC cases had a higher prevalence of Nakaseomyses glabratus (former Candida glabrata) compared to controls. Alpha diversity metrics were similar between groups, but beta diversity analysis revealed significant differences in vaginal microbiota composition. The Firmicutes abundance was altered in RVVC cases, with genus Bifidobacterium and phylum Actinobacteriota being more abundant than in the controls. At the genus level, Lactobacillus dominated controls using antibiotics, while Bifidobacterium was higher in cases with no antibiotic intake. Our study provides evidence that Nakaseomyses glabratus (former Candida glabrata) is a significant pathogen in RVVC, while Candida albicans was more prevalent in healthy women. The vaginal microbiota composition differs significantly between the two groups, with distinct patterns of bacterial abundance and changes in Firmicutes abundance.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Characterization and Biotechnology of Three New Strains of Basidial Fungi as Promising Sources of Biologically Active Substances
by
Maria Alexandrovna Sysoeva, Ilyuza Shamilevna Prozorova, Elena Vladislavovna Sysoeva, Tatyana Vladimirovna Grigoryeva and Ruzilya Kamilevna Ismagilova
BioTech 2025, 14(2), 30; https://doi.org/10.3390/biotech14020030 - 25 Apr 2025
Abstract
The study of new strains of basidiomycetes as sources of biologically active substances is a promising direction in modern biotechnology. This work aims to isolate new cultures of the fungi Daedaleopsis tricolor, Pycnoporellus fulgens and Trichaptum abietinum from natural fruiting bodies and
[...] Read more.
The study of new strains of basidiomycetes as sources of biologically active substances is a promising direction in modern biotechnology. This work aims to isolate new cultures of the fungi Daedaleopsis tricolor, Pycnoporellus fulgens and Trichaptum abietinum from natural fruiting bodies and to improve their growth conditions on solid nutrient media. The identification of fungi was performed based on their morphological features and using the Sanger sequencing method. Cultivation was carried out by placing inoculum in the middle of a Petri dish and at the edge, which provided a more comprehensive definition of the characteristics of colonies and fungus hyphae. New strains were registered in Genbank Overview. The optimal cultivation temperature was 27 °C for all studied strains. The highest radial growth was observed on synthetic medium for D. tricolor (5.26 mm/day) and T. abietinum (7.5 mm/day), and on synthetic medium with lignin for P. fulgens (2.98 mm/day). The biomass amount of D. tricolor KS11 was 133.25 mg at 9 days of cultivation, that of P. fulgens KS12 was 86.73 mg at 16 days, and that of T. abietinum KS10 was 227.33 mg at 6 days. New strains of fungi can be used to obtain biologically active substances for the food, pharmaceutical and cosmetic industries.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Industry, Agriculture and Food Biotechnology)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Direct Shoot Regeneration from the Finger Millet’s In Vitro-Derived Shoot Apex and Genetic Fidelity Study with ISSR Markers
by
Theivanayagam Maharajan, Veeramuthu Duraipandiyan and Thumadath Palayullaparambil Ajeesh Krishna
BioTech 2025, 14(2), 29; https://doi.org/10.3390/biotech14020029 - 18 Apr 2025
Abstract
Globally, people are cultivating finger millet, an important cereal, to improve food availability and health benefits for humans. However, the biotechnological research on this millet is limited and insufficient in this field. The primary focus of this study is to optimize an efficient
[...] Read more.
Globally, people are cultivating finger millet, an important cereal, to improve food availability and health benefits for humans. However, the biotechnological research on this millet is limited and insufficient in this field. The primary focus of this study is to optimize an efficient regenerated protocol for initiating further plant transformation studies, using the shoot apex as an explant and various growth regulators. For example, three cytokinins (BAP, TDZ, and Kin) at different concentrations were used to induce multiple shoots of finger millet. Among these, TDZ (4.5 µM) provided the maximum number (17.3) of shoots as compared to BAP and Kin. IBA (2.46 µM), along with MS medium, was used for the induction of roots, where 5.6 roots were produced in an individual shoot and the length of the root was longer with a size of 8.2 cm after two weeks of incubation. The clonal fidelity of the in vitro regenerated plantlets of finger millet was confirmed by ISSR primers. Overall, the present work developed a robust and reliable procedure for the establishment of efficient and reproducible regeneration through the shoot apex that will be useful for the genetic improvement of this crop. The genetic enhancement of these millets as well as the successful creation of transgenic plant varieties modified for resistance to biotic and abiotic challenges in the near future would be aided by this study.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Industry, Agriculture and Food Biotechnology)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessReview
Matrix Metalloproteinases in Glioma: Drivers of Invasion and Therapeutic Targets
by
Ella E. Aitchison, Alexandra M. Dimesa and Alireza Shoari
BioTech 2025, 14(2), 28; https://doi.org/10.3390/biotech14020028 - 15 Apr 2025
Abstract
Matrix metalloproteinases (MMPs) are a family of zinc-dependent proteolytic enzymes that are crucial for the remodeling of the extracellular matrix, a process that is often co-opted by cancers, including brain tumors, to facilitate growth, invasion, and metastasis. In gliomas, MMPs contribute to a
[...] Read more.
Matrix metalloproteinases (MMPs) are a family of zinc-dependent proteolytic enzymes that are crucial for the remodeling of the extracellular matrix, a process that is often co-opted by cancers, including brain tumors, to facilitate growth, invasion, and metastasis. In gliomas, MMPs contribute to a complex interplay involving tumor proliferation, angiogenesis, and immune modulation, thereby influencing tumor progression and patient prognosis. This review provides a comprehensive analysis of the roles of various MMPs in different types of gliomas, from highly malignant gliomas to metastatic lesions. Emphasis is placed on how the dysregulation of MMPs impacts tumor behavior, the association between specific MMPs and the tumor grade, and their potential as biomarkers for diagnosis and prognosis. Additionally, the current therapeutic approaches targeting MMP activity are discussed, exploring both their challenges and future potential. By synthesizing recent findings, this paper aims to clarify the broad significance of MMPs in gliomas and propose avenues for translational research that could enhance treatment strategies and clinical outcomes.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Medical Biotechnology)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Highly Accessed Articles
Latest Books
E-Mail Alert
News
Topics
Topic in
Applied Sciences, BioMedInformatics, BioTech, Genes, Computation, Applied Biosciences
Computational Intelligence and Bioinformatics (CIB)
Topic Editors: Marco Mesiti, Giorgio Valentini, Elena Casiraghi, Tiffany J. CallahanDeadline: 30 September 2025
Topic in
Energies, Membranes, Molecules, Separations, Water, Sustainability, BioTech
Sustainable Water Purification Technologies for Multiple Applications
Topic Editors: Marco Pellegrini, Cesare Saccani, Alessandro GuzziniDeadline: 31 October 2025
Topic in
BioTech, DNA, Genes, IJMS, CIMB
Single-Cell Technologies: From Research to Application
Topic Editors: Ken-Hong Lim, Chung-Der Hsiao, Pei-Ming YangDeadline: 31 December 2025
Topic in
IJPB, Molecules, Plants, Toxins, Pharmaceuticals, BioTech
From Plant to Pharmacology: Understanding the Metabolism of Natural Products
Topic Editors: Fawzy A. Elbarbry, Mike EspirituDeadline: 31 August 2026

Conferences
Special Issues
Special Issue in
BioTech
Natural Antioxidants: Determination in Food and Nutraceuticals and Implications on Human Health
Guest Editor: Gregorio PeronDeadline: 31 July 2025
Special Issue in
BioTech
Volatile Fatty Acids (VFAs) and Their Potential in Waste-Based Biorefineries
Guest Editors: Amir Mahboubi Soufiani, Konstantinos ChandoliasDeadline: 30 September 2025
Special Issue in
BioTech
Advances in Bioimaging Technology
Guest Editor: Tomoaki KahyoDeadline: 31 December 2025
Special Issue in
BioTech
BioTech: 5th Anniversary
Guest Editors: Massimo Negrini, Francesco Secundo, Gary HardimanDeadline: 31 December 2025












