Highly Crystalline Ordered Cu-dopedTiO2Nanostructure by Paper Templated Method: Hydrogen Production and Dye Degradation under Natural Sunlight
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Experimental Section
2.1. Materials
2.2. Synthesis of TiO2 and Cu-TiO2
2.3. Characterization
2.4. PhotocatalyticActivity
2.4.1. Rhodamine B (RhB) Degradation
2.4.2. Photocatalytic H2Production
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Structural Study
3.2. Optical Study
3.3. Morphological Study
3.4. Photocatalytic Study
3.4.1. RhB Degradation
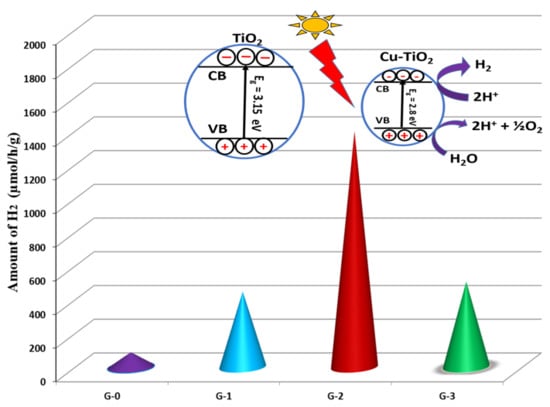
3.4.2. Photocatalytic Hydrogen Production
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sahoo, D.P.; Rath, D.; Nanda, B.; Parida, K.M. Transition metal/metal oxide modified MCM-41 for pollutant degradation and hydrogen energy production: A review. ACS Adv. 2015, 5, 83707–83724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, M.; Zeng, G.; Huang, D.; Lai, C.; Xu, P.; Zhang, C.; Liu, Y. Hydroxyl radicals based advanced oxidation processes (AOPs) for remediation of soils contaminated with organic compounds: A review. Chem. Eng. J. 2016, 284, 582–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andreozzi, R.; Caprio, V.; Insola, A.; Marotta, R. Advanced oxidation processes (AOP) for water purification and recovery. Catal. Today 1999, 53, 51–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raman, C.D.; Kanmani, S. Textile dye degradation using nano zero valent iron: A review. J. Environ. Manag. 2016, 177, 341–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cardoso, J.C.; Bessegato, G.G.; Zanoni, M.V. Efficiency comparison of ozonation, photolysis, photocatalysis and photoelectrocatalysis methods in real textile wastewater decolorization. Water Res. 2016, 98, 39–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujishima, A.; Honda, K. Electrochemical photolysis of water at a semiconductor electrode. Nature 1972, 238, 37–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leary, R.; Westwood, A. Carbonaceous nanomaterials for the enhancement of TiO2 photocatalysis. Carbon 2011, 49, 741–772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, J.; Hai, Y.; Jaroniec, M. Photocatalytic hydrogen production over CuO-modified titania. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2011, 357, 223–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, S.; Sun, D.D. Significant improvement of photocatalytic hydrogen generation rate over TiO2 with deposited CuO. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 2009, 34, 6096–6104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakthivel, S.; Shankar, M.V.; Palanichamy, M.; Arabindoo, B.; Bahnemann, D.W.; Murugesan, V. Enhancement of photocatalytic activity by metal deposition: Characterisation and photonic efficiency of Pt, Au and Pd deposited on TiO2 catalyst. Water Res. 2004, 38, 3001–3008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.; Hwang, S.-J.; Choi, W. Visible light active platinum-ion-doped TiO2 photocatalyst. J. Phys. Chem. B 2005, 109, 24260–24267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caudillo-Flores, U.; Munoz-Batista, M.J.; Fernandez-Garcia, M.; Kubacka, A. Bimetallic Pt-Pd co-catalyst Nb-doped TiO2 materials for H2 photo-production under UV and Visible light illumination. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2018, 238, 533–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.; Wang, Y.; Shang, S.; Ni, Y.; Zhang, N.; Cao, M.; Hu, C. One-step synthesis of mulberry-shaped TiO2-Au nanocomposite and its H2 evolution property under visible light. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2018, 553, 203–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bera, P.; Hegde, M.S. Noble metal ions in CeO2 and TiO2: Synthesis, structure and catalytic properties. ACS Adv. 2015, 5, 94949–94979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devi, L.G.; Kavitha, R. A review on non metal ion doped titania for the photocatalytic degradation of organic pollutants under UV/solar light: Role of photogenerated charge carrier dynamics in enhancing the activity. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2013, 140–141, 559–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zong, X.; Lu, G.; Wang, L. Nonmetal doping in TiO2 toward visible-light-induced photocatalysis. In Environmental Photochemistry Part III; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2013; pp. 87–113. [Google Scholar]
- Ismael, M. Enhanced photocatalytic hydrogen production and degradation of organic pollutants from Fe (III) doped TiO2 nanoparticles. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2020, 8, 103676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simsek, E.B. Solvothermal synthesized boron doped TiO2 catalysts: Photocatalytic degradation of endocrine disrupting compounds and pharmaceuticals under visible light irradiation. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2017, 200, 309–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Burda, C. The electronic origin of the visible-light absorption properties of C-, N-and S-doped TiO2 nanomaterials. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2008, 130, 5018–5019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, D.-D.; Wang, Q.-H.; Chen, J.; He, C.-H.; Li, Y.; Wang, C.-H.; Quan, J.-J.; Tao, C.-L.; Lu, X.-Q. Phosphorus-doped TiO2 nanotube arrays for visible-light-driven photoelectrochemical water oxidation. Sustain. Energy Fuels 2017, 1, 248–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakar, S.A.; Ribeiro, C. Rapid and morphology controlled synthesis of anionic S-doped TiO2 photocatalysts for the visible-light-driven photodegradation of organic pollutants. ACS Adv. 2016, 6, 36516–36527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, J.; Liu, Q.; Sun, Z.; Yan, W.; Zhang, G.; Qi, Z.; Xu, P.; Wu, Z.; Wei, S. High photocatalytic activity of rutile TiO2 induced by iodine doping. J. Phys. Chem. C 2010, 114, 6035–6038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brauer, J.I.; Szulczewski, G. Important role of surface fluoride in nitrogen-doped TiO2 nanoparticles with visible light photocatalytic activity. J. Phys. Chem. B 2014, 118, 14188–14195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ciocarlan, R.-G.; Seftel, E.M.; Mertens, M.; Pui, A.; Mazaj, M.; Tusar, N.N.; Cool, P. Novel magnetic nanocomposites containing quaternary ferrites systems Co0.5Zn0.25M0.25Fe2O4 (M = Ni, Cu, Mn, Mg) and TiO2-anatase phase as photocatalysts for wastewater remediation under solar light irradiation. Mater. Sci. Eng. B 2018, 230, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dholam, R.; Patel, N.; Adami, M.; Miotello, A. Hydrogen production by photocatalytic water-splitting using Cr-or Fe-doped TiO2 composite thin films photocatalyst. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 2009, 34, 5337–5346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ampelli, C.; Passalacqua, R.; Genovese, C.; Perathoner, S.; Centi, G.; Montini, T.; Gombac, V.; Jaen, J.J.D.; Fornasiero, P. H2 production by selective photo-dehydrogenation of ethanol in gas and liquid phase on CuOx/TiO2 nanocomposites. ACS Adv. 2013, 3, 21776–21788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Sun, R.; Li, Y.; Shi, Q.; Xie, L.; Chen, J.; Xu, X.; Shi, H.; Zhao, W. High H2 evolution from quantum Cu (II) nanodot-doped two-dimensional ultrathin TiO2 nanosheets with dominant exposed {001} facets for reforming glycerol with multiple electron transport pathways. J. Phys. Chem. C 2016, 120, 10746–10756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, S.; Liu, P.; Zhu, W.; Li, G.; Zhang, D.; Li, H. Copper nanowires: A substitute for noble metals to enhance photocatalytic H2 generation. Nano Lett. 2015, 15, 4853–4858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Gao, Z.; Cui, Z.; Liang, Y.; Li, Z.; Zhu, S.; Yang, X.; Ma, J. Synthesis of Cu2O octadecahedron/TiO2 quantum dot heterojunctions with high visible light photocatalytic activity and high stability. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2016, 8, 91–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barreca, D.; Fornasiero, P.; Gasparotto, A.; Gombac, V.; Maccato, C.; Montini, T.; Tondello, E. The potential of supported Cu2O and CuO nanosystems in photocatalytic H2 production. ChemSusChem 2009, 2, 230–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xi, Z.; Li, C.; Zhang, L.; Xing, M.; Zhang, J. Synergistic effect of Cu2O/TiO2 heterostructure nanoparticle and its high H2 evolution activity. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 2014, 39, 6345–6353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colon, G.; Maicu, M.; Hidalgo, M.C.; Navio, J.A. Cu-doped TiO2 systems with improved photocatalytic activity. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2006, 67, 41–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gombac, V.; Sordelli, L.; Montini, T.; Delgado, J.J.; Adamski, A.; Adami, G.; Cargnello, M.; Bernal, S.; Fornasiero, P. CuOx− TiO2 Photocatalysts for H2 Production from Ethanol and Glycerol Solutions. J. Phys. Chem. A 2010, 114, 3916–3925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valero, J.M.; Obregon, S.; Colon, G. Active site considerations on the photocatalytic H2 evolution performance of Cu-doped TiO2 obtained by different doping methods. ACS Catal. 2014, 4, 3320–3329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajamannan, B.; Mugundan, S.; Viruthagiri, G.; Praveen, P.; Shanmugam, N. Sol–gel synthesis and characterization of pure and manganese doped TiO2 nanoparticles—A new NLO active material. Spectrochim. Acta Part A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2014, 118, 651–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, D.P.; Reddy, N.L.; Kumari, M.M.; Srinivas, B.; Kumari, V.D.; Sreedhar, B.; Roddatis, V.; Bondarchuk, O.; Karthik, M.; Neppolian, B.; et al. Cu2O-sensitized TiO2 nanorods with nanocavities for highly efficient photocatalytic hydrogen production under solar irradiation. Sol. Energy Mater. Sol. Cells 2015, 136, 157–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, S.; Liang, S.; Tong, Y.; An, X.; Long, J.; Fu, X.; Wang, X. Photocatalytic reduction of CO2 with H2O to CH4 on Cu (i) supported TiO2 nanosheets with defective {001} facets. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2015, 17, 9761–9770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kale, G.; Arbuj, S.; Kawade, U.; Rane, S.; Ambekar, J.; Kale, B. Synthesis of porous nitrogen doped zinc oxide nanostructures using a novel paper mediated template method and their photocatalytic study for dye degradation under natural sunlight. Mater. Chem. Front. 2017, 2, 163–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arbuj, S.S.; Hawaldar, R.R.; Mulik, U.P.; Wani, B.N.; Amalnerkar, D.P.; Waghmode, S.B. Preparation, characterization and photocatalytic activity of TiO2 towards methylene blue degradation. Mater. Sci. Eng. B 2010, 168, 90–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mollavali, M.; Falamaki, C.; Rohani, S. High performance NiS-nanoparticles sensitized TiO2 nanotube arrays for water reduction. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 2016, 41, 5887–5901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaiswal, R.; Bharambe, J.; Patel, N.; Dashora, A.; Kothari, D.C.; Miotello, A. Copper and Nitrogen co-doped TiO2 photocatalyst with enhanced optical absorption and catalytic activity. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2015, 168–169, 333–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murashkina, A.A.; Murzin, P.D.; Rudakova, A.V.; Ryabchuk, V.K.; Emeline, A.V.; Bahnemann, D.W. Influence of the dopant concentration on the photocatalytic activity: Al-doped TiO2. J. Phys. Chem. C 2015, 119, 24695–24703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khore, S.K.; Tellabati, N.V.; Apte, S.K.; Naik, S.D.; Ojha, P.; Kale, B.B.; Sonawane, R.S. Green sol–gel route for selective growth of 1D rutile N–TiO2: A highly active photocatalyst for H2 generation and environmental remediation under natural sunlight. ACS Adv. 2017, 7, 33029–33042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biesinger, M.C.; Lau, L.W.M.; Gerson, A.R.; Smart, R.S.C. Resolving surface chemical states in XPS analysis of first row transition metals, oxides and hydroxides: Cr, Mn, Fe, Co and Ni. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2010, 257, 887–898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aguilar, T.; Navas, J.; Alcantara, R.; Fernandez-Lorenzo, C.; Gallardo, J.J.; Blanco, G.; Martin-Calleja, J. A route for the synthesis of Cu-doped TiO2 nanoparticles with a very low band gap. Chem. Phys. Lett. 2013, 571, 49–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, Y.-C.; Hu, C.-Y.; Liang, Y.-C. Crystallographic phase evolution of ternary Zn–Ti–O nanomaterials during high-temperature annealing of ZnO–TiO2 nanocomposites. CrystEngComm 2012, 14, 5579–5584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussain, Z.; Salim, M.A.; Khan, M.A.; Khawaja, E.E. X-ray photoelectron and auger spectroscopy study of copper-sodium-germanate glasses. J. Non-Cryst. Solids 1989, 110, 44–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.-J.; Shu, W.A.; Sun, H.-M.; Wang, X.-B.; Lian, J.-S. Preparation and photocatalytic performance of Cu-doped TiO2 nanoparticles. Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China 2015, 25, 504–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]









| Sr. No | Catalyst | Band Gap (eV) | Rate Constant (min−1) | H2 Production (µmol/g/h) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | G-0 (Pure) | 3.15 | 0.03664 | 90 |
| 2 | G-1 (1%) | 3.00 | 0.04767 | 450 |
| 3 | G-2 (2%) | 2.80 | 0.1228 | 1400 |
| 4 | G-3 (3%) | 2.94 | 0.06597 | 509 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kale, G.; Arbuj, S.; Chothe, U.; Khore, S.; Nikam, L.; Kale, B. Highly Crystalline Ordered Cu-dopedTiO2Nanostructure by Paper Templated Method: Hydrogen Production and Dye Degradation under Natural Sunlight. J. Compos. Sci. 2020, 4, 48. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcs4020048
Kale G, Arbuj S, Chothe U, Khore S, Nikam L, Kale B. Highly Crystalline Ordered Cu-dopedTiO2Nanostructure by Paper Templated Method: Hydrogen Production and Dye Degradation under Natural Sunlight. Journal of Composites Science. 2020; 4(2):48. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcs4020048
Chicago/Turabian StyleKale, Gajanan, Sudhir Arbuj, Ujjwala Chothe, Supriya Khore, Latesh Nikam, and Bharat Kale. 2020. "Highly Crystalline Ordered Cu-dopedTiO2Nanostructure by Paper Templated Method: Hydrogen Production and Dye Degradation under Natural Sunlight" Journal of Composites Science 4, no. 2: 48. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcs4020048
APA StyleKale, G., Arbuj, S., Chothe, U., Khore, S., Nikam, L., & Kale, B. (2020). Highly Crystalline Ordered Cu-dopedTiO2Nanostructure by Paper Templated Method: Hydrogen Production and Dye Degradation under Natural Sunlight. Journal of Composites Science, 4(2), 48. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcs4020048