Integration of Antifouling and Underwater Sound Absorption Properties into PDMS/MWCNT/SiO2 Coatings
Abstract
1. Introduction
- (1)
- The coatings have both underwater sound absorption and antifouling properties, which will fill the gap in this filed.
- (2)
- Without adding any environmentally-unfriendly fungicide into the sample, we prepare non-toxic sound-absorbing and antifouling coatings.
- (3)
- In this study, we tested the tensile properties and water erosion resistance of the coatings to prove its durability.
2. Experimental Section
2.1. Materials
2.2. Fabrication of Nanocomposite Material
2.3. Morphology and Chemistry Characteristics
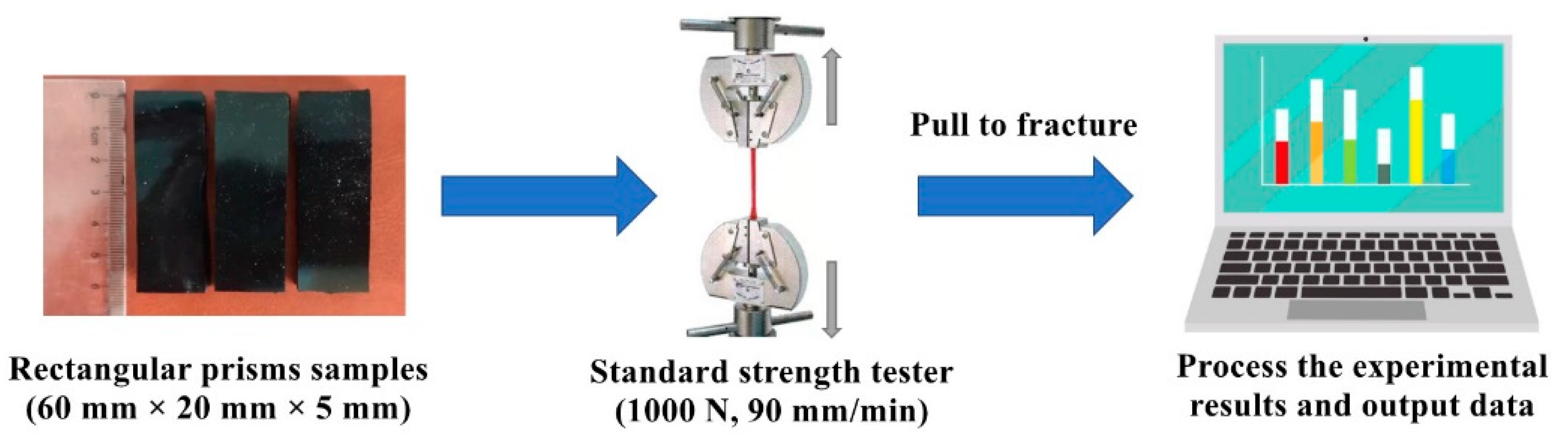
2.4. Mechanical Property Test
2.4.1. Tensile Test
2.4.2. Water Erosion Test
2.5. Antifouling Test
2.5.1. Bacterial Culture
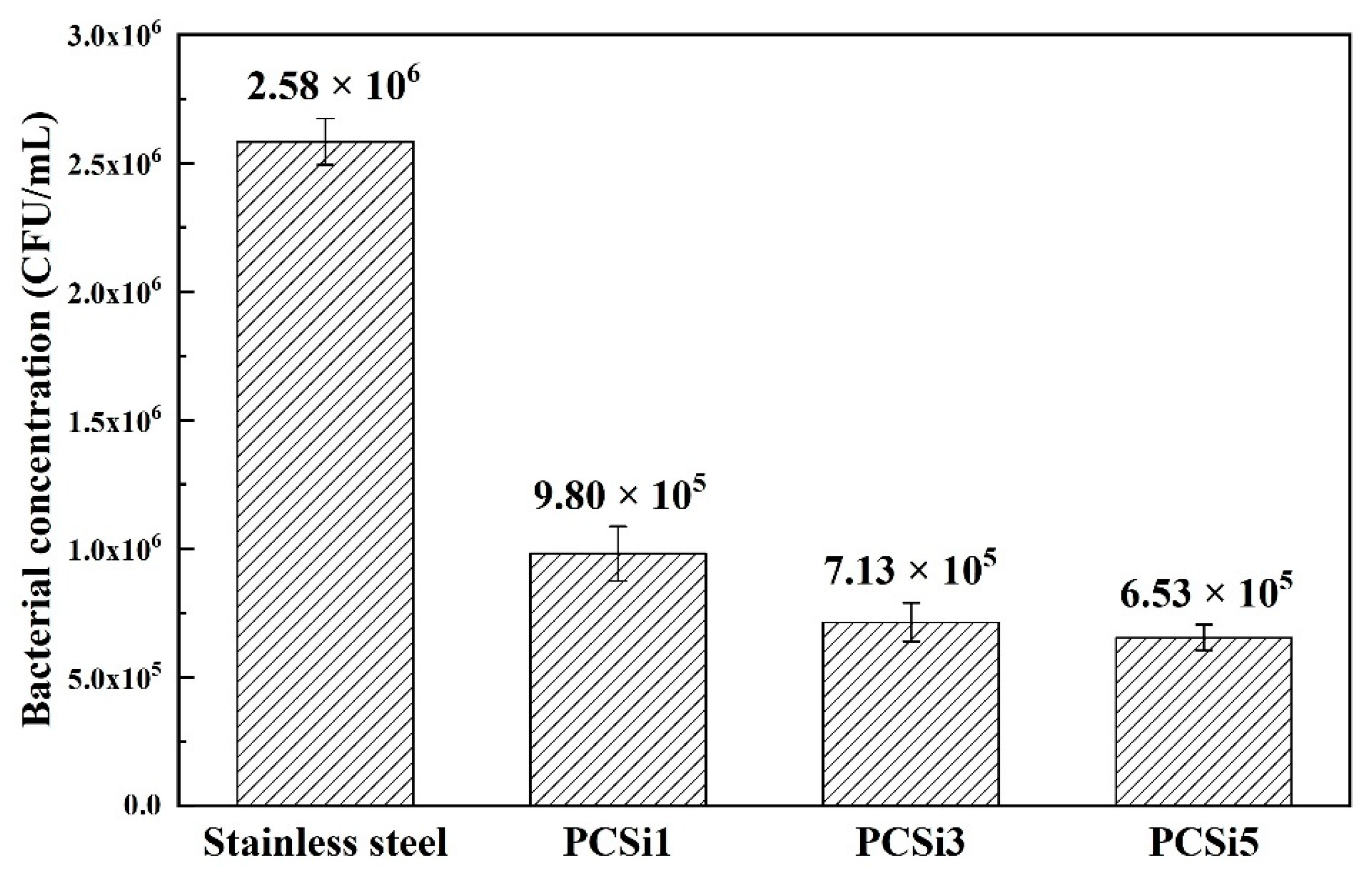
2.5.2. Plate Counting
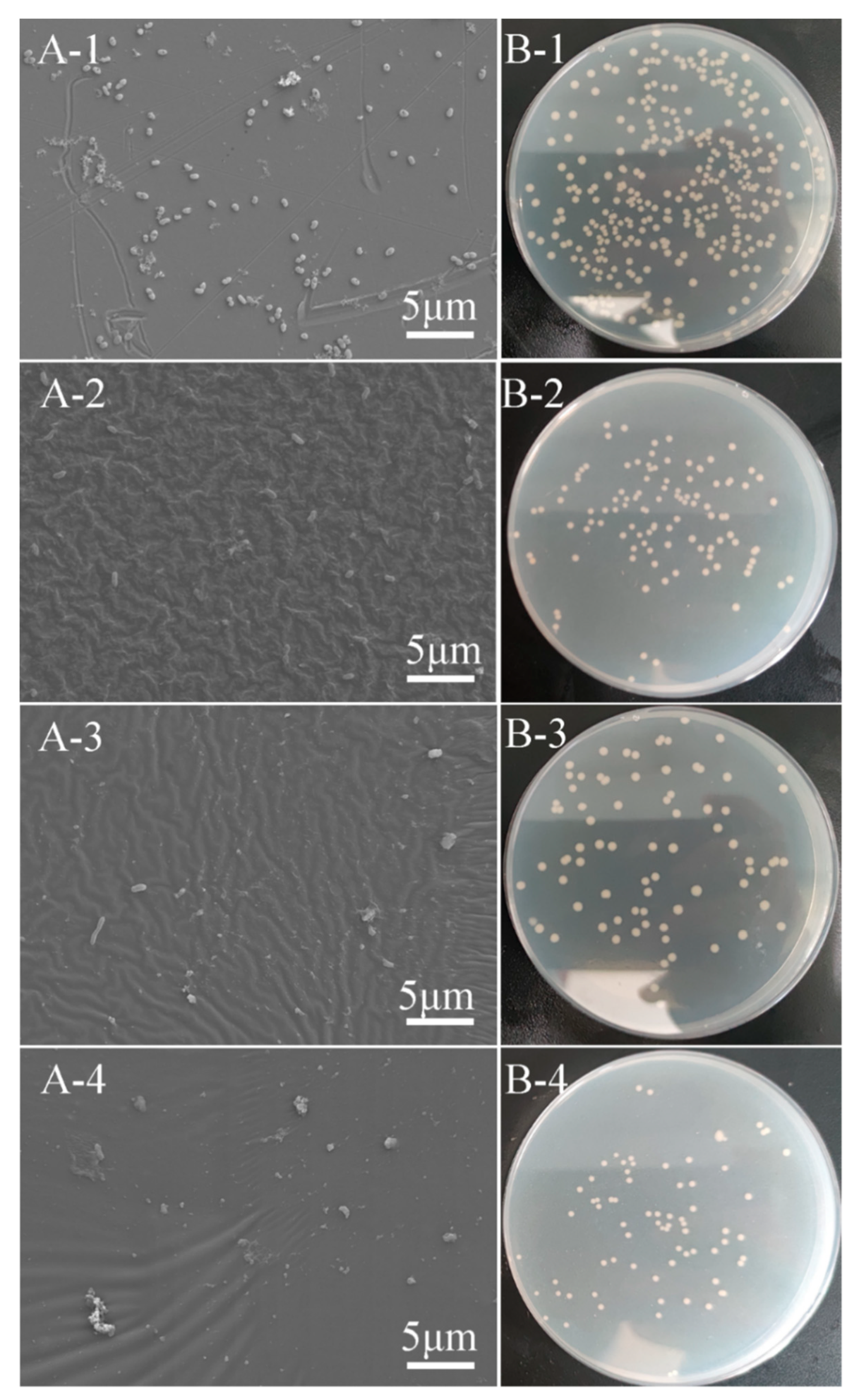
2.5.3. FE-SEM Observation
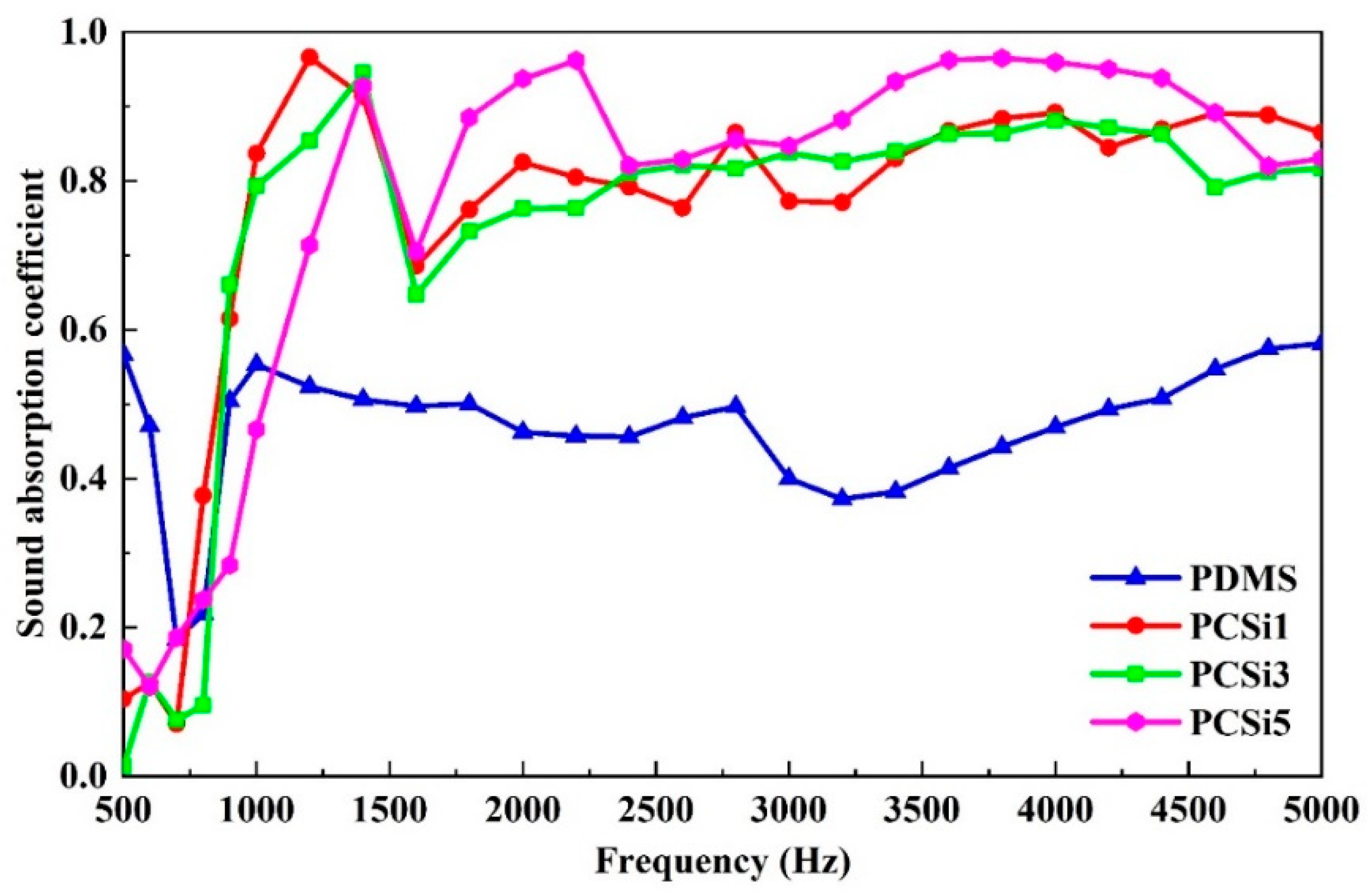
2.6. Underwater Sound Absorption Test
3. Results
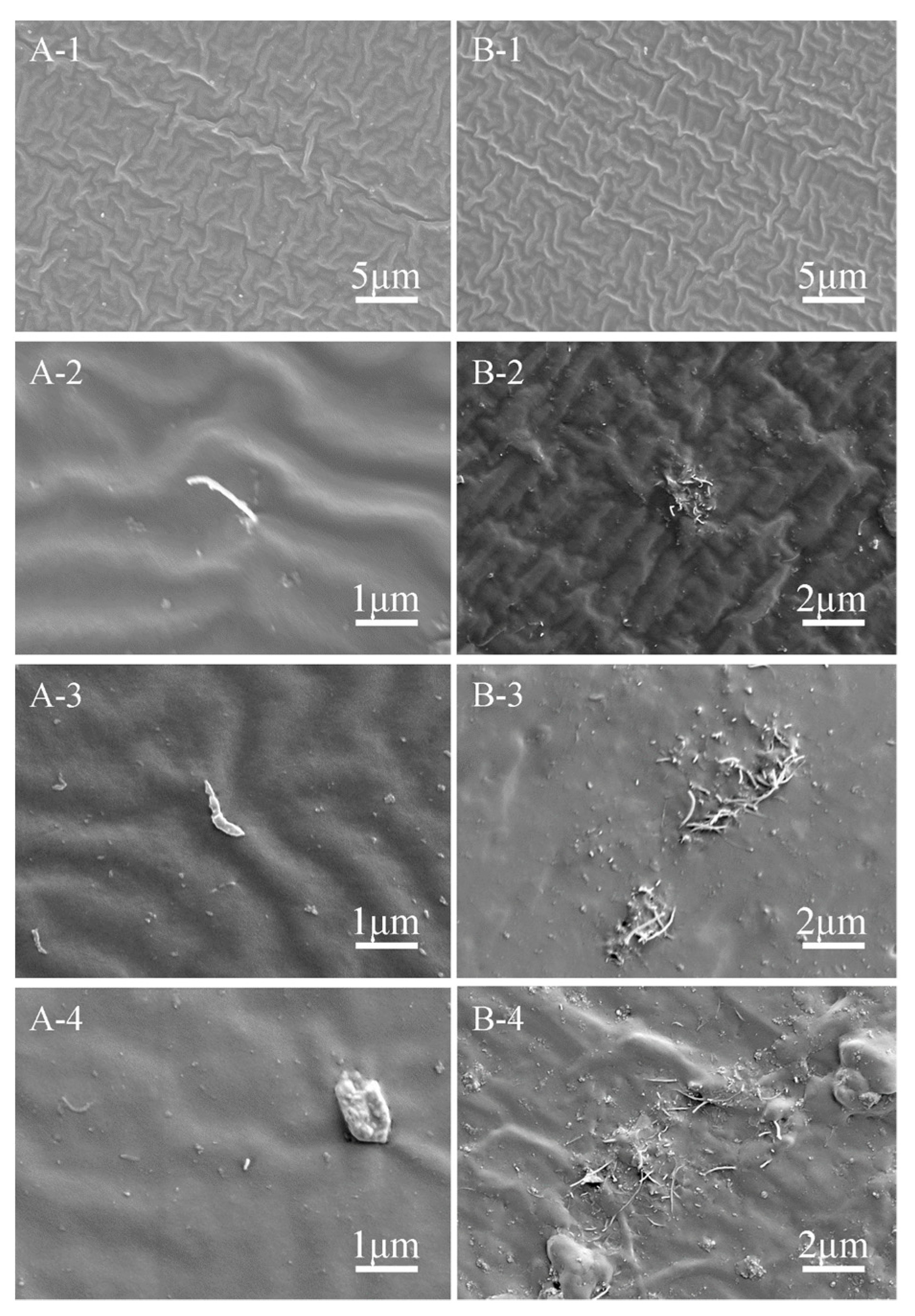
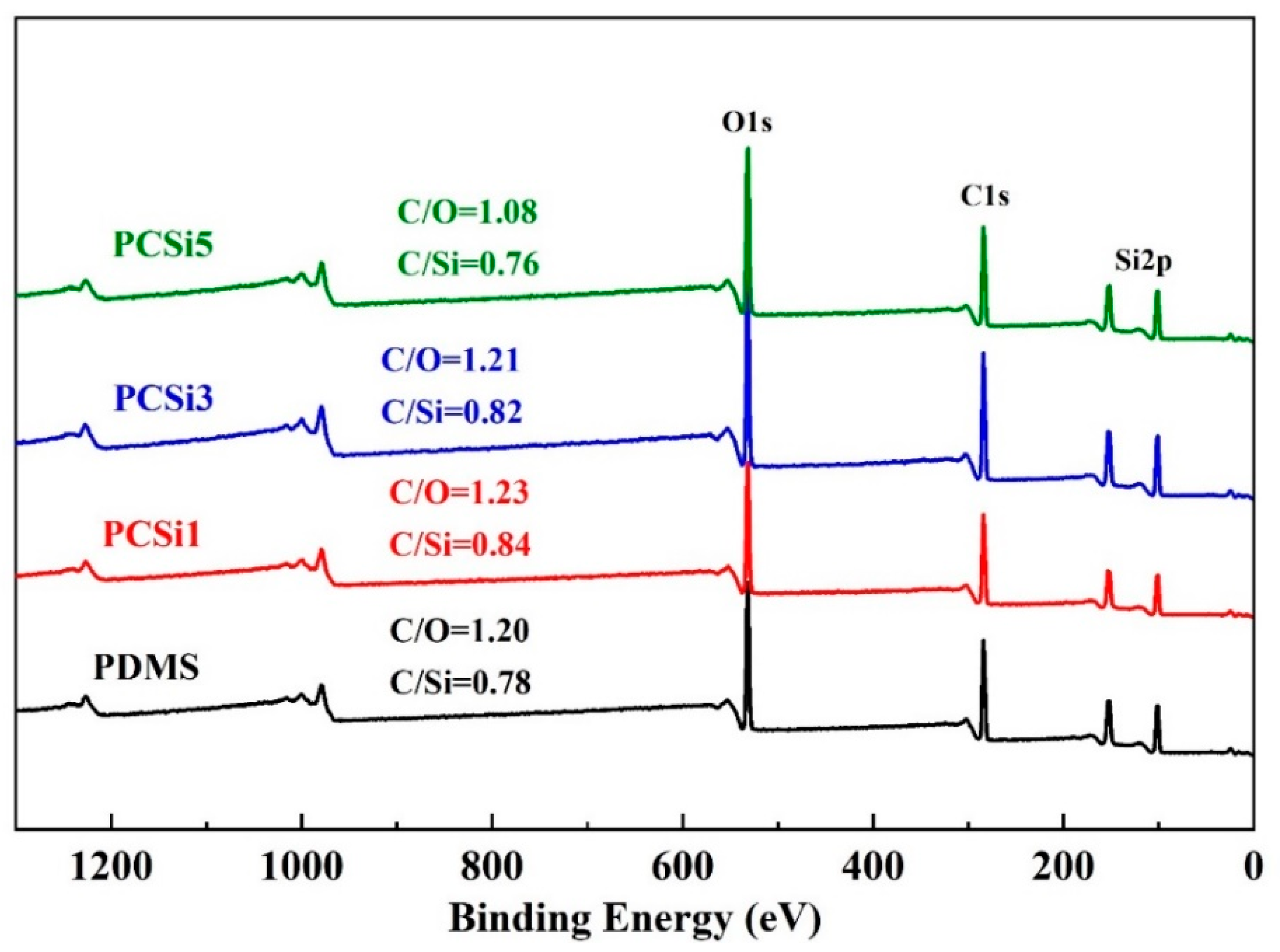
3.1. Morphology and Chemistry Characteristics
3.2. Mechanical Property Test
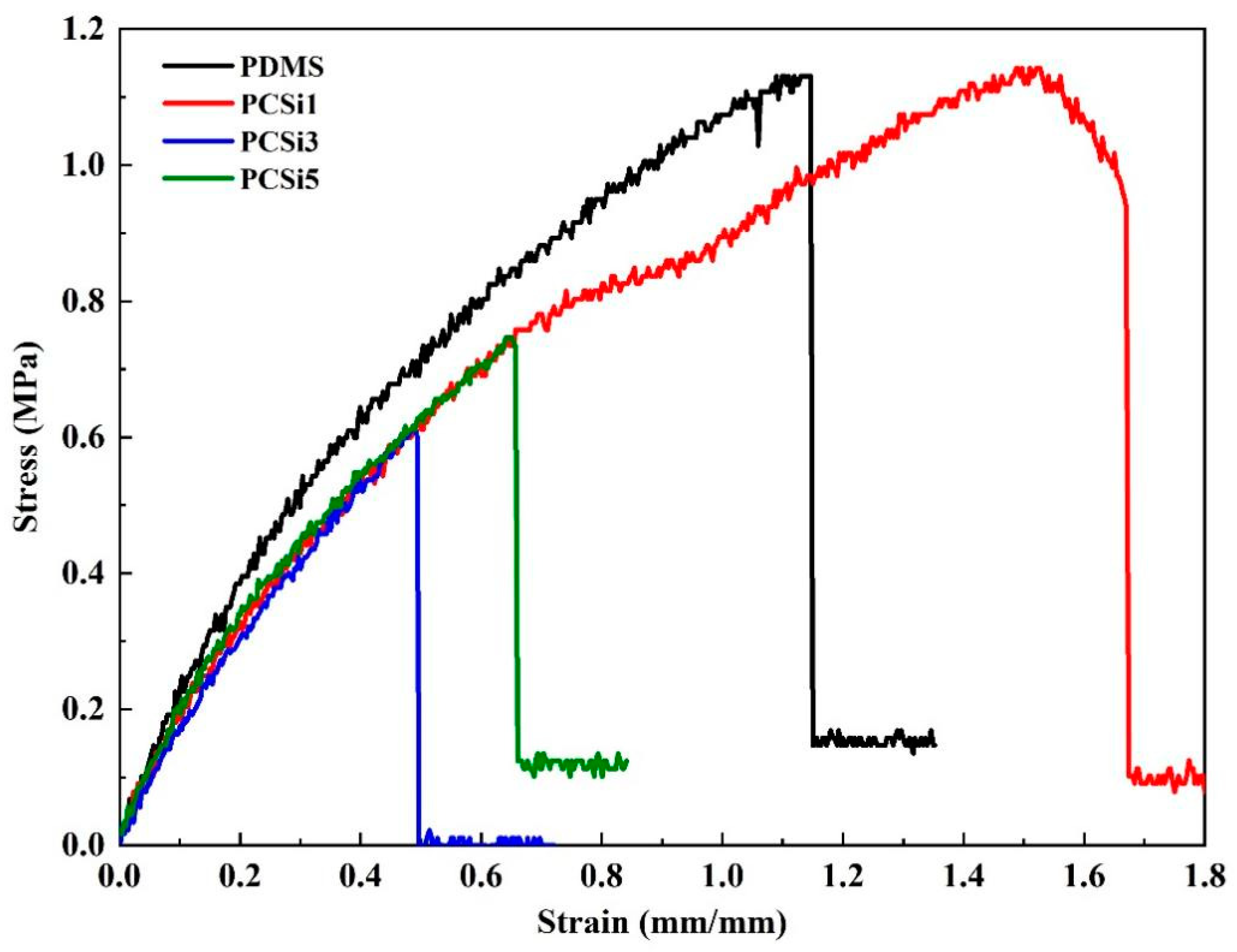
3.2.1. Tensile Test
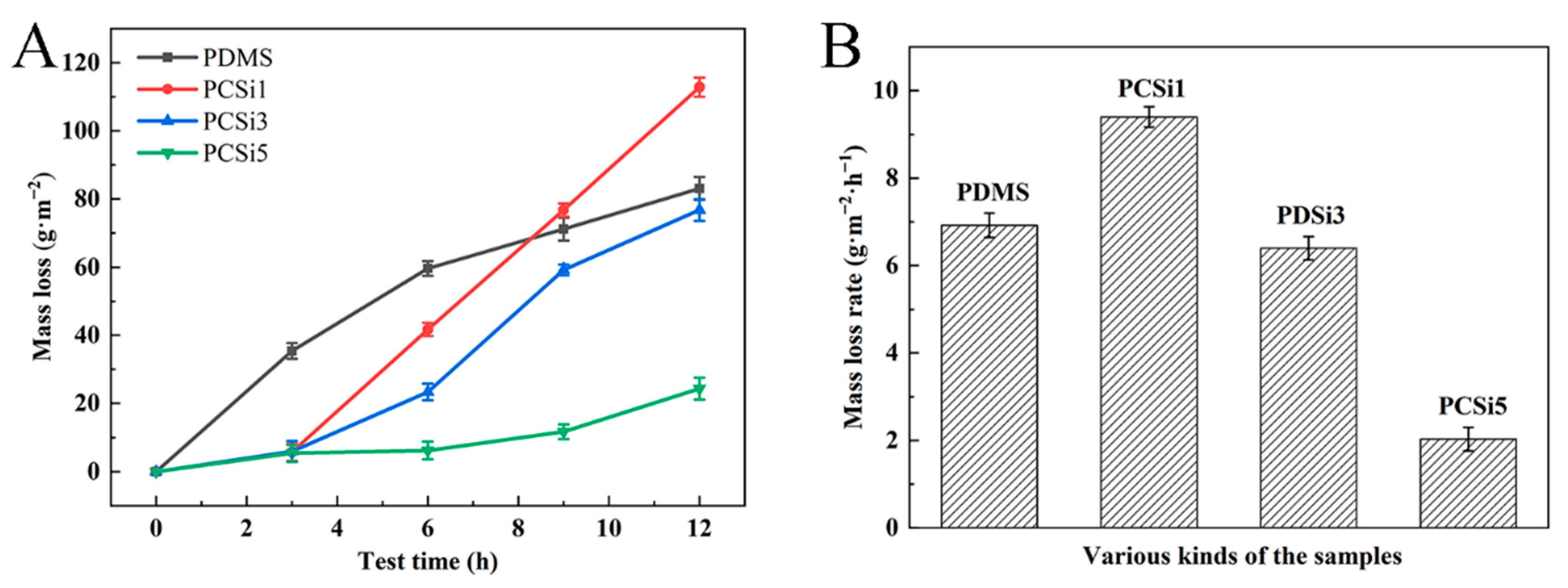
3.2.2. Water Erosion Test
3.3. Antifouling Test
3.4. Underwater Sound Absorption Test
4. Discussion
| Number | Components | Bacteria | Antibacterial Efficiency | Characteristics | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | PDMS/MWCNTs-COOH/SiO2 | V. natriegens | 74.69% | Environmental friendly Simple structure | / |
| 2 | NH2-UiO-66/NH2-PDMS/epoxy resin | E. coli | 79.42% | Best antifouling property Environmental unfriendly | [35] |
| 3 | NH2-UiO-66/NH2-PDMS/epoxy resin/triclosan | >99.98% | |||
| 4 | PDMS/HD-SiO2 | 37.8% | Complex structure | [36] | |
| 5 | Composite coating with outer PDMS/PAA-ZnO and inner PDMS/HD-SiO2 layer | 81.1% |
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lejars, M.; Margaillan, A.; Bressy, C. Fouling release coatings: A nontoxic alternative to biocidal antifouling coatings. Chem. Rev. 2012, 112, 4347–4390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yebra, D.M.; Kiil, S.; Dam-Johansen, K. Antifouling technology—Past, present and future steps towards efficient and environmentally friendly antifouling coatings. Prog. Org. Coat. 2004, 50, 75–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schultz, M.P. Effects of coating roughness and biofouling on ship resistance and powering. Biofouling 2007, 23, 331–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, P.; Huang, K. Key Anechoic Technology of Submarines-the Design of Acoustic Coating; Shanghai Jiao Tong University Press: Shanghai, China, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Fu, Y.F.; Kabir, I.I.; Yeoh, G.H.; Peng, Z.X. A review on polymer-based materials for underwater sound absorption. Polym. Test. 2021, 96, 107115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, P.; Xie, Q.Y.; Ma, C.F.; Zhang, G.Z. Silicone-based fouling-release coatings for marine antifouling. Langmuir 2020, 36, 2170–2183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Z.; Zhu, X.; Li, Y.Q. Influence of interpenetrating polymer networks (IPN) microstructure on underwater acoustic stealth performance. J. Wuhan Univ. Tehnol. 2010, 25, 272–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, B.E.; Huang, C.Y.; Shen, T.H.; Lee, Y.L. Effects of multiwall carbon nanotube addition on the corrosion resistance and underwater acoustic absorption properties of polyurethane coatings. Prog. Org. Coat. 2018, 121, 226–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cavas, L.; Yildiz, P.G.; Mimigianni, P.; Sapalidis, A.; Nitodas, S. Reinforcement effects of multiwall carbon nanotubes and graphene oxide on PDMS marine coatings. J. Coat. Technol. Res. 2018, 15, 105–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, Y.F.; Fischer, J.; Pan, K.Q.; Yeoh, G.H.; Peng, Z.X. Underwater sound absorption properties of polydimethylsiloxane/carbon nanotube composites with steel plate backing. Appl. Acoust. 2021, 171, 107668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Sun, Y.; Wu, W.; Liu, X.; Lin, X.Y.; Shen, X.; Wang, Z.Y.; Li, R.K.Y.; Yang, Z.Y.; Lau, K.T.; et al. Graphene foam/carbon nanotube/poly (dimethyl siloxane) composites as excellent sound absorber. Compos. Part A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 2017, 102, 391–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selim, M.S.; El-Safty, S.A.; El-Sockary, M.A.; Hashem, A.I.; Elenien, O.M.A.; EL-Saeed, A.M.; Fatthallah, N.A. Smart photo-induced silicone/TiO2 nanocomposites with dominant [110] exposed surfaces for self-cleaning foul-release coatings of ship hulls. Mater. Des. 2016, 101, 218–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jena, G.; George, R.P.; Philip, J. Fabrication of a robust graphene oxide-nano SiO2-polydimethylsiloxane composite coating on carbon steel for marine applications. Prog. Org. Coat. 2021, 161, 106462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, H.; Tian, L.M.; Bing, W.; Zhao, J.; Ren, L.Q. Bioinspired marine antifouling coatings: Status, prospects, and future. Prog. Mater. Sci. 2022, 124, 100889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selim, M.S.; Fatthallah, N.A.; Higazy, S.A.; Hao, Z.F.; Mo, P.J. A comparative study between two novel silicone/graphene-based nanostructured surfaces for maritime antifouling. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2022, 606, 367–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holland, R.; Dugdale, T.M.; Wetherbee, R.; Brennan, A.B.; Finlay, J.A.; Callow, J.A.; Callow, M.E. Adhesion and motility of fouling diatoms on a silicone elastomer. Biofouling 2004, 20, 323329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Molino, P.J.; Childs, S.; Hubbard, M.R.E.; Carey, J.M.; Burgman, M.A.; Wetherbee, R. Development of the primary bacterial microfouling layer on antifouling and fouling release coatings in temperate and tropical environments in Eastern Australia. Biofouling 2009, 25, 149–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molino, P.J.; Campbell, E.; Wetherbee, R. Development of the initial diatom microfouling layer on antifouling and fouling-release surfaces in temperate and tropical Australia. Biofouling 2009, 25, 685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, Y.J.; Song, G.L.; Zheng, D.J.; Zhang, Y.M. Fabrication and synergistic antibacterial and antifouling effect of an organic/inorganic hybrid coating embedded with nanocomposite Ag@TA-SiO2 particles. Colloids Surf. A 2021, 613, 126085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.H.; Liu, H.Y.; Yang, J.L.; Zhou, S.X. Seawater-induced healable underwater superoleophobic antifouling coatings. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2019, 11, 1353–1362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.X.; Bhushan, B. Wear-resistant and antismudge superoleophobic coating on polyethylene terephthalate substrate using SiO2 nanoparticles. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2015, 7, 743–755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Z.S.; Quan, Y.Y.; Mao, J.J.; Wang, Y.L.; Lai, Y.K.; Zheng, J.; Chen, Z.; Wei, K.; Li, H.Q. Multifunctional superhydrophobic composite materials with remarkable mechanochemical robustness, stain repellency, oil-water separation and sound-absorption properties. Chem. Eng. J. 2019, 358, 1610–1619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozbolat, V.; Dey, M.; Ayan, B.; Povilianskas, A.; Demirel, M.C.; Ozbolat, I.T. Printing of PDMS improves its mechanical and cell adhesion properties. ACS Biomater. Sci. Eng. 2018, 4, 682–693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bala, A.M.; Killian, W.G.; Plascencia, C.; Storer, J.A.; Norfleet, A.T.; Peereboom, L.; Jackson, J.E.; Lira, C.T. Quantitative analysis of infrared spectra of binary alcohol + cyclohexane solutions with quantum chemical calculations. J. Phys. Chem. A 2020, 124, 3077–3089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jentoft, F.C.; Kröhnert, J.; Subbotina, I.R.; Kazansky, V.B. Quantitative analysis of IR intensities of alkanes adsorbed on solid acid catalysts. J. Phys. Chem. C 2013, 117, 5873–5881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baier, R.E. Surface behaviour of biomaterials: The theta surface for biocompatibility. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Med. 2006, 17, 1057–1062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jr, R.F.B.; Singer, I.L. Mechanical factors favoring release from fouling release coatings. Biofouling 2000, 15, 73–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jarzynski, J. Mechanisms of sound attenuation in materials. Sound Vib. Damping Polym. 1990, 10, 167–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, G.S.; Skvortsov, A.; MacGillivray, I.; Kessissoglou, N. Sound absorption by rubber coatings with periodic voids and hard inclusions. Appl. Acoust. 2019, 143, 200–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, G.S.; Skvortsov, A.; MacGillivray, I.; Kessissoglou, N. Acoustic performance of periodic steel cylinders embedded in a viscoelastic medium. J. Sound. Vib. 2019, 443, 652–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Díez-Pascual, A.M.; Gómez-Fatou, M.A.; Ania, F.; Flores, A. Nanoindentation in polymer nanocomposites. Prog. Mater. Sci. 2015, 67, 1–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zare, Y.; Rhee, K.Y. Tensile modulus prediction of carbon nanotubes-reinforced nanocomposites by a combined model for dispersion and networking of nanoparticles. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2020, 9, 22–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bahramnia, H.; Semnani, H.M.; Habibolahzadeh, A.; Abdoos, H. Epoxy/polyurethane nanocomposite coatings for anti-erosion/wear applications: A review. J. Compos. Mater. 2020, 54, 3189–3203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bahramnia, H.; Semnani, H.M.; Habibolahzadeh, A.; Abdoos, H. Epoxy/polyurethane hybrid nanocomposite coatings reinforced with MWCNTs and SiO2 nanoparticles: Processing, mechanical properties and wear behavior. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2021, 415, 127121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Xu, T.; Hu, J.M. A robust room-temperature curable and molecular-level superhydrophobic coating with excellent antibacterial and antifouling properties. Chem. Eng. J. 2022, 136557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, X.C.; Cao, X.K.; Cai, G.Y.; Jiang, D.; Zhang, F.; Dong, Z.H. Underwater superoleophobic composite coating characteristic of durable antifouling and anticorrosion properties in marine environment. Colloids Surf. A 2021, 628, 127323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Name | PDMS | Disperbyk-191 and 192 | MWCNTs-COOH | SiO2 | Ratio |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PCSi1 | 97% | 2% | 0.5% | 0.5% | 1:1 |
| PCSi3 | 96% | 2% | 0.5% | 1.5% | 1:3 |
| PCSi5 | 95% | 2% | 0.5% | 2.5% | 1:5 |
| PDMS | 100% | 0% | 0% | 0% | N/A |
| Sample | C | O | Si | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| wt% | Atomic% | wt% | Atomic% | wt% | Atomic% | |
| PDMS | 32.14 | 39.77 | 26.69 | 24.78 | 41.17 | 21.84 |
| PCSi1 | 33.34 | 41.02 | 27.06 | 24.97 | 39.60 | 20.88 |
| PCSi3 | 32.81 | 40.58 | 27.08 | 25.13 | 40.11 | 21.27 |
| PCSi5 | 30.96 | 38.58 | 28.51 | 26.64 | 40.53 | 21.64 |
| Samples | 0 h | 3 h | 6 h | 9 h | 12 h |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PDMS |  |  | 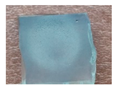 |  |  |
| PCSi1 |  |  |  |  | 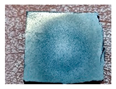 |
| PCSi3 |  |  |  |  |  |
| PCSi5 |  | 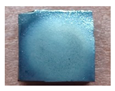 |  |  |  |
| Test Time | 0 h | 3 h | 6 h | 9 h | 12 h |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PDMS | 1.957 g | 1.951 g | 1.947 g | 1.945 g | 1.943 g |
| PCSi1 | 2.078 g | 2.077 g | 2.071 g | 2.065 g | 2.059 g |
| PCSi3 | 2.002 g | 2.001 g | 1.998 g | 1.992 g | 1.989 g |
| PCSi5 | 2.055 g | 2.054 g | 2.054 g | 2.053 g | 2.051 g |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cao, P.; Wang, H.; Zhu, M.; Fu, Y.; Yuan, C. Integration of Antifouling and Underwater Sound Absorption Properties into PDMS/MWCNT/SiO2 Coatings. Biomimetics 2022, 7, 248. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomimetics7040248
Cao P, Wang H, Zhu M, Fu Y, Yuan C. Integration of Antifouling and Underwater Sound Absorption Properties into PDMS/MWCNT/SiO2 Coatings. Biomimetics. 2022; 7(4):248. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomimetics7040248
Chicago/Turabian StyleCao, Pan, Huming Wang, Mingyi Zhu, Yifeng Fu, and Chengqing Yuan. 2022. "Integration of Antifouling and Underwater Sound Absorption Properties into PDMS/MWCNT/SiO2 Coatings" Biomimetics 7, no. 4: 248. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomimetics7040248
APA StyleCao, P., Wang, H., Zhu, M., Fu, Y., & Yuan, C. (2022). Integration of Antifouling and Underwater Sound Absorption Properties into PDMS/MWCNT/SiO2 Coatings. Biomimetics, 7(4), 248. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomimetics7040248






