An Overview of Infrared Remote Sensing of Volcanic Activity
Abstract
:1. Introduction
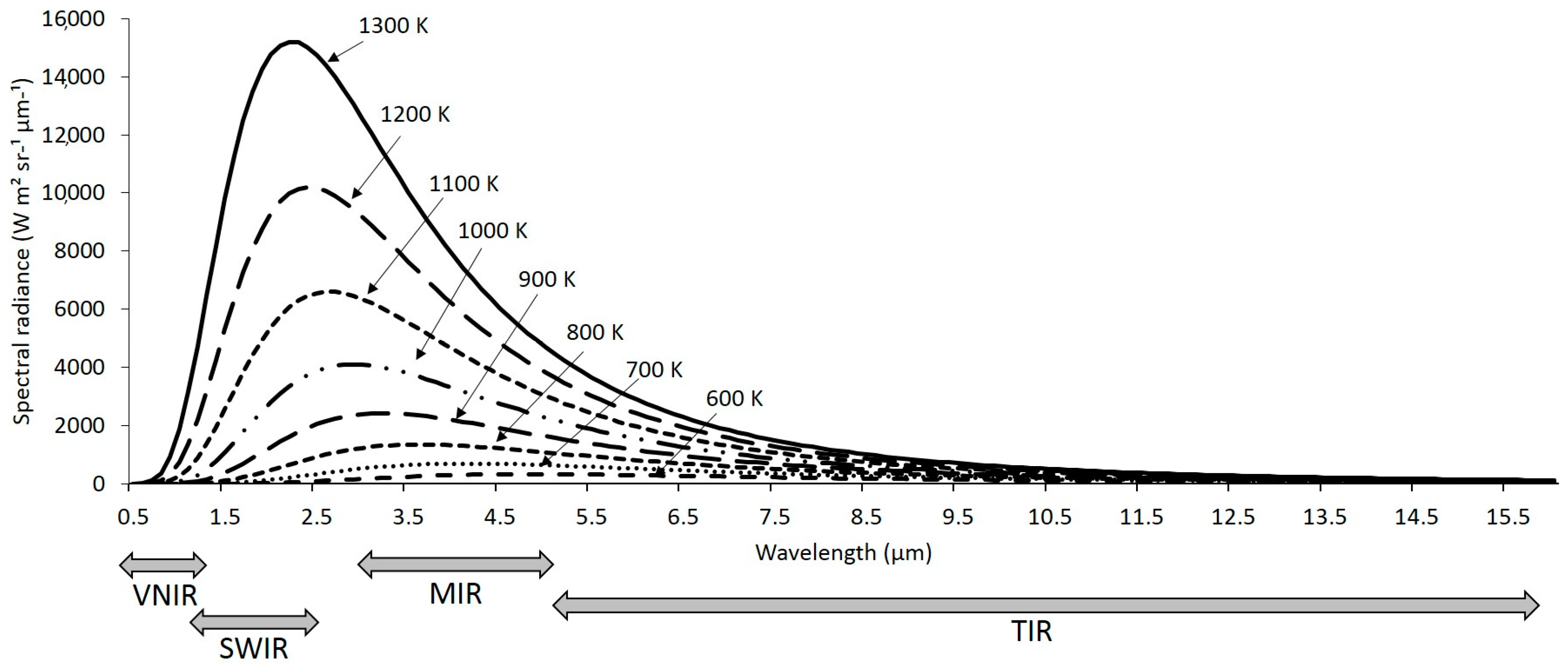
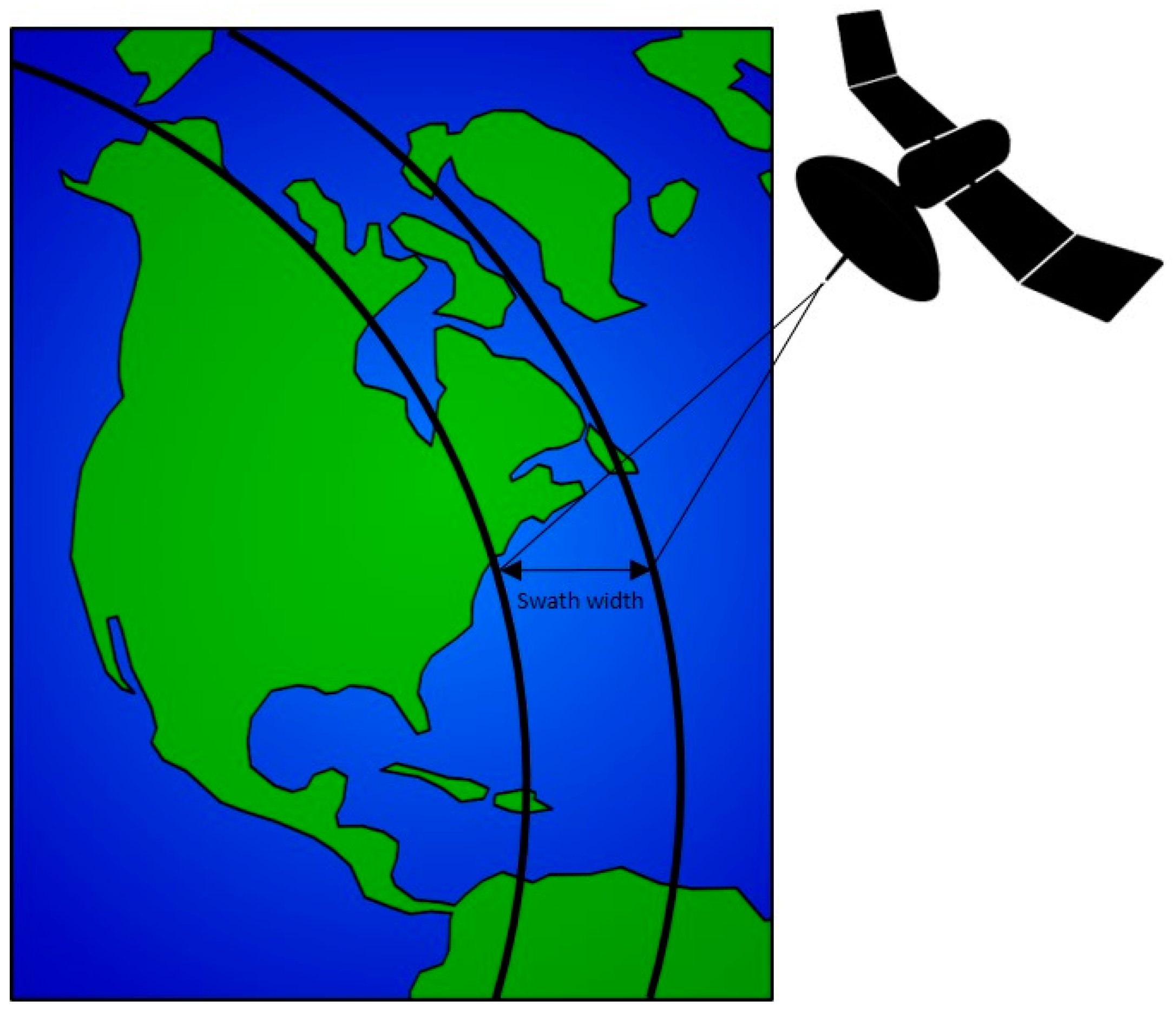
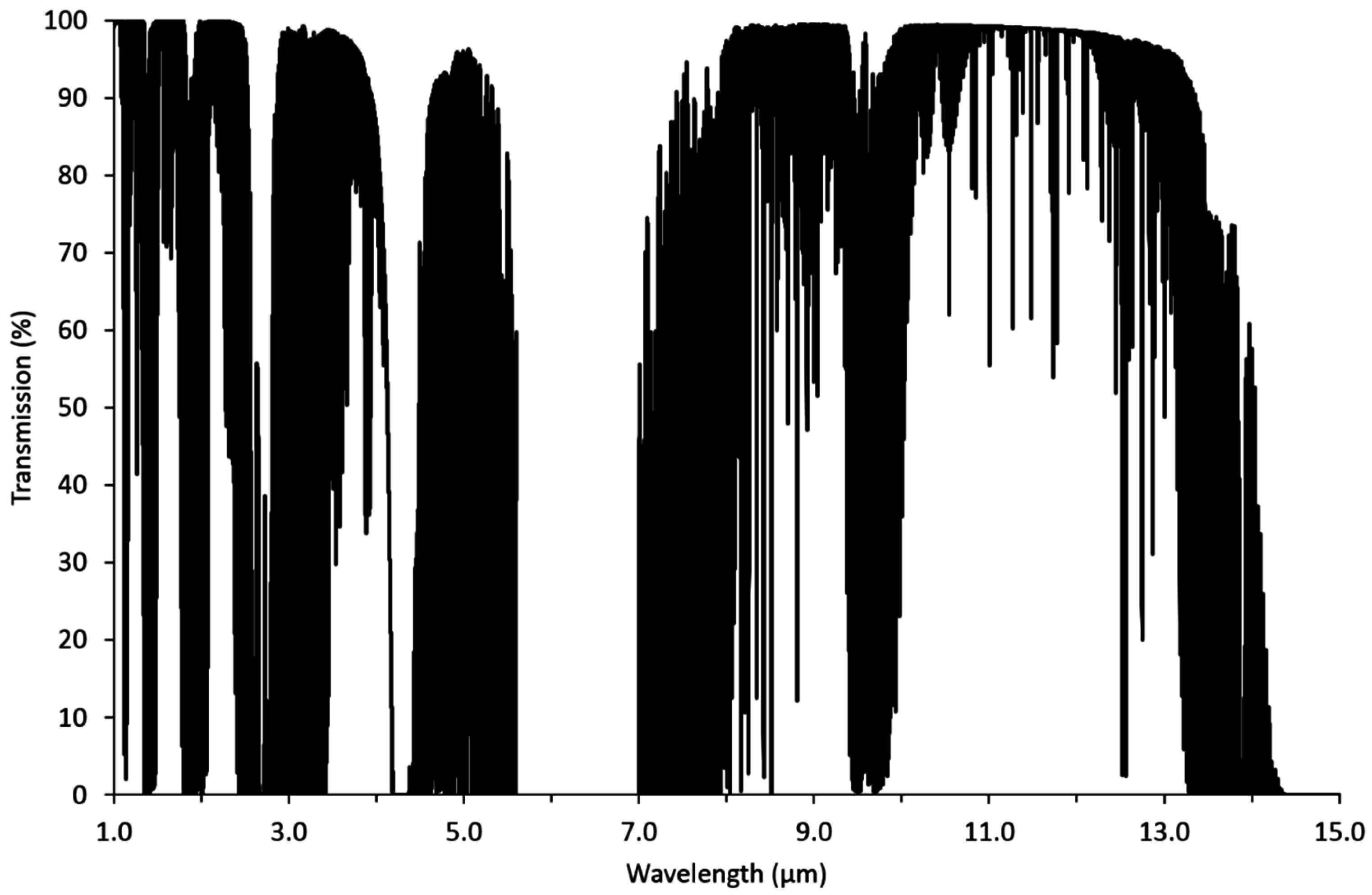
2. Infrared Remote Sensing: Theory
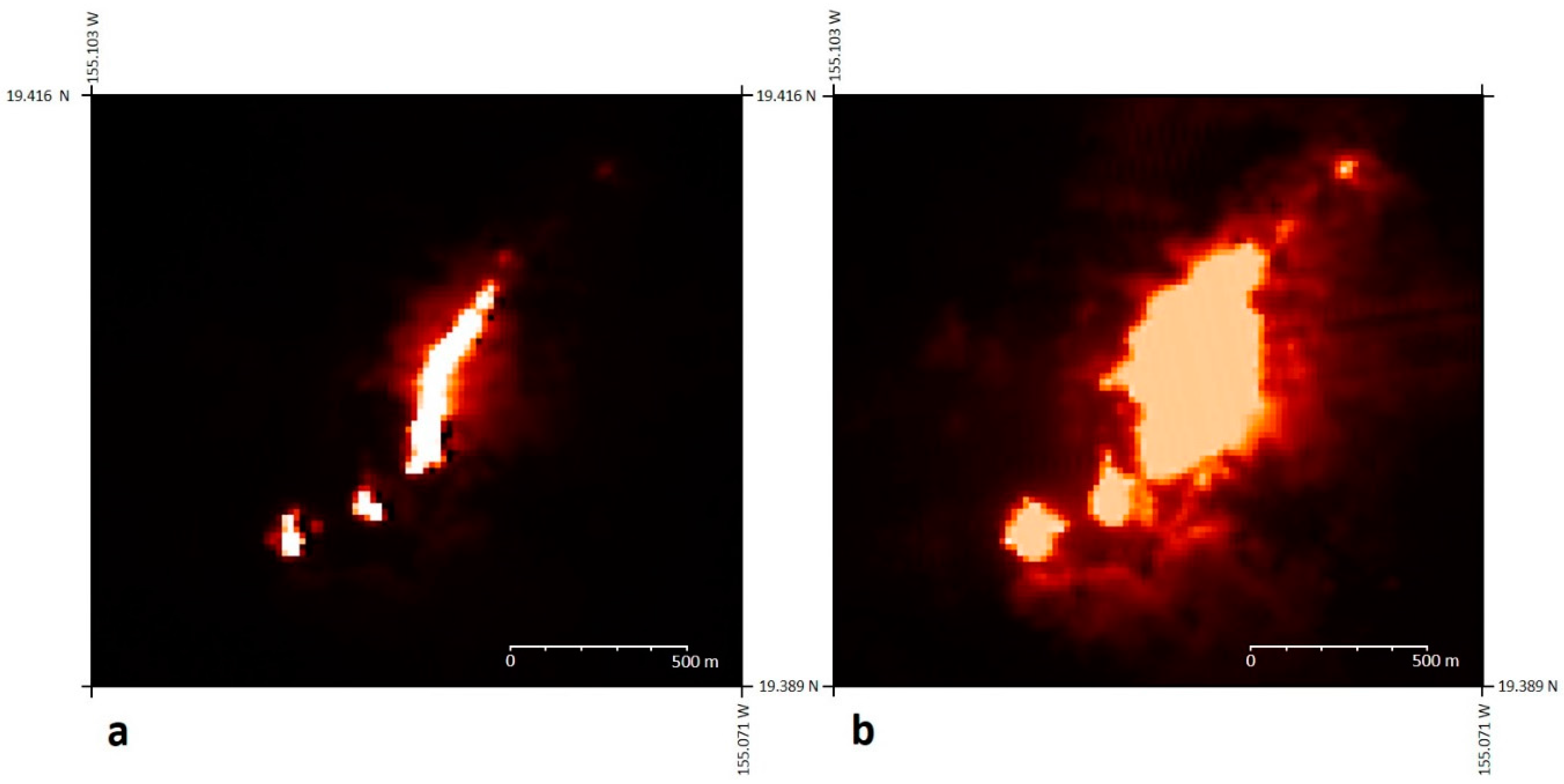
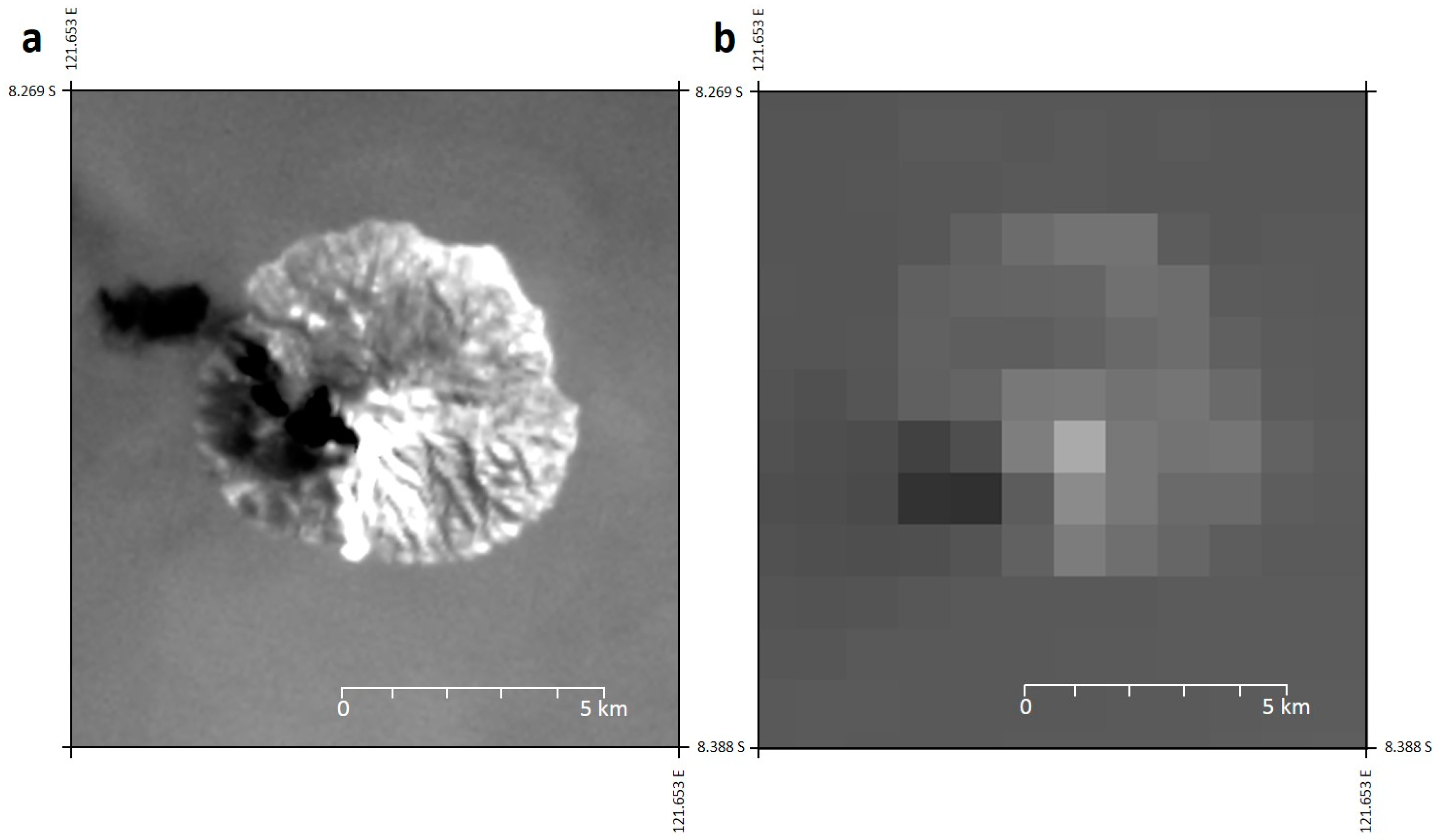
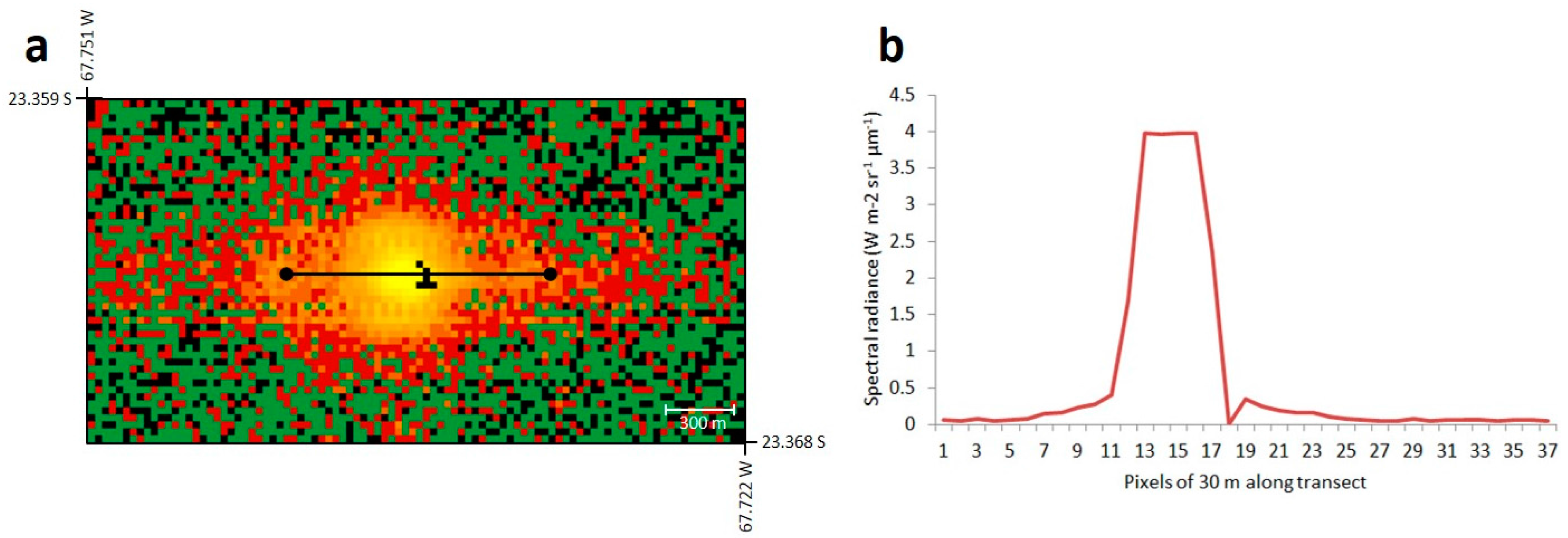
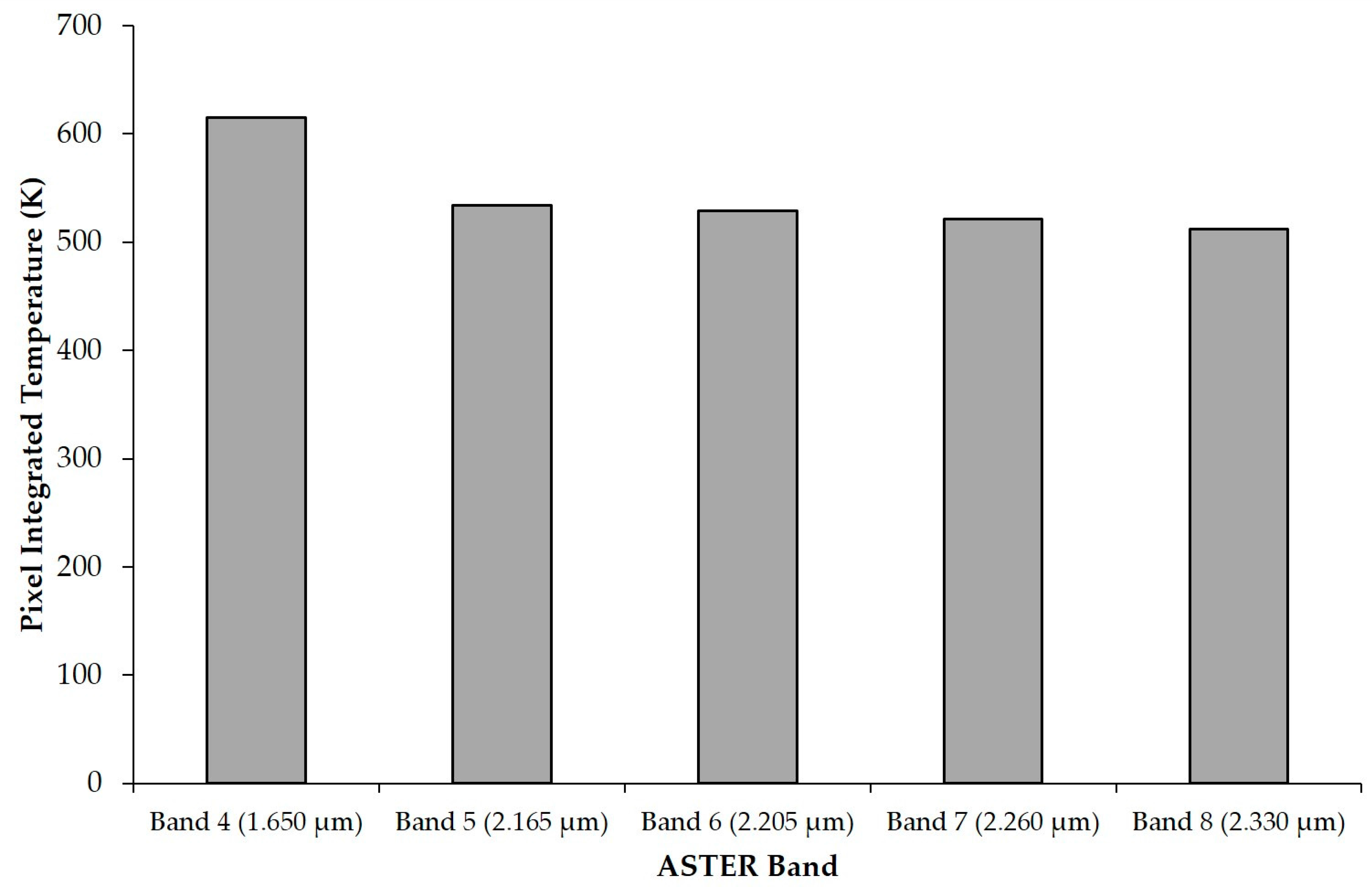
3. Specific Considerations for the Infrared Remote Sensing of Volcanic Activity
4. Historical Perspective on Sensors Used for Volcanic Observation
5. Infrared Remote Sensing of Volcanoes: A History
6. Prospects for the Future
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Oppenheimer, C. Review article: Volcanological applications of meteorological satellites. Int. J. Remote Sens. 1998, 19, 2829–2864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stefan, J. Über die Beziehung Zwischen der Wärmestrahlung und der Temperatur; Sitzungsberichte der mathematisch-naturwissenschaftlichen Classe der kaiserlichen Akademie der Wissenschaften: Wien, Austria, 1879; pp. 391–428. (In German) [Google Scholar]
- Boltzmann, L. Ableitung des Stefan’schen Gesetzes, betreffend die Abhängigkeit der Wärmestrahlung von der Temperatur aus der electromagnetischen Lichttheorie. Ann. Phys. Chem. 1884, 22, 291–294. (In German) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wien, W. Uber die Energieverteilung in Emissionspektrum eines schwarzen Korpers. Ann. Phys. Chem. 1896, 58, 662–669. (In German) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Planck, M. Ueber das Gesetz der Energieverteilung im Normalspectrum. Ann. Phys. 1901, 4, 553–563. (In German) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wooster, M.J.; Rothery, D.A. Volcano Surveillance Using Shortwave Infrared Thermal Data from the ERS Along Track Scanning Radiometers. In Proceedings of the ATSR Workshop: Applications of the ERS along Track Scanning Radiometer (ESRIN), Frascati, Italy, 23–25 June 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Fink, J.H.; Srivastava, A.; Sylvester, D.; Blaauw, D. Lava Flows and Domes: Emplacement Mechanisms and Hazard Implications; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Oppenheimer, C.; Yirgu, G. Thermal imaging of an active lava lake: Erta ‘ale volcano, Ethiopia. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2002, 23, 4777–4782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carter, A.J.; Girina, O.; Ramsey, M.S.; Demyanchuk, Y.V. ASTER and field observations of the 24 December 2006 eruption of Bezymianny volcano, Russia. Remote Sens. Environ. 2008, 112, 2569–2577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carter, A.J.; Ramsey, M.S. ASTER- and field-based observations at Bezymianny volcano: Focus on the 11 May 2007 pyroclastic flow deposit. Remote Sens. Environ. 2009, 113, 2142–2151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wessels, R.L.; Vaughan, R.G.; Patrick, M.R.; Coombs, M.L. High-resolution satellite and airborne thermal infrared imaging of precursory unrest and 2009 eruption at redoubt volcano, Alaska. J. Volcanol. Geotherm. Res. 2013, 259, 248–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carr, B.B.; Clarke, A.B.; Vanderkluysen, L. The 2006 lava dome eruption of Merapi volcano (Indonesia): Detailed analysis using MODIS TIR. J. Volcanol. Geotherm. Res. 2016, 311, 60–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wright, R.; Pilger, E. Satellite observations reveal little inter-annual variability in the radiant flux from the Mount Erebus lava lake. J. Volcanol. Geotherm. Res. 2008, 177, 687–694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wright, R.; Pilger, E. Radiant flux from Earth’s subaerially erupting volcanoes. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2008, 29, 6443–6466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coppola, D.; Laiolo, M.; Cigolini, C.; Donne, D.D.; Ripepe, M. Enhanced volcanic hot-spot detection using MODIS IR data. In Detecting, Modelling and Responding to Effusive Eruptions; Geological Society of London: London, UK, 2016; pp. 181–205. [Google Scholar]
- Rowan, L.C.; Mars, J.C. Lithologic mapping in the mountain pass, California area using advanced Spaceborne thermal emission and reflection Radiometer (ASTER) data. Remote Sens. Environ. 2003, 84, 350–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rothery, D.A. The need for volcano monitoring and the ability to detect activity using emitted short wavelength infrared. In Proceedings of the International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, “Remote Sensing: Moving Toward the 21st Century”, Edinburgh, UK, 12–16 September 1988. [Google Scholar]
- Pieri, D.; Abrams, M. ASTER watches the world’s volcanoes: A new paradigm for volcanological observations from orbit. J. Volcanol. Geotherm. Res. 2004, 135, 13–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blackett, M.; Wooster, M.J. Evaluation of SWIR-based methods for quantifying active volcano radiant emissions using NASA EOS-ASTER data. Geomat. Nat. Hazards Risk 2011, 2, 51–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blackett, M. Early analysis of Landsat-8 thermal infrared sensor imagery of volcanic activity. Remote Sens. 2014, 6, 2282–2295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.; Kim, H.; Lim, H.; Choi, H. Space-Based Earth Observation Activities in South Korea [Space Agencies]. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Mag. 2015, 3, 34–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rogalski, A. Infrared detectors: Status and trends. Prog. Quantum Electron. 2003, 27, 59–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tupin, F.; Inglada, J.; Nicolas, J.-M. (Eds.) Remote Sensing Imagery; Wiley-ISTE: London, UK, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Francis, P.; Rothery, D. Remote sensing of active volcanoes. Annu. Rev. Earth Planet. Sci. 2000, 28, 81–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lillesand, T.M.; Kiefer, R.W.; Chipman, J.W.; Lilles, T.M. Remote Sensing and Image Interpretation, 5th ed.; Wiley, John & Sons: New York, NY, USA, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- NASA. HyspIRI Mission Concept Overview. 2012. Available online: http://hyspiri.jpl.nasa.gov/downloads/2012_Workshop/day1/16_HyspIRI_Mission_Concept_Overview-Workshop_FY12_ULR.pdf (accessed on 27 December 2016).
- Chien, S.; Silverman, D.; Davies, A.G.; Mandl, D. Onboard science processing concepts for the HyspIRI mission. IEEE Intell. Syst. 2009, 24, 12–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.M.; Cable, M.L.; Hook, S.J.; Green, R.O.; Ustin, S.L.; Mandl, D.J.; Middleton, E.M. An introduction to the NASA Hyperspectral infraRed Imager (HyspIRI) mission and preparatory activities. Remote Sens. Environ. 2015, 167, 6–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- NASA Earth Observatory. Catalog of Earth Satellite Orbits. Available online: http://earthobservatory.nasa.gov/Features/OrbitsCatalog/ (accessed on 27 December 2016).
- Lord, S.D. NASA Technical Memorandum 103957; Gemini Observatory: Hilo, HI, USA, 1992; Available online: http://www.gemini.edu/ (accessed on 7 April 2017).
- Wooster, M.J.; Rothery, D.A. Thermal monitoring of Lascar volcano, Chile, using infrared data from the along-track scanning radiometer: A 1992–1995 time series. Bull. Volcanol. 1997, 58, 566–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mouginis-Mark, P.; Rowland, S.; Francis, P.; Friedman, T.; Garbeil, H.; Gradie, J.; Self, S.; Wilson, L.; Crisp, J.; Glaze, L.; et al. Analysis of active volcanoes from the earth observing system. Remote Sens. Environ. 1991, 36, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morfitt, R.; Barsi, J.; Levy, R.; Markham, B.; Micijevic, E.; Ong, L.; Scaramuzza, P.; Vanderwerff, K. Landsat-8 operational land Imager (OLI) Radiometric performance on-orbit. Remote Sens. 2015, 7, 2208–2237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamaguchi, Y.; Kahle, A.B.; Tsu, H.; Kawakami, T.; Pniel, M. Overview of advanced Spaceborne thermal emission and reflection Radiometer (ASTER). IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 1998, 36, 1062–1071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wright, R.; Rothery, D.A.; Blake, S.; Harris, A.J.L.; Pieri, D.C. Simulating the response of the EOS terra ASTER sensor to high-temperature volcanic targets. Geophys. Res. Lett. 1999, 26, 1773–1776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harris, A. Thermal Remote Sensing of Active Volcanoes: A User’s Manual; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Jensen, J.R. Introductory Digital Image Processing: A Remote Sensing Perspective, 2nd ed.; Prentice Hall: Upper Saddle River, NJ, USA, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Wiesnet, D.R.; D’Aguanno, J. Thermal imagery of Mount Erebus from the NOAA-6 satellite. Antarct. J. U. S. 1982, 17, 32–34. [Google Scholar]
- Bonneville, A.; Vasseur, G.; Kerr, Y. Satellite Thermal Infrared Observations of Mt. Etna after the 17th March 1981 Eruption. J. Volcanol. Geotherm. Res. 1985, 24, 293–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harris, A.J.L.; Blake, S.; Rothery, D.A.; Stevens, N.F. A chronology of the 1991 to 1993 mount Etna eruption using advanced very high resolution radiometer data: Implications for real-time thermal volcano monitoring. J. Geophys. Res. 1997, 102, 7985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harris, A.J.L.; Flynn, L.P.; Dean, K.; Pilger, E.; Wooster, M.; Okubo, C.; Mouginis-Mark, P.; Garbeil, H.; Thornber, C.; De la Cruz-Reyna, S.; et al. Real-time satellite monitoring of volcanic hot spots. In Remote Sensing of Active Volcanism; Wiley-Blackwell: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2000; pp. 139–159. [Google Scholar]
- Dehn, J.; Dean, K.; Engle, K. Thermal monitoring of north pacific volcanoes from space. Geology 2000, 28, 755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- AVO Alaska Volcano Observatory—about AVO—Operations. 2014. Available online: https://www.avo.alaska.edu/about/operations (accessed on 30 September 2016).
- Blackett, M. Review of the utility of infrared remote sensing for detecting and monitoring volcanic activity with the case study of shortwave infrared data for Lascar volcano from 2001–2005. In Geological Society, London, Special Publications; Geological Society of London: London, UK, 2013; Volume 380, pp. 107–135. [Google Scholar]
- Flynn, L.P.; Mouginis-Mark, P.J.; Horton, K.A. Distribution of thermal areas on an active lava flow field: Landsat observations of Kilauea, Hawaii, July 1991. Bull. Volcanol. 1994, 56, 284–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flynn, L.P.; Harris, A.J.L.; Rothery, D.A.; Oppenheimer, C. High-spatial-resolution thermal remote sensing of active volcanic features using Landsat and hyperspectral data. In Remote Sensing of Active Volcanism; Wiley-Blackwell: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2000; pp. 161–177. [Google Scholar]
- Flynn, L.P.; Harris, A.J.L.; Wright, R. Improved identification of volcanic features using Landsat 7 ETM+. Remote Sens. Environ. 2001, 78, 180–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lombardo, V.; Buongiorno, M.F.; Pieri, D.; Merucci, L. Differences in Landsat TM derived lava flow thermal structures during summit and flank eruption at mount Etna. J. Volcanol. Geotherm. Res. 2004, 134, 15–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Irons, J.R.; Dwyer, J.L. An overview of the Landsat data continuity mission. Proc. SPIE 2010, 7695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Irons, J.R.; Dwyer, J.L.; Barsi, J.A. The next Landsat satellite: The Landsat data continuity mission. Remote Sens. Environ. 2012, 122, 11–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harris, A.J.L.; Keszthelyi, L.; Flynn, L.P.; Mouginis-Mark, P.J.; Thornber, C.; Kauahikaua, J.; Sherrod, D.; Trusdell, F.; Sawyer, M.W.; Flament, P. Chronology of the episode 54 eruption at Kilauea volcano, Hawaii, from GOES-9 satellite data. Geophys. Res. Lett. 1997, 24, 3281–3284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harris, A.J.L.; Pilger, E.; Flynn, L.P.; Garbeil, H.; Mouginis-Mark, P.J.; Kauahikaua, J.; Thornber, C. Automated, high temporal resolution, thermal analysis of Kilauea volcano, Hawai’i, using GOES satellite data. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2001, 22, 945–967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ganci, G.; Vicari, A.; Fortuna, L.; Del Negro, C. The HOTSAT volcano monitoring system based on combined use of SEVIRI and MODIS multispectral data. Ann. Geophys. 2011, 54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ganci, G.; Bilotta, G.; Cappello, A.; Herault, A.; Negro, C.D. HOTSAT. In Detecting, Modelling and Responding to Effusive Eruptions; Geological Society of London: London, UK, 2016; pp. 207–221. [Google Scholar]
- NASA. Earth Observing System. Data and Information System. Report of the EOS Data Panel. Available online: http://ntrs.nasa.gov/archive/nasa/casi.ntrs.nasa.gov/19860021622.pdf (accessed on 1 October 2016).
- Pieri, D.C.; Crisp, J.; Kahle, A.B. Observing Volcanism and Other Transient Phenomena with ASTER. J. Remote Sens. Soc. Jpn. 1995, 15, 56–61. [Google Scholar]
- Abrams, M. The advanced Spaceborne thermal emission and reflection Radiometer (ASTER): Data products for the high spatial resolution imager on NASA’s terra platform. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2000, 21, 847–859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pieri, D.; Abrams, M. ASTER observations of thermal anomalies preceding the April 2003 eruption of Chikurachki volcano, Kurile islands, Russia. Remote Sens. Environ. 2005, 99, 84–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carter, A.; Ramsey, M. Long-term volcanic activity at Shiveluch volcano: Nine years of ASTER Spaceborne thermal infrared observations. Remote Sens. 2010, 2, 2571–2583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Urai, M.; Ishizuka, Y. Advantages and challenges of space-borne remote sensing for volcanic Explosivity index (VEI): The 2009 eruption of Sarychev peak on Matua Island, Kuril Islands, Russia. J. Volcanol. Geotherm. Res. 2011, 208, 163–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- LP DAAC: NASA Land Data Products and Services. Available online: https://lpdaac.usgs.gov/15_years_terra_modis (accessed on 1 October 2016).
- Kaufman, Y.J.; Justice, C.O.; Flynn, L.P.; Kendall, J.D.; Prins, E.M.; Giglio, L.; Ward, D.E.; Menzel, W.P.; Setzer, A.W. Potential global fire monitoring from EOS-MODIS. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 1998, 103, 32215–32238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Justice, C.; Giglio, L.; Korontzi, S.; Owens, J.; Morisette, J.; Roy, D.; Descloitres, J.; Alleaume, S.; Petitcolin, F.; Kaufman, Y. The MODIS fire products. Remote Sens. Environ. 2002, 83, 244–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wright, R.; Flynn, L.; Garbeil, H.; Harris, A.; Pilger, E. Automated volcanic eruption detection using MODIS. Remote Sens. Environ. 2002, 82, 135–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wright, R.; Flynn, L.P. Space-based estimate of the volcanic heat flux into the atmosphere during 2001 and 2002. Geology 2004, 32, 189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wright, R.; Blackett, M.; Hill-Butler, C. Some observations regarding the thermal flux from Earth’s erupting volcanoes for the period of 2000 to 2014. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2015, 42, 282–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blackett, M. An initial comparison of the thermal anomaly detection products of MODIS and VIIRS in their observation of Indonesian volcanic activity. Remote Sens. Environ. 2015, 171, 75–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Justice, C.O.; Román, M.O.; Csiszar, I.; Vermote, E.F.; Wolfe, R.E.; Hook, S.J.; Friedl, M.; Wang, Z.; Schaaf, C.B.; Miura, T.; et al. Land and cryosphere products from Suomi NPP VIIRS: Overview and status. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2013, 118, 9753–9765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Csiszar, I.; Schroeder, W.; Giglio, L.; Ellicott, E.; Vadrevu, K.P.; Justice, C.O.; Wind, B. Active fires from the Suomi NPP visible infrared imaging Radiometer suite: Product status and first evaluation results. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2014, 119, 803–816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barnhart, D.J.; Vladimirova, T.; Sweeting, M.N. Very-small-satellite design for distributed space missions. J. Spacecr. Rockets 2007, 44, 1294–1306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandau, R. Small Satellite Missions. In Advances in Photogrammetry, Remote Sensing and Spatial Information Sciences: 2008 ISPRS Congress Book; Li, Z., Chen, J., Baltsavias, E., Eds.; CRC Press: Cullompton, UK, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Brieβ, K.; Bärwald, W.; Gerlich, T.; Jahn, H.; Lura, F.; Studemund, H. The DLR small satellite mission BIRD. Acta Astronaut. 2000, 46, 111–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhukov, B.; Lorenz, E.; Oertel, D.; Wooster, M.; Roberts, G. Spaceborne detection and characterization of fires during the bi-spectral infrared detection (BIRD) experimental small satellite mission (2001–2004). Remote Sens. Environ. 2006, 100, 29–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruecker, G.; Menz, G.; Heinemann, S.; Hartmann, M.; Oertel, D. VISIR-SAT—A Prospective micro-satellite based multi-spectral thermal mission for land applications. In Proceedings of the ISPRS International Archives of the Photogrammetry, Remote Sensing and Spatial Information Sciences, Berlin, Germany, 11–15 May 2015; Volume XL-7/W3, pp. 1283–1289. [Google Scholar]
- Zakšek, K.; Hort, M.; Lorenz, E. Satellite and ground based thermal observation of the 2014 effusive eruption at Stromboli volcano. Remote Sens. 2015, 7, 17190–17211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wooster, M.J.; Rothery, D.A. Time-series analysis of effusive volcanic activity using the ERS along track scanning radiometer: The 1995 eruption of Fernandina volcano, Galápagos Islands. Remote Sens. Environ. 1997, 62, 109–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rothery, D.; Coltelli, M.; Pieri, D.; Wooster, M.; Wright, R. Documenting surface magmatic activity at Mount Etna using ATSR remote sensing. Bull. Volcanol. 2001, 63, 387–397. [Google Scholar]
- Wooster, M.J.; Rothery, D.A. A Review of Volcano Surveillance Applications Using the ATSR Instrument Series. Adv. Environ. Monit. Model. 2002, 1, 97–123. [Google Scholar]
- Wooster, M.J.; Rothery, D.A.; Kaneko, T. Geometric considerations for the remote monitoring of volcanoes: Studies of lava domes using ATSR and the implications for MODIS. Int. J. Remote Sens. 1998, 19, 2585–2591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dennis, A.M.; Harris, A.J.L.; Carlton, R.W.; Francis, P.W.; Rothery, D.A. Cover the 1993 Lascar pyroclastic flow imaged by JERS-1. Int. J. Remote Sens. 1996, 17, 1975–1980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramsey, M.S.; Harris, A.J.L. Volcanology 2020: How will thermal remote sensing of volcanic surface activity evolve over the next decade? J. Volcanol. Geotherm. Res. 2013, 249, 217–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fisher, W.A.; Mozham, R.M.; Polcyn, F.; Landis, G.H. Infrared surveys of Hawaiian Volcanoes. Science 1964, 146, 733–742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Williams, R.S., Jr.; Friedman, J.D.; Thórarinsson, S.; Sigurgeirsson, T.; Pálmason, G. Analysis of 1966 Infrared Imagery of Surtsey, Iceland. Surtsey Research Progress Report IV. 1968. Available online: http://www.surtsey.is/SRS_publ/1968-IV/1968_IV_5_04.pdf (accessed on 7 April 2017).
- Freidman, J.D.; Williams, R.S., Jr.; Þórarinsson, S.; Pálmarsson, G. Infrared Emission from KverkfjöllSubglacial Volcanic and Geothermal Area, Iceland. Jökull 1972, 22, 27–43. [Google Scholar]
- Cassinis, R.; Lechi, G.M. The Use of Infrared Radiometry in Geothermal Areas. In Physical Volcanology (Development in Solid Earth Geophysics); Civetta, L., Ed.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1974. [Google Scholar]
- Kieffer, H.H.; Frank, D.; Friedman, J.D. Thermal infrared surveys at Mount St. Helens-Observations prior to the eruption of May 18. In The 1980 Eruptions of Mount St. Helens, Washington; Lipman, P.W., Mullineaux, D.R., Eds.; USGS Professional Paper 1250; U.S. Government Printing Office: Washington, DC, USA, 1981; pp. 257–277. [Google Scholar]
- Gawarecki, S.J.; Lyon, R.J.P.; Nordberg, W. Infrared spectral returns and imagery of the Earth from space and their application to geological problems: Scientific experiments for manned orbital flight. Am. Astronaut. Soc. Sci. Technol. 1965, 4, 13–133. [Google Scholar]
- Francis, P.W.; McAllister, R. Volcanology from space: Using Landsat thematic Mapper data in the central Andes. Eos Trans. Am. Geophys. Union 1986, 67, 170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Francis, P.W.; Rothery, D.A. Using the Landsat Thematic Mapper to detect and monitor active volcanoes: An example from Lascar volcano, Northern Chile. Geology 1987, 15, 614–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rothery, D.A.; Francis, P.W.; Wood, C.A. Volcano monitoring using short wavelength infrared data from satellites. J. Geophys. Res. 1988, 93, 7993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glaze, L.; Francis, P.W.; Rothery, D.A. Measuring thermal budgets of active volcanoes by satellite remote sensing. Nature 1989, 338, 144–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oppenheimer, C.; Francis, P.W.; Rothery, D.A.; Carlton, R.W.T.; Glaze, L.S. Infrared image analysis of volcanic thermal features: Láscar volcano, Chile, 1984–1992. J. Geophys. Res. 1993, 98, 4269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flynn, L.P.; Mouginis-Mark, P.J. Temperature of an active lava channel from spectral measurements, Kilauea volcano, Hawaii. Bull. Volcanol. 1994, 56, 297–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harris, A.J.L.; Flynn, L.P.; Keszthelyi, L.; Mouginis-Mark, P.J.; Rowland, S.K.; Resing, J.A. Calculation of lava effusion rates from Landsat TM data. Bull. Volcanol. 1998, 60, 52–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harris, A.J.L.; Vaughan, R.A.; Rothery, D.A. Volcano detection and monitoring using AVHRR data: The Krafla eruption, 1984. Int. J. Remote Sens. 1995, 16, 1001–1020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dean, K.; Servilla, M.; Roach, A.; Foster, B.; Engle, K. Satellite monitoring of remote volcanoes improves study efforts in alaska. Eos Trans. Am. Geophys. Union 1998, 79, 413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flynn, L.P.; Wright, R.; Garbeil, H.; Harrism, A.J.L.; Pilger, E. A global thermal alert system using MODIS: Initial results from 2000–2001. Adv. Environ. Monit. Model. 2002, 1, 37–69. [Google Scholar]
- Wright, R.; Flynn, L.P.; Garbeil, H.; Harris, A.J.; Pilger, E. MODVOLC: Near-real-time thermal monitoring of global volcanism. J. Volcanol. Geotherm. Res. 2004, 135, 29–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colin, O.; Rubio, M.; Landart, P.; Mathot, E. VoMIR: Over 300 volcanoes monitored in near real-time by AATSR. In Proceedings of the Envisat Symposium 2007, Montreux, Switzerland, 23–27 April 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Davies, A.G.; Chien, S.; Baker, V.; Doggett, T.; Dohm, J.; Greeley, R.; Ip, F.; Castan˘o, R.; Cichy, B.; Rabideau, G.; et al. Monitoring active volcanism with the autonomous Sciencecraft experiment on EO-1. Remote Sens. Environ. 2006, 101, 427–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davies, A.G.; Chien, S.; Doubleday, J.; Tran, D.; Thordarson, T.; Gudmundsson, M.T.; Höskuldsson, Á.; Jakobsdóttir, S.S.; Wright, R.; Mandl, D. Observing Iceland’s Eyjafjallajökull 2010 eruptions with the autonomous NASA volcano sensor web. J. Geophys. Res. Solid Earth 2013, 118, 1936–1956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davies, A.G.; Chien, S.; Tran, D.Q.; Doubleday, J. Onboard processing of multispectral and hyperspectral data of volcanic activity for future earth-orbiting and planetary missions. In Proceedings of the 2010 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Honolulu, HI, USA, 25–30 July 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Dozier, J. A method for satellite identification of surface temperature fields of subpixel resolution. Remote Sens. Environ. 1981, 11, 221–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matson, M.; Dozier, J. Identification of Subresolution High Temperature Sources Using a Thermal IR Sensor. Photogramm. Eng. Remote Sens. 1981, 47, 1311–1318. [Google Scholar]
- Oppenheimer, C. Lava flow cooling estimated from Landsat thematic Mapper infrared data: The Lonquimay eruption (Chile, 1989). J. Geophys. Res. Solid Earth 1991, 96, 21865–21878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wooster, M.J.; Wright, R.; Blake, S.; Rothery, D.A. Cooling mechanisms and an approximate thermal budget for the 1991–1993 Mount Etna lava flow. Geophys. Res. Lett. 1997, 24, 3277–3280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wright, R.; Flynn, L.P. On the retrieval of lava-flow surface temperatures from infrared satellite data. Geology 2003, 31, 893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wright, R.; Glaze, L.; Baloga, S.M. Constraints on determining the eruption style and composition of terrestrial lavas from space. Geology 2011, 39, 1127–1130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pergola, N.; Marchese, F.; Tramutoli, V. Automated detection of thermal features of active volcanoes by means of infrared AVHRR records. Remote Sens. Environ. 2004, 93, 311–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blackett, M.; Wooster, M.J.; Malamud, B.D. Exploring land surface temperature earthquake precursors: A focus on the Gujarat (India) earthquake of 2001. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2011, 38, L15303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koeppen, W.C.; Pilger, E.; Wright, R. Time series analysis of infrared satellite data for detecting thermal anomalies: A hybrid approach. Bull. Volcanol. 2010, 73, 577–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wright, R.; Carn, S.A.; Flynn, L.P. A satellite chronology of the May–June 2003 eruption of Anatahan volcano. J. Volcanol. Geotherm. Res. 2005, 146, 102–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rose, S.; Ramsey, M. The 2005 eruption of Kliuchevskoi volcano: Chronology and processes derived from ASTER spaceborne and field-based data. J. Volcanol. Geotherm. Res. 2009, 184, 367–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rybin, A.; Chibisova, M.; Webley, P.; Steensen, T.; Izbekov, P.; Neal, C.; Realmuto, V. Satellite and ground observations of the June 2009 eruption of Sarychev peak volcano, Matua island, central Kuriles. Bull. Volcanol. 2011, 73, 1377–1392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coppola, D.; Laiolo, M.; Cigolini, C. Fifteen years of thermal activity at Vanuatu’s volcanoes (2000–2015) revealed by MIROVA. J. Volcanol. Geotherm. Res. 2015, 322, 6–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wright, R. MODVOLC. In Detecting, Modelling and Responding to Effusive Eruptions; Geological Society of London: London, UK, 2015; pp. 23–53. [Google Scholar]
- Flower, V.J.B.; Carn, S.A.; Wright, R. The impact of satellite sensor viewing geometry on time-series analysis of volcanic emissions. Remote Sens. Environ. 2016, 183, 282–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Realmuto, V.J.; Dennison, P.E.; Foote, M.; Ramsey, M.S.; Wooster, M.J.; Wright, R. Specifying the saturation temperature for the HyspIRI 4-μm channel. Remote Sens. Environ. 2015, 167, 40–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abrams, M.; Pieri, D.; Realmuto, V.; Wright, R. Using EO-1 Hyperion data as HyspIRI preparatory data sets for Volcanology applied to Mt Etna, Italy. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2013, 6, 375–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hochberg, E.J.; Roberts, D.A.; Dennison, P.E.; Hulley, G.C. Special issue on the Hyperspectral infrared Imager (HyspIRI): Emerging science in terrestrial and aquatic ecology, radiation balance and hazards. Remote Sens. Environ. 2015, 167, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wooster, M.J.; Xu, W.; Nightingale, T. Sentinel-3 SLSTR active fire detection and FRP product: Pre-launch algorithm development and performance evaluation using MODIS and ASTER datasets. Remote Sens. Environ. 2012, 120, 236–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- User Guides—Sentinel-3 SLSTR—Heritage—Sentinel. Available online: https://earth.esa.int/web/sentinel/user-guides/sentinel-3-slstr/overview/heritage (accessed on 1 October 2016).
- Schmit, T.J.; Gunshor, M.M.; Menzel, W.P.; Gurka, J.J.; Li, J.; Bachmeier, A.S. Introducing the next-generation Advanced Baseline Imager on GOES-R. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2005, 86, 1079–1096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takahashi, M. Status of Next Generation Japanese Geostationary Meteorological Satellites Himawari-8/9 and Their Products. In Proceedings of the NOAS Satellite Science Week, GOES-R Algorithm Working Group, Kansas City, MO, USA, 30 April–4 May 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Kinter, H.; Just, D.; Mullet, B. Meteosat third generation navigation approach. In Proceedings of the 22nd International Symposium on Space Flight Dynamics, São José dos Campos, Brazil, 28 February–4 March 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Puschell, J.; Cook, L.; Shaham, Y.; Makowski, M.; Silny, J. System engineering studies for advanced geosynchronous remote sensors: Some initial thoughts on the 4th generation. Proc. SPIE 2008, 7087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, Y.; Li, Y.; Guang, J.; Zhang, X.; Guo, J. Small satellite remote sensing and applications—History, current and future. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2008, 29, 4339–4372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Fan, Y.; Gao, M. Natural disaster reduction applications of the Chinese small satellite constellation for environment and disaster monitoring and forecasting. Proc. SPIE 2013, 8921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheng, H.; Chao, H.; Coopmans, C.; Han, J.; McKee, M.; Chen, Y. Low-cost UAV-based thermal infrared remote sensing: Platform, calibration and applications. In Proceedings of the 2010 IEEE/ASME International Conference on Mechatronic and Embedded Systems and Applications, Qingdao, China, 15–17 July 2010; pp. 38–43. [Google Scholar]



| Sensor | Characteristics |
|---|---|
| Advanced Along-Track Scanning Radiometer (AATSR) on-board the European Space Agency (ESA) Envisat satellite | 7 bands: VNIR-MIR-TIR Resolution: 1000 m |
| Advanced Land Imager (ALI) on-board the NASA Earth Observation (EO)-1 satellite | 9 bands: VNIR-SWIR Resolution: 30 m |
| Advanced Spaceborne Thermal Emission and Reflection Radiometer (ASTER) on-board NASA Terra | 14 bands: VNIR-SWIR-TIR Resolution: 15, 30 and 90 m |
| Along Track Scanning Radiometer (ATSR)-1 and ATSR-2 on-board the ESA European Remote Sensing (ERS) Satellites | 4 bands: SWIR-MIR-TIR Resolution: 1000 m |
| Advanced Very High Resolution Radiometer (AVHRR) on-board the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA) satellites | 5 bands: VNIR-SWIR-MIR-TIR Resolution: 1100 m |
| Enhanced Thematic Mapper Plus (ETM+) on-board the NASA Landsat 7 satellite | 8 bands: VNIR-SWIR-TIR Resolution: 15, 30 and 60 m |
| Imager on-board the NASA Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite (GOES) | 5 bands: VNIR-MIR-TIR Resolutions: 1000–4000 m |
| Hyperion on-board the NASA EO-1 satellite | 220 bands: VNIR-SWIR Resolution: 30 m |
| Meteosat Visible and InfraRed Imager (MVIRI) on-board the ESA Meteosat First Generation satellites | 3 bands: VIS-TIR Resolutions: 250–5000 m |
| Moderate-resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer (MODIS) on-board NASA Terra and Aqua satellites | 32 bands: VNIR-MIR-TIR Resolutions: 250, 500 and 1000 m |
| Operational Land Imager (OLI) on-board the NASA Landsat-8 satellite | 9 bands: VNIR-SWIR Resolutions: 15–30 m |
| OPtical Sensor (OPS) on-board the Japanese Earth Resources Satellite 1 (JERS-1) satellite | 7 bands: VNIR-SWIR Resolution: 18 m × 24 m |
| Spinning Enhanced Visible & Infrared Imager (SEVERI) on-board the ESA Meteosat Second Generation satellites | 12 bands: VNIR-TIR Resolution: 1000–3000 m |
| Thermal Infrared Sensor (TIRS) on-board the NASA Lansdsat-8 satellite | 2 bands: TIR Resolution: 100 m |
| Visible Infrared Imaging Radiometer Suite (VIIRS) on board the NASA Suomi National Polar-Orbiting Partnership (S-NPP) satellite | 22 bands: VNIR-SWIR-TIR Resolutions: 375–750 m |
© 2017 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Blackett, M. An Overview of Infrared Remote Sensing of Volcanic Activity. J. Imaging 2017, 3, 13. https://doi.org/10.3390/jimaging3020013
Blackett M. An Overview of Infrared Remote Sensing of Volcanic Activity. Journal of Imaging. 2017; 3(2):13. https://doi.org/10.3390/jimaging3020013
Chicago/Turabian StyleBlackett, Matthew. 2017. "An Overview of Infrared Remote Sensing of Volcanic Activity" Journal of Imaging 3, no. 2: 13. https://doi.org/10.3390/jimaging3020013






