Extraction of Ursolic Acid from Apple Peel with Hydrophobic Deep Eutectic Solvents: Comparison between Response Surface Methodology and Artificial Neural Networks
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Preparation of HDESs
2.3. Viscosity of HDESs
2.4. Solubility of UA
2.4.1. Screening Different Types of HDESs
2.4.2. Screening the Ration of HBA and HBD of HDESs
2.5. HDES Extracts UA from Apple Peels
2.6. Single-Factor Test for UA Extraction by HDES
2.7. Response Surface Optimization of Extraction Process
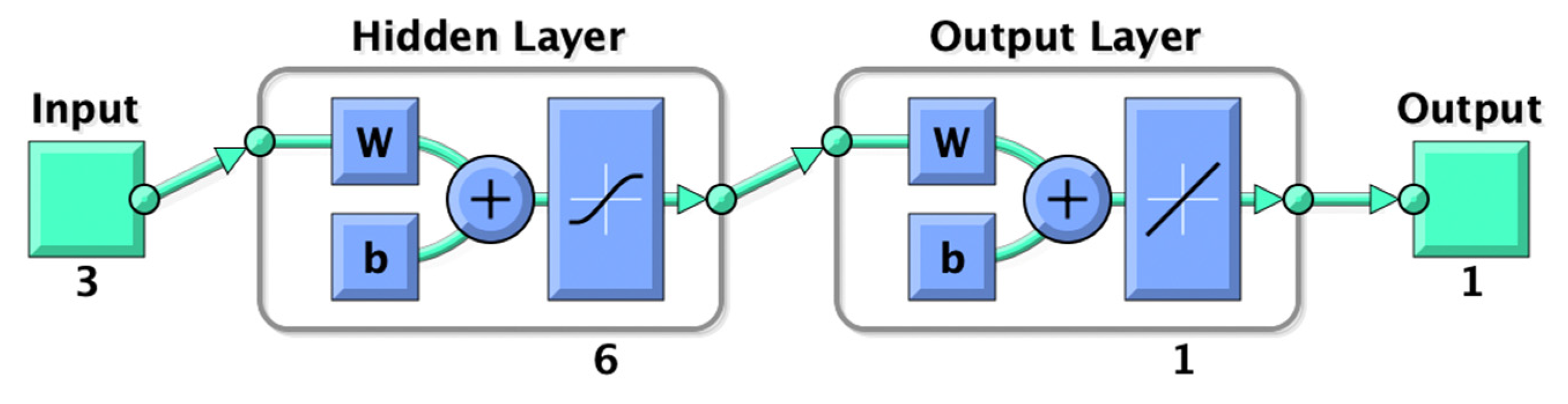
2.8. ANN Modeling of Extraction Process
2.9. Comparison of Predictive Capability of RSM and ANN
2.10. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
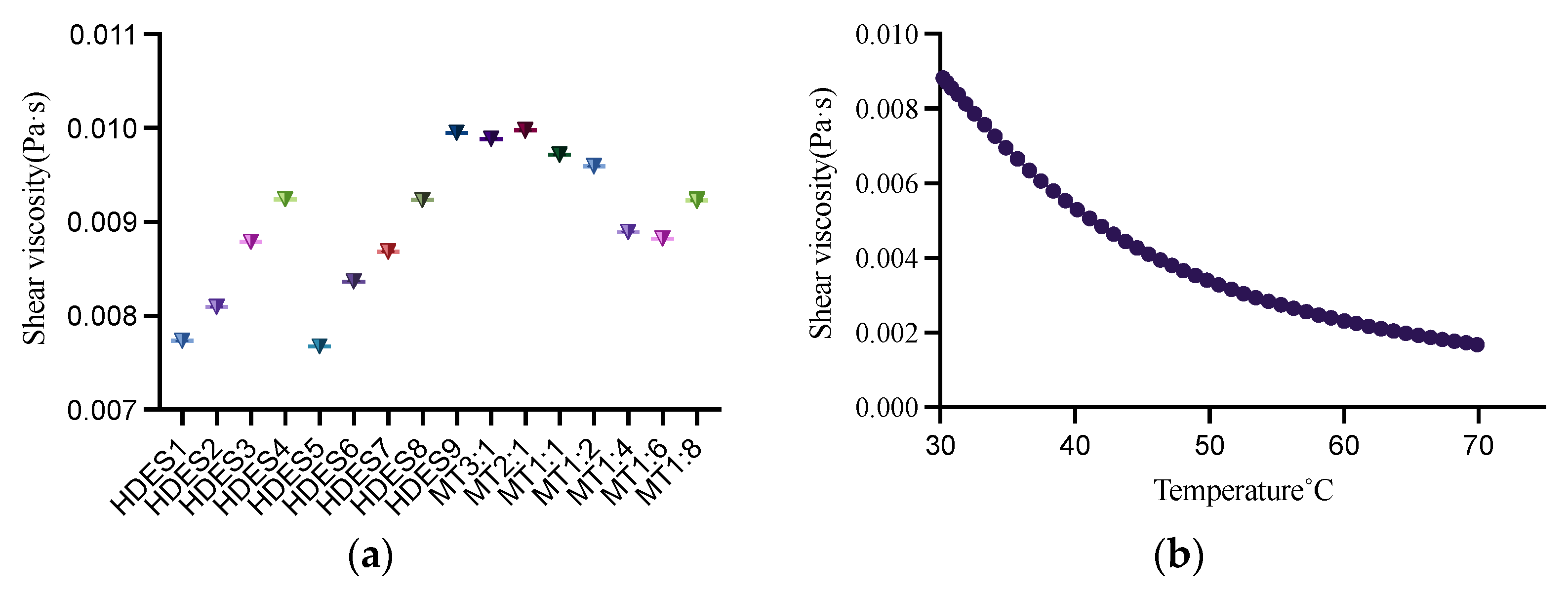
3.1. Physical Properties of HDESs
3.2. Solubility of UA
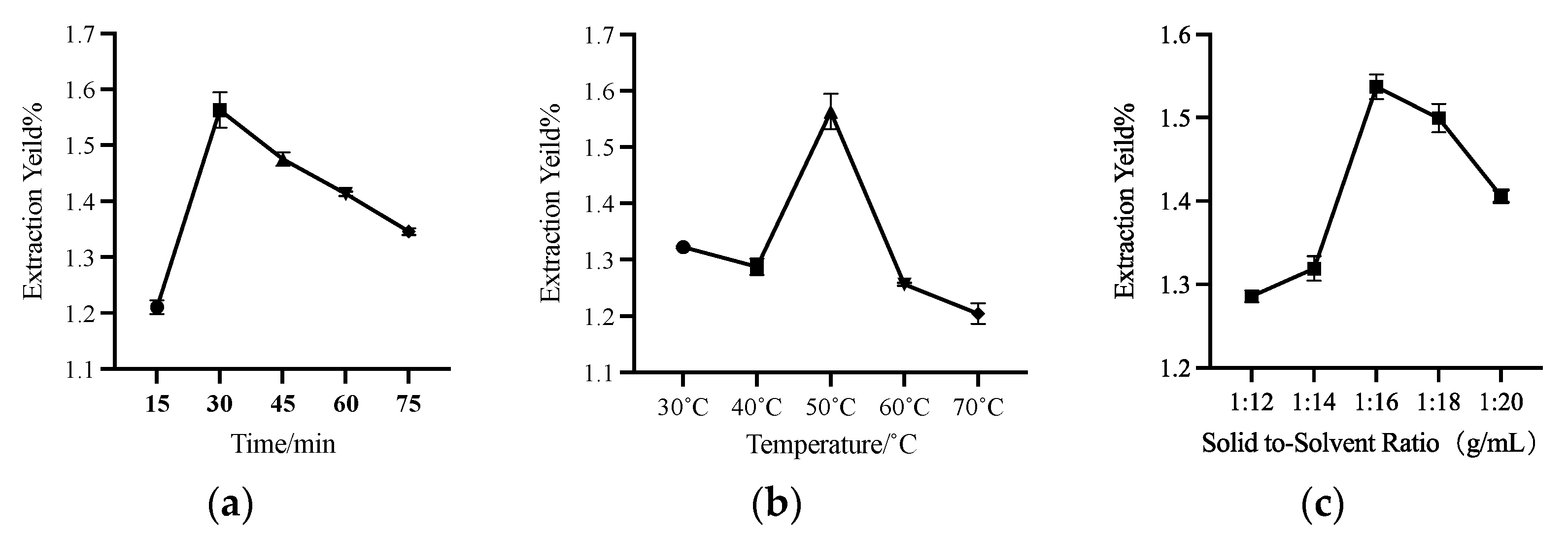
3.3. Single Factor Experiment
3.4. Optimization Method
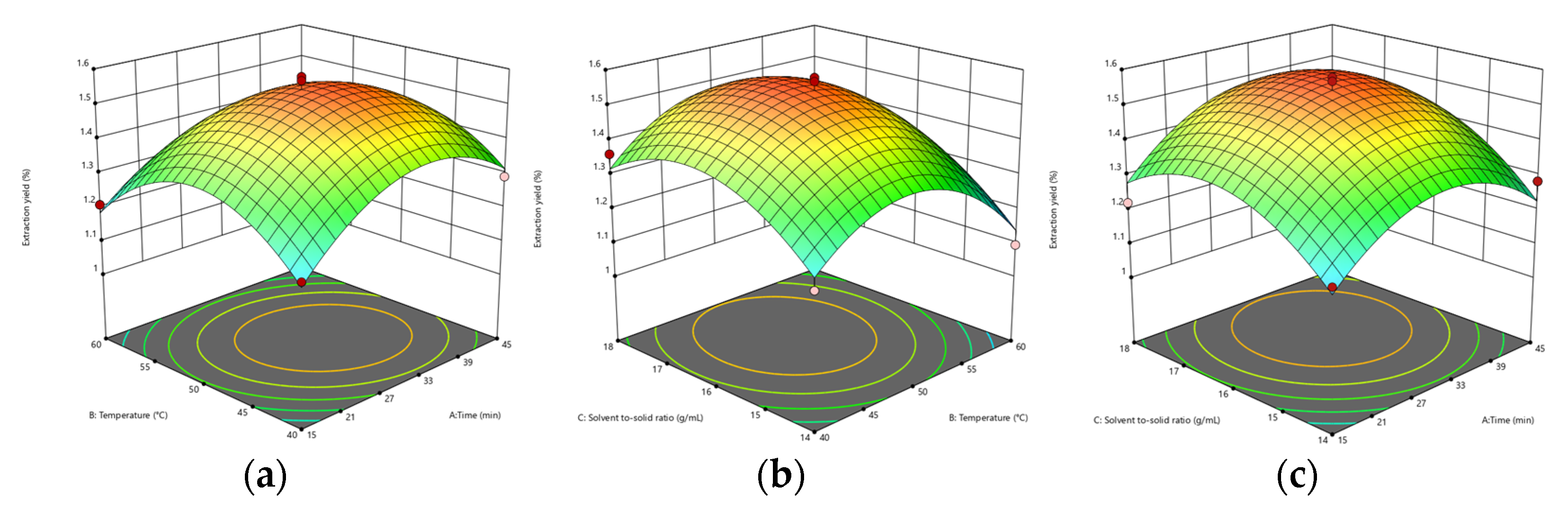
3.4.1. Response Surface Methodology
3.4.2. ANN Modeling
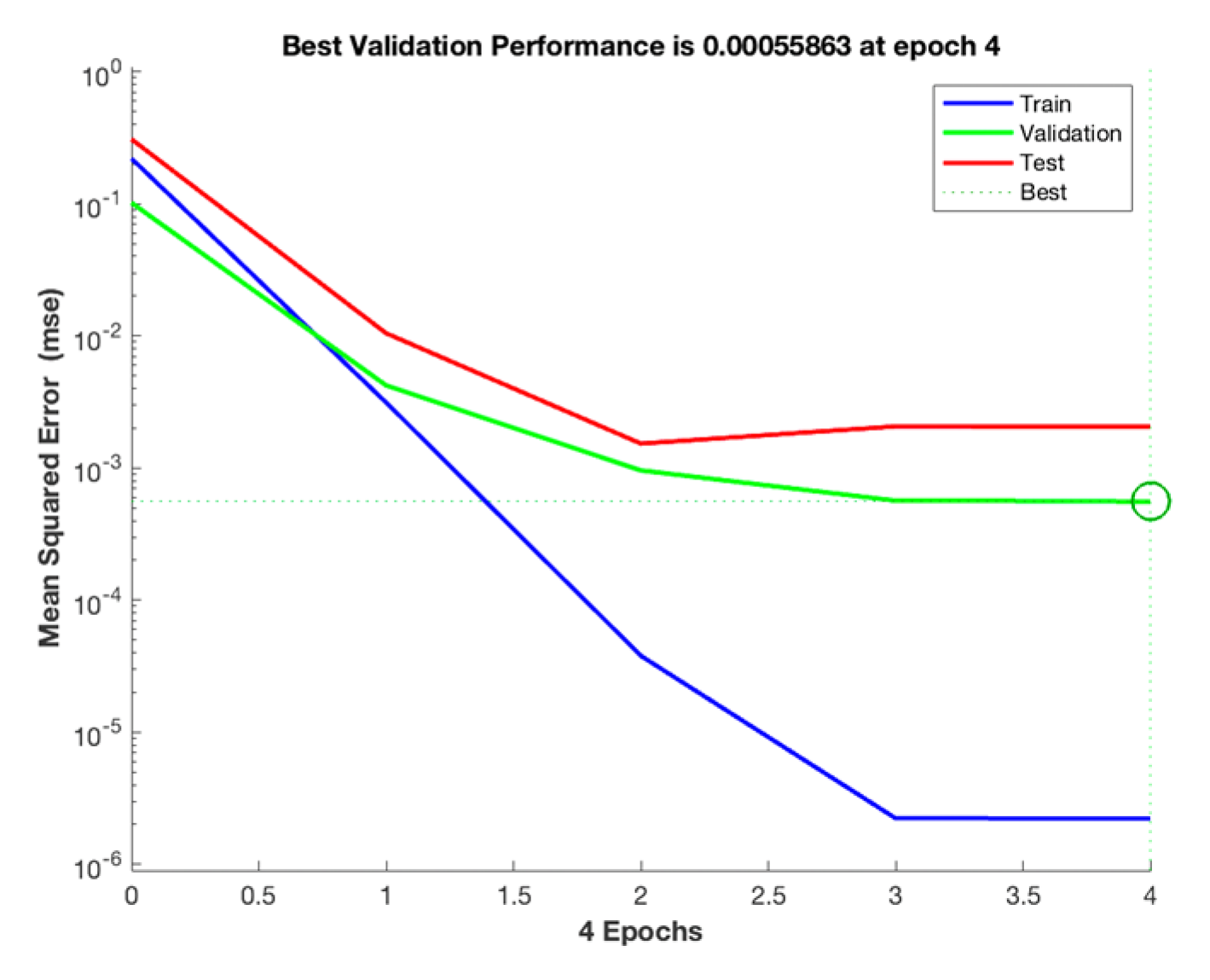
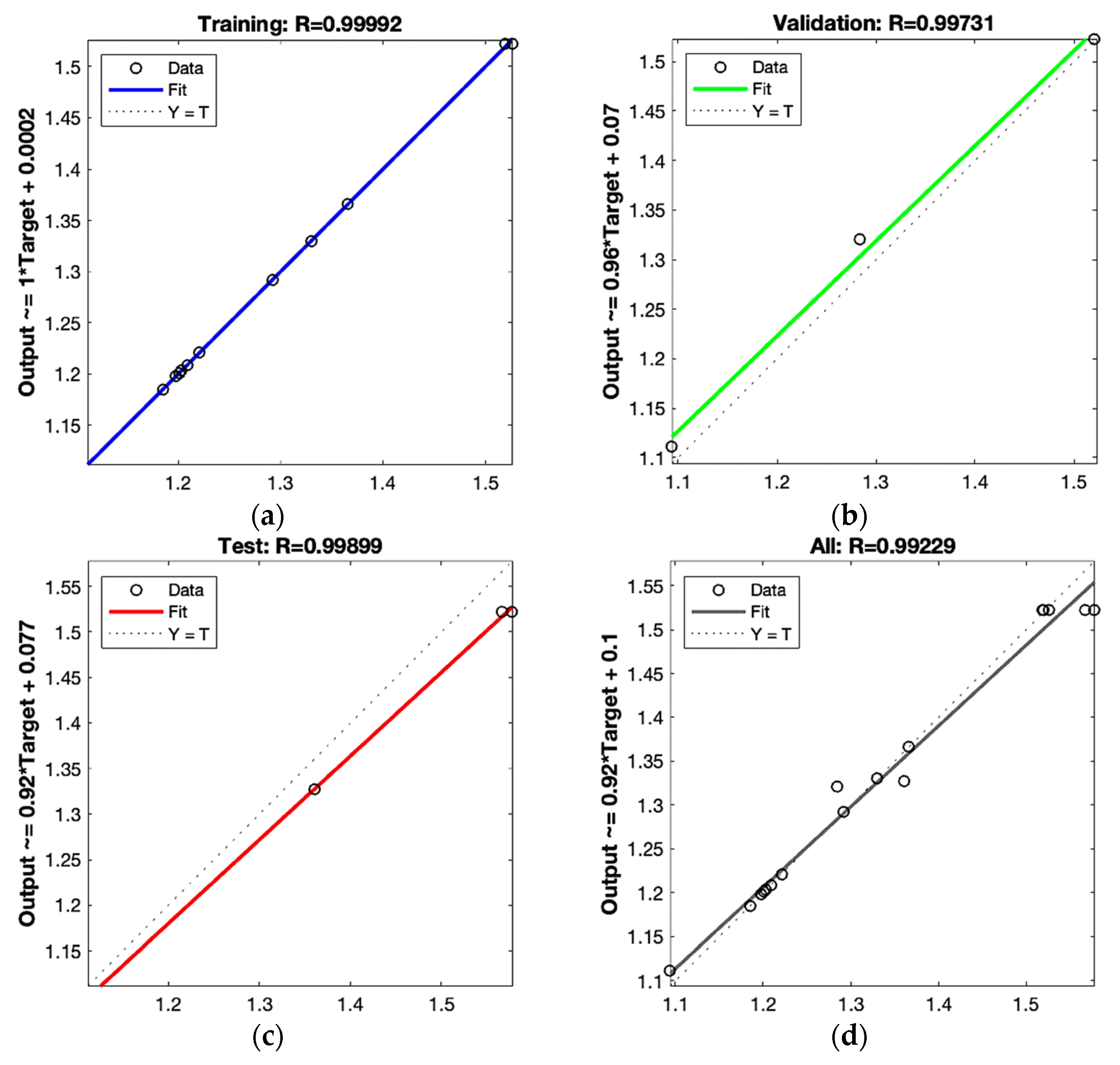
3.4.3. Comparison of Predictive Capability of RSM and ANN
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bachorik, J.; Urban, M. Biocatalysis in the Chemistry of Lupane Triterpenoids. Molecules 2021, 26, 2271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, C.; Wang, B.; Pu, Y.; Tao, J.; Zhang, T. Techniques for the analysis of pentacyclic triterpenoids in medicinal plants. J. Sep. Sci. 2018, 41, 6–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alqahtani, A.; Hamid, K.; Kam, A.; Wong, K.H.; Abdelhak, Z.; Razmovski-Naumovski, V.; Chan, K.; Li, K.M.; Groundwater, P.W.; Li, G.Q. The pentacyclic triterpenoids in herbal medicines and their pharmacological activities in diabetes and diabetic complications. Curr. Med. Chem. 2013, 20, 908–931. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Chung, P.Y. Novel targets of pentacyclic triterpenoids in Staphylococcus aureus: A systematic review. Phytomedicine 2020, 73, 152933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Checker, R.; Sandur, S.K.; Sharma, D.; Patwardhan, R.S.; Jayakumar, S.; Kohli, V.; Sethi, G.; Aggarwal, B.B.; Sainis, K.B. Potent anti-inflammatory activity of ursolic acid, a triterpenoid antioxidant, is mediated through suppression of NF-kappaB, AP-1 and NF-AT. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e31318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Do Nascimento, P.G.; Lemos, T.L.; Bizerra, A.M.; Arriaga, Â.M.; Ferreira, D.A.; Santiago, G.M. Antibacterial and Antioxidant Activities of Ursolic Acid and Derivatives. Molecules 2014, 19, 1317–1327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.; Gan, D.; Luo, F.; Wan, S.; Chen, J.; Wang, A.; Li, B.; Zhu, X. Interaction Mechanisms Between the NOX4/ROS and RhoA/ROCK1 Signaling Pathways as New Anti- fibrosis Targets of Ursolic Acid in Hepatic Stellate Cells. Front. Pharm. 2019, 10, 431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tohme, M.J.; Gimenez, M.C.; Peralta, A.; Colombo, M.I.; Delgui, L.R. Ursolic acid: A novel antiviral compound inhibiting rotavirus infection in vitro. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 2019, 54, 601–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Zheng, H.; Sui, Z.; Jing, F.; Quan, X.; Zhao, W.; Liu, G. Ursolic acid exhibits anti-inflammatory effects through blocking TLR4-MyD88 pathway mediated by autophagy. Cytokine 2019, 123, 154726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, W.; Kwek, E.; He, Z.; Zhu, H.; Liu, J.; Zhao, Y.; Ma, K.Y.; He, W.S.; Chen, Z.Y. Ursolic acid alleviates hypercholesterolemia and modulates the gut microbiota in hamsters. Food Funct. 2020, 11, 6091–6103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopez-Hortas, L.; Perez-Larran, P.; Gonzalez-Munoz, M.J.; Falque, E.; Dominguez, H. Recent developments on the extraction and application of ursolic acid. A review. Food Res. Int. 2018, 103, 130–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vendruscolo, F.; Albuquerque, P.M.; Streit, F.; Esposito, E.; Ninow, J.L. Apple pomace: A versatile substrate for biotechnological applications. Crit. Rev. Biotechnol. 2008, 28, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cargnin, S.T.; Gnoatto, S.B. Ursolic acid from apple pomace and traditional plants: A valuable triterpenoid with functional properties. Food Chem. 2017, 220, 477–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kikowska, M.A.; Chmielewska, M.; Włodarczyk, A.; Studzińska-Sroka, E.; Żuchowski, J.; Stochmal, A. Effect of Pentacyclic Triterpenoids-Rich Callus Extract of Chaenomeles japonica (Thunb.) Lindl. ex Spach on Viability, Morphology, and Proliferation of Normal Human Skin Fibroblasts. Molecules 2018, 23, 3009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lourenco, A.; Marques, A.V.; Gominho, J. The Identification of New Triterpenoids in Eucalyptus globulus Wood. Molecules 2021, 26, 3495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, E.Q.; Wang, B.W.; Xu, X.R.; Zhu, L.; Song, Y.; Li, H.B. Microwave-Assisted Extraction of Oleanolic Acid and Ursolic Acid from Ligustrum lucidum Ait. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2011, 12, 5319–5329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, E.L.; Abbott, A.P.; Ryder, K.S. Deep eutectic solvents (DESs) and their applications. Chem. Rev. 2014, 114, 11060–11082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tang, W.; Liu, L.; Li, G.; Zhu, T.; Row, K.H. Optimal separation of phenol from model oils by forming deep eutectic solvents with quaternary ammonium salts. Korean J. Chem. Eng. 2016, 34, 814–821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbott, A.P.; Capper, G.; Davies, D.L.; Rasheed, R.K.; Tambyrajah, V. Novel solvent properties of choline chloride/urea mixtures. Chem. Commun. 2003, 39, 70–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Van Osch, D.J.G.P.; Zubeir, L.F.; van den Bruinhorst, A.; Rocha, M.A.A.; Kroon, M.C. Hydrophobic deep eutectic solvents as water-immiscible extractants. Green Chem. 2015, 17, 4518–4521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, S.; Jin, X.; Wei, H.; Liu, Y.; Guo, M. Hydrophobic deep eutectic solvent-based ultrasonic-assisted liquid-liquid micro-extraction combined with HPLC-FLD for diphenylamine determination in fruit. Food Addit. Contam. Part A Chem. Anal. Control Expo. Risk Assess. 2021, 38, 339–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khare, L.; Karve, T.; Jain, R.; Dandekar, P. Menthol based hydrophobic deep eutectic solvent for extraction and purification of ergosterol using response surface methodology. Food Chem. 2021, 340, 127979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, S.; Zhou, J.; Jia, H.; Zhang, H. Liquid-liquid microextraction of synthetic pigments in beverages using a hydrophobic deep eutectic solvent. Food Chem. 2018, 243, 351–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silva, N.; Morais, E.S.; Freire, C.S.R.; Freire, M.G.; Silvestre, A.J.D. Extraction of High Value Triterpenic Acids from Eucalyptus globulus Biomass Using Hydrophobic Deep Eutectic Solvents. Molecules 2020, 25, 210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Huang, S.M.; Kuo, C.H.; Chen, C.A.; Liu, Y.C.; Shieh, C.J. RSM and ANN modeling-based optimization approach for the development of ultrasound-assisted liposome encapsulation of piceid. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2017, 36, 112–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chouaibi, M.; Daoued, K.B.; Riguane, K.; Rouissi, T.; Ferrari, G. Production of bioethanol from pumpkin peel wastes: Comparison between response surface methodology (RSM) and artificial neural networks (ANN). Ind. Crops Prod. 2020, 155, 112822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Musa, K.H.; Abdullah, A.; Al-Haiqi, A. Determination of DPPH free radical scavenging activity: Application of artificial neural networks. Food Chem. 2016, 194, 705–711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ciric, A.; Krajnc, B.; Heath, D.; Ogrinc, N. Response surface methodology and artificial neural network approach for the optimization of ultrasound-assisted extraction of polyphenols from garlic. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2020, 135, 110976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gammoudi, N.; Mabrouk, M.; Bouhemda, T.; Nagaz, K.; Ferchichi, A. Modeling and optimization of capsaicin extraction from Capsicum annuum L. using response surface methodology (RSM), artificial neural network (ANN), and Simulink simulation. Ind. Crops Prod. 2021, 171, 113869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, X.; Duan, M.-H.; Yao, X.-H.; Zhang, Y.-H.; Zhao, C.-J.; Zu, Y.-G.; Fu, Y.-J. Green extraction of five target phenolic acids from Lonicerae japonicae Flos with deep eutectic solvent. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2016, 157, 249–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, C.; Wu, S.; Wang, C.; Yang, Y.; Sun, D.; Li, F.; Tan, Z. Deep eutectic solvents used as adjuvants for improving the salting-out extraction of ursolic acid from Cynomorium songaricum Rupr. in aqueous two-phase system. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2019, 209, 112–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.-T.; Yang, Q.; Cui, Q.; Fan, X.-H.; Dong, M.-Z.; Gao, M.-Z.; Lv, M.-J.; An, J.-Y.; Meng, D.; Zhao, X.-H.; et al. Recyclable menthol-based deep eutectic solvent micellar system for extracting phytochemicals from Ginkgo biloba leaves. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 244, 118648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, C.; Liu, Y.; Ding, Z.; Xia, H.; Guo, S. Physicochemical properties and antibacterial activity of hydrophobic deep eutectic solvent-in-water nanoemulsion. J. Mol. Liq. 2021, 338, 116950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.; Cai, Y.; Ma, Q.; Zhao, Z.; Yang, D.; Xu, X. Optimization of Extraction of Bioactive Compounds from Baphicacanthus cusia Leaves by Hydrophobic Deep Eutectic Solvents. Molecules 2021, 26, 1729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, X.-H.; Wang, L.-T.; Chang, Y.-H.; An, J.-Y.; Zhu, Y.-W.; Yang, Q.; Meng, D.; Fu, Y.-j. Application of green and recyclable menthol-based hydrophobic deep eutectic solvents aqueous for the extraction of main taxanes from Taxus chinensis needles. J. Mol. Liq. 2021, 326, 114970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alhadid, A.; Mokrushina, L.; Minceva, M. Influence of the Molecular Structure of Constituents and Liquid Phase Non-Ideality on the Viscosity of Deep Eutectic Solvents. Molecules 2021, 26, 4208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Q.; De Oliveira Vigier, K.; Royer, S.; Jerome, F. Deep eutectic solvents: Syntheses, properties and applications. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2012, 41, 7108–7146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naser, J.; Mjalli, F.; Jibril, B.; Al-Hatmi, S.; Gano, Z. Potassium Carbonate as a Salt for Deep Eutectic Solvents. Int. J. Chem. Eng. Appl. 2013, 4, 114–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Makoś, P.; Słupek, E.; Gębicki, J. Hydrophobic deep eutectic solvents in microextraction techniques—A review. Microchem. J. 2020, 152, 104384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, G.; Sequeira, R.A.; Pereira, M.M.; Maity, T.K.; Chudasama, N.A.; Prasad, K. Are ionic liquids and deep eutectic solvents the same?: Fundamental investigation from DNA dissolution point of view. J. Mol. Liq. 2021, 328, 104384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, E.Q.; Yu, Y.Y.; Xu, X.R.; Deng, G.F.; Guo, Y.J.; Li, H.B. Ultrasound-assisted extraction of oleanolic acid and ursolic acid from Ligustrum lucidum Ait. Ultrason Sonochem. 2012, 19, 772–776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maran, J.P.; Priya, B.; Nivetha, C.V. Optimization of ultrasound-assisted extraction of natural pigments from Bougainvillea glabra flowers. Ind. Crops Prod. 2015, 63, 182–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siani, A.C.; Nakamura, M.J.; Dos Santos, D.S.; Mazzei, J.L.; do Nascimento, A.C.; Valente, L.M. Efficiency and selectivity of triterpene acid extraction from decoctions and tinctures prepared from apple peels. Pharm. Mag. 2014, 10 (Suppl. S2), S225–S231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sha, W.; Edwards, K.L. The use of artificial neural networks in materials science based research. Mater. Des. 2007, 28, 1747–1752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Abbreviation | HBA | HBD | Molar Ratio | Aspect | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MT 1:1 | Men | Thy | 1:1 | Transparent colorless liquid | [24] |
| HDES 1 | Formic acid | 1:1 | White emulsion | [32] | |
| HDES 2 | Acetic acid | 1:1 | Transparent colorless liquid | [22] | |
| HDES 3 | Propionic acid | 1:1 | Transparent colorless liquid | [32] | |
| HDES 4 | Decanoic acid | 1:1 | Transparent colorless liquid | [33] | |
| HDES 5 | Isopropanol | 1:2 | Transparent colorless liquid | [34] | |
| HDES 6 | n-Butanol | 1:1 | Transparent colorless liquid | [35] | |
| HDES 7 | Pyruvic acid | 1:2 | Transparent yellow liquid | [22] | |
| HDES 8 | Lactic acid | 1:1 | Transparent colorless liquid | [34] | |
| HDES 9 | Levulinic acid | 1:1 | Transparent yellow liquid | [34] |
| Abbreviation | HBA | HBD | Molar Ratio | Aspect |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| MT 4:1 | 4:1 | Transparent colorless solid | ||
| MT 3:1 | Men | Thy | 3:1 | Transparent colorless liquid |
| MT 2:1 | 2:1 | Transparent colorless liquid | ||
| MT 1:1 | 1:1 | Transparent colorless liquid | ||
| MT 1:2 | 1:2 | Transparent colorless liquid | ||
| MT 1:4 | 1:4 | Transparent colorless liquid | ||
| MT 1:6 | 1:6 | Transparent colorless liquid | ||
| MT 1:8 | 1:8 | Transparent colorless liquid |
| Levels | Independent Variables | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| A (Time, min) | B (Temperature, °C) | C (Solvent to-Solid Ratio, g/mL) | |
| −1 | 15 | 40 | 14 |
| 0 | 30 | 50 | 16 |
| 1 | 45 | 60 | 18 |
| Run | Factor | EY/% | RSM Calculated | ANN Calculated | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A | B | C | ||||
| 1 | 30 | 40 | 18 | 1.361 | 1.3168 | 1.3277 |
| 2 | 30 | 50 | 16 | 1.526 | 1.5402 | 1.5225 |
| 3 | 15 | 60 | 16 | 1.209 | 1.1836 | 1.2090 |
| 4 | 45 | 40 | 16 | 1.292 | 1.3136 | 1.2920 |
| 5 | 30 | 50 | 16 | 1.567 | 1.5402 | 1.5225 |
| 6 | 45 | 60 | 16 | 1.201 | 1.2121 | 1.2010 |
| 7 | 45 | 50 | 18 | 1.366 | 1.3833 | 1.3660 |
| 8 | 30 | 50 | 16 | 1.52 | 1.5402 | 1.5225 |
| 9 | 15 | 50 | 18 | 1.221 | 1.2767 | 1.2210 |
| 10 | 15 | 40 | 16 | 1.203 | 1.1880 | 1.2030 |
| 11 | 30 | 50 | 16 | 1.519 | 1.5402 | 1.5225 |
| 12 | 30 | 60 | 14 | 1.094 | 1.1345 | 1.1115 |
| 13 | 30 | 60 | 18 | 1.33 | 1.2938 | 1.3300 |
| 14 | 45 | 50 | 14 | 1.284 | 1.2245 | 1.3209 |
| 15 | 15 | 50 | 14 | 1.198 | 1.1769 | 1.1980 |
| 16 | 30 | 40 | 14 | 1.185 | 1.2173 | 1.1850 |
| 17 | 30 | 50 | 16 | 1.578 | 1.5402 | 1.5225 |
| Source | Sum of Squares | df | Mean Square | F-Value | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Model | 0.3691 | 9 | 0.0410 | 15.99 | 0.0007 | significant |
| A | 0.0122 | 1 | 0.0122 | 4.74 | 0.0658 | |
| B | 0.0054 | 1 | 0.0054 | 2.09 | 0.1917 | |
| C | 0.0334 | 1 | 0.0334 | 13.03 | 0.0086 | |
| AB | 0.0024 | 1 | 0..0024 | 0.9171 | 0.3701 | |
| BC | 0.0009 | 1 | 0.0009 | 0.3393 | 0.5785 | |
| AC | 0.0009 | 1 | 0.0009 | 0.3509 | 0.5722 | |
| A2 | 0.0891 | 1 | 0.0891 | 34.75 | 0.0006 | |
| B2 | 0.1220 | 1 | 0.1220 | 47.58 | 0.0002 | |
| C2 | 0.0703 | 1 | 0.0703 | 27.42 | 0.0012 | |
| Residual | 0.0180 | 7 | 0.0026 | |||
| Lack of fit | 0.0148 | 3 | 0.0049 | 6.17 | 0.0556 | Not significant |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, H.; Liu, Y.; Guo, S.; Shi, M.; Qin, S.; Zeng, C. Extraction of Ursolic Acid from Apple Peel with Hydrophobic Deep Eutectic Solvents: Comparison between Response Surface Methodology and Artificial Neural Networks. Foods 2023, 12, 310. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods12020310
Li H, Liu Y, Guo S, Shi M, Qin S, Zeng C. Extraction of Ursolic Acid from Apple Peel with Hydrophobic Deep Eutectic Solvents: Comparison between Response Surface Methodology and Artificial Neural Networks. Foods. 2023; 12(2):310. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods12020310
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Haiyan, Yugang Liu, Shiyin Guo, Meng Shi, Si Qin, and Chaoxi Zeng. 2023. "Extraction of Ursolic Acid from Apple Peel with Hydrophobic Deep Eutectic Solvents: Comparison between Response Surface Methodology and Artificial Neural Networks" Foods 12, no. 2: 310. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods12020310








