Optimization of Ultrasound-Assisted Extraction of Spent Coffee Grounds Oil Using Response Surface Methodology
Abstract
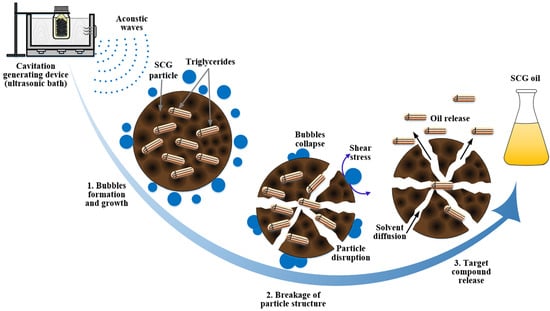
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Spent Coffee Grounds (SCG) Samples
2.2. Statistical Design
- temperature (X1),
- extraction time (X2), and
- liquid/solid (L/S) rate of solvent (X3).
2.3. Ultrasonic Extraction Process
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Factorial Design for SCG Oil Extraction
3.2. Statistical Analysis
3.3. Response Surface Analysis
3.4. Optimal Extraction Conditions
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Girotto, F.; Pivato, A.; Cossu, R.; Nkeng, G.E.; Lavagnolo, M.C. The broad spectrum of possibilities for spent coffee grounds valorisation. J. Mater. Cycles Waste Manag. 2018, 20, 695–701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ICO. ICO Trade Statistics Tables; International Coffee Organization (ICO): London, UK, 2021; Available online: http://www.ico.org/trade_statistics.asp (accessed on 22 June 2021).
- Murthy, P.S.; Naidu, M.M. Sustainable management of coffee industry by-products and value addition—A review. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2012, 66, 45–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- USDA Foreign Agriculture Service; U.S. Department of Agriculture. USDA Coffee: World Markets and Trade. 2021. Available online: https://www.fas.usda.gov/data/coffee-world-markets-and-trade (accessed on 22 June 2021).
- Campos-Vega, R.; Loarca-Piña, G.; Vergara-Castañeda, H.A.; Dave Oomah, B. Spent coffee grounds: A review on current research and future prospects. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2015, 45, 24–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mata, T.M.; Martins, A.A.; Caetano, N.S. Bio-refinery approach for spent coffee grounds valorization. Bioresour. Technol. 2018, 247, 1077–1084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stylianou, M.; Agapiou, A.; Omirou, M.; Vyrides, I.; Ioannides, I.M.; Maratheftis, G.; Fasoula, D. Converting environmental risks to benefits by using spent coffee grounds (SCG) as a valuable resource. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2018, 25, 35776–35790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- European Commission. EC The Waste Framework Directive 2008/98/EC; European Commission: Luxembourg, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Martins, A.A.; Simaria, M.; Barbosa, J.; Barbosa, R.; Silva, D.T.; Rocha, C.S.; Mata, T.M.; Caetano, N.S. Life cycle assessment tool of electricity generation in Portugal. Environ. Dev. Sustain. 2018, 20, 129–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Caetano, N.S.; Silva, V.F.M.; Melo, A.C.; Martins, A.A.; Mata, T.M. Spent coffee grounds for biodiesel production and other applications. Clean Technol. Environ. Policy 2014, 16, 1423–1430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Caetano, N.S.; Mata, T.M.; Martins, A.A.; Felgueiras, M.C. New Trends in Energy Production and Utilization. Energy Procedia 2017, 107, 7–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ribeiro, H.; Marto, J.; Raposo, S.; Agapito, M.; Isaac, V.; Chiari, B.G.; Lisboa, P.F.; Paiva, A.; Barreiros, S.; Simões, P. From coffee industry waste materials to skin-friendly products with improved skin fat levels. Eur. J. Lipid Sci. Technol. 2013, 115, 330–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saratale, G.D.; Bhosale, R.; Shobana, S.; Banu, J.R.; Pugazhendhi, A.; Mahmoud, E.; Sirohi, R.; Kant Bhatia, S.; Atabani, A.E.; Mulone, V.; et al. A review on valorization of spent coffee grounds (SCG) towards biopolymers and biocatalysts production. Bioresour. Technol. 2020, 314, 123800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caetano, N.S.; Silva, V.F.M.; Melo, A.C.; Mata, T.M. Potential of spent coffee grounds for biodiesel production and other applications. Chem. Eng. Trans. 2013, 35, 1063–1068. [Google Scholar]
- Mussatto, S.I.; Machado, E.M.S.; Carneiro, L.M.; Teixeira, J.A. Sugars metabolism and ethanol production by different yeast strains from coffee industry wastes hydrolysates. Appl. Energy 2012, 92, 763–768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kwon, E.E.; Yi, H.; Jeon, Y.J. Sequential co-production of biodiesel and bioethanol with spent coffee grounds. Bioresour. Technol. 2013, 136, 475–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panusa, A.; Zuorro, A.; Lavecchia, R.; Marrosu, G.; Petrucci, R. Recovery of natural antioxidants from spent coffee grounds. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2013, 61, 4162–4168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gu, J.; Pei, W.; Tang, S.; Yan, F.; Peng, Z.; Huang, C.; Yang, J.; Yong, Q. Procuring biologically active galactomannans from spent coffee ground (SCG) by autohydrolysis and enzymatic hydrolysis. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 149, 572–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, L.; Pandey, A.; Mohan, R.; Soccol, C.R. Use of various coffee industry residues for the cultivation of Pleurotus ostreatus in solid state fermentation. Acta Biotechnol. 2000, 20, 41–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anastopoulos, I.; Karamesouti, M.; Mitropoulos, A.C.; Kyzas, G.Z. A review for coffee adsorbents. J. Mol. Liq. 2017, 229, 555–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vardon, D.R.; Moser, B.R.; Zheng, W.; Witkin, K.; Evangelista, R.L.; Strathmann, T.J.; Rajagopalan, K.; Sharma, B.K. Complete utilization of spent coffee grounds to produce biodiesel, bio-oil, and biochar. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2013, 1, 1286–1294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panda, D.; Manickam, S. Cavitation Technology—The Future of Greener Extraction Method: A Review on the Extraction of Natural Products and Process Intensification Mechanism and Perspectives. Appl. Sci. 2019, 9, 766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chemat, F.; Rombaut, N.; Sicaire, A.G.; Meullemiestre, A.; Fabiano-Tixier, A.S.; Abert-Vian, M. Ultrasound assisted extraction of food and natural products. Mechanisms, techniques, combinations, protocols and applications. A review. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2017, 34, 540–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Couto, R.M.; Fernandes, J.; da Silva, M.D.R.G.; Simões, P.C. Supercritical fluid extraction of lipids from spent coffee grounds. J. Supercrit. Fluids 2009, 51, 159–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Danlami, J.M.; Arsad, A.; Zaini, M.A.A.; Sulaiman, H. A comparative study of various oil extraction techniques from plants. Rev. Chem. Eng. 2014, 30, 605–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vilkhu, K.; Mawson, R.; Simons, L.; Bates, D. Applications and opportunities for ultrasound assisted extraction in the food industry—A review. Innov. Food Sci. Emerg. Technol. 2008, 9, 161–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiwari, B.K. Ultrasound: A clean, green extraction technology. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2015, 71, 100–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shirsath, S.R.; Sonawane, S.H.; Gogate, P.R. Intensification of extraction of natural products using ultrasonic irradiations-A review of current status. Chem. Eng. Process. Process Intensif. 2012, 53, 10–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tavares, G.R.; Massa, T.B.; Gonçalves, J.E.; da Silva, C.; dos Santos, W.D. Assessment of ultrasound-assisted extraction of crambe seed oil for biodiesel synthesis by in situ interesterification. Renew. Energy 2017, 111, 659–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Pan, Y.G.; Huang, W.; Chen, H.; Yang, H. Optimized ultrasonic-assisted extraction of papaya seed oil from Hainan/Eksotika variety. Food Sci. Nutr. 2019, 7, 2692–2701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chanioti, S.; Tzia, C. Optimization of ultrasound-assisted extraction of oil from olive pomace using response surface technology: Oil recovery, unsaponifiable matter, total phenol content and antioxidant activity. LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 2017, 79, 178–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdullah, M.; Bulent Koc, A. Oil removal from waste coffee grounds using two-phase solvent extraction enhanced with ultrasonication. Renew. Energy 2013, 50, 965–970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kentish, S.; Ashokkumar, M. The Physical and Chemical Effects of Ultrasound. In Ultrasound Technologies for Food Bioprocessing; Food Engineering Series; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2011; pp. 1–12. ISBN 9788578110796. [Google Scholar]
- Rocha, M.V.P.; de Matos, L.J.B.L.; de Lima, L.P.; Figueiredo, P.M.d.S.; Lucena, I.L.; Fernandes, F.A.N.; Gonçalves, L.R.B. Ultrasound-assisted production of biodiesel and ethanol from spent coffee grounds. Bioresour. Technol. 2014, 167, 343–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le, P.T.K.; Vu, Q.T.H.; Nguyen, Q.T.V.; Tran, K.A.; Le, K.A. Extraction and evaluation the biological activities of oil from spent coffee grounds. Chem. Eng. Trans. 2017, 56, 1729–1734. [Google Scholar]
- Ahangari, B.; Sargolzaei, J. Extraction of lipids from spent coffee grounds using organic solvents and supercritical carbon dioxide. J. Food Process. Preserv. 2013, 37, 1014–1021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nde, D.B.; Anuanwen, C.F. Optimization methods for the extraction of vegetable oils: A review. Processes 2020, 8, 209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Latimer, G.W.J. Chapter 3: Plants. Official Methods of Analysis of AOAC International, 21st ed.; The Scientific Association of Official Analytical Chemists (AOAC): Rockville, MD, USA, 2019; Volume 3, ISBN 0935584544. [Google Scholar]
- Said, K.A.M.; Amin, M.A.M. Overview on the Response Surface Methodology (RSM) in Extraction Processes. J. Appl. Sci. Process Eng. 2016, 2, 8–17. [Google Scholar]
- Montgomery, D.C. Design and Analysis of Experiments; John Wiley & Sons, Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Mofijur, M.; Kusumo, F.; Rizwanul Fattah, I.M.; Mahmudul, H.M.; Rasul, M.G.; Shamsuddin, A.H.; Mahlia, T.M.I. Resource recovery from waste coffee grounds using ultrasonic-assisted technology for bioenergy production. Energies 2020, 13, 1770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Al-Hamamre, Z.; Foerster, S.; Hartmann, F.; Kröger, M.; Kaltschmitt, M. Oil extracted from spent coffee grounds as a renewable source for fatty acid methyl ester manufacturing. Fuel 2012, 96, 70–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Somnuk, K.; Eawlex, P.; Prateepchaikul, G. Optimization of coffee oil extraction from spent coffee grounds using four solvents and prototype-scale extraction using circulation process. Agric. Nat. Resour. 2017, 51, 181–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goh, B.H.H.; Ong, H.C.; Chong, C.T.; Chen, W.H.; Leong, K.Y.; Tan, S.X.; Lee, X.J. Ultrasonic assisted oil extraction and biodiesel synthesis of Spent Coffee Ground. Fuel 2020, 261, 116121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Hajjaji, S.; Bouladab, C.; Chergaoui, S.; Fadli, S. Biorefining of Waste Coffee Grounds: Turning an Environmental Problem into an Opportunity. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2020, 505, 12026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira, L.S.; Franca, A.S.; Camargos, R.R.S.; Ferraz, V.P. Coffee oil as a potential feedstock for biodiesel production. Bioresour. Technol. 2008, 99, 3244–3250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capelo-Martinez, J.L. Microwaves in Organic Synthesis Practical Microwave Synthesis for Organic Chemists Microinstrumentation; Wiley-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA: Darmstadt, Germany, 2009; ISBN 9783527314522. [Google Scholar]
- Mäkelä, M. Experimental design and response surface methodology in energy applications: A tutorial review. Energy Convers. Manag. 2017, 151, 630–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moradi, N.; Rahimi, M.; Moeini, A.; Parsamoghadam, M.A. Impact of ultrasound on oil yield and content of functional food ingredients at the oil extraction from sunflower. Sep. Sci. Technol. 2018, 53, 261–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, G.E. Solvent Extraction; AOCS Lipid Library: Urbana, IL, USA, 2021; Available online: https://lipidlibrary.aocs.org/edible-oil-processing/solvent-extraction (accessed on 22 June 2021).
- Bart, J.C.J.; Palmeri, N.; Cavalaro, S. Chapter 3—Oleochemical sources: Basic science, processing and applications of oil. In Biodiesel Science and Technology: From Soil to Oil; Woodhead Publishing Series in Energy 7; CRC—Woodhead Publishing Limited: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]



| Independent Variables | Code | Coded Levels | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| −1.68 | −1 | 0 | +1 | +1.68 | ||
| Temperature (°C) | X1 | 26.00 | 32.70 | 42.50 | 52.30 | 59.00 |
| Time (min) | X2 | 10.30 | 15.00 | 52.50 | 90.00 | 115.70 |
| L/S ratio (mL g−1) | X3 | 1.000 | 5.82 | 12.91 | 20.00 | 24.82 |
| Run | x1 | x2 | x3 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 2 | 0 | 0 | +1.68 |
| 3 | −1 | +1 | +1 |
| 4 | −1.68 | 0 | 0 |
| 5 | +1 | −1 | +1 |
| 6 | +1 | +1 | −1 |
| 7 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 8 | −1 | −1 | −1 |
| 9 | +1 | −1 | −1 |
| 10 | +1 | +1 | +1 |
| 11 | 0 | +1.68 | 0 |
| 12 | −1 | −1 | +1 |
| 13 | −1 | +1 | −1 |
| 14 | +1.68 | 0 | 0 |
| 15 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 16 | 0 | 0 | −1.68 |
| 17 | 0 | −1.68 | 0 |
| Nº Assay | X1 Temperature (°C) | X2 Time (min) | X3 L/S Ratio (mL g−1) | Oil Yield (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 42.50 | 52.50 | 12.91 | 9.59 |
| 2 | 42.50 | 52.50 | 24.82 | 5.68 |
| 3 | 32.67 | 90.00 | 20.00 | 12.19 |
| 4 | 26.00 | 52.50 | 12.91 | 5.34 |
| 5 | 52.32 | 15.00 | 20.00 | 10.38 |
| 6 | 52.32 | 90.0 | 5.82 | 8.79 |
| 7 | 42.50 | 52.50 | 12.91 | 8.37 |
| 8 | 32.67 | 15.00 | 5.82 | 4.32 |
| 9 | 52.32 | 15.00 | 5.82 | 6.33 |
| 10 | 52.32 | 90.00 | 20.00 | 12.34 |
| 11 | 42.50 | 115.70 | 12.91 | 10.87 |
| 12 | 32.67 | 15.00 | 20.00 | 7.21 |
| 13 | 32.67 | 90.00 | 5.82 | 7.70 |
| 14 | 59.00 | 52.50 | 12.91 | 11.75 |
| 15 | 42.50 | 52.50 | 12.91 | 9.11 |
| 16 | 42.50 | 52.50 | 1.00 | 0.69 |
| 17 | 42.50 | 10.30 | 12.91 | 3.76 |
| Independent Variable | Coefficient | Effect | SE | t-Value | p-Value | Significance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Temperature (°C), L | 2.64 | 0.99 | 2.66 | 0.0237 | Significant | |
| Temperature (°C), Q | 1.02 | 1.04 | 0.98 | 0.3486 | Not significant | |
| Sonication time (min), L | 3.05 | 1.06 | 2.86 | 0.0169 | Significant | |
| Sonication time (min), Q | 0.67 | 1.24 | 0.54 | 0.6029 | Not significant | |
| L/S ratio (mL g−1), L | 3.79 | 0.99 | 3.83 | 0.0033 | Significant | |
| L/S ratio (mL g−1), Q | −2.78 | 1.04 | −2.67 | 0.0236 | Significant |
| Variation Source | SS | df | MS | F | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Calculated | Tabulated * | |||||
| Regression | 137.76 | 6 | 22.96 | 7.197 | 3.22 | <0.05 |
| Sediments | 31.89 | 10 | 3.19 | - | - | - |
| Total | 169.65 | 16 | - | - | - | - |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Miladi, M.; Martins, A.A.; Mata, T.M.; Vegara, M.; Pérez-Infantes, M.; Remmani, R.; Ruiz-Canales, A.; Núñez-Gómez, D. Optimization of Ultrasound-Assisted Extraction of Spent Coffee Grounds Oil Using Response Surface Methodology. Processes 2021, 9, 2085. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr9112085
Miladi M, Martins AA, Mata TM, Vegara M, Pérez-Infantes M, Remmani R, Ruiz-Canales A, Núñez-Gómez D. Optimization of Ultrasound-Assisted Extraction of Spent Coffee Grounds Oil Using Response Surface Methodology. Processes. 2021; 9(11):2085. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr9112085
Chicago/Turabian StyleMiladi, Malek, António A. Martins, Teresa M. Mata, Miguel Vegara, María Pérez-Infantes, Rania Remmani, Antonio Ruiz-Canales, and Dámaris Núñez-Gómez. 2021. "Optimization of Ultrasound-Assisted Extraction of Spent Coffee Grounds Oil Using Response Surface Methodology" Processes 9, no. 11: 2085. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr9112085
APA StyleMiladi, M., Martins, A. A., Mata, T. M., Vegara, M., Pérez-Infantes, M., Remmani, R., Ruiz-Canales, A., & Núñez-Gómez, D. (2021). Optimization of Ultrasound-Assisted Extraction of Spent Coffee Grounds Oil Using Response Surface Methodology. Processes, 9(11), 2085. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr9112085