Annealing-Driven Structural and Optical Evolution of Amorphous Ge–C:H Alloys
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Thermogravimetric Analysis
3.2. Elemental Analysis and Density
3.3. Infrared and Raman Spectroscopy
3.4. X-Ray Powder Diffraction
3.5. Scanning Electron Microscopy
3.6. Optical Properties
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Drüsedau, T.P.; Annen, A.; Schröder, B.; Freistedt, H. Vibrational, optical and electronic properties of the hydrogenated amorphous germanium-carbon alloy system. Philos. Mag. B 1994, 69, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biederman, H.; Stundžia, V.; Slavínská, D.; Žalman, J.; Pešička, J.; Vaněček, M.; Zemek, J.; Fukarek, W. Composite germanium/C:H films prepared by DC unbalanced magnetron sputtering. Thin Solid. Film. 1999, 351, 151–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vilcarromero, J.; Marques, F.C. Hardness and elastic modulus of carbon–germanium alloys. Thin Solid. Film. 2001, 398–399, 275–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shinar, J.; Wu, H.S.; Shinar, R.; Shanks, H.R. An IR, optical, and electron-spin-resonance study of as-deposited and annealed a-Ge1−xCx:H prepared by rf sputtering in Ar/H2/C3H8. J. Appl. Phys. 1987, 62, 808–812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saito, N.; Nakaaki, I.; Yamaguchi, T.; Yoshioka, S.; Nakamura, S. Influence of deposition conditions on the properties of a-GeC:H and a-Ge:H films prepared by r.f. magnetron sputtering. Thin Solid. Film. 1995, 269, 69–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacobsohn, L.G.; Freire, F.L.; Mariotto, G. Investigation on the chemical, structural and mechanical properties of carbon-germanium films deposited by dc-magnetron sputtering. Diam. Relat. Mater. 1998, 7, 440–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vilcarromero, J.; Marques, F.C.; Freire, F.L. Optoelectronic and structural properties of a-Ge1−xCx:H prepared by rf reactive cosputtering. J. Appl. Phys. 1998, 84, 174–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mariotto, G.; Vinegoni, C.; Jacobsohn, L.G.; Freire, F.L. Raman spectroscopy and scanning electron microscopy investigation of annealed amorphous carbon–germanium films deposited by d.c. magnetron sputtering. Diam. Relat. Mater. 1999, 2–5, 668–672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maruyama, T.; Akagi, H. Thin Films of Amorphous Germanium-Carbon Alloy Prepared by Radio-Frequency Magnetron Sputtering. J. Electrochem. Soc. 1996, 143, 4087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumeda, M.; Masuda, A.; Shimizu, T. Structural Studies on Hydrogenated Amorphous Germanium-Carbon Films Prepared by RF Sputtering. Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. Part 1 1998, 37, 1754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.T.; Zhu, J.Z.; Xu, N.K.; Zheng, X.L. Structure and properties of germanium carbide films prepared by RF reactive sputtering in Ar/CH4. Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 1997, 36, 3625–3628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, C.Q.; Zheng, W.T.; Zheng, B.; Li, J.J.; Jin, Z.S.; Bai, X.M.; Tian, H.W.; Jiang, Q.; Wang, X.Y.; Zhu, J.Q.; et al. Chemical bonding of a-Ge1−xCx:H films grown by RF reactive sputtering. Vacuum 2004, 77, 63–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, H.; Williams, R.S. Synthesis by laser ablation and characterization of pure germanium-carbon alloy thin films. Chem. Mater. 1993, 5, 479–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, D.A.; Spear, W.E. Electrical and optical properties of amorphous silicon carbide, silicon nitride and germanium carbide prepared by the glow discharge technique. Philos. Mag. 1977, 35, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.; Kashyap, S.C.; Chopra, K.L. Structure and transport properties of amorphous Ge1−xCx:H thin films obtained by activated reactive evaporation. J. Non-Cryst. Solids 1988, 101, 287–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tyczkowski, J.; Kazimierski, P.; Szymanowski, H. Correlations between process parameters, chemical structure and electronic properties of amorphous hydrogenated GexC1−x films prepared by plasma-enhanced chemical vapour deposition in a three-electrode reactor. Thin Solid. Film. 1994, 241, 291–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gazicki, M.; Janowska, G. Thermal stability of semiconducting thin germanium/carbon alloy films produced from tetraethylgermanium in an RF glow discharge. Thin Solid. Films 1999, 352, 6–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Booth, D.C.; Voss, K.J. The optical and structural properties of CVD Germanium Carbide. Phys. Colloq. 1981, 42, C4-1033–C4-1036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gazicki, M. Plasma Deposition of Thin Carbon/Germanium Alloy Films from Organogermanium Compounds. Chaos Solitons Fractals 1999, 10, 1983–2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kazimierski, P.; Tyczkowski, J.; Kozanecki, M.; Hatanaka, Y.; Aoki, T. Transition from Amorphous Semiconductor to Amorphous Insulator in Hydrogenated Carbon−Germanium Films Investigated by Raman Spectroscopy. Chem. Mater. 2002, 14, 4694–4701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gazicki, M.; Ledzion, R.; Mazurczyk, R.; Pawlowski, S. Deposition and properties of germanium/carbon films deposited from tetramethylgermanium in a parallel plate RF discharge. Thin Solid. Film. 1998, 322, 123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kazimierski, P.; Tyczkowski, J. Deposition technology of a new nanostructured material for reversible charge storage. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2003, 174–175, 770–773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inagaki, N.; Mitsuuchi, M. Photoconductive films prepared by glow discharge polymerization. J. Polym. Sci. B Polym. Lett. Ed. 1984, 22, 301–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szmidt, J.; Gazicki-Lipman, M.; Szymanowski, H.; Mazurczyk, R.; Werbowy, A.; Kudła, A. Electrophysical properties of thin germanium/carbon layers produced on silicon using organometallic radio frequency plasma enhanced chemical vapor deposition process. Thin Solid. Films 2003, 441, 192–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadhir, R.K.; James, W.J.; Auerbach, R.A. Synthesis of Organogermanium films by Glow Discharge Polymerization. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 1984, 38, 99–104. [Google Scholar]
- Jamali, H.; Mozafarinia, R.; Eshaghi, A. The effect of carbon content on the phase structure of amorphous/nanocrystalline Ge1−xCx films prepared by PECVD. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2017, 310, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gazicki, M.; Szymanowski, H.; Tyczkowski, J.; Malinovský, L’.; Schalko, J.; Fallmann, W. Chemical bonding in thin Ge/C films deposited from tetraethylgermanium in an r.f. glow discharge-an FTIR study. Thin Solid. Film. 1995, 256, 1–2, 31–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, C.Z.; Zhu, J.Q.; Han, J.C.; Jia, Z.C.; Yin, X.B. Chemical bonding and optical properties of germanium–carbon alloy films prepared by magnetron co-sputtering as a function of substrate temperature. J. Non-Cryst. Solids 2011, 357, 3952–3956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, J.; Jiang, C.; Zhu, J. Non-hydrogenated amorphous germanium carbide with adjustable microstructure and properties: A potential anti-reflection and protective coating for infrared windows. Surf. Interface Anal. 2013, 45, 685–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.; Zou, Y.; Ren, D.; Lin, L.; Zhan, C. Components and performance of graded Ge1-xCx:H coatings deposited by magnetron co-sputtering for IR wideband antireflection. Optik 2020, 206, 163366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, C.; Qiao, L.; Tian, H.; Lu, X.; Jiang, Q.; Zheng, W. Role of carbon in the formation of hard Ge1−xCx thin films by reactive magnetron sputtering. Phys. B Condens. Matter 2011, 406, 2658–2662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, P.; Liu, H.; Cheng, J.; Liu, D.; Leng, J.; Ji, Y. Germanium carbon (Ge1-xCx)/diamond-like carbon (DLC) antireflective and protective coating on zinc sulfide window. Opt. Mater. 2022, 124, 111984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Zhang, W.; Yan, L.; Luo, R. The deposition and optical properties of Ge1-xCx thin film and infrared multilayer antireflection coatings. Thin Solid. Film. 2008, 516, 3189–3195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, C.; Zhu, J.; Han, J.; Cao, W. The surface topography, structural and mechanical properties of Ge1−xCx films prepared by magnetron co-sputtering. J. Non-Cryst. Solids 2014, 383, 126–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.Q.; Jiang, C.Z.; Han, X.; Han, J.C.; Meng, S.H.; Hu, C.Q.; Zheng, W.T. Multilayer antireflective and protective coatings comprising amorphous diamond and amorphous hydrogenated germanium carbide for ZnS optical elements. Thin Solid. Film. 2008, 516, 3117–3122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, K.; Jin, Y.; Shang, P.; Liu, Y.; He, K.; Xu, B.; Zhao, H.; Chen, W.; Zu, C. The effect of Ge content on the structure and properties of low temperature deposited infrared Ge100-xCx films on As40Se60 chalcogenide glass. Optik 2020, 224, 165413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, P.; Hu, M.; Zhang, F.; Ji, Y.-Q.; Liu, H.-S.; Liu, D.-D.; Leng, J.; Yang, M.; Li, Y. The infrared optical and mechanical properties of germanium carbide films prepared by ion beam sputtering. J. Infrared Millim. Waves 2016, 35, 133–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, K.; Jin, Y.; Zu, C.; He, K.; Xu, B.; Zhao, H.; Liu, Y.; Chen, W. The structure and properties of low temperature deposited durable infrared Ge1-xCx films on As40Se60 chalcogenide glass. J. Non-Cryst. Solids 2019, 519, 119453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jamali, H.; Mozafarinia, R.; Eshaghi, A. Effect of deposition parameters on the microstructure and deposition rate of germanium-carbon coatings prepared by plasma enhanced chemical vapor deposition. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2016, 302, 07–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jamali, H.; Mozafarinia, R.; Eshaghi, A. Evaluation of chemical and structural properties of germanium-carbon coatings deposited by plasma enhanced chemical vapor deposition. J. Alloys Compd. 2015, 646, 360–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sousani, F.; Jamali, H.; Mozafarinia, R.; Eshaghi, A. Thermal stability of germanium-carbon coatings prepared by a RF plasma enhanced chemical vapor deposition method. Infrared Phys. Techn. 2018, 93, 255–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jamali, H.; Mozaffarinia, R.; Eshaghi, A.; Ghasemi, A.; Tavoosi, M.; Gordani, G.R.; Rezazadeh, M.; Ahmadi-Pidani, R.; Torkian, S.; Mohammad Sharifi, E.; et al. Evaluating the Ge:C ratio on the bonding structure, hardness, and residual stress of Ge1-x-Cx coatings fabricated by the PE-CVD method. Vacuum 2024, 220, 112827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernández, M.P.; Farías, M.H.; Castillón, F.F.; Díaz, J.A.; Avalos, M.; Ulloa, L.; Gallegos, J.A.; Yee-Madeiros, H. Growth and characterization of polycrystalline Ge1−xCx by reactive pulsed laser deposition. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2011, 257, 5007–5011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saito, N.; Iwata, H.; Nakaaki, I.; Nishioka, K. Amorphous and microcrystalline GeC:H films prepared by magnetron sputtering. Phys. Status Solidi (A) 2009, 206, 238–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.Q.; Jiang, C.Z.; Han, J.C.; Yu, H.L.; Wang, J.Z.; Jia, Z.C.; Chen, R.R. Optical and electrical properties of nonstoichiometric a-Ge1−xCx films prepared by magnetron co-sputtering. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2012, 258, 3877–3881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shrestha, S.; Gupta, N.; Aliberti, P.; Conibeer, G. Growth and characterization of germanium carbide films for hot carrier solar cell absorber. In Proceedings of the 38th IEEE Photovoltaic Specialists Conference, Austin, TX, USA, 3–8 June 2012; pp. 002601–002604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, N.; Veettill, B.P.; Conibeer, G.; Shrestha, S. Effect of substrate temperature and radio frequency power on compositional, structural and optical properties of amorphous germanium carbide films deposited using sputtering. J. Non-Cryst. Solids 2016, 443, 97–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Broderick, C.A.; Dunne, M.D.; Tanner, S.P.; O’Reilly, E.P. Electronic structure evolution in dilute carbide Ge1−xCx alloys and implications for device applications. J. Appl. Phys. 2019, 126, 195702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stephenson, C.A.; O’Brien, W.A.; Penninger, M.W.; Schneider, W.F.; Gillett-Kunnath, M.; Zajicek, J.; Yu, K.M.; Kudrawiec, R.; Stillwell, R.A.; Wistey, M.A. Band structure of germanium carbides for direct bandgap silicon photonics. J. Appl. Phys. 2016, 120, 053102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Vrijer, T.; van Dingen, J.E.C.; Roelandschap, P.J.; Roodenburg, K.; Smets, A.H.M. Improved PECVD processed hydrogenated germanium films through temperature induced densification. Mat. Sci. Semicond. Proc. 2022, 138, 106285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Zhang, W.; Luo, R.; Yan, Y. Mechanical and environmental properties of Ge1−xCx thin film. Vacuum 2008, 82, 448–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jamali, H.; Mozafarinia, R.; Sousani, F.; Eshaghi, A. The growth mechanism of Ge1−x-Cx:H films deposited by PECVD method. Diam. Relat. Mat. 2020, 103, 107709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, C.Q.; Zhu, J.Q.; Zheng, W.T.; Han, J.C. Annealing effects on the bonding structures, optical and mechanical properties for radio frequency reactive sputtered germanium carbide films. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2009, 255, 3552–3557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaiser, R.J.; Koffel, S.; Pichler, P.; Bauer, A.J.; Amon, B.; Frey, L.; Ryssel, H. Germanium substrate loss during thermal processing. Microelectron. Eng. 2011, 88, 499–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benzi, P.; Castiglioni, M.; Truffa, E.; Volpe, P. Thin film deposition of GexCyHz by radiolysis of GeH4-C3H8 mixtures. J. Mater. Chem. 1996, 6, 1507–1509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benzi, P.; Castiglioni, M.; Truffa, E.; Volpe, P. Characterisation and properties of amorphous non stoichiometric Ge1-x-Cx:H compounds obtained from X-ray radiolysis of germane/ethylene mixtures. Eur. J. Inorg. Chem. 2001, 1235–1242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benzi, P.; Bottizzo, E.; Operti, L.; Volpe, P. Characterisation and properties of amorphous non stoichiometric Ge1-x-Cx:H compounds obtained by Radiolysis-CVD of Germane/Ethyne Systems. Chem. Mater. 2004, 16, 1068–1074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benzi, P.; Bottizzo, E.; Operti, L.; Rabezzana, R.; Vaglio, G.A.; Volpe, P. Amorpous germanium carbides by radiolysis. CVD of germane/ethyne systems: Preparation and reaction mechanisms. Chem. Mater. 2002, 14, 2506–2513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benzi, P.; Bottizzo, E.; Demaria, C. Characterization and properties of Ge1-x-Cx:H compounds obtained by X-Ray Chemical Vapor Deposition of Germane/Ethyne Systems: Effect of the irradiation dose. Chem. Vap. Dep. 2006, 12, 25–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benzi, P.; Bottizzo, E.; Demaria, C.; Infante, G.; Iucci, G.; Polzonetti, G. Amorphous nonstoichiometric Ge1−x–Cx:H compounds obtained by radiolysis-chemical vapor deposition of germane/ethyne or germane/allene systems: A bonding and microstructure investigation performed by x-ray photoelectron spectroscopy and Raman spectroscopy. J. Appl. Phys. 2007, 101, 124906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demaria, C.; Benzi, P.; Arrais, A.; Bottizzo, E.; Antoniotti, P.; Rabezzana, R.; Operti, L. Growth and thermal annealing of amorphous germanium carbide obtained by X-ray chemical vapor deposition. J. Mat. Sci. 2013, 48, 6357–6366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antoniotti, P.; Benzi, P.; Castiglioni, M.; Operti, L.; Volpe, P. Studies on the solid obtained from radiolysis of germane/methane mixtures. Chem. Mater. 1992, 4, 717–720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- CRC Handbook of Chemistry and Physics, 78th ed.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 1997.
- Rübel, H.; Schröder, B.; Fuhs, W.; Krauskopf, J.; Rupp, T.; Bethge, K. IR Spectroscopy and Structure of RF Magnetron Sputtered a-SiC:H Films. Phys. Stat. Sol. 1987, 139, 131–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cardona, M. Vibrational spectra of hydrogen in silicon and germanium. Phys. Stat. Sol. 1983, 118, 463–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bellamy, L.J. The Infrared Spectra of Complex Molecules, 3rd ed.; Chapman and Hall: London, UK, 1975; pp. 13–36. [Google Scholar]
- Schrader, B. Infrared and Raman Spectroscopy; VCH: Weinheim, Germany, 1995; pp. 192–195. [Google Scholar]
- Luo, Y.R. Handbook of Bond Dissociation Energies in Organic Compounds; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Vilcarromero, J.; Marques, F.C. Hydrogen in amorphous germanium-carbon. Thin Solid. Film. 1999, 343–344, 445–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taga, K.; Hamada, S.; Fukui, H.; Yoshida, H.; Ohno, K.; Matsuura, H. Vibrational spectra and density functional study of propylgermane. J. Mol. Struct. 2002, 610, 85–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vilcarromero, J.; Marques, F.C.; Andreu, J. Bonding properties of rf-co-sputtering amorphous Ge–C films studied by X-ray photoelectron and Raman spectroscopies. J. Non-Cryst. Solids 1998, 227–230, 427–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morimoto, A.; Kataoka, T.; Kumeda, M.; Shimizu, T. Annealing and crystallization processes in tetrahedrally bonded binary amorphous semiconductors. Philos. Mag. B 1984, 50, 517–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lannin, J.S.; Maley, N.; Kshirsagar, S.T. Raman scattering and short range order in amorphous germanium. Solid. State Commun. 1985, 53, 939–942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Theye, M.L.; Paret, V. Spatial organization of the sp2-hybridized carbon atoms and electronic density of states of hydrogenated amorphous carbon films. Carbon 2002, 40, 1153–1166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chambouleyron, I.; Fajardo, F.; Zanatta, A.R. Microscopic mechanisms behind the Al-induced crystallization of a-Ge:H films. J. Non-Cryst. Solids 2002, 299–302, 145–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muniz, L.R.; Ribeiro, C.T.M.; Zanatta, A.R.; Chambouleyron, I. Aluminium-induced nanocrystalline Ge formation at low temperatures. J. Phys. Condens. Matter 2007, 19, 076206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, J.R.; Shi, X.; Sun, Z.; Lau, S.P.; Tay, B.K.; Tan, H.S. Resonant Raman studies of tetrahedral amorphous carbon films. Diam. Relat. Mater. 2001, 10, 76–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adamopoulos, G.; Gilkes, K.W.R.; Robertson, J.; Conway, N.M.J.; Kleinsorge, B.Y.; Buckley, A.; Batchelder, D.N. Ultraviolet Raman characterisation of diamond-like carbon films. Diam. Relat. Mater. 1999, 8, 541–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, Y.S.; Myung, H.S.; Han, J.G.; Hong, B. The electrical and structural properties of the hydrogenated amorphous carbon films grown by close field unbalanced magnetron sputtering. Thin Solid. Film. 2005, 482, 275–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrari, A.C. Determination of bonding in diamond-like carbon by Raman spectroscopy. Diam. Relat. Mater. 2002, 11, 1053–1061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guha, S.; Wall, M.; Chase, L.L. Growth and characterization of Ge nanocrystals. Nucl. Instrum. Methods Phys. Res. B 1999, 147, 367–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reynolds, S.; Carius, R.; Finger, F.; Smirnov, V. Correlation of structural and optoelectronic properties of thin film silicon prepared at the transition from microcrystalline to amorphous growth. Thin Solid. Film. 2009, 517, 6392–6395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jie, Y.X.; Wee, A.T.S.; Huan, C.H.A.; Sun, W.X.; Shen, Z.X.; Chua, S.J. Raman and photoluminescence properties of Ge nanocrystals in silicon oxide matrix. Mater. Sci. Eng. B 2004, 107, 8–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Z.; Chen, X. Raman spectra of coal-based graphite. Sci. China 1995, 38, 97–106. [Google Scholar]
- Chu, P.K.; Li, L. Characterization of amorphous and nanocrystalline carbon films. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2006, 96, 253–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arrais, A.; Benzi, P.; Bottizzo, E.; Demaria, C. Correlations among hydrogen bonding configuration, structural order and optical coefficients in hydrogenated amorphous germanium obtained by x-ray-activated chemical vapour deposition. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 2009, 42, 105406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knauber, B.J.; Eslamisaray, M.A.; Kakalios, J. Conductance fluctuations in hydrogenated amorphous germanium. J. Appl. Phys. 2021, 130, 105107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goriparti, S.; Miele, E.; Scarpellini, A.; Marras, S.; Prato, M.; Ansaldo, A.; DeAngelis, F.; Manna, L.; Zaccaria, R.P.; Capiglia, C. Germanium Nanocrystals-MWCNTs Composites as Anode Materials for Lithium Ion Batteries. ECS Trans. 2014, 62, 19–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patterson, A.L. The Scherrer Formula for X-Ray Particle Size Determination. Phys. Rev. 1939, 56, 978–982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ley, L. The Physics of Hydrogenated Amorphous Silicon II; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 1984; p. 61. [Google Scholar]
- Tauc, J. Amorphous and Liquid Semiconductors; Plenum Press: London, UK; New York, NY, USA, 1974; p. 159. [Google Scholar]
- Mott, N.F.; Davis, E.A. Electronic Processes in Non-Crystalline Materials, 2nd ed.; Clarendon Press: Oxford, UK, 1979; pp. 287–318. [Google Scholar]
- Masuda, A.; Kumeda, M.; Shimizu, T. Relationship between photodarkening and light-induced ESR in amorphous Ge-S films alloyed with lead. Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 1991, 30, L1075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
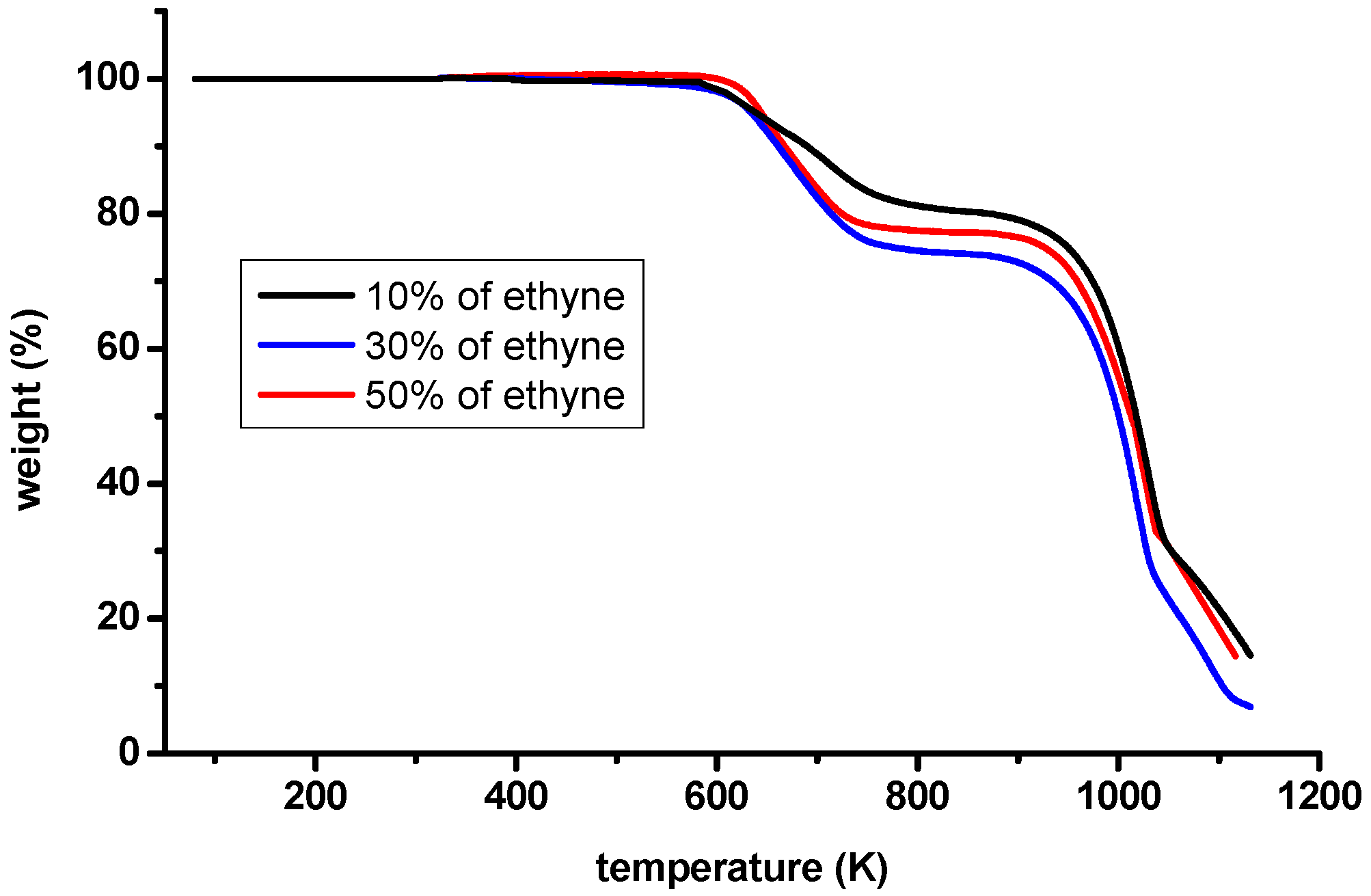
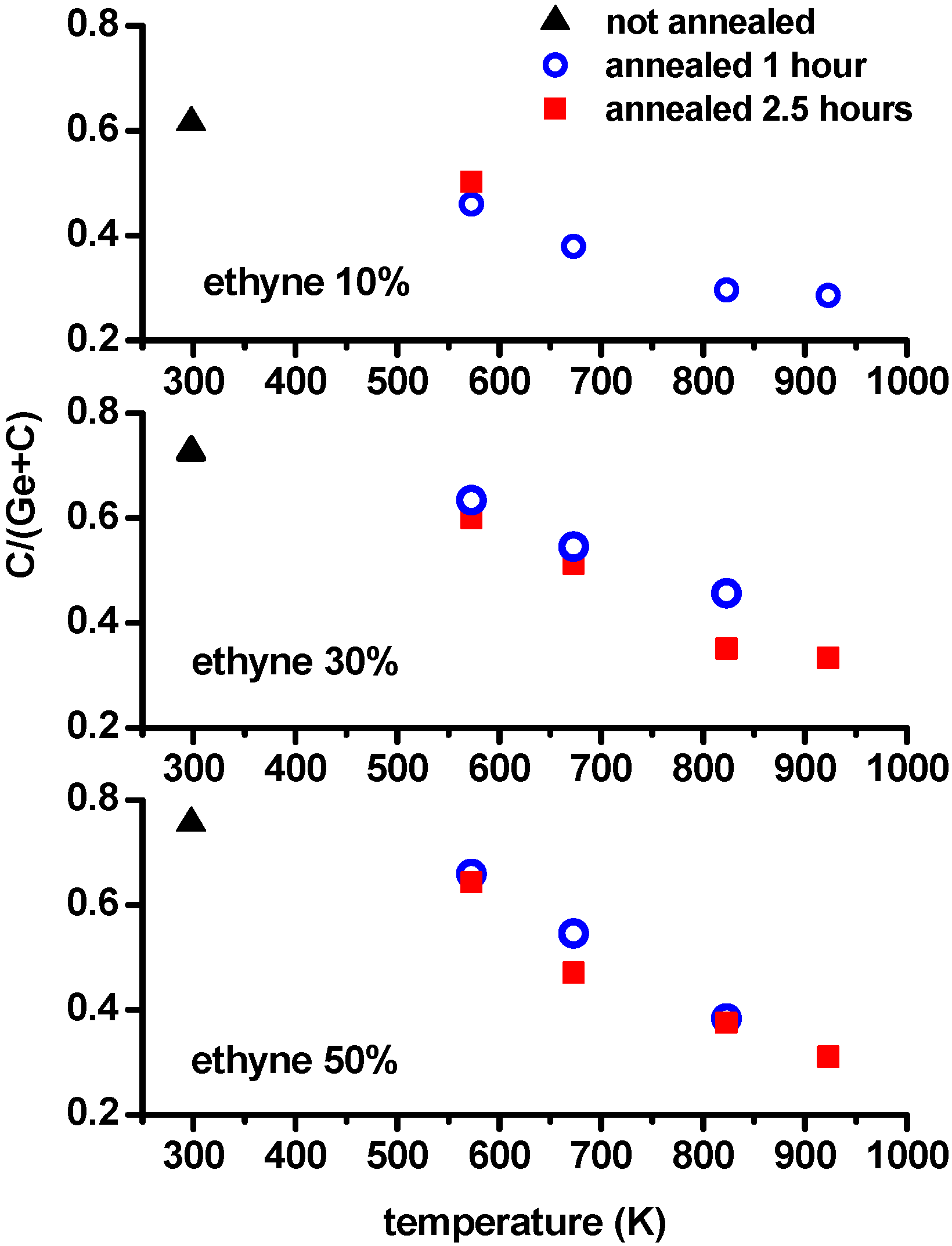
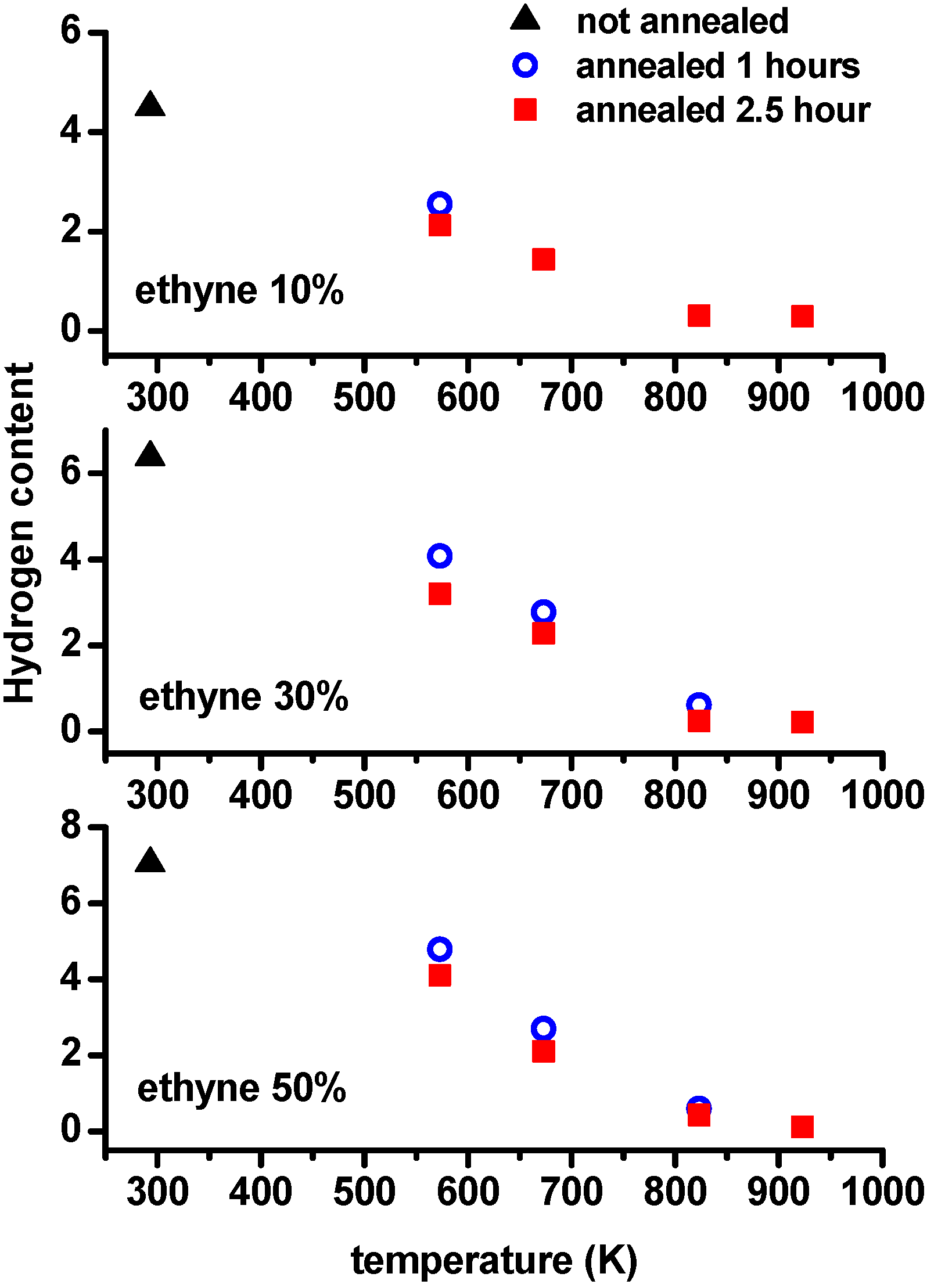
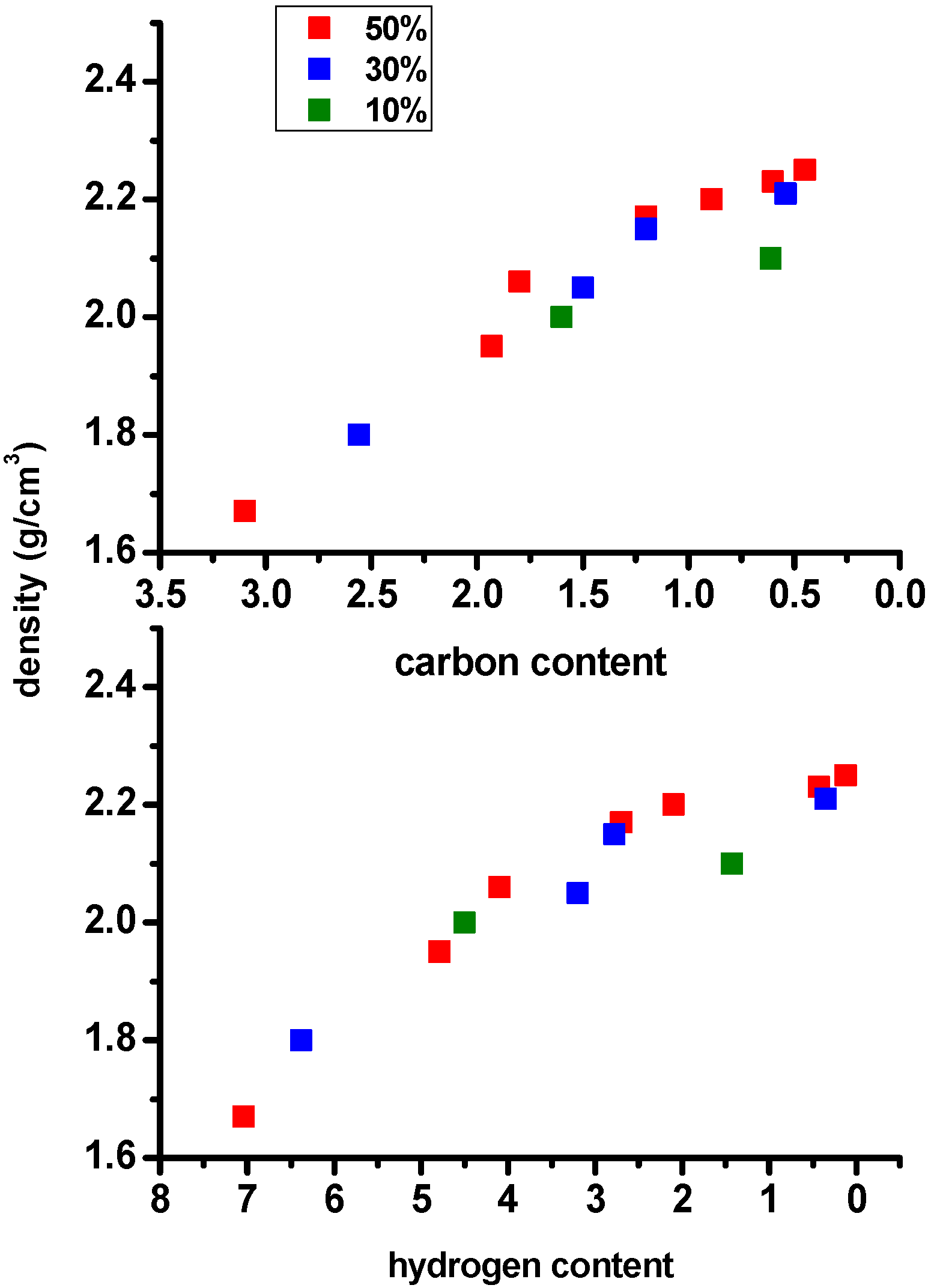

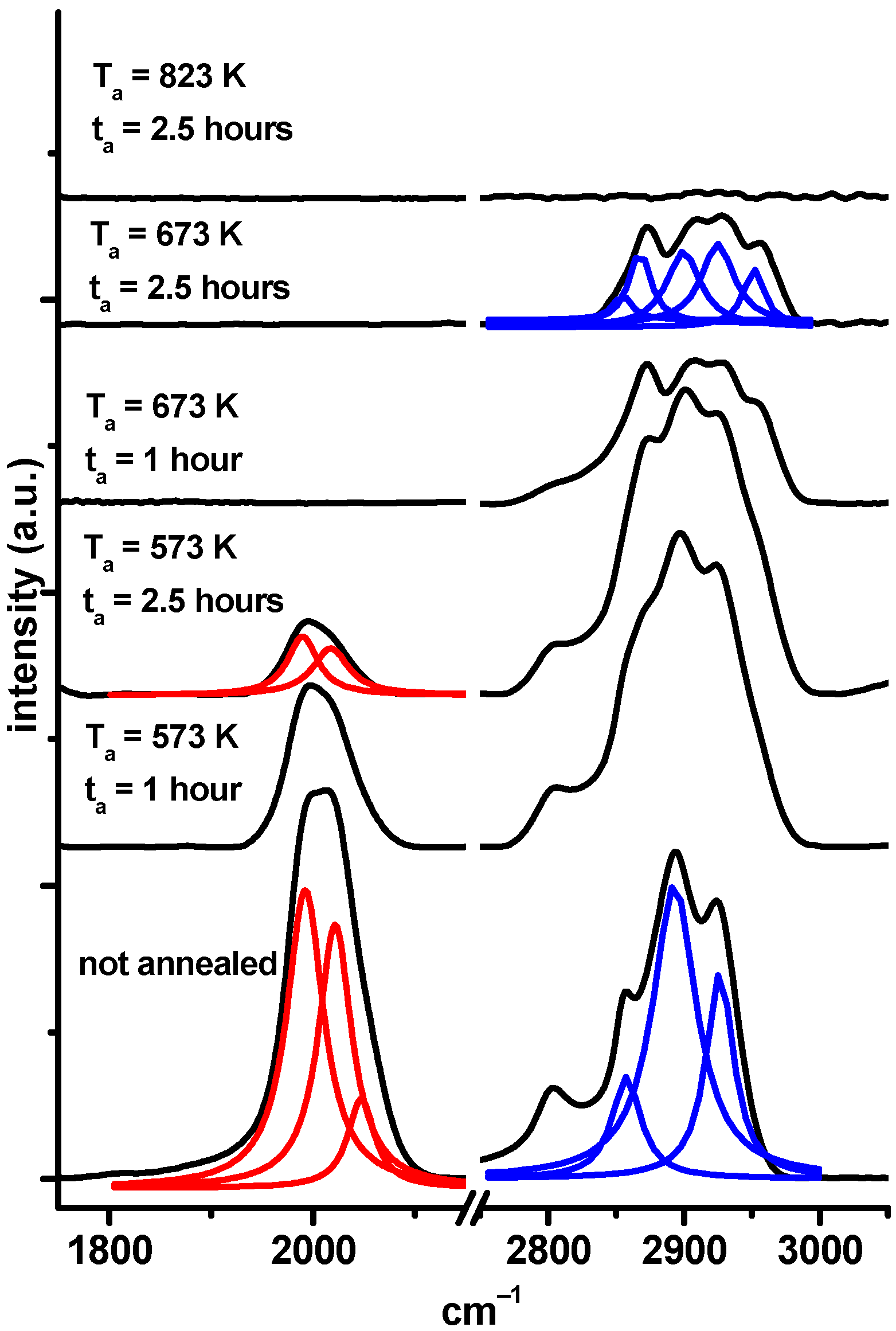

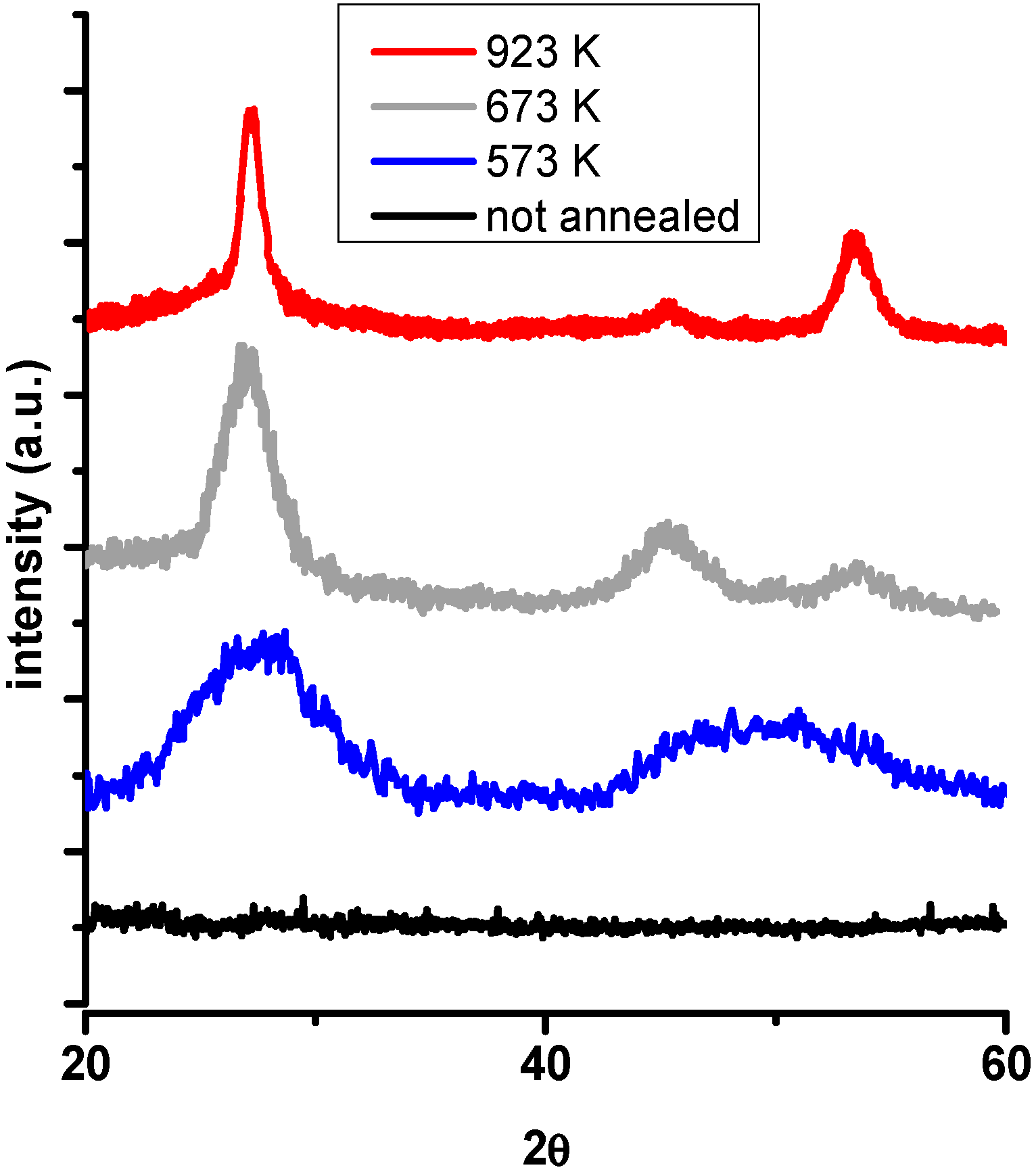


| Gas Mixture C2H2 Percentage | Series Sample Name | Temperature (K) and Time (Hours) | Solid Products Empirical Formula a |
|---|---|---|---|
| not annealed | GeC1.60H4.50 | ||
| 573—1 h | GeC1.01H2.55 | ||
| 10% | Ac10 | 573—2.5 h | GeC0.85H2.12 |
| 673—2.5 h | GeC0.61H1.43 | ||
| 823—2.5 h | GeC0.42H0.30 | ||
| 923—2.5 h | GeC0.40H0.29 | ||
| not annealed | GeC2.65H6.38 | ||
| 573—1 h | GeC1.73H4.08 | ||
| 573—2.5 h | GeC1.50H3.20 | ||
| 30% | Ac30 | 673—1 h | GeC1.20H2.78 |
| 673—2.5 h | GeC1.05H2.28 | ||
| 823—1 h | GeC0.84H0.62 | ||
| 823—2.5 h | GeC0.54H0.35 | ||
| 923—2.5 h | GeC0.50H0.22 | ||
| not annealed | GeC3.10H7.05 | ||
| 573—1 h | GeC1.93H4.79 | ||
| 573—2.5 h | GeC1.80H4.10 | ||
| 50% | Ac50 | 673—1 h | GeC1.20H2.70 |
| 673—2.5 h | GeC0.89H2.10 | ||
| 823—1 h | GeC0.62H0.60 | ||
| 823—2.5 h | GeC0.60H0.43 | ||
| 923—2.5 h | GeC0.45H0.12 |
| C2H2 Percentage | Temperature (K) and Time (Hours) | Eopt | B1/2 |
|---|---|---|---|
| not annealed | 2.00 | 110.4 | |
| 573—1 h | 1.31 | 57.7 | |
| 10% | 573—2.5 h | 1.16 | 89.9 |
| 673—2.5 h | 0.94 | 130.0 | |
| 823—2.5 h | 0.66 | 107.5 | |
| 923—2.5 h | |||
| not annealed | 2.89 | 73.0 | |
| 573—1 h | 2.46 | 49.7 | |
| 573—2.5 h | 2.20 | 73.8 | |
| 30% | 673—1 h | 1.50 | 82.7 |
| 673—2.5 h | 0.88 | 64.6 | |
| 823—1 h | 50.5 | ||
| 823—2.5 h | 0.87 | ||
| not annealed | 3.5 | 107.0 | |
| 573—1 h | 2.7 | 91.0 | |
| 573—2.5 h | 2.3 | 73.0 | |
| 50% | 673—1 h | 1.11 | 89.2 |
| 673—2.5 h | 1.02 | 70.0 | |
| 823—1 h | 0.76 | 60.0 | |
| 823—2.5 h | 44.3 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Marabello, D.; Cioci, A.; Sgroi, M.; Benzi, P. Annealing-Driven Structural and Optical Evolution of Amorphous Ge–C:H Alloys. Processes 2025, 13, 3457. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr13113457
Marabello D, Cioci A, Sgroi M, Benzi P. Annealing-Driven Structural and Optical Evolution of Amorphous Ge–C:H Alloys. Processes. 2025; 13(11):3457. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr13113457
Chicago/Turabian StyleMarabello, Domenica, Alma Cioci, Mauro Sgroi, and Paola Benzi. 2025. "Annealing-Driven Structural and Optical Evolution of Amorphous Ge–C:H Alloys" Processes 13, no. 11: 3457. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr13113457
APA StyleMarabello, D., Cioci, A., Sgroi, M., & Benzi, P. (2025). Annealing-Driven Structural and Optical Evolution of Amorphous Ge–C:H Alloys. Processes, 13(11), 3457. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr13113457







