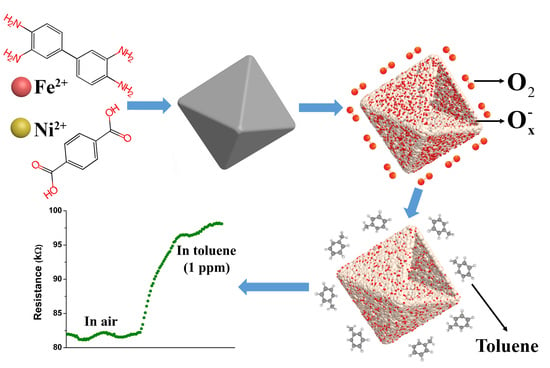
MOFs-Derived Porous NiFe2O4 Nano-Octahedrons with Hollow Interiors for an Excellent Toluene Gas Sensor
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
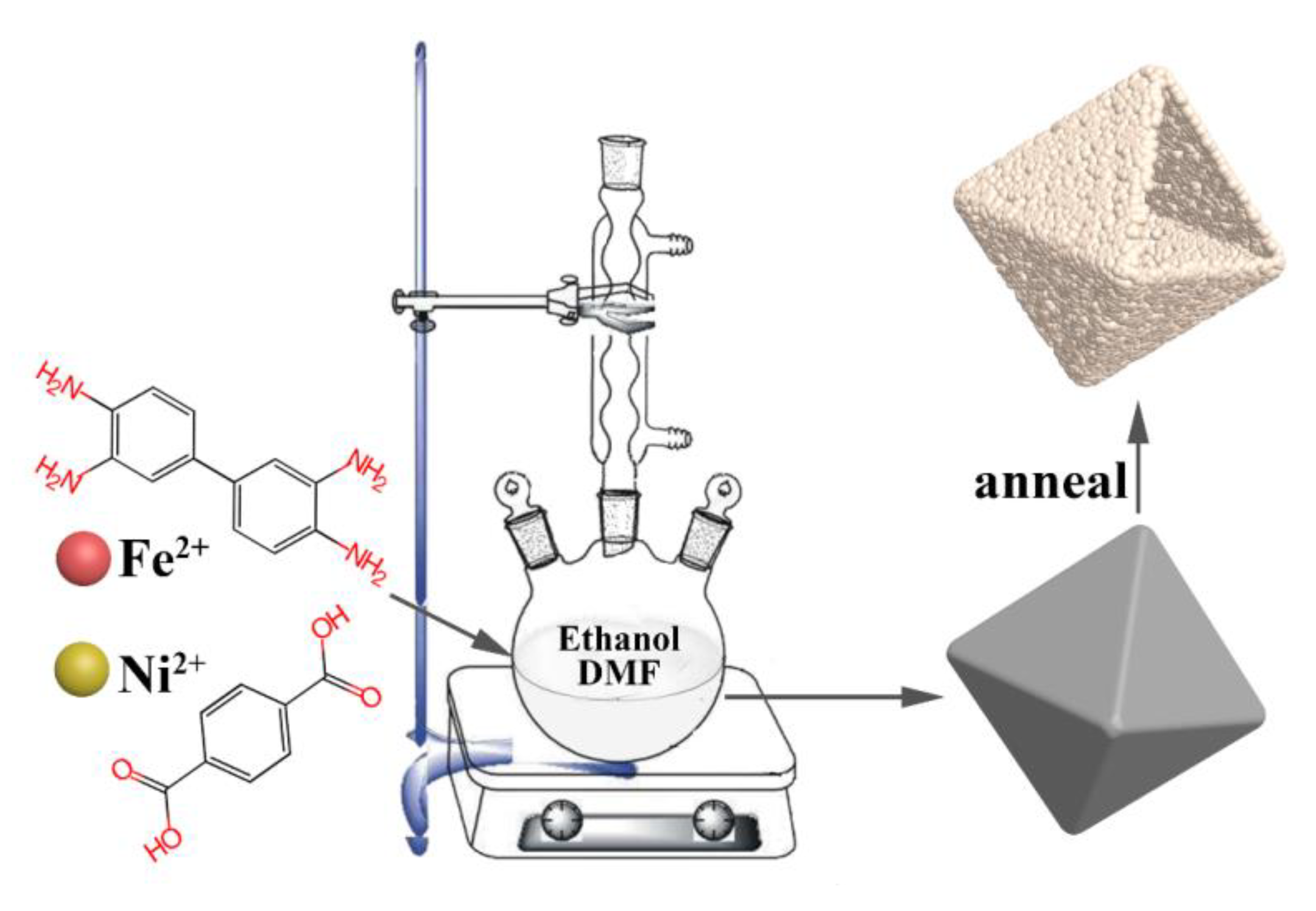
2.1. Materials Synthesis
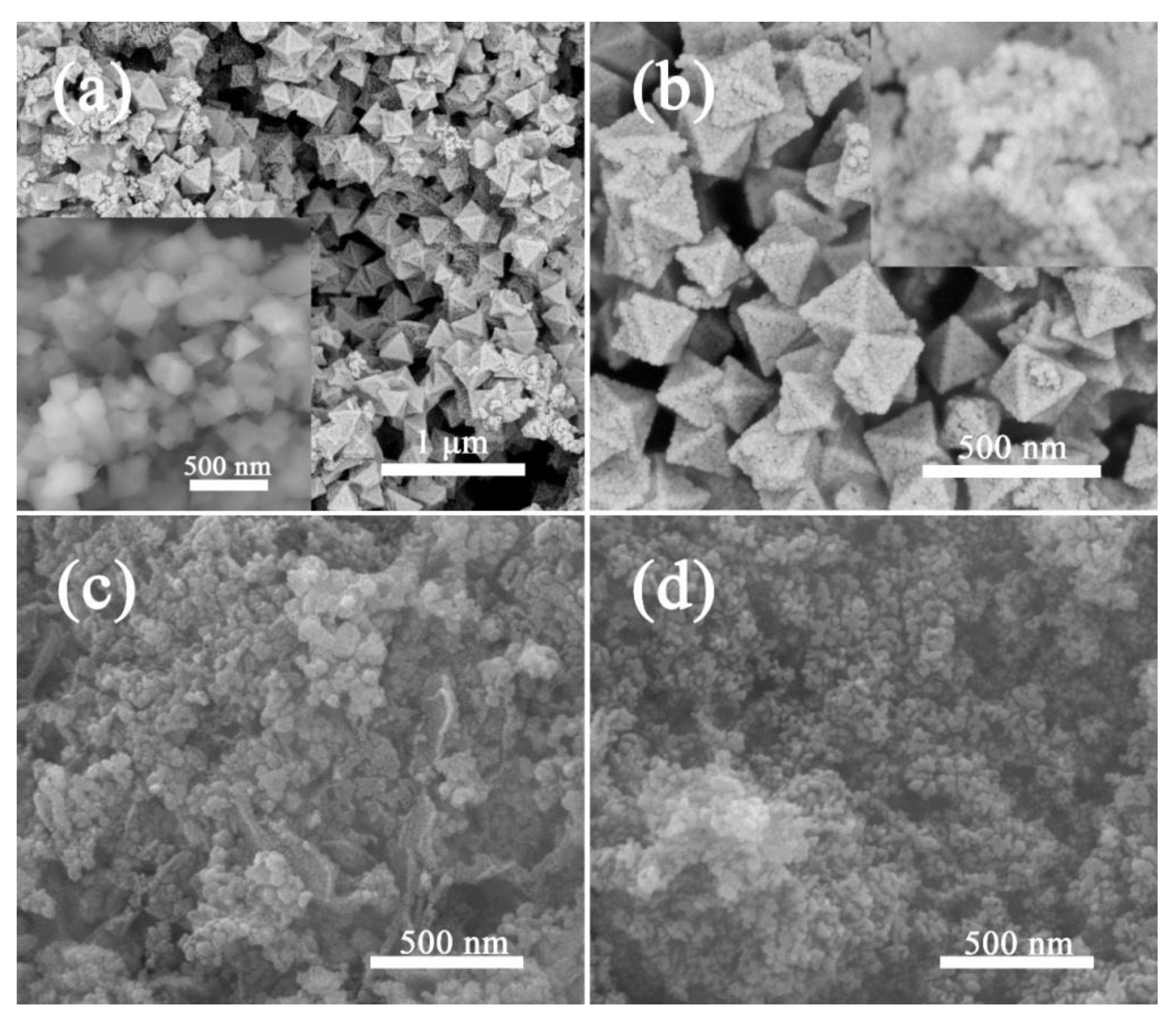
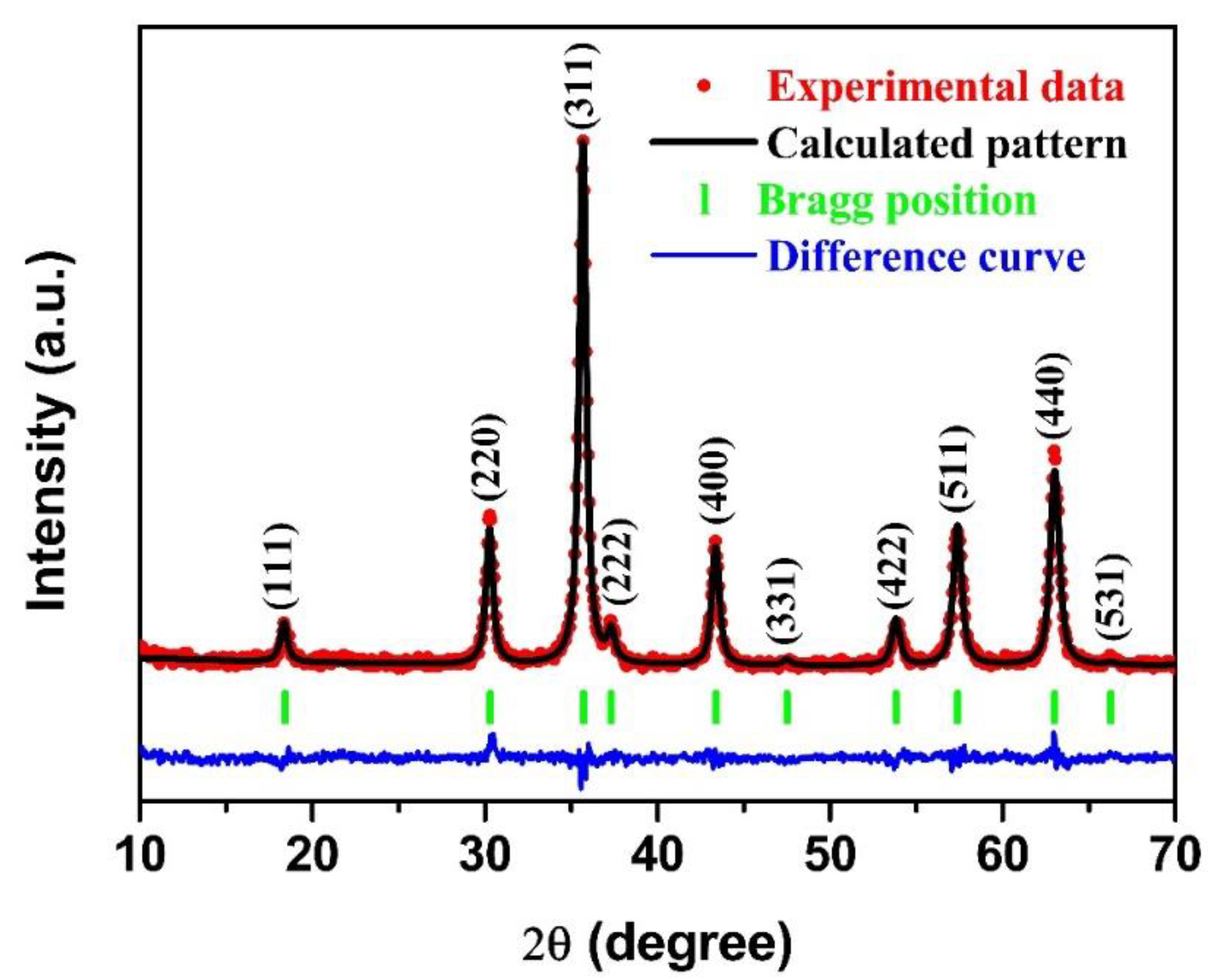
2.2. Materials Characterization
2.3. Fabrication and Measurement of the Gas Sensor
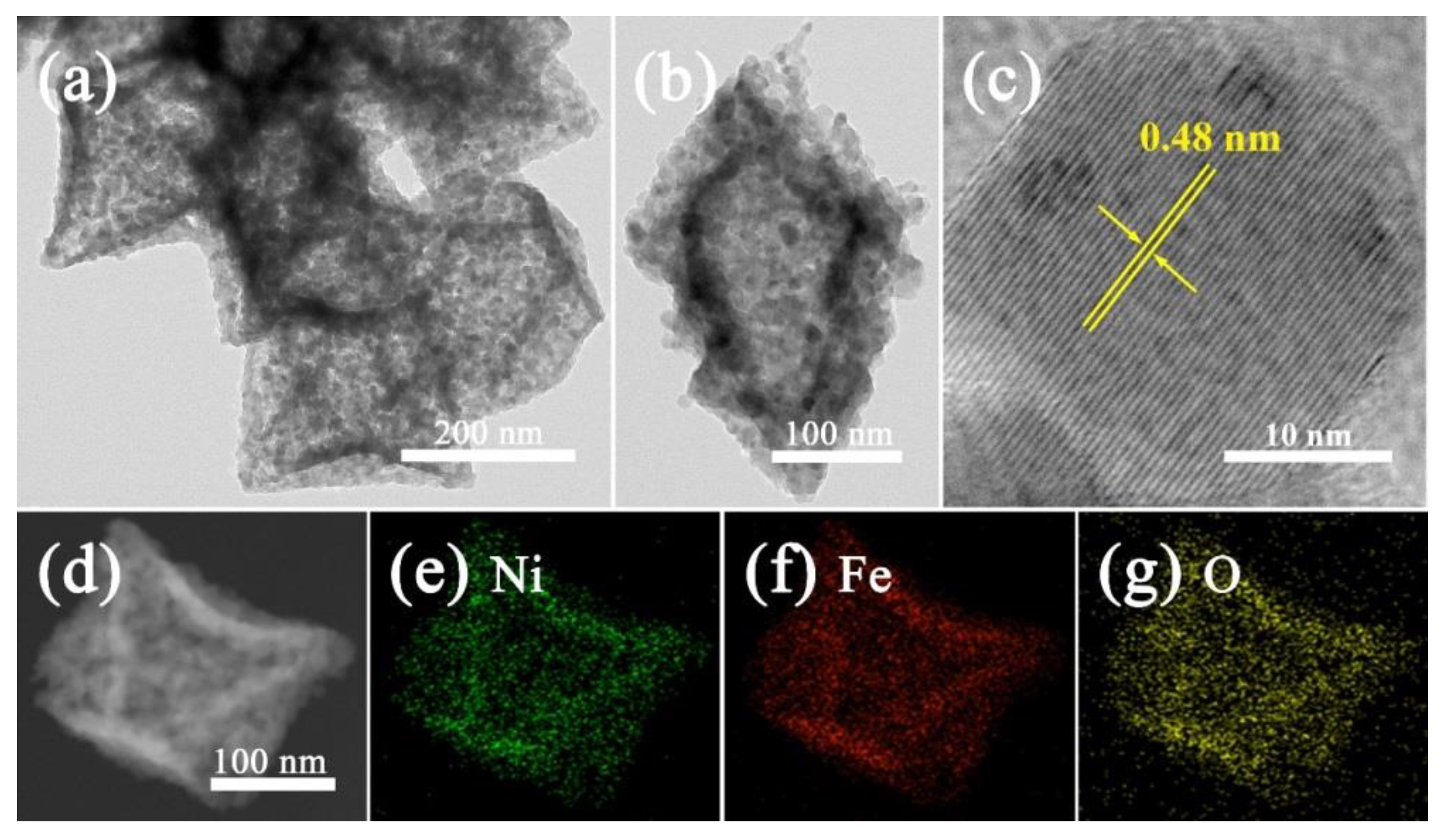
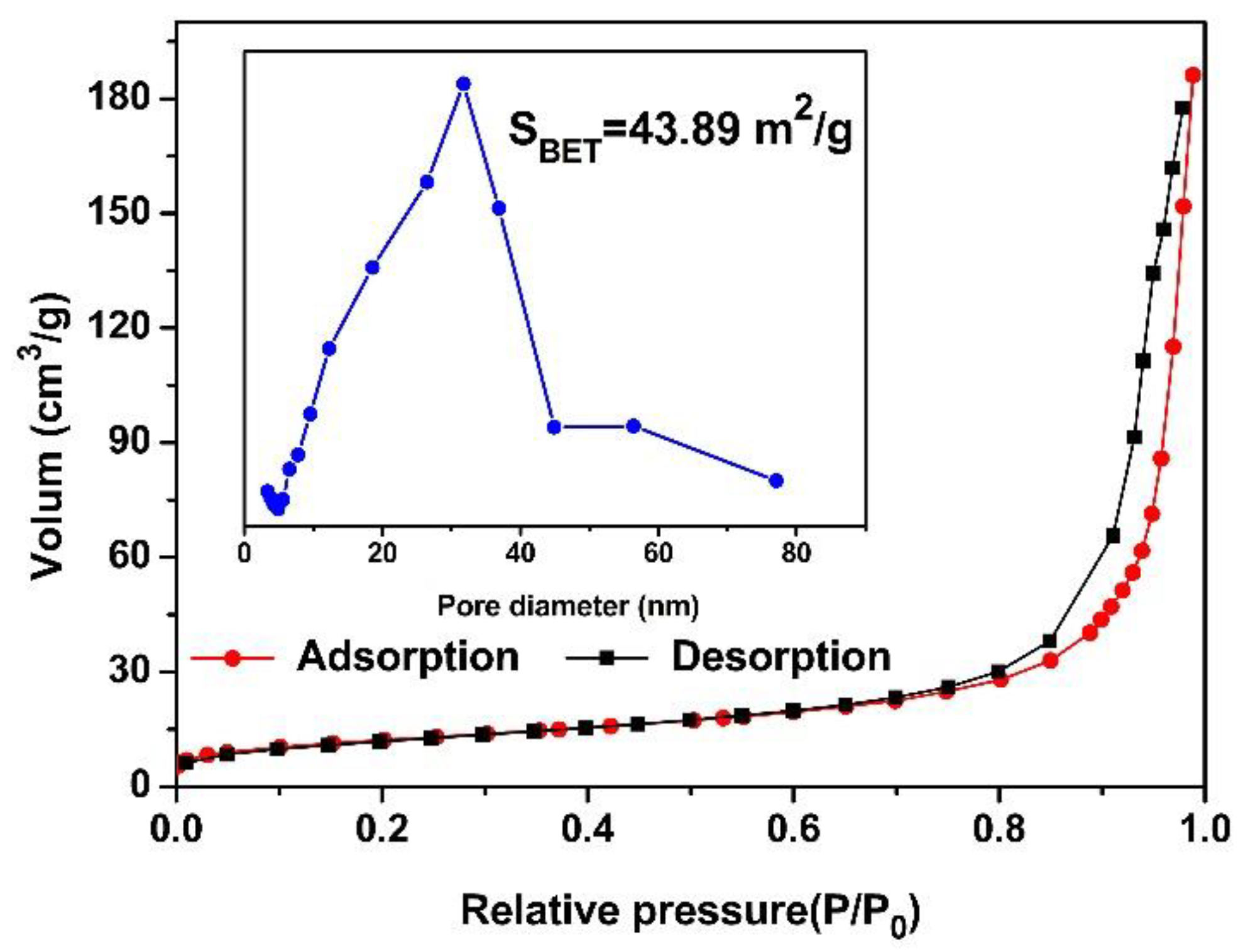
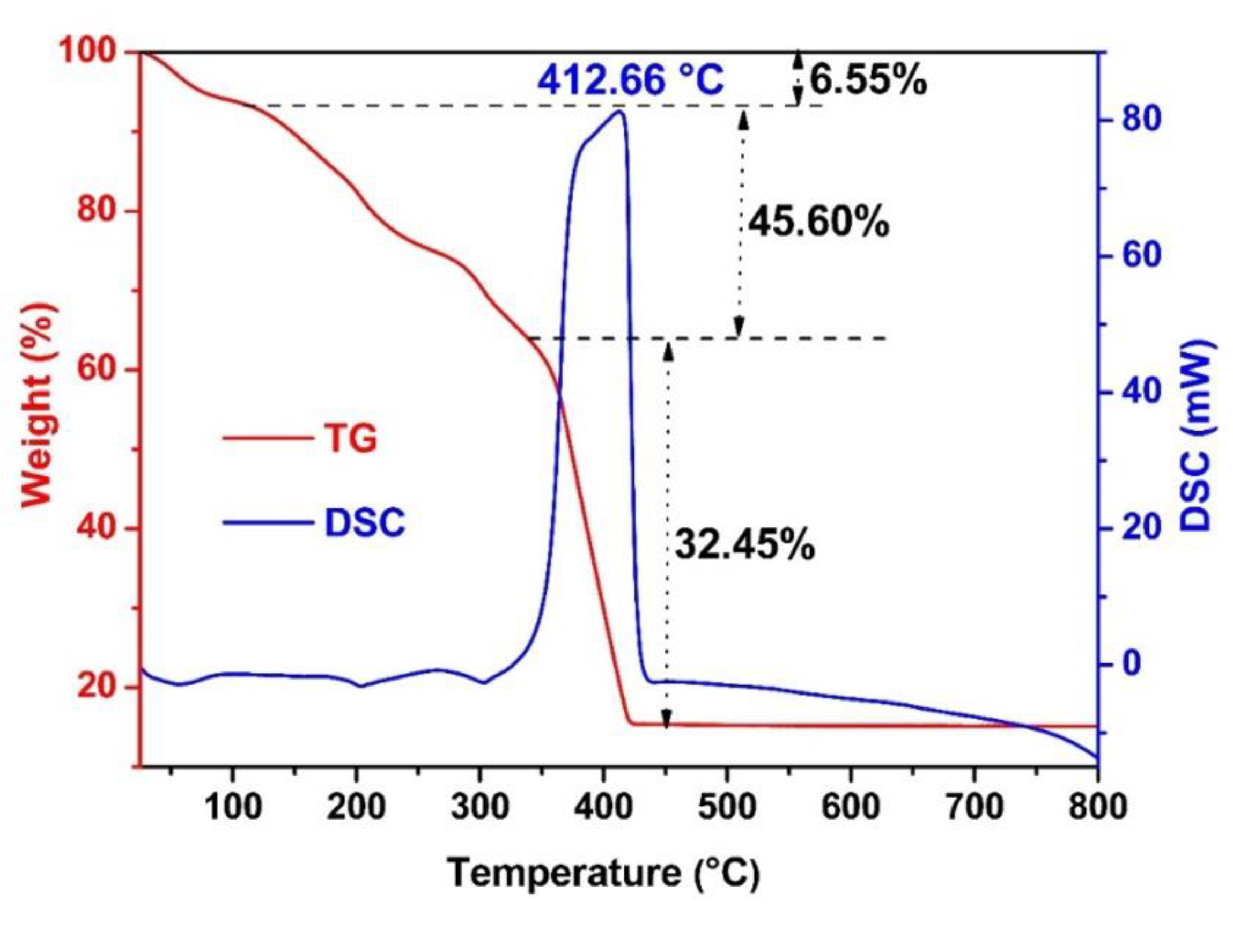
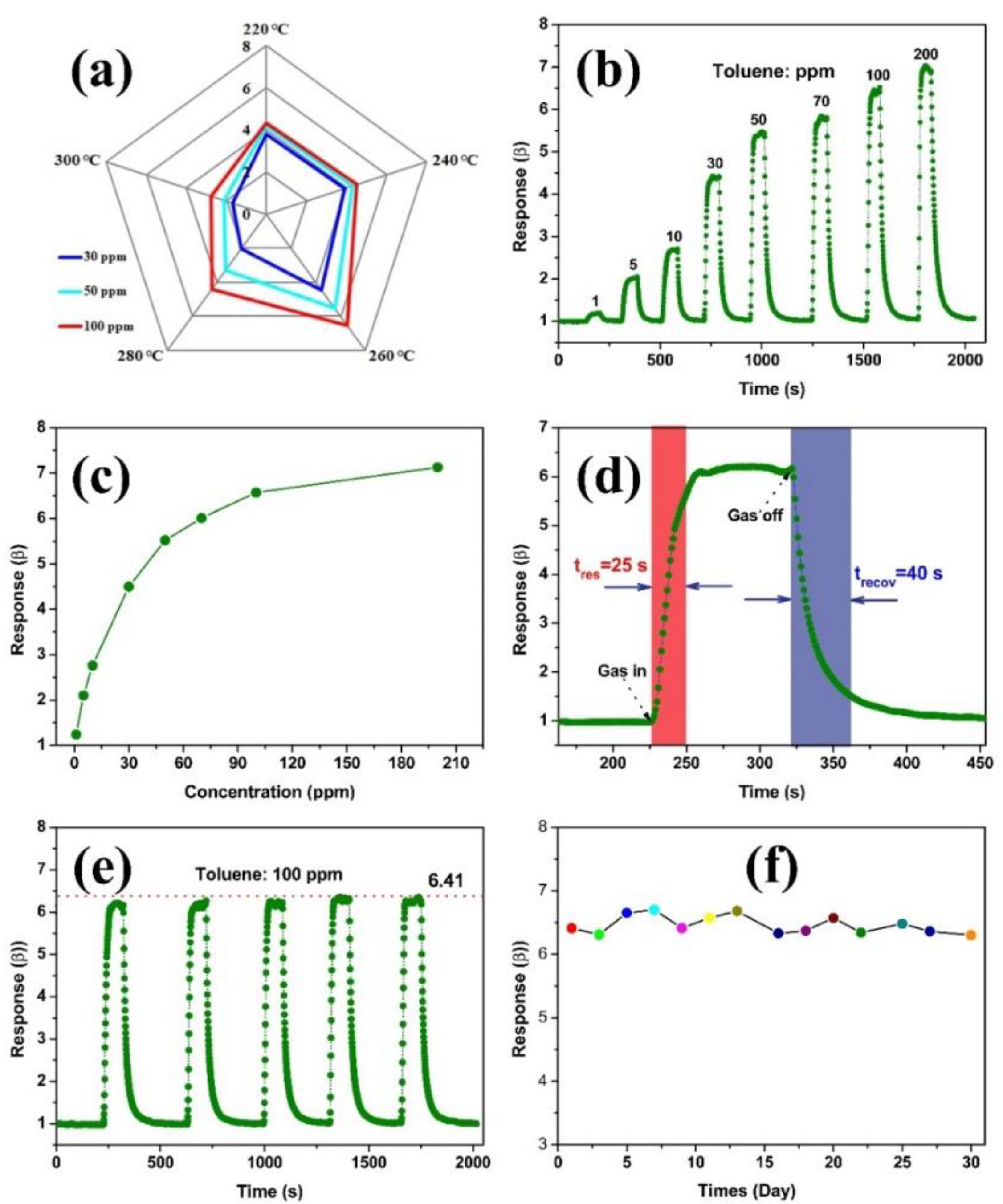
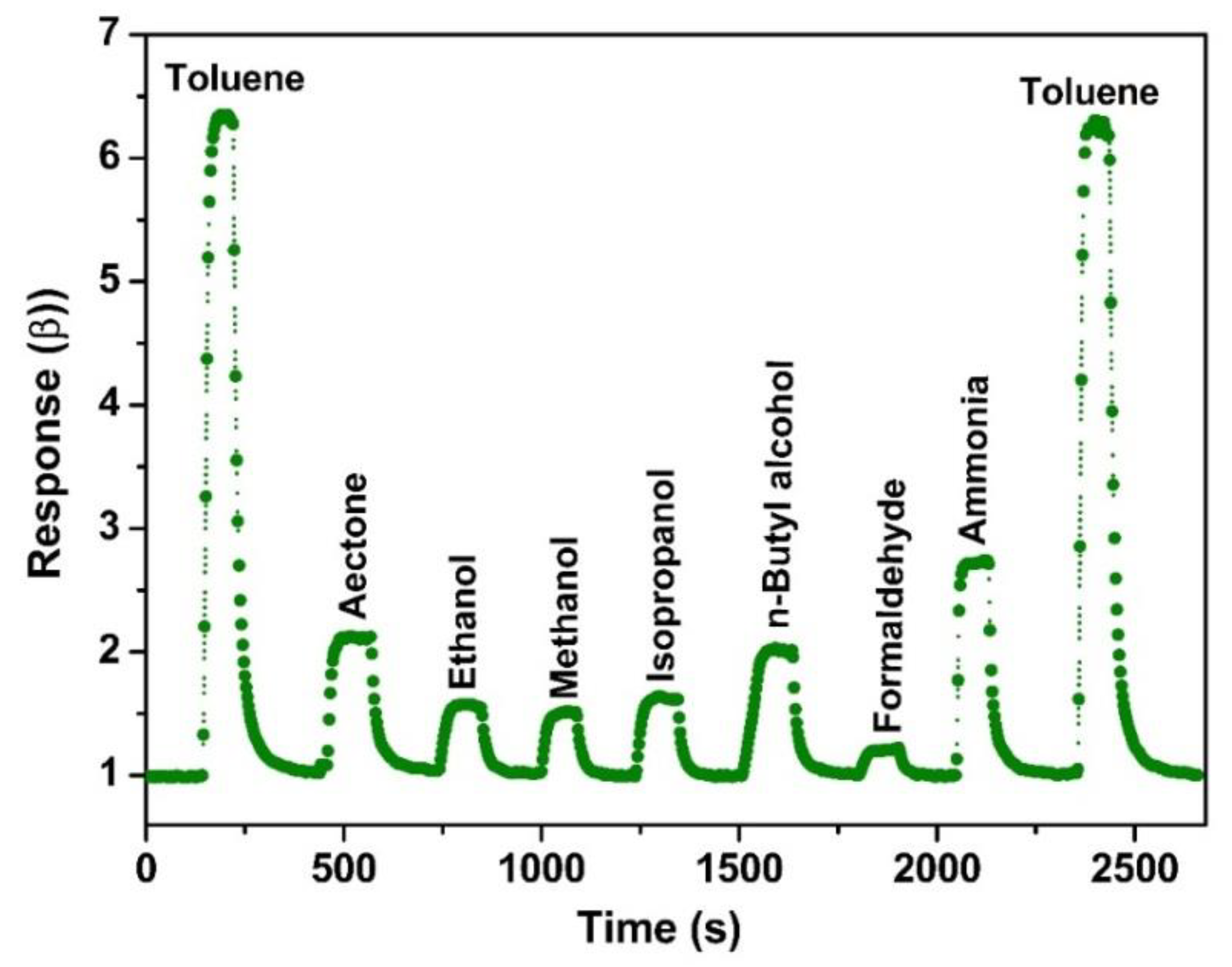
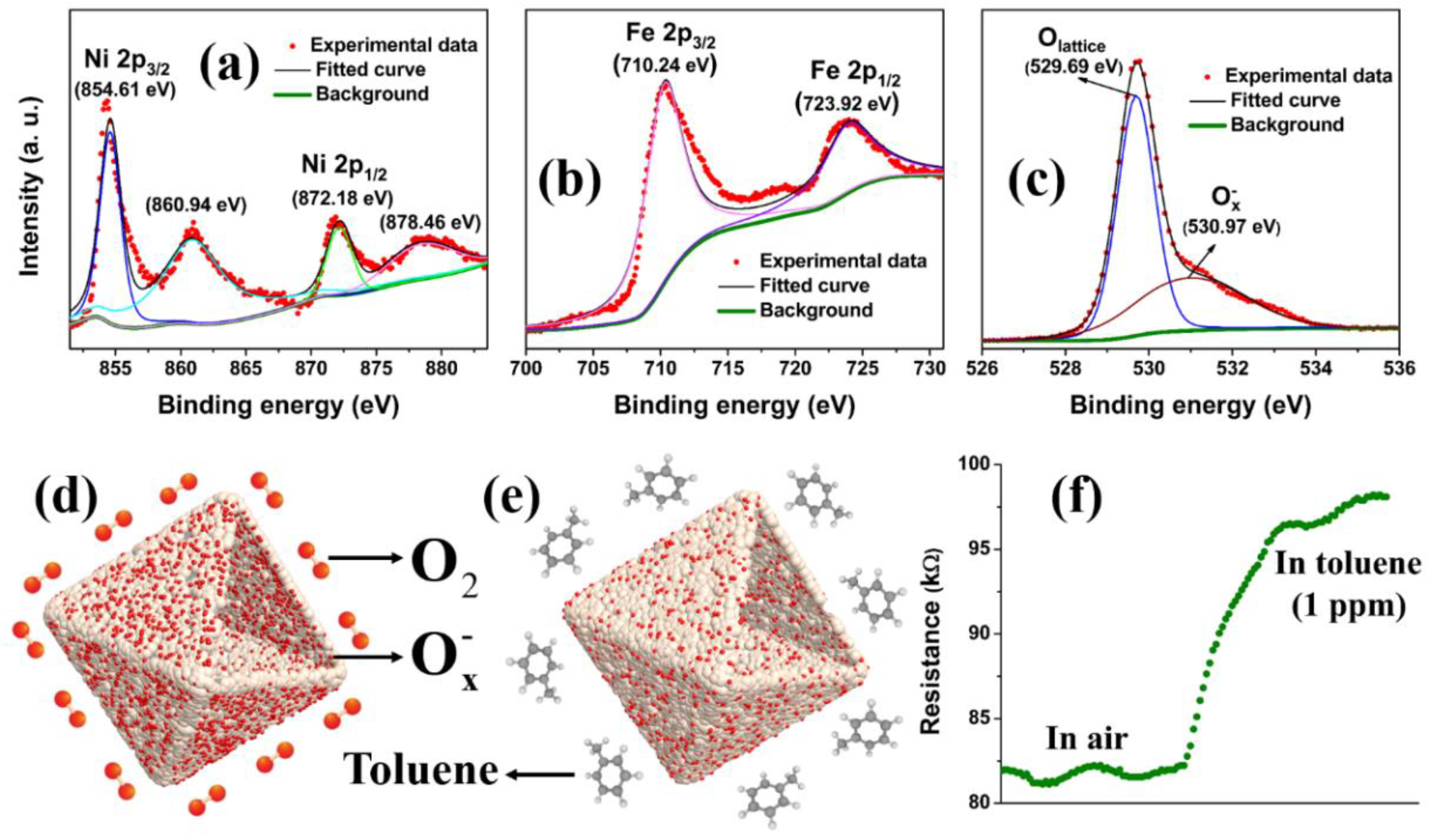
3. Results
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mirzaei, A.; Kim, J.H.; Kim, H.W.; Kim, S.S. Resistive-based gas sensors for detection of benzene, toluene and xylene (BTX) gases: A review. J. Mater. Chem. C 2018, 6, 4342–4370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malik, R.; Tomer, V.K.; Vandna, C.; Dahiya, M.S.; Nehra, S.P.; Duhan, S.; Kailasam, K. A low temperature, highly sensitive and fast response toluene gas sensor based on In(III)-SnO2 loaded cubic mesoporous graphitic carbon nitride. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2018, 255, 3564–3575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, G.; Tisch, U.; Adams, O.; Hakim, M.; Shehada, N.; Broza, Y.Y.; Billan, S.; Bortnyak, R.A.; Kuten, A.; Haick, H. Diagnosing lung cancer in exhaled breath using gold nanoparticles. Nat. Naotechnol. 2009, 4, 669–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, N.H.; Choi, S.J.; Yang, D.J.; Bae, J.; Park, J.; Kim, I. Highly sensitive and selective hydrogen sulfide and toluene sensors using Pd functionalized WO3 nanofibers for potential diagnosis of halitosis and lung cancer. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2014, 193, 574–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donald, J.M.; Hooper, K.; Rich, C.H. Reproductive and developmental toxicity of toluene: A review. Environ. Health Perspect. 1991, 94, 237–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yücel, M.; Takagi, M.; Walterfang, M.; Lubman, D.I. Toluene misuse andlong-term harms: A systematic review of the neuropsychological andneuroimaging literature. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2008, 32, 910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, H.J.; Lee, J.H. Highly sensitive and selective gas sensors using p-type oxide semiconductors: Overview. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2014, 192, 607–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Majhi, S.M.; Naik, G.K.; Lee, H.J.; Song, H.G.; Lee, C.R.; Lee, I.H.; Yu, Y.T. Au@NiO core-shell nanoparticles as a p-type gas sensor: Novel synthesi, characterization, and their gas sensing properties with sensing mechanism. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2018, 268, 223–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.; Zou, C.; Su, Y.J.; Li, M.; Han, Y.T.; Kong, E.S.W.; Yang, Z.; Zhang, Y.F. An ultrasensitive NO2 gas sensor based on a hierarchical Cu2O/CuO mesocrystal nanoflower. J. Mater. Chem. A 2018, 6, 17120–17131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Wang, Y.; Ikram, M.; Lv, H.; Chang, J.B.; Li, Z.K.; Ma, L.F.; Rehman, A.U.; Lu, G.; Chen, J.H.; et al. Facile synthesis of highly dispersed Co3O4 nanoparticles on expanded, thin black phosphorus for a ppb-level NO2 gas sensor. ACS Sens. 2018, 3, 1576–1583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, B.Y.; Yoon, J.W.; Lim, K.; Park, S.H.; Yoon, J.W.; Lee, J.H. Hollow spheres of CoCr2O4-Cr2O3 mixed oxides with nanoscale heterojunctions for exclusive detection of indoor xylene. J. Mater. Chem. C 2018, 6, 10767–10774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bigiani, L.; Maccato, C.; Carraro, G.; Gasparotto, A.; Sada, C.; Comini, E.; Barreca, D. Tailoring vapor-phase fabrication of Mn3O4 nanosystems: From synthesis to gas-sensing applications. ACS Appl. Nano Mater. 2018, 1, 2962–2970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, C.J.; Liu, X.; Xiao, X.C.; Du, S.F.; Wang, Y.D. Monodisperse ZnFe2O4 nanospheres synthesized by a nonaqueous route for a highly selective low-ppm-level toluene gas sensor. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2017, 239, 1231–1236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Virumbrales, M.; Regino, S.P.; Torralvo, M.J.; Veronica, B.G. Mesoporous Silica Matrix as a Tool for Minimizing Dipolar Interactions in NiFe2O4 and ZnFe2O4 Nanoparticles. Nanomaterials 2017, 7, 151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, X.Z.; Sun, F.F.; Dai, S.T.; Lin, X.; Sun, K.M.; Wang, X.F. Hollow NiFe2O4 microspindles derived from Ni/Fe bimetallic MOFs for highly sensitive acetone sensing at low operating temperatures. Inorg. Chem. Front. 2018, 5, 1107–1114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.F.; Ma, W.; Jiang, F.; Cao, E.S.; Sun, K.M.; Cheng, L.; Song, X.Z. Prussian blue analogue derived porous NiFe2O4 nanocubes for low concentration acetone sensing at low working temperature. Chem. Eng. J. 2018, 338, 504–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, T.T.; Zhang, T.; Zeng, Y.; Zhang, R.; Lou, Z.; Deng, J.N.; Wang, L.L. Structure-driven efficient NiFe2O4 materials for ultra-fast response electronic sensing platform. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2018, 225, 1436–1444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Jiao, W.L. The effect of microstructure on the gas properties of NiFe2O4 sensors: Nanotube and nanoparticle. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2015, 216, 293–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anggraini, S.A.; Yoshida, S.; Ikeda, H.; Miura, N. Selective NO2 detection using YSZ-based amperometric sensor attached with NiFe2O4 (+Fe2O3) sensing electrode. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2018, 259, 30–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, X.Z.; Meng, Y.L.; Chen, X.; Sun, K.M.; Wang, X.F. Hollow NiFe2O4 hexagonal biyramids for high-performance n-propanol sensing at low temperature. New J. Chem. 2015, 5, 76229–76248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, X.F.; Jiang, D.L.; Zheng, C.M. The preparation and gas-sensing properties of NiFe2O4 nanocubes and nanorods. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2007, 123, 739–797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yadav, R.S.; Kuřitka, I.; Vilčáková, J.; Machovský, M.; Škoda, D.; Urbánek, P.; Masař, M.; Gořalik, M.; Urbánek, M.; Kalina, L.; et al. Polypropylene Nanocomposite Filled with Spinel Ferrite NiFe2O4 Nanoparticles and In-Situ Thermally-Reduced Graphene Oxide for Electromagnetic Interference Shielding Application. Nanomaterials 2019, 9, 621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, Y.; Wang, B.; Wang, C.; Li, X.D.; Huang, J.Q.; Zhang, H.B.; Xia, F.; Xiao, J.Z. Effects of CoFe2O4 electrode microstructure on the sensing properties for mixed potential NH3 sensor. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2017, 239, 462–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Wang, G.; Yu, F.; Zhang, Y.; Ye, B.C.; Li, Y.C. Facile synthesis of hollow MnFe2O4 nanoboxes based on galvanic replacement reaction for fast and sensitive VOCs sensor. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2018, 258, 589–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Virlan, C.; Tudorache, F.; Pui, A. Increased sensibility of mixed ferrite humidity sensors by subsequent heat treatment. Int. J. Appl. Ceram. Technol. 2017, 14, 1174–1182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Virlan, C.; Tudorache, F.; Pui, A. Tertiary NiCuZn ferrites for improved humidity sensors: A systematic study. Arab. J Chem. 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.D.; Goebl, J.; Yin, Y.D. Templated synthesis of nanostructured materials. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2013, 42, 2610–2653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petkovich, N.D.; Stein, A. Controlling macro- and mesostructures with hierarchical porosity through combined hard and soft templating. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2013, 42, 3721–3739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, J.L.; Lin, L.Q.; Sun, D.H.; Chen, H.M.; Yang, D.P.; Li, Q.B. Bio-inspired synthesis of metal nanomaterials and applications. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2015, 44, 6330–6374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, X.H.; Tan, C.L.; Sindoro, M.; Zhang, H. Hybrid micro/nano-structures derived from metal-organic frameworks: Preparation and applications in energy storage and conversion. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2017, 46, 2660–2677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, W.; Mahmood, A.; Zou, R.Q.; Xu, Q. Metal-organic frameworks and their derived nanostructures for electrochemical energy storage and conversion. Energy Environ. Sci. 2015, 8, 1837–1866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhakshinamoorthy, A.; Li, Z.H.; Garcia, H. Catalysis and photocatalysis by metal organic frameworks. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2018, 47, 8134–8172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stassen, I.; Burtch, N.; Talin, A.; Falcaro, P.; Allendorf, M.; Ameloot, R. An updated roadmap for the integration of metal-organic frameworks with electronic devices and chemical sensors. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2017, 46, 3185–3241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, M.X.; Yang, Y.W. Metal-Organic Framework (MOF)-Based Drug/Cargo Delivery and Cancer Therapy. Adv. Mater. 2017, 29, 1606134–1606153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Wang, X.X.; Zhao, G.X.; Chen, C.L.; Chai, Z.F.; Alsaedi, A.; Hayat, T.; Wang, X.K. Metal-organic framework-based materials: Superior adsorbents for the capture of toxic and radioactive metal ions. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2018, 47, 2322–2356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Liu, Y.X.; Wang, J.; Gascon, J.; Li, J.S.; Bruggen, B.V. Metal-organic frameworks based membranes for liquid separation. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2017, 46, 7124–7144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, Q.; Wang, H.; Huang, B.B.; Yuan, X.Z.; Zhang, J.J.; Zhang, J.; Jiang, L.B.; Xiong, T.; Zeng, G.M. State-of-the-art advances and challenges of iron-based metal organic frameworks from attractive features, synthesis to multifunctional applications. Small 2018, 15, 1803088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, X.D.; Cao, R.G.; Jeong, S.; Cho, J. Spindle-like mesoporous α-Fe2O3 anode material prepared from MOF template for high-rate lithium batteries. Nano Lett. 2012, 12, 4988–4991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, T.T.; Zhang, R.; Wang, Y.B.; Zhang, T. MOF-derived 1D α-Fe2O3/NiFe2O4 heterojunction as efficient sensing materials of acetone vapors. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2019, 281, 885–892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhng, Y.L.; Jia, C.W.; Wang, Q.Y.; Kong, Q.; Chen, G.; Guan, H.T.; Dong, C.J. Highly Sensitive and Selective Toluene Sensor of Bimetallic Ni/Fe-MOFs Derived Porous NiFe2O4 Nanorods. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2019, 58, 9450–9457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, C.J.; Liu, X.; Xiao, X.C.; Chen, G.; Wang, Y.D.; Djerdj, I. Combustion synthesis of porous Pt-functionalized SnO2 sheets for isopropanol gas detection with a significant enhancement in response. J. Mater. Chem. A 2014, 2, 20089–20095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, C.J.; Jiang, M.; Tao, Y.; Shen, Y.Y.; Lu, Y.X.; Yuan, Y.; Wang, Y.D. Nonaqueous synthesis of Pd-functionalized SnO2/In2O3 nanocomposites for excellent butane sensing properties. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2018, 257, 419–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrari, M.; Lutterotti, L. Method for the simultaneous determination of anisotropic residual stresses and texture by X-ray diffraction. J. Appl. Phys. 1994, 76, 7246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, D.Z.; Jiang, J.X.; Sun, D.M.; Qian, X.Y.; Wang, Y.W.; Li, L.C.; Wang, Z.W.; Chai, X.L.; Gan, L.H.; Liu, M.X. A general strategy to synthesize high-level N-doped porous carbons via Schiff-base chemistry for supercapacitors. J. Mater. Chem. A 2018, 6, 12334–12343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R.; Zhou, T.T.; Wang, L.L.; Zhang, T. Metal-organic frameworks (MOFs) derived hierarchical Co3O4 structures as efficient sensing materials for acetone detection. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2018, 10, 9765–9773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, H.-M.; Kim, J.-H.; Jeong, S.-Y.; Kwak, C.-H.; Lee, J.-H. Co3O4−SnO2 Hollow Heteronanostructures: Facile Control of Gas Selectivity by Compositional Tuning of Sensing Materials via Galvanic Replacement. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2016, 8, 7877–7883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Li, X.W.; Sun, H.B.; Sun, P.; Liang, X.S.; Liu, F.M.; Hu, X.L.; Lu, G.Y. Nanosheet-Assembled ZnFe2O4 Hollow Microspheres for High-Sensitive Acetone Sensor. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2015, 7, 15414–15421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, C.X.; Li, H.R.; Xie, L.Z.; Wang, F.; Deng, H.; Chang, F.Z.; Sun, Y.Z. Flower-like NiO nanostructures synthesized by electrodeposition method for efficient detection of toluene gas. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 92128–92133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.Y.; He, Y.H.; Nagashima, K.; Meng, G.; Dai, T.T.; Tong, B.; Deng, Z.H.; Wang, S.M.; Zhu, N.W.; Yanagida, T.; et al. Discrimination of VOCs molecules via extracting concealed features from a emperature-modulated p-type NiO sensor. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2019, 293, 342–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.; Xiao, F.; Wang, J.D.; Su, X.T. 3D flower- and 2D sheet-like CuO nanostructures: Microwave-assisted synthesis and application in gas sensors. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2015, 207, 177–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.L.; Deng, J.N.; Lou, Z.; Zhang, T. Nanoparticles-assembled Co3O4 nanorods p-type nanomaterials: One-pot synthesis and toluene-sensing properties. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2014, 201, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, C.H.; Huang, B.Y.; Zhou, J.Y.; Xie, E.Q. Synthesis of porous Co3O4 nanonetworks to detect toluene at low concentration. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2014, 16, 19327–19332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, J.; Wang, S.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, T. Facile construction of Co3O4 porous microspheres with enhanced acetone gas sensing performances. Mater. Sci. Semicond. Proc. 2019, 101, 10–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, H.; Xu, Y.; Rong, Z.; Cheng, X.; Gao, S.; Zhang, X.; Zhao, H.; Huo, L. Highly toluene sensing performance based on monodispersed Cr2O3 porous microspheres. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2012, 174, 325–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.P.; Zhang, D.M.; Hu, J.C.; Wang, H.P.; Zhang, Y.M.; Li, K.J.; Rong, Q.; Zhou, S.Q.; Zhang, J.; Zhu, Z.Q.; et al. Excellent toluene gas sensing properties of molecular imprinted Ag-LaFeO3 nanostructures synthesized by microwave-assisted process. Mater. Res. Bull. 2019, 111, 320–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Ao, S.S.R.; Li, G.D.; Gao, Q.; Zou, X.X.; Wei, C.D. Enhanced sensing performance to toluene and xylene by construvting NiGa2O4-NiO heterostructures. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2019, 282, 331–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, X.; Gao, K.; Shen, G.; Xue, P.; Wang, D.; Hu, F.; Zhang, J.; Yang, Q.; Wang, X. Ordered mesoporous NiFe2O4 with ultrathin framework for low-ppb toluene sensing. Sci. Bull. 2018, 63, 187–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, B.Y.; Yoon, J.W.; Kim, J.K.; Kang, Y.C.; Lee, J.H. Dual role of multiroom-structured Sn-doped NiO microspheres for ultrasensitive and highly selective detection of xylene. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2018, 10, 16605–16612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Wang, Y.R.; Hu, Q.; Mu, X.M.; Zhang, Y.X.; Bai, J.L.; Wang, Q.; Shen, Y.Z.; Shen, Z.X.; Xie, E.Q. A low temperature and highly sensitive ethanol sensor based on Au modified In2O3 nanofibers by coaxial electrosponning. J. Mater. Chem. C 2018, 6, 10935–10943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franke, M.E.; Koplin, T.J.; Simon, U. Metal and metal oxide nanoparticles inchemiresistors: Does the nanoscale matter? Small 2006, 2, 36–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tudorache, F.; Popa, P.D.; Dobromir, M.; Iacomi, F. Studies on the structure and gas sensing properties of nickel–cobalt ferrite thin films prepared by spin coating. Mater. Sci. Eng. B 2013, 178, 1334–1338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dumitrescu, A.M.; Lisa, G.; Iordan, A.R.; Tudorache, F.; Petrila, I.; Borhan, A.I.; Palamaru, M.N.; Mihailescu, C.; Leontie, L.; Munteanu, C. Ni ferrite highly organized as humidity sensors. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2015, 156, 170–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gurlo, T.A.; Bârsan, N.; Weimar, U. Basics of oxygen and SnO2 interaction: Work function change and conductivity measurements. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2006, 118, 78–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, Y.Z.; Wang, H.; Yang, R.S.; Lai, X.Y.; Wan, J.W.; Lin, G.; Liu, D. Controlled synthesis and enhanced toluene-sensing properties of mesoporous NixCo1-xFe2O4 nanostructured microspheres with tunable composite. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2019, 280, 227–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Materials | Microstructures | Concentration (ppm) | T (°C) | Response | Limit of Detection | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NiO | Flower-like | 5 | 250 | 2.63 | 0.5 ppm | [48] |
| NiO | Nanoparticle | 200 | 210 | 1.6 | 100 ppm | [49] |
| CuO | Flower | 500 | 260 | 2.5 | 10 ppm | [50] |
| Co3O4 | Nanorod | 200 | 200 | 35 | 10 ppm | [51] |
| Co3O4 | Nanosheet | 100 | 150 | 6.08 | 1 ppm | [52] |
| Co3O4 | Microsphere | 100 | 180 | 2.2 | [53] | |
| Cr2O3 | Microsphere | 100 | 170 | 33.64 | 1 ppm | [54] |
| Ag-LaFeO3 | Nanoparticle | 5 | 215 | 24 | 5 ppm | [55] |
| NiGa2O4-NiO | Nanosphere | 100 | 230 | 12.7 | 0.5 ppm | [56] |
| NiFe2O4 | Ordered mesoporous | 1 | 230 | 77.3 | 2 ppb | [57] |
| NiFe2O4 | Hexagonal biyramid | 200 | 140 | 5.73 | 5 ppm | [20] |
| NiFe2O4 | Nano-octahedron | 100 | 260 | 6.41 | 1 ppm | This work |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, Y.; Jia, C.; Wang, Q.; Kong, Q.; Chen, G.; Guan, H.; Dong, C. MOFs-Derived Porous NiFe2O4 Nano-Octahedrons with Hollow Interiors for an Excellent Toluene Gas Sensor. Nanomaterials 2019, 9, 1059. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano9081059
Zhang Y, Jia C, Wang Q, Kong Q, Chen G, Guan H, Dong C. MOFs-Derived Porous NiFe2O4 Nano-Octahedrons with Hollow Interiors for an Excellent Toluene Gas Sensor. Nanomaterials. 2019; 9(8):1059. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano9081059
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Yanlin, Chaowei Jia, Qiuyue Wang, Quan Kong, Gang Chen, Hongtao Guan, and Chengjun Dong. 2019. "MOFs-Derived Porous NiFe2O4 Nano-Octahedrons with Hollow Interiors for an Excellent Toluene Gas Sensor" Nanomaterials 9, no. 8: 1059. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano9081059
APA StyleZhang, Y., Jia, C., Wang, Q., Kong, Q., Chen, G., Guan, H., & Dong, C. (2019). MOFs-Derived Porous NiFe2O4 Nano-Octahedrons with Hollow Interiors for an Excellent Toluene Gas Sensor. Nanomaterials, 9(8), 1059. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano9081059