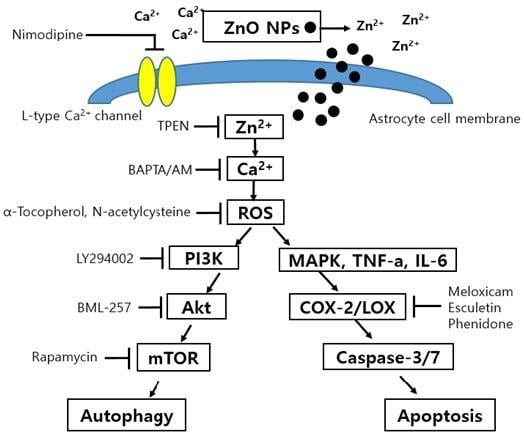
Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles Induce Autophagy and Apoptosis via Oxidative Injury and Pro-Inflammatory Cytokines in Primary Astrocyte Cultures
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals and ZnO NP Suspension
2.2. Astrocyte Cultures and ZnO NP Treatment
2.3. Measurement of Lactate Dehydrogenase (LDH) Activity
2.4. MTT Assay
2.5. LC3-Antibody Detection
2.6. Transmission Electron Microscopy (TEM)
2.7. ELISA Assay
2.8. Protein Assay
2.9. PI3K/MAPK Dual Pathway Activation Assay
2.10. Caspase-3/7 Assay
2.11. DAPI Staining
2.12. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Nanoparticle Characterization
3.2. Dose-Dependent ZnO NP-Induced Toxicity in Neocortical Astrocyte Cultures
3.3. TEM Analyses of Astrocyte Morphology Following Exposure to ZnO NPs
3.4. ZnO NP-Mediated Enhancement of Autophagy of Cultured Astrocytes
3.5. Effects of ZnO NPs on Caspase-3/7 Activity and DAPI Staining
3.6. Effects of ZnO NPs on IL-6, TNF-α, SOD, and GPx Levels in Cultured Astrocyte Cells
3.7. Effect of ZnO NPs on PI3K/MAPK Activation in Cultured Astrocytes
3.8. Effects of Meloxicam, Esculetin, and Phenidone on ZnO NP-Induced Toxicity
3.9. Effects of BML-257 and Rapamycin on ZnO NP-Induced Toxicity
3.10. Effects of Calcium Modulators, Antioxidants, and Metal Chelators on ZnO NP-Induced Toxicity
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ancona, A.; Dumontel, B.; Garino, N.; Demarco, B.; Chatzitheodoridou, D.; Fazzini, W.; Engelke, H.; Cauda, V. Lipid-Coated Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles as Innovative ROS-Generators for Photodynamic Therapy in Cancer Cells. Nanomaterials 2018, 8, 143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Sun, L.; Webster, T.J. The Investigation of ZnO/Poly(vinylidene fluoride) Nanocomposites with Improved Mechanical, Piezoelectric, and Antimicrobial Properties for Orthopedic Applications. J. Biomed. Nanotechnol. 2018, 14, 536–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marino, A.; Genchi, G.G.; Mattoli, V.; Ciofani, G. Piezoelectric nanotransducers: The future of neural stimulation. Nanotoday 2017, 14, 9–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marino, A.; Genchi, G.G.; Sinibaldi, E.; Ciofani, G. Piezoelectric Effects of Materials on Bio-Interfaces. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2017, 9, 17663–17680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, S.J.; Choy, J.H. Biokinetics of zinc oxide nanoparticels: Toxicokinetics, biological fates, and protein interaction. Int. J. Nanomed. 2014, 9, 261–269. [Google Scholar]
- Choi, J.S.; Kim, R.O.; Yoon, S.; Kim, W.K. Developmental toxicity of zinc oxide nanoparticles (Danio rerio): A transcriptomic analysis. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0160763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Subramaniam, V.D.; Prasad, S.V.; Banerjee, A.; Gopinath, M.; Murugesan, R.; Marotta, F.; Sun, X.F.; Pathak, S. Health hazard of nanoparticles: Understanding the toxicity mechanism of nanosized ZnO in cosmetic products. Drug Chem. Toxicol. 2019, 42, 84–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manzoor, U.; Siddique, S.; Ahmed, R.; Noreen, Z.; Bokhari, H.; Ahmad, I. Antibacterial, Structural and Optical Characterization of Mechano-Chemically Prepared ZnO Nanoparticles. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0154704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Gao, S.; Wang, S.; Xu, Z.; Wei, L. Zinc oxide nanoparticles induce toxicity in CAL 27 oral cancer cell lines by activating PINK1/Parkin-mediated mitophagy. Int. J. Nanomed. 2018, 13, 3441–3450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.-L.; Gao, J.-Q. Potential neurotoxicity of nanoparticles. Int. J. Pharm. 2010, 394, 115–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kao, Y.-Y.; Cheng, T.-J.; Yang, D.-M.; Wang, C.-T.; Chiung, Y.-M.; Liu, P.-S. Demonstration of an Olfactory Bulb–Brain Translocation Pathway for ZnO Nanoparticles in Rodent Cells in vitro and in vivo. J. Mol. Neurosci. 2012, 48, 464–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tian, L.; Lin, B.; Wu, L.; Li, K.; Liu, H.; Yan, J.; Liu, X.; Xi, Z. Neurotoxicity induced by zinc oxide nanoparticles: Age-related differences and interaction. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 16117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Deng, X.; Zhang, F.; Chen, D.; Ding, W. ZnO nanoparticle-induced oxidative stress triggers apoptosis by activating JNK signaling pathway in cultured primary astrocytes. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 2014, 9, 117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sudhakaran, S.; Athira, S.; Mohanan, P. Zinc oxide nanoparticle induced neurotoxic potential upon interaction with primary astrocytes. NeuroToxicology 2019, 73, 213–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barceloux, D.G. Zinc. J. Toxicol. Clin. Toxicol. 1999, 37, 279–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tian, Y.; Yang, Z.; Zhang, T. Zinc ion as modulator effects on excitability and synaptic transmission in hippocampal CA1 neurons in Wistar rats. Neurosci. Res. 2010, 68, 167–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Capasso, M.; Jeng, J.-M.; Malavolta, M.; Mocchegiani, E.; Sensi, S.L. Zinc dyshomeostasis: A key modulator of neuronal injury. J. Alzheimers Dis. 2005, 8, 93–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawahara, M.; Mizuno, D.; Koyama, H.; Konoha, K.; Ohkawara, S.; Sadakane, Y. Disruption of zinc homeostasis and the pathogenesis of senile dementia. Metallomics 2014, 6, 209–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.-H.; Jeong, M.S.; Kim, D.-Y.; Her, S.; Wie, M.-B. Zinc oxide nanoparticles induce lipoxygenase-mediated apoptosis and necrosis in human neuroblastoma SH-SY5Y cells. Neurochem. Int. 2015, 90, 204–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, H.; Chen, A.; Lai, X.; Liu, J.; Wu, J.; Kang, Y.; Wang, X.; Shao, L. Neuroinflammation is induced by tongue-instilled ZnO nanoparticles via the Ca2+-dependent NF-κB and MAPK pathways. Part. Fibre Toxicol. 2018, 15, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.-J.; Koh, J.-Y. Roles of zinc and metallothionein-3 in oxidative stress-induced lysosomal dysfunction, cell death, and autophagy in neurons and astrocytes. Mol. Brain 2010, 3, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pan, R.; Timmins, G.S.; Liu, W.; Liu, K.J. Autophagy Mediates Astrocyte Death during Zinc-Potentiated Ischemia–Reperfusion Injury. Boil. Trace Element Res. 2015, 166, 89–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sruthi, S.; Mohanan, P. Investigation on cellular interactions of astrocytes with zinc oxide nanoparticles using rat C6 cell lines. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2015, 133, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amer, M.G.; Karam, A.R. Morphological and Biochemical Features of Cerebellar Cortex after Exposure to Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles: Possible Protective Role of Curcumin. Anat. Rec. Adv. Integr. Anat. Evol. Boil. 2018, 301, 1454–1466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kermanizadeh, A.; Jantzen, K.; Ward, M.B.; Durhuus, J.A.; Rasmussen, L.J.; Loft, S.; Møller, P. Nanomaterial-induced cell death in pulmonary and hepatic cells following exposure to three different metallic materials: The role of autophagy and apoptosis. Nanotoxicology 2017, 11, 184–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, W.-L.; Pei, J.-J.; Nishimura, T.; Winblad, B.; Cowburn, R.F. Zinc-induced anti-apoptotic effects in SH-SY5Y neuroblastoma cells via the extracellular signal-regulated kinase 1/2. Mol. Brain Res. 2005, 135, 40–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.-Y.; Kim, J.-H.; Lee, J.-C.; Won, M.-H.; Yang, S.-R.; Kim, H.-C.; Wie, M.-B. Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles Exhibit Both Cyclooxygenase- and Lipoxygenase-Mediated Apoptosis in Human Bone Marrow-Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells. Toxicol. Res. 2019, 35, 83–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldberg, M.; Choi, D. Combined oxygen and glucose deprivation in cortical cell culture: Calcium-dependent and calcium-independent mechanisms of neuronal injury. J. Neurosci. 1993, 13, 3510–3524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sensi, S.L.; Rockabrand, E.; Canzoniero, L.M. Acidosis enhances toxicity induced by kainite and zinc exposure in aged cultured astrocyte. Biogerontology 2006, 7, 367–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koh, J.Y.; Choi, D.W. Quantitative determination of glutamate mediated cortical neuronal injury in cell culture by lactate dehydrogenase efflux assay. J. Neurosci. Methods 1987, 20, 83–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, K.-N.; Yoon, T.-J.; Minai-Tehrani, A.; Kim, J.-E.; Park, S.J.; Jeong, M.S.; Ha, S.-W.; Lee, J.-K.; Kim, J.S.; Cho, M.-H. Zinc oxide nanoparticle induced autophagic cell death and mitochondrial damage via reactive oxygen species generation. Toxicol. Vitr. 2013, 27, 1187–1195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, A.; Najafzadeh, M.; Jacob, B.K.; Dhawan, A.; Anderson, D. Zinc oxide nanoparticles affect the expression of p53, Ras p21 and JNKs: An ex vivo/in vitro exposure study in respiratory disease patients. Mutagenesis 2015, 30, 237–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quinta-Ferreira, M.; Matias, C.; Arif, M.; Dionísio, J.; Matias, C. Measurement of presynaptic zinc changes in hippocampal mossy fibers. Brain Res. 2004, 1026, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Y.; Yan, F.; Yin, J.; Pan, R.; Shi, W.; Qi, Z.; Fang, Y.; Huang, Y.; Li, S.; Luo, Y.; et al. Synergistic Interaction Between Zinc and Reactive Oxygen Species Amplifies Ischemic Brain Injury in Rats. Stroke 2018, 49, 2200–2210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, L.B.; Wang, Z.Y. Disruption of brain zinc homeostasis promotes the pathophysiological progress of Alzheimer’s disease. Histol. Histopathol. 2016, 31, 623–627. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Sharma, A.K.; Singh, V.; Gera, R.; Purohit, M.P.; Ghosh, D. Zinc oxide nanoparticle induces microglial death by NADPH oxidase-independent reactive oxygen species as well as energy depletion. Mol. Neurobiol. 2017, 54, 6273–6286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dineley, K.E.; Scanlon, J.M.; Kress, G.J.; Stout, A.K.; Reynolds, I.J. Astrocyte are more resistant than neurons to the cytotoxic effects of increased [Zn2+]i. Neurobiol. Dis. 2000, 7, 310–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Metaxakis, A.; Ploumi, C.; Tavernarakis, N. Autophagy in Age-Associated Neurodegeneration. Cells 2018, 7, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, D.-P.; Zhang, X.-F.; Huang, Y.-F.; Gurunathan, S. Zinc oxide nanoparticles induce apoptosis and autophagy in human ovarian cancer cells. Int. J. Nanomed. 2017, 12, 6521–6535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, R.; Singh, S.K.; Chauhan, L.; Das, M.; Tripathi, A.; Dwivedi, P.D. Zinc oxide nanoparticles induce apoptosis by enhancement of autophagy via PI3K/Akt/mTOR inhibition. Toxicol. Lett. 2014, 227, 29–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.-J.; Cho, K.S.; Koh, J.-Y. Oxidative injury triggers autophagy in astrocytes: The role of endogenous zinc. Glia 2009, 57, 1351–1361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, T.; Liang, H.; Liu, L.; Gong, Y.; Ding, Y.; Liao, G.; Cao, Y. Influence of pristine and hydrophobic ZnO nanoparticles on cytotoxicity and endoplasmic reticulum (ER) stress-autophagy-apoptosis gene expression in A549-macrophage co-culture. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2019, 167, 188–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roy, R.; Parashar, V.; Chauhan, L.K.; Shanker, R.; Das, M.; Tripathi, A.; Qwivedi, P.D. Mechanism of uptake of ZnO nanoparticles and inflammatory response in macropahges require PI3K mediated MAPKs signaling. Toxicol. In Vitro 2014, 28, 457–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; He, X.; Wu, X.; Lei, M.; Wei, Z.; Zhang, X.; Wen, L.; Xu, P.; Li, S.; Qu, S. Rapamycin upregulates glutamate transporter and IL-6 expression in astrocytes in a mouse model of Parkinson’s disease. Cell Death Dis. 2017, 8, e2611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, D.; Zou, J.; Wong, M. Rapamycin Attenuates Acute Seizure-induced Astrocyte Injury in Mice in Vivo. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 2867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldshmit, Y.; Kanner, S.; Zacs, M.; Frisca, F.; Pinto, A.R.; Currie, P.D.; Pinkas-Kramarski, R. Rapamycin increases neuronal survival, reduces inflammation and astrocyte proliferation after spinal cord injury. Mol. Cell. Neurosci. 2015, 68, 82–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.-C.; Aronstam, R.S.; Chen, D.-R.; Huang, Y.-W. Oxidative stress, calcium homeostasis, and altered gene expression in human lung epithelial cells exposed to ZnO nanoparticles. Toxicol. In Vitro 2010, 24, 45–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chouraqui, E.; Leon, A.; Repessé, Y.; Prigent-Tessier, A.; Bouhallab, S.; Bouglé, D.; Marie, C.; Duval, D. Deferoxamine blocks death induced by glutathione depletion in PC 12 cells. NeuroToxicology 2013, 37, 221–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, A.M.Y. Antioxidative Effect of Vitamin D3 on Zinc-Induced Oxidative Stress in CNS. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2005, 1053, 319–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]











© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Song, W.-J.; Jeong, M.-S.; Choi, D.-M.; Kim, K.-N.; Wie, M.-B. Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles Induce Autophagy and Apoptosis via Oxidative Injury and Pro-Inflammatory Cytokines in Primary Astrocyte Cultures. Nanomaterials 2019, 9, 1043. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano9071043
Song W-J, Jeong M-S, Choi D-M, Kim K-N, Wie M-B. Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles Induce Autophagy and Apoptosis via Oxidative Injury and Pro-Inflammatory Cytokines in Primary Astrocyte Cultures. Nanomaterials. 2019; 9(7):1043. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano9071043
Chicago/Turabian StyleSong, Woo-Ju, Myung-Seon Jeong, Dong-Min Choi, Kil-Nam Kim, and Myung-Bok Wie. 2019. "Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles Induce Autophagy and Apoptosis via Oxidative Injury and Pro-Inflammatory Cytokines in Primary Astrocyte Cultures" Nanomaterials 9, no. 7: 1043. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano9071043
APA StyleSong, W.-J., Jeong, M.-S., Choi, D.-M., Kim, K.-N., & Wie, M.-B. (2019). Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles Induce Autophagy and Apoptosis via Oxidative Injury and Pro-Inflammatory Cytokines in Primary Astrocyte Cultures. Nanomaterials, 9(7), 1043. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano9071043