1-Laurin-3-Palmitin as a Novel Matrix of Solid Lipid Particles: Higher Loading Capacity of Thymol and Better Stability of Dispersions Than Those of Glyceryl Monostearate and Glyceryl Tripalmitate
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Synthesis and Characterization of 1,3-LP
2.3. High Performance Liquid Chromatography Coupled with Evaporative Light Scattering Detection (HPLC-ELSD) Analysis of 1,3-LP
2.4. Preparation of SLNs
2.5. Determination of Z-Average Mean Diameter, Polydispersity Index (PDI), and Zeta-Potential
2.6. Comparison of the Loading Capacity and Entrapment Efficiency of SLNs
2.7. X-ray Powder Diffraction (XRD) Spectroscopy Analysis
2.8. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
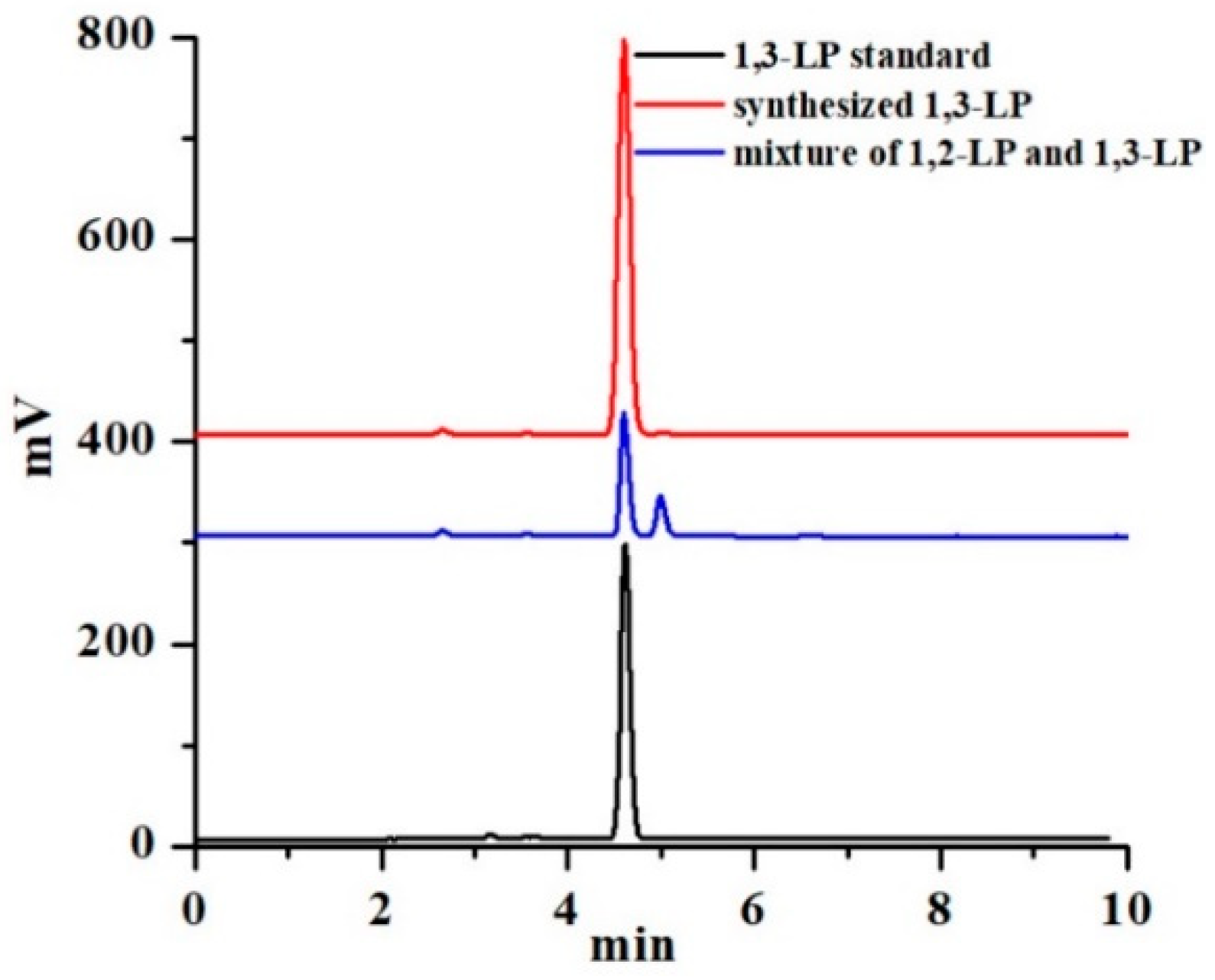
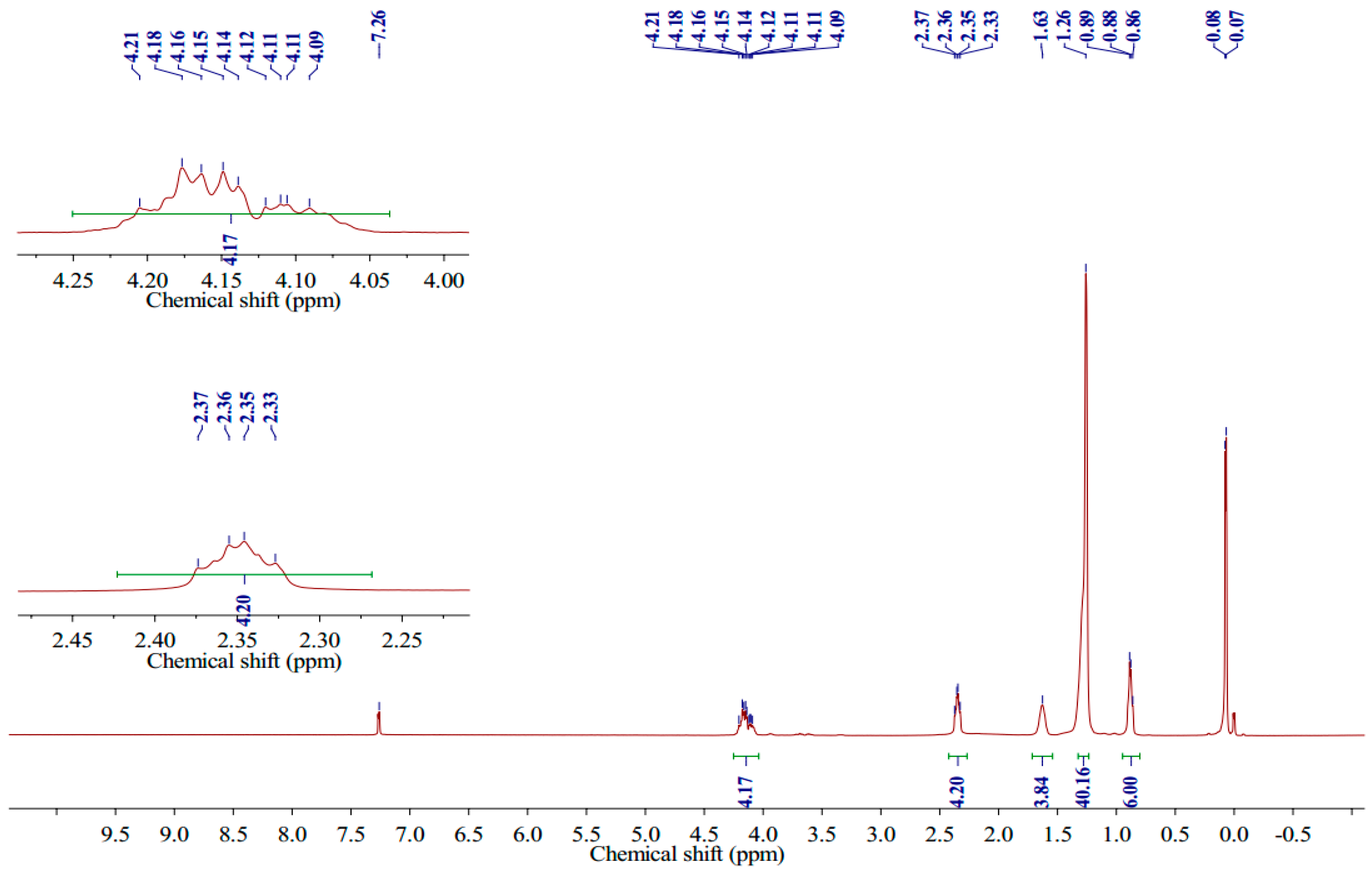
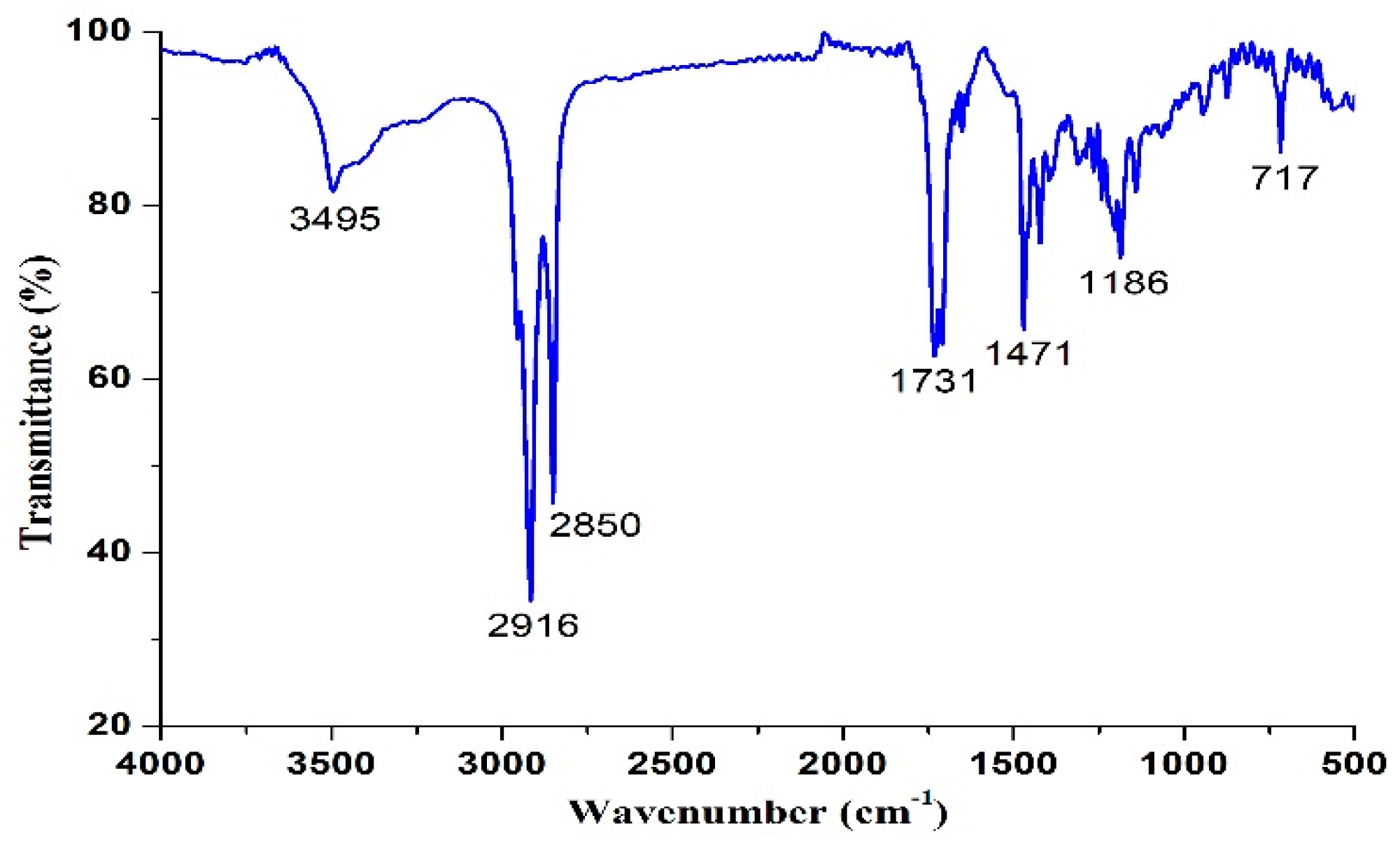
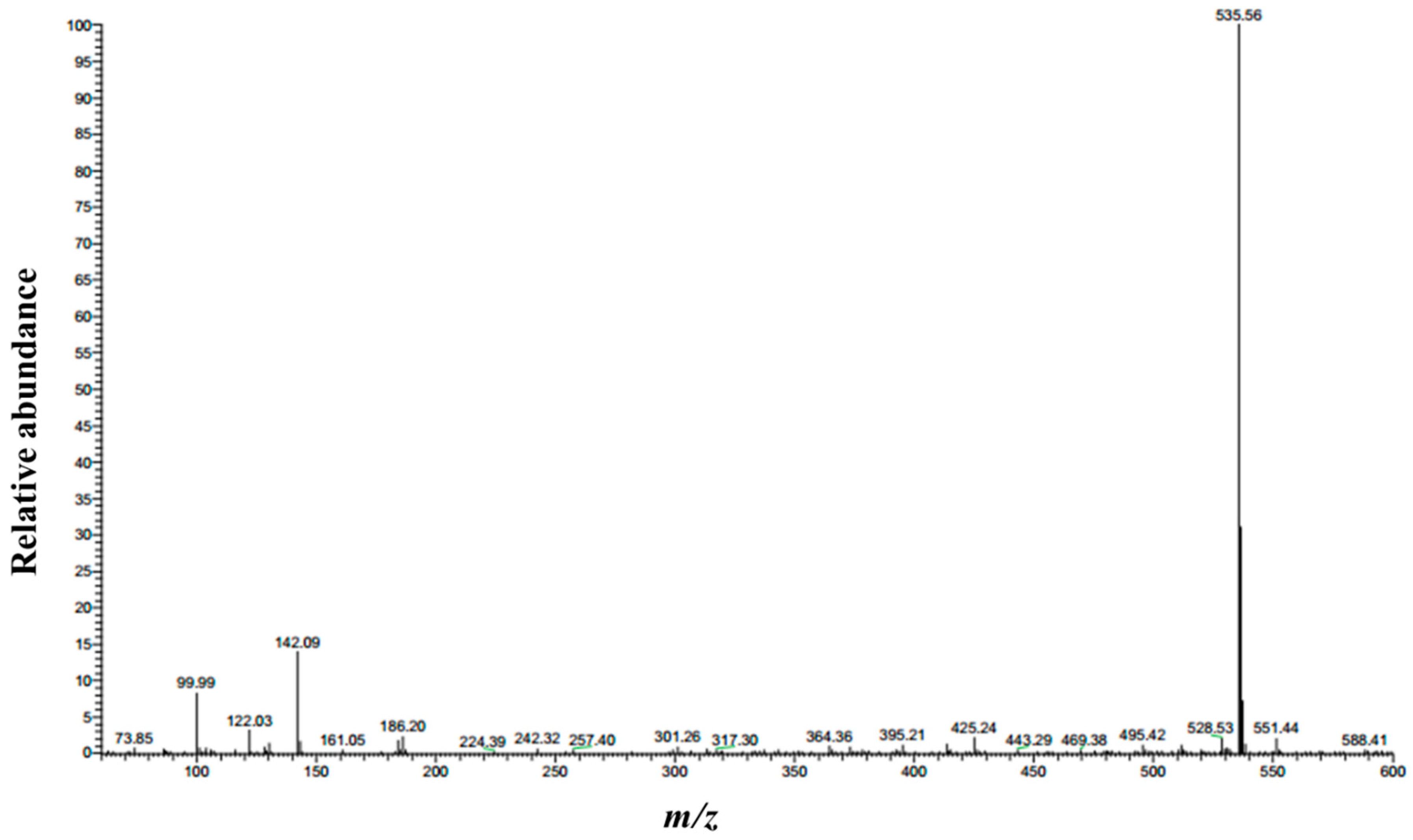
3.1. Synthesis of 1,3-LP
3.2. Optimization of Formulations for the Preparation of SLNs
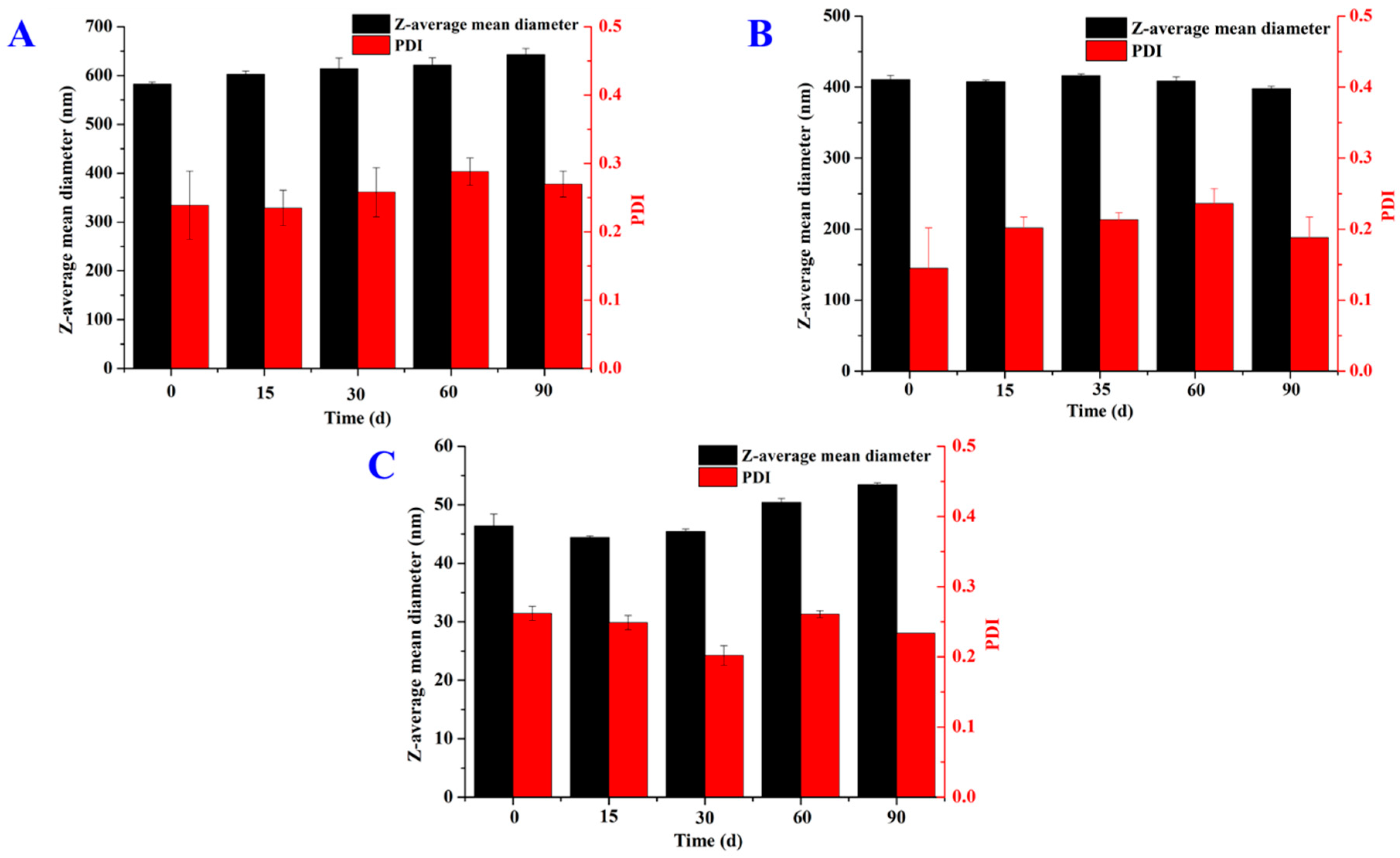
3.3. Properties of SLNs Loaded with Thymol
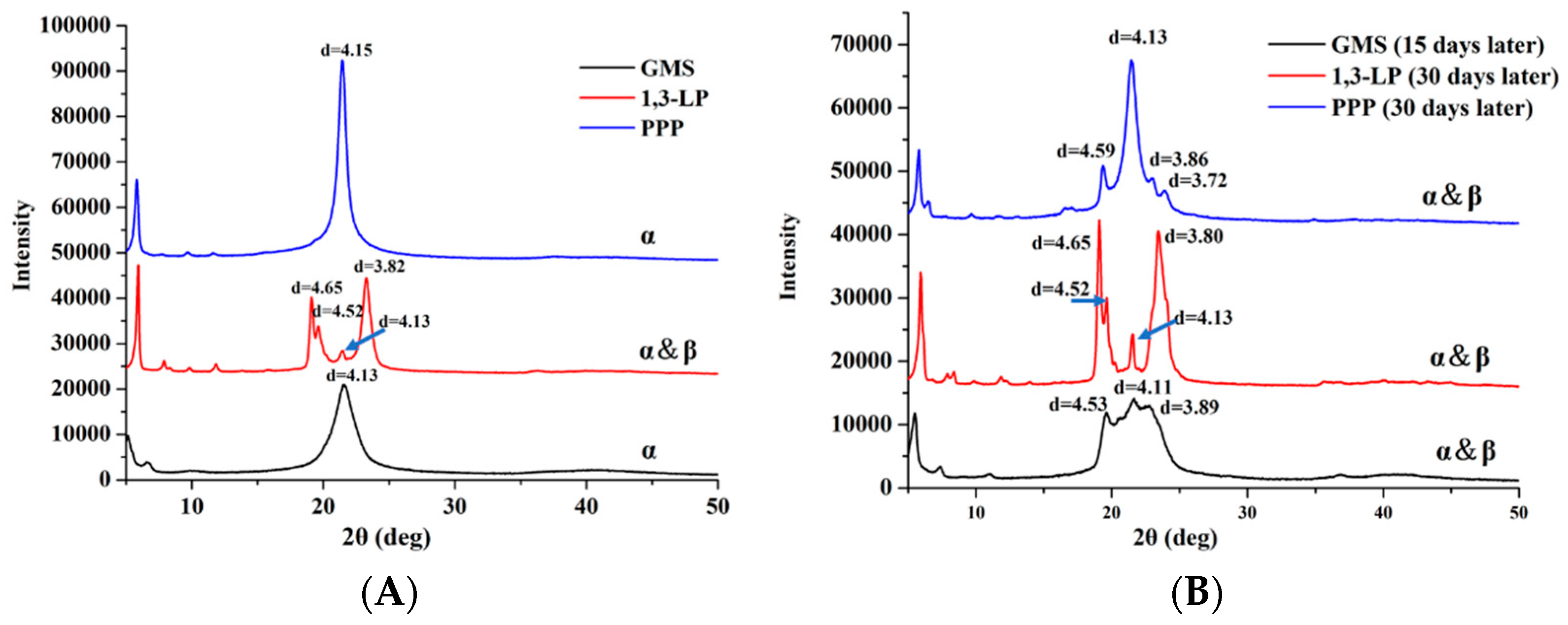
3.4. Polymorphic Structures of Lipids Studied with X-ray Powder Diffraction Spectroscopy
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Patel, A.R.; Velikow, K.P. Colloidal delivery systems in foods: A general comparison with oral drug delivery. LWT Food Sci. Technol. 2011, 44, 1958–1964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnston, A.P.R.; Such, G.K.; Ng, S.L.; Caruso, F. Challenges facing colloidal delivery systems: From synthesis to the clinic. Curr. Opin. Colloid Interface Sci. 2011, 16, 171–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McClements, D.J. Encapsulation, protection, and release of hydrophilic active components: Potential and limitations of colloidal delivery systems. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2015, 219, 27–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.; Jin, J.; Zheng, M.; Zheng, Y.; Xu, X.; Liu, Y.; Wang, X. Co-surfactant free microemulsions: Preparation, characterization and stability evaluation for food application. Food Chem. 2016, 204, 194–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montes de Oca-Ávalos, J.M.; Candal, R.J.; Herrera, M.L. Nanoemulsions: Stability and physical properties. Curr. Opin. Food Sci. 2017, 16, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aditya, N.P.; Ko, S. Solid lipid nanoparticles (SLNs): Delivery vehicles for food bioactives. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 30902–30911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cinay, G.E.; Erkoc, P.; Alipour, M.; Hashimoto, Y.; Sasaki, Y.; Akiyoshi, K.; Kizilel, S. Nanogel-Integrated pH-Responsive Composite Hydrogels for Controlled Drug Delivery. ACS Biomater. Sci. Eng. 2017, 3, 370–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, G.H.; Chung, S.K.; Kim, J.T.; Joung, H.J.; Park, H.J. Preparation of chitosan-coated nanoliposomes for improving the mucoadhesive property of curcumin using the ethanol injection method. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2013, 61, 11119–11126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Cai, T.; Huang, Y.; Xia, X.; Cole, S.P.C.; Cai, Y. A Review of the Structure, Preparation, and Application of NLCs, PNPs, and PLNs. Nanomaterials 2017, 7, 122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.K.; Howard, M.D.; Dziubla, T.D.; Rinehart, J.J.; Jay, M.; Lu, X. Uniformity of drug payload and its effect on stability of solid lipid nanoparticles containing an ester prodrug. ACS Nano 2011, 5, 209–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geszke-Moritz, M.; Moritz, M. Solid lipid nanoparticles as attractive drug vehicles: Composition, properties and therapeutic strategies. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2016, 68, 982–994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, H.; Chen, J.; Du, Y.Z.; Hu, F.Q.; Zeng, S.; Zhao, H.L. Studies on oral absorption of stearic acid SLN by a novel fluorometric method. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2007, 58, 157–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Bi, C.; Chan, H.M.; Sun, S.; Zhang, Q.; Zheng, Y. Curcumin-loaded solid lipid nanoparticles have prolonged in vitro antitumour activity, cellular uptake and improved in vivo bioavailability. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2013, 111, 367–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cortesi, R.; Esposjto, E.; Luca, G.; Nastruzzi, C. Production of lipospheres as carriers for bioactive compounds. Biomaterials 2002, 23, 2283–2294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baek, J.-S.; Na, Y.-G.; Cho, C.-W. Sustained cytotoxicity of wogonin on breast cancer cells by encapsulation in solid lipid nanoparticles. Nanomaterials 2018, 8, 159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tatke, A.; Dudhipala, N.; Janga, K.Y.; Balguri, S.P.; Avula, B.; Jablonski, M.M.; Majumdar, S. In situ gel of triamcinolone acetonide-loaded solid lipid nanoparticles for improved topical ocular delivery: Tear kinetics and ocular disposition studies. Nanomaterials 2019, 9, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Zhao, X.; Ma, Y.; Zhai, G.; Li, L.; Lou, H. Enhancement of gastrointestinal absorption of quercetin by solid lipid nanoparticles. J. Control. Release 2009, 133, 238–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Smith, E. Percutaneous permeation of betamethasone 17-valerate incorporated in lipid nanoparticles. J. Pharm. Sci. 2011, 100, 896–903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Montenegro, L.; Panico, A.M.; Santagati, L.M.; Siciliano, E.A.; Intagliata, S.; Modica, M.N. Solid lipid nanoparticles loading idebenone ester with pyroglutamic acid: In vitro antioxidant activity and in vivo topical efficacy. Nanomaterials 2019, 9, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lo, S.-K.; Tan, C.-P.; Long, K.; Yusoff, M.S.A.; Lai, O.-M. Diacylglycerol Oil—Properties, Processes and Products: A Review. Food Bioprocess. Technol. 2008, 1, 223–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lehner, R.; Kuksis, A. Triacylglycerol synthesis by an sn-1,2(2,3)-diacylglycerol transacylase from rat intestinal microsomes. J. Biol. Chem. 1993, 268, 8781–8786. [Google Scholar]
- Xue, J.; Zhong, Q. Blending lecithin and gelatin improves the formation of thymol nanodispersions. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2014, 62, 2956–2962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marchese, A.; Orhan, I.E.; Daglia, M.; Barbieri, R.; Lorenzo, A.D.; Nabavi, S.F.; Gortzi, O.; Izadi, M.; Nabavi, S.M. Antibacterial and antifungal activities of thymol: A brief review of the literature. Food Chem. 2016, 210, 402–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.-X.; Hu, Z.-X.; He, J.-B.; Zhang, W.-L.; Qi, Y.-T. Phase transfer catalytic synthesis and characterization of glycidyl laurate. J. Food Saf. Qual. 2015, 6, 4103–4109. [Google Scholar]
- Ikeda, I.; Gu, X.P.; Miyamoto, I.; Okahara, M. Preparation of 1,3-diacylglycerols and 1-alkyl-3-acylglycerols in the presence of quaternary ammonium salt. J. Am. Oil Chem. Soc. 1989, 66, 822–824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehnert, W.; Mäder, K. Solid lipid nanoparticles, production, characterization and applications. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2001, 47, 165–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Behbahani, E.S.; Ghaedi, M.; Abbaspour, M.; Rostamizadeh, K. Optimization and characterization of ultrasound assisted preparation of curcumin-loaded solid lipid nanoparticles: Application of central composite design, thermal analysis and X-ray diffraction techniques. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2017, 38, 271–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, R.; Malherbe, F.; Eldridge, D.; Palomobo, E.A.; Harding, I. Physicochemical characterization of solid lipid nanoparticles (SLNs) prepared by a novel microemulsion technique. J. Colloids Interface Sci. 2014, 428, 286–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kheradmandnia, S.; Vasheghani-Farahani, E.; Nosrati, M.; Atyabi, F. Preparation and characterization of ketoprofen-loaded solid lipid nanoparticles made from beeswax and carnauba wax. Nanomed. Nanotechnol. Biol. Med. 2010, 6, 753–759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, C.-C.; Lin, H.-Y.; Chen, H.-C.; Yu, M.-W.; Lee, M.-H. Stability and characterization of phospholipid-based curcumin-encapsulated microemulsions. Food Chem. 2009, 116, 923–928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friedrich, I.; Müller-Goymann, C.C. Characterization of solidified reverse micellar solutions (SRMS) and production development of SRMS-based nanosuspensions. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2003, 56, 111–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McClements, J.D. Food Emulsions: Principles, Practices, and Techniques, 2nd ed.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Kumari, S.; Pathak, K. Cavamax W7 composite psoralen ethosomal gel versus cavamax W7 psoralen solid complex gel for topical delivery: A comparative evaluation. Int. J. Pharm. Investig. 2013, 3, 171–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clogston, J.D.; Patri, A.K. Zeta potential measurement. Methods Mol. Biol. 2011, 697, 63–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matsaridou, I.; Barmpalexis, P.; Salis, A.; Nikolakakis, I. The influence of surfactant HLB and oil/surfactant ratio on the formation and properties of self-emulsifying pellets and microemulsion reconstitution. AAPS PharmSciTech 2012, 13, 1319–1330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernanda, P. Methods used in the study of the physical properties of fats. In Structure-Function Analysis of Edible Fats, 2nd ed.; Marangoni, A.G., Ed.; AOCS Press: Urbana, IL, USA, 2018; Chapter 11; pp. 327–328. [Google Scholar]
- Larsson, K. Classification of glyceride crystal forms. Acta Chem. Scand. 1966, 20, 2555–2560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Small, D.M. Handbook of Lipid Research; Plenum Press: New York, NY, USA; London, UK, 1966. [Google Scholar]

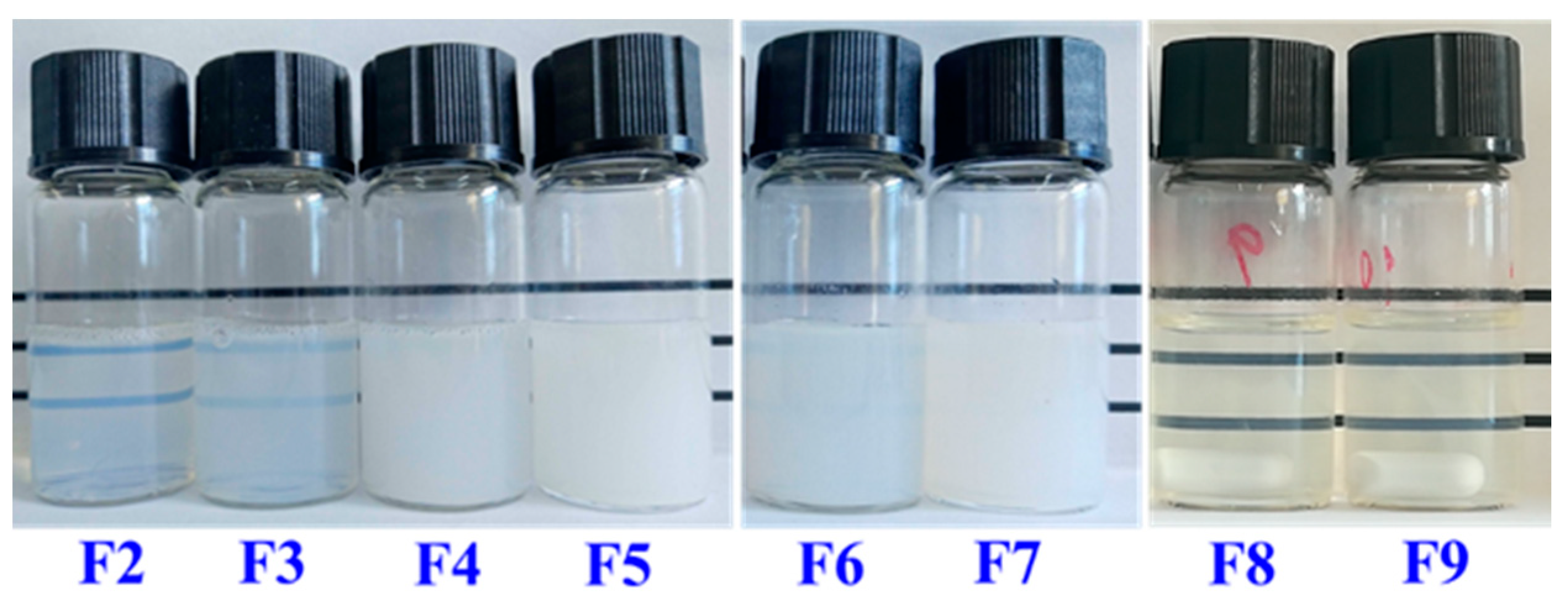

| Lipid | F 1 | Lecithin/T80 | Z-Average (nm) | PDI | Zeta (mV) 2 | Visual Stability |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| GMS | F1 | 1:3 | 91 ± 4 | 0.39 ± 0.01 | ND | Precipitate |
| F2 | 1:2 | 178 ± 3 | 0.32 ± 0.03 | ND | Stable for 2 weeks | |
| F3 | 1:1 | 290 ± 8 | 0.30 ± 0.01 | ND | Stable for 1 month | |
| F4 | 2:1 | 425 ± 8 | 0.28 ± 0.01 | −25.60 ± 2.50 | Stable for 2 months | |
| F5 | 3:1 | 473 ± 19 | 0.27 ± 0.01 | −34.10 ± 2.00 | Stable for 2 months | |
| 1,3-LP | F6 | 2:1 | 300 ± 5 | 0.26 ± 0.01 | −24.50 ± 1.42 | Stable for 2 months |
| F7 | 3:1 | 327 ± 4 | 0.28 ± 0.01 | −29.50 ± 1.85 | Stable for 2 months | |
| PPP | F8 | 2:1 | 38 ± 2 | 0.25 ± 0.02 | −22.00 ± 2.91 | Stable for 2 months |
| F9 | 3:1 | 38 ± 1 | 0.26 ± 0.01 | −24.50 ± 1.51 | Stable for 2 months |
| Lipid | F 1 | Thymol/Lipid (%) | Z-Average (nm) | PDI | Zeta (mV) | EE (%) 2 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Day 0 | Day 60 | ||||||
| GMS | F10 | 4 | 582 ± 5 | 0.24 ± 0.05 | −14.30 ± 0.25 | 99 | 85 |
| F11 | 8 | 591 ± 4 | 0.27 ± 0.01 | −16.50 ± 1.15 | 99 | ND | |
| F12 | 12 | 620 ± 14 | 0.26 ± 0.02 | −12.60 ± 0.45 | 99 | ND | |
| F13 | 16 | 675 ± 16 | 0.33 ± 0.03 | −15.60 ± 0.55 | ND | ND | |
| 1,3-LP | F14 | 4 | 265 ± 1 | 0.28 ± 0.01 | −14.20 ± 0.40 | >99/ | >99 |
| F15 | 8 | 311 ± 3 | 0.22 ± 0.02 | −17.80 ± 1.22 | >99/ | >99 | |
| F16 | 12 | 379 ± 5 | 0.26 ± 0.01 | −14.60± 2.59 | >99/ | >99 | |
| F17 | 16 | 410 ± 6 | 0.15 ± 0.06 | −16.00 ± 0.20 | >99 | >99 | |
| F18 | 20 | 476 ± 7 | 0.22 ± 0.01 | −17.60 ± 0.50 | 99 | ND | |
| F19 | 24 | 510 ± 6 | 0.28 ± 0.03 | −18.20 ± 1.17 | 98 | ND | |
| PPP | F20 | 4 | 31 ± 0 | 0.15 ± 0.01 | −11.70 ± 0.95 | >99 | >99 |
| F21 | 8 | 39 ± 2 | 0.25 ± 0.01 | −13.30 ± 0.78 | >99 | 98 | |
| F22 | 12 | 46 ± 2 | 0.26 ± 0.01 | −13.00 ± 0.55 | >99 | 95 | |
| F23 | 16 | 58 ± 4 | 0.32 ± 0.05 | −15.90 ± 1.05 | ND | ND | |
| F24 | 20 | 97 ± 1 | 0.41 ± 0.01 | −18.50 ± 0.36 | ND | ND | |
| F25 | 24 | 94 ± 1 | 0.79 ± 0.01 | −26.60 ± 1.67 | ND | ND | |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Shi, H.; Huang, S.; He, J.; Han, L.; Zhang, W.; Zhong, Q. 1-Laurin-3-Palmitin as a Novel Matrix of Solid Lipid Particles: Higher Loading Capacity of Thymol and Better Stability of Dispersions Than Those of Glyceryl Monostearate and Glyceryl Tripalmitate. Nanomaterials 2019, 9, 489. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano9040489
Shi H, Huang S, He J, Han L, Zhang W, Zhong Q. 1-Laurin-3-Palmitin as a Novel Matrix of Solid Lipid Particles: Higher Loading Capacity of Thymol and Better Stability of Dispersions Than Those of Glyceryl Monostearate and Glyceryl Tripalmitate. Nanomaterials. 2019; 9(4):489. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano9040489
Chicago/Turabian StyleShi, Hao, Shuangshuang Huang, Junbo He, Lijuan Han, Weinong Zhang, and Qixin Zhong. 2019. "1-Laurin-3-Palmitin as a Novel Matrix of Solid Lipid Particles: Higher Loading Capacity of Thymol and Better Stability of Dispersions Than Those of Glyceryl Monostearate and Glyceryl Tripalmitate" Nanomaterials 9, no. 4: 489. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano9040489
APA StyleShi, H., Huang, S., He, J., Han, L., Zhang, W., & Zhong, Q. (2019). 1-Laurin-3-Palmitin as a Novel Matrix of Solid Lipid Particles: Higher Loading Capacity of Thymol and Better Stability of Dispersions Than Those of Glyceryl Monostearate and Glyceryl Tripalmitate. Nanomaterials, 9(4), 489. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano9040489






