Classification of Children’s Sitting Postures Using Machine Learning Algorithms
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Related Work
2.1. Sitting Posture Classification
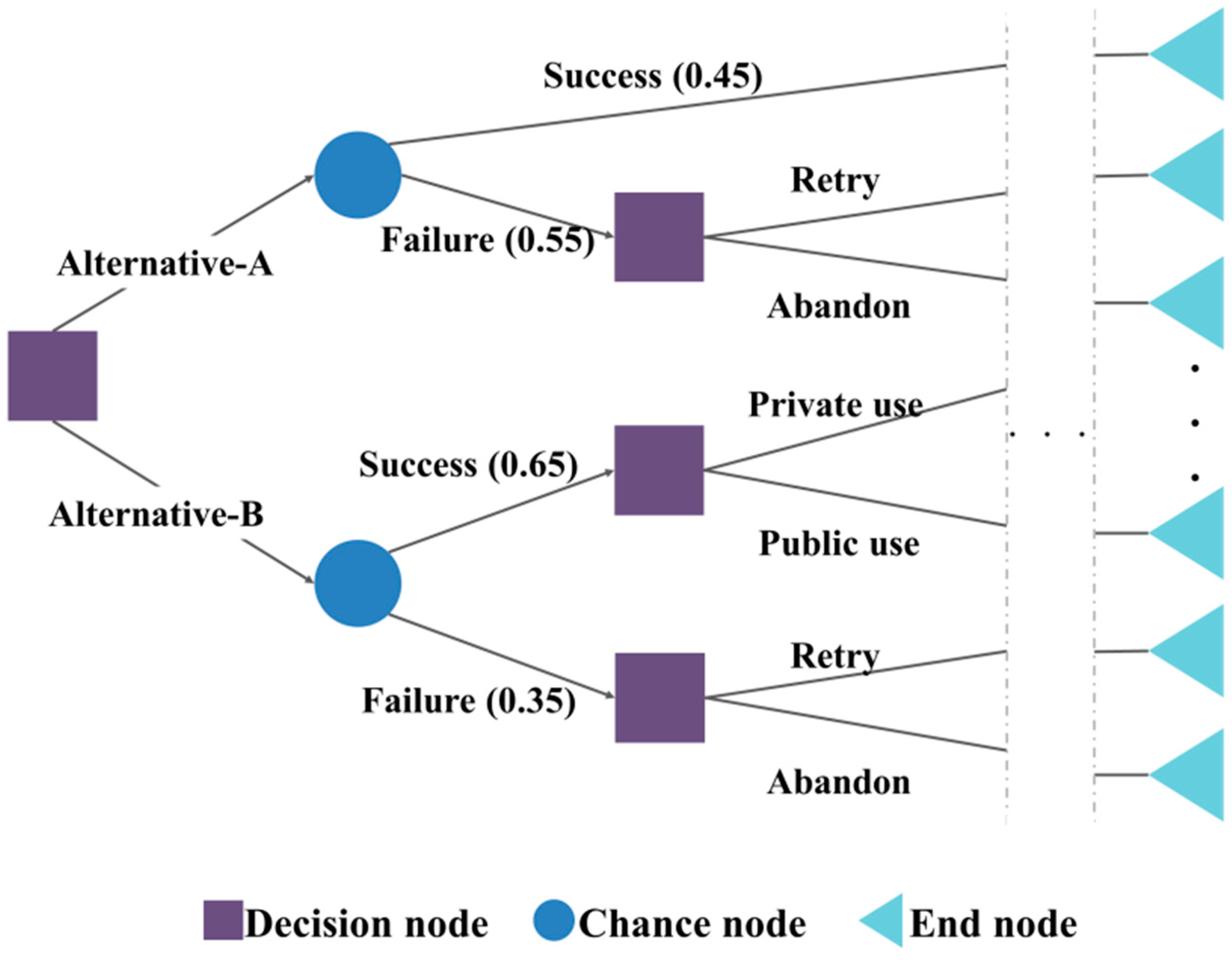
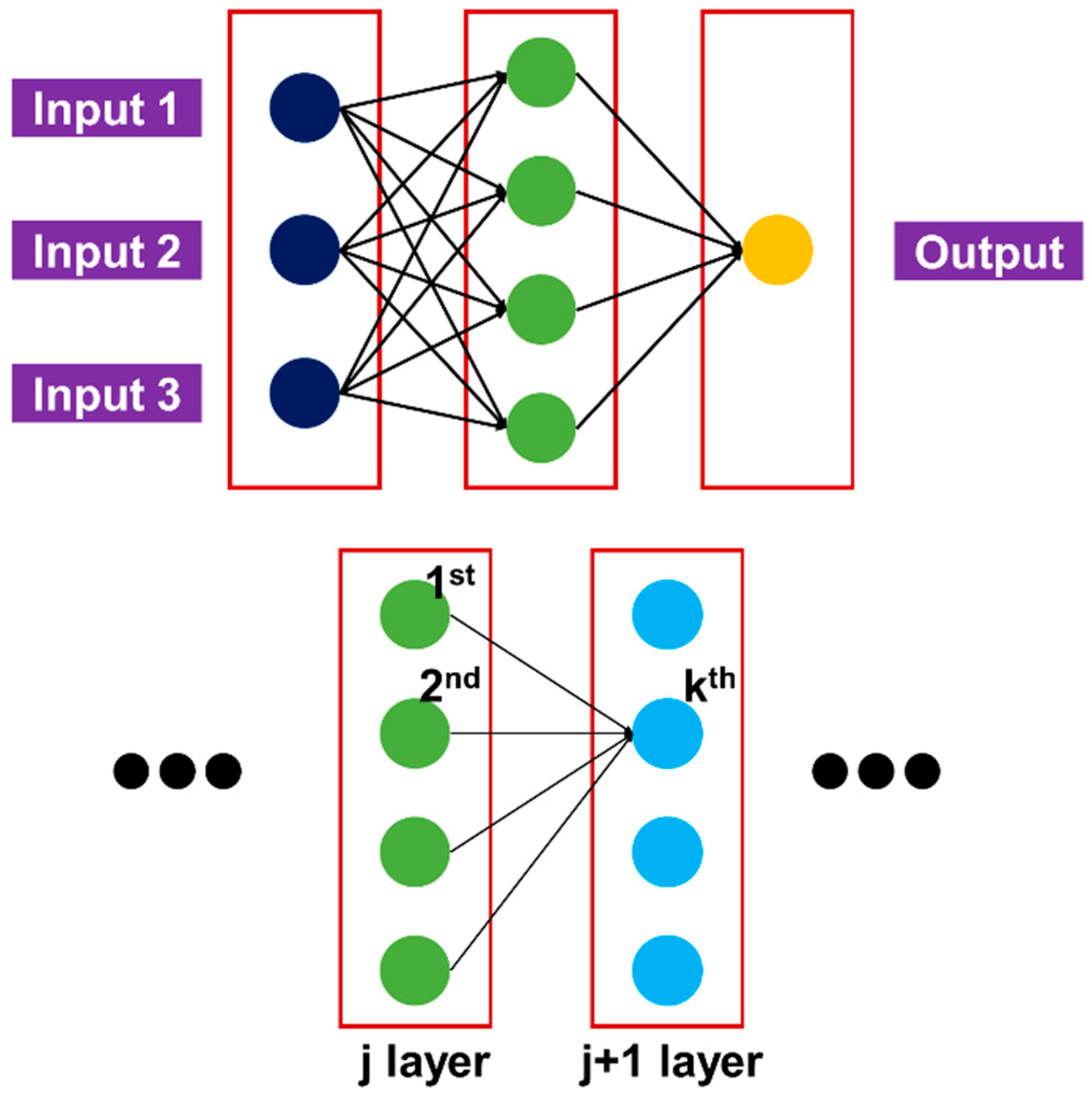
2.2. Learning Algorithm
3. Methods
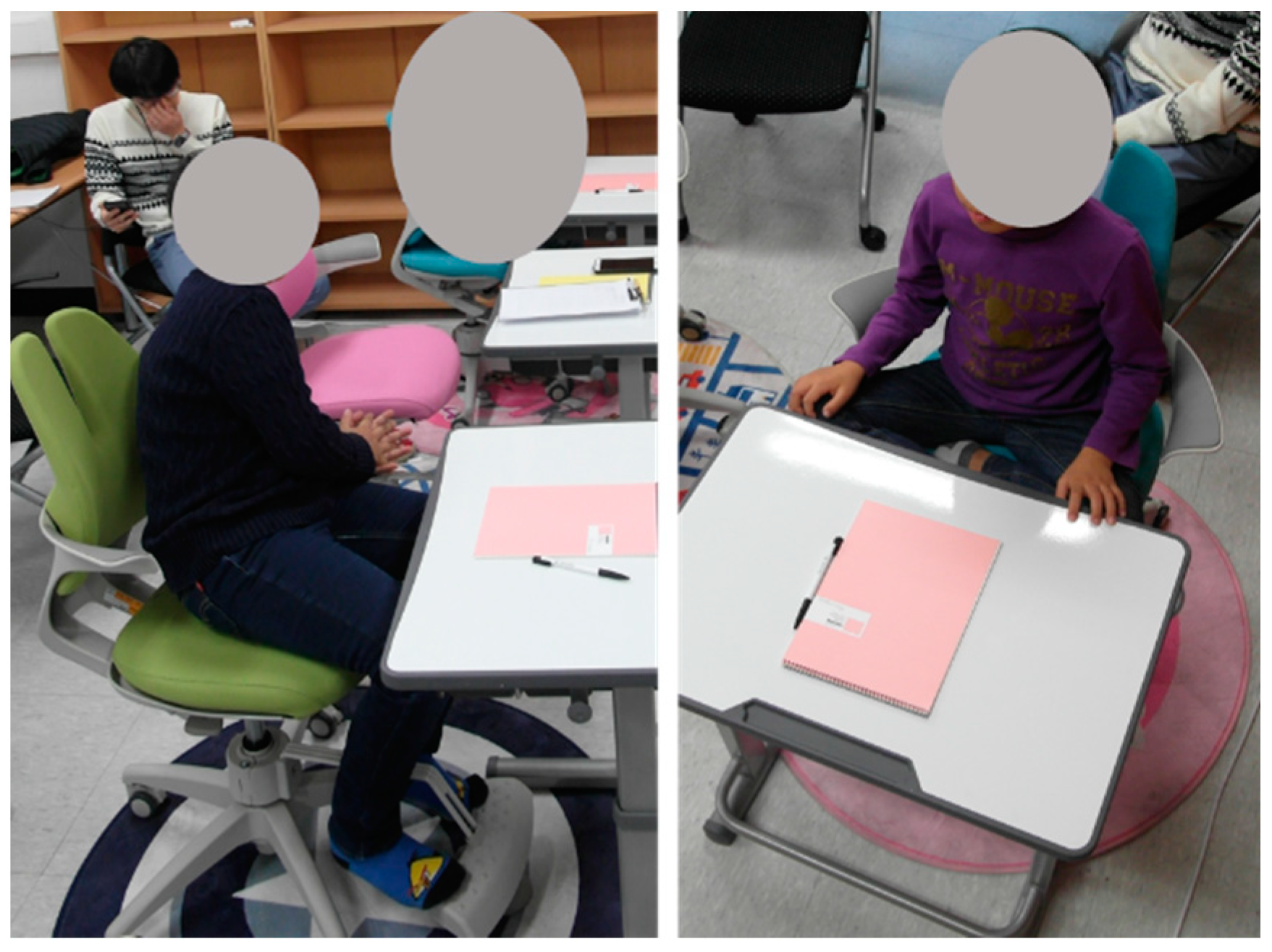
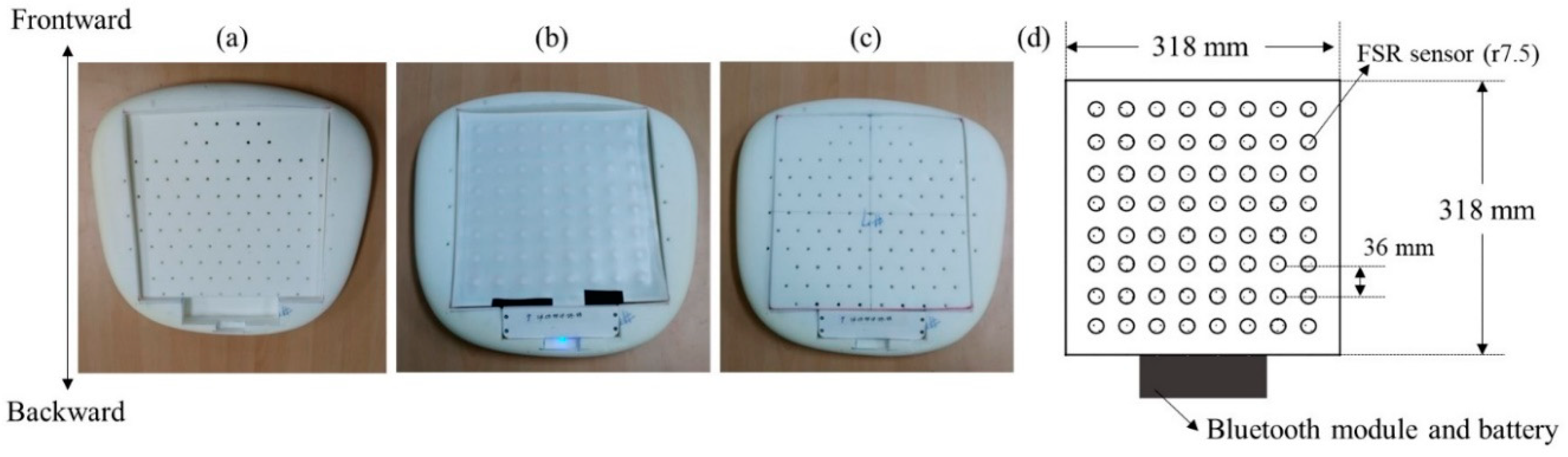
3.1. Sensor Apparatus
3.2. Participants
3.3. Selected Sitting Postures
3.4. Data Collection
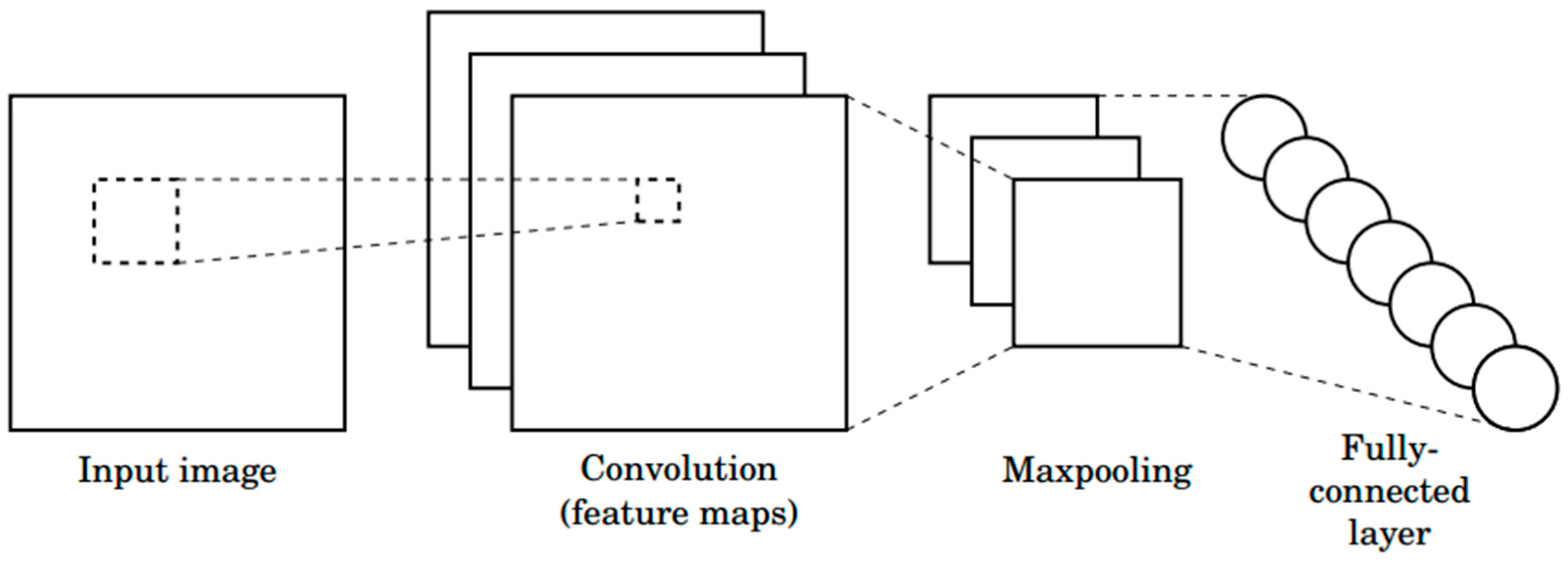
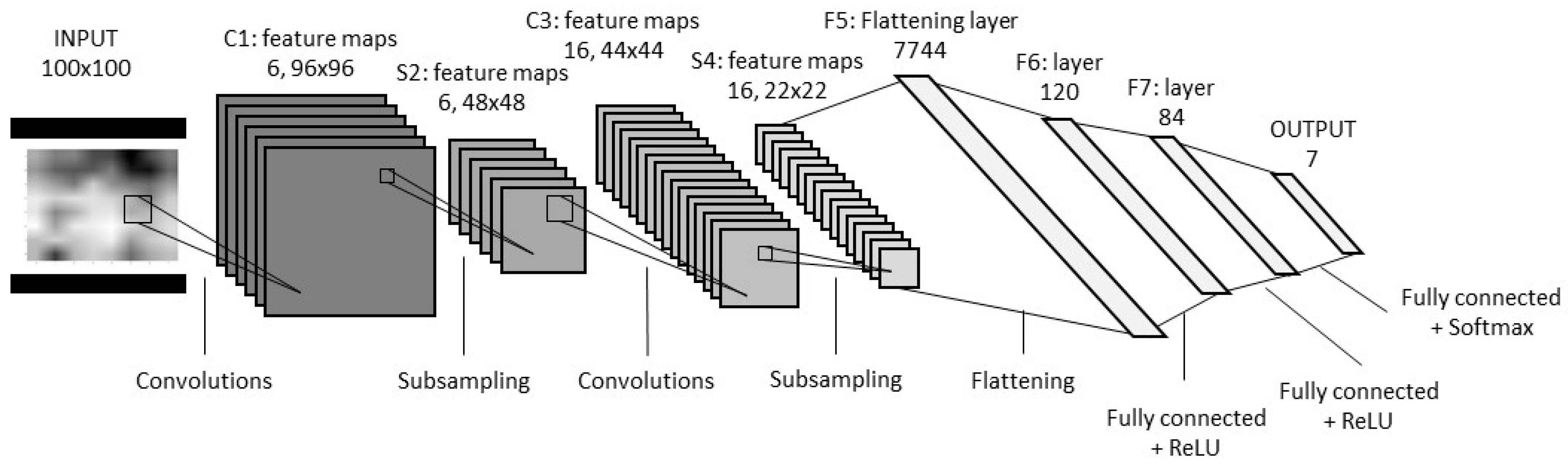
3.5. Sitting Posture Classification Model: LeNet-5
3.6. Training and Test Procedure
4. Results
4.1. Results Comparison with Individual Validation
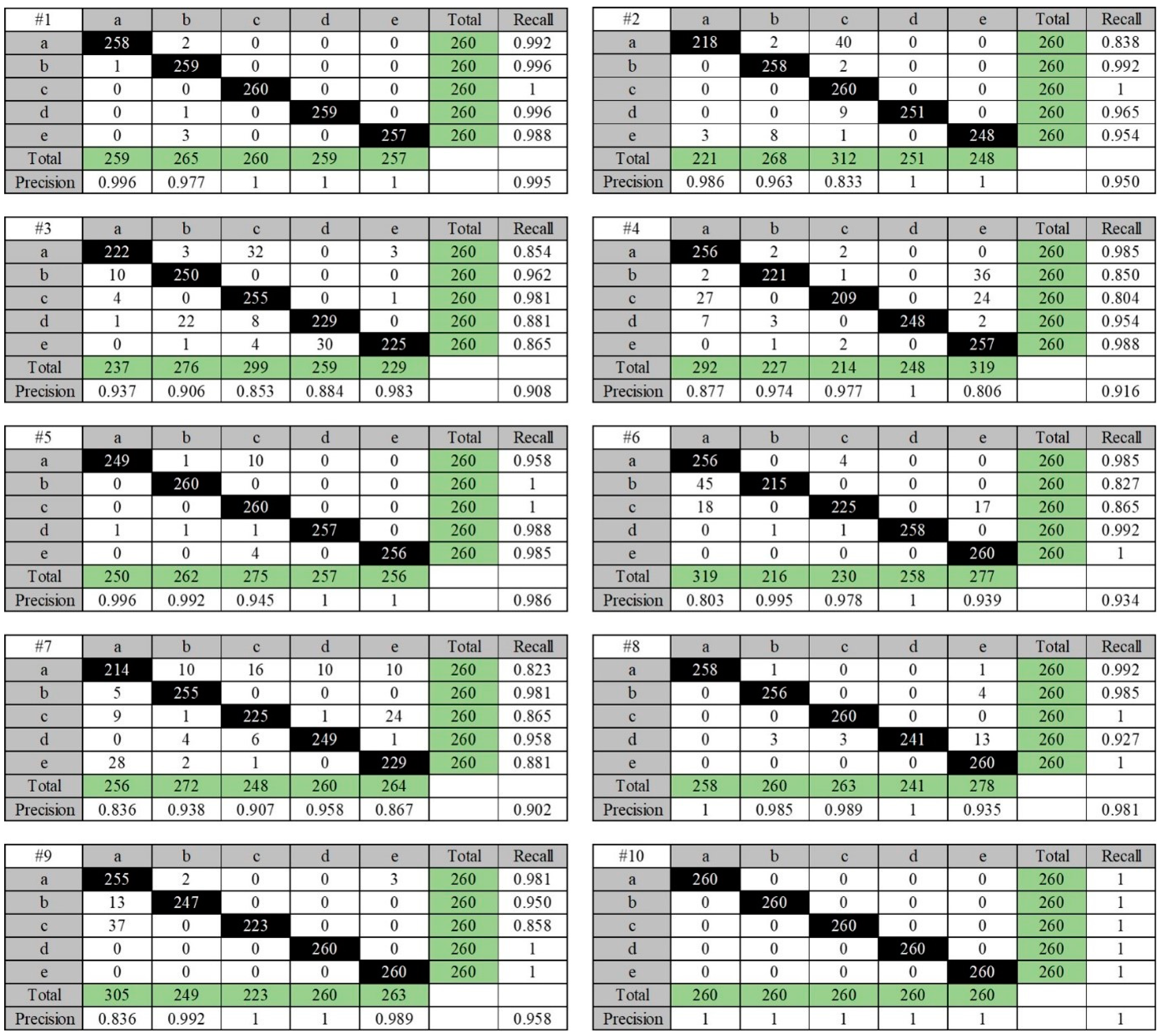
4.2. Results of Confusion Matrix for CNN
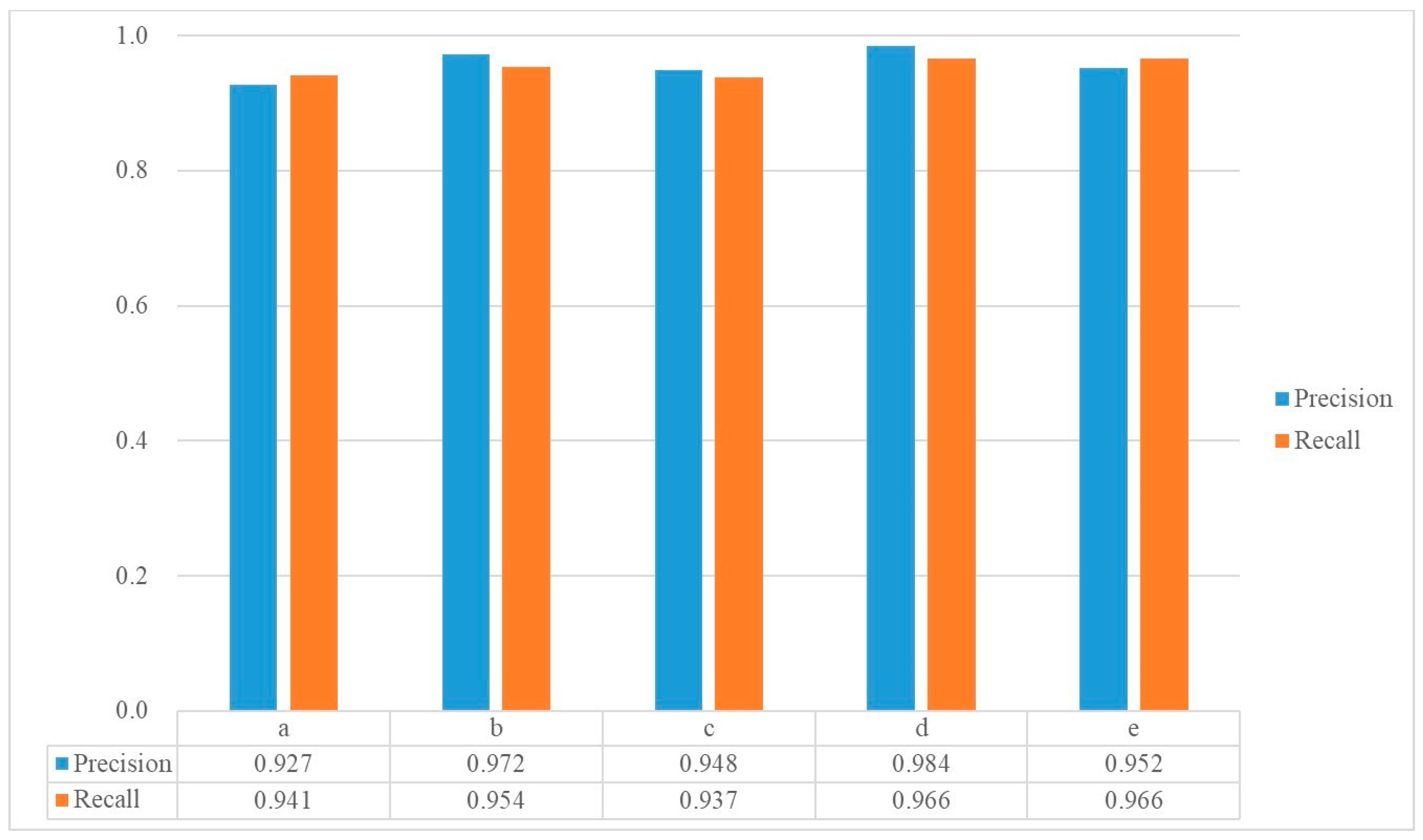
4.3. Relationship between Group of Body Weight and Accuracy
5. Discussion
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| CNN | Convolutional neural networks |
| NB | Naïve Bayes Classifier |
| MLR | Multinomial Logistic Regression |
| DT | Decision Tree |
| NN | Neural Network |
| SVM | Support Vector Machine |
| TP | True positive |
| FP | False positive |
| FN | False negative |
| TN | True negative |
| Pa | Precision in posture (a) |
| Pb | Precision in posture (b) |
| Pc | Precision in posture (c) |
| Pd | Precision in posture (d) |
| Pe | Precision in posture (e) |
| Ra | Recall in posture (a) |
| Rb | Recall in posture (b) |
| Rc | Recall in posture (c) |
| Rd | Recall in posture (d) |
| Re | Recall in posture (e) |
References
- Dunstan, D.; Barr, E.; Healy, G.; Salmon, J.; Shaw, J.; Balkau, B.; Magliano, D.; Cameron, A.; Zimmet, P.; Owen, N. Television viewing time and mortality: The Australian diabetes, obesity and lifestyle study (AusDiab). Circulation 2010, 121, 384–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hamilton, M.T.; Hamilton, D.G.; Zderic, T.W. Role of low energy expenditure and sitting in obesity, metabolic syndrome, type 2 diabetes, and cardiovascular disease. Diabetes 2007, 56, 2655–2667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Healy, G.N.; Wijndaele, K.; Dunstan, D.W.; Shaw, J.E.; Salmon, J.; Zimmet, P.Z.; Owen, N. Objectively measured sedentary time, physical activity, and metabolic risk: The Australian Diabetes, Obesity and Lifestyle Study (AusDiab). Diabetes Care 2008, 31, 369–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Inoue, M.; Yamamoto, S.; Kurahashi, N.; Iwasaki, M.; Sasazuki, S.; Tsugane, S.; Japan Public Health Center-based Prospective Study Group. Daily total physical activity level and total cancer risk in men and women: Results from a large-scale population-based cohort study in Japan. Am. J. Epidemiol. 2008, 168, 391–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’sullivan, P.B.; Grahamslaw, K.M.; Kendell, M.; Lapenskie, S.C.; Möller, N.E.; Richards, K.V. The effect of different standing and sitting postures on trunk muscle activity in a pain-free population. Spine 2002, 27, 1238–1244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, M.; Hajizadeh, K.; Gibson, I.; Lee, T. Analysis of compressive load on intervertebral joint in standing and sitting postures. Technol. Health Care 2016, 24, 215–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grimmer, K.; Nyland, L.; Milanese, S. Longitudinal investigation of low back pain in Australian adolescents: A five-year study. Physiother. Res. Int. 2006, 11, 161–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benocci, M.; Farella, E.; Benini, L. A Context-Aware Smart Seat. In Proceedings of the 2011 4th IEEE International Workshop on Advances in Sensors and Interfaces (IWASI), Savelletri di Fasano, Italy, 28–29 June 2011; pp. 104–109. [Google Scholar]
- Meyer, J.; Arnrich, B.; Schumm, J.; Troster, G. Design and modeling of a textile pressure sensor for sitting posture classification. IEEE Sens. J. 2010, 10, 1391–1398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mota, S.; Picard, R.W. Automated Posture Analysis for Detecting Learner’s Interest Level. In Proceedings of the 2003 Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Workshop (CVPRW’03), Madison, WI, USA, 28–29 June 2003; p. 49. [Google Scholar]
- Glowacz, A. Acoustic based fault diagnosis of three-phase induction motor. Appl. Acoust. 2018, 137, 82–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Sun, Z.; Chen, Y. Fault detection using the clustering-kNN rule for gas sensor arrays. Sensors 2016, 16, 2069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dit Leksir, Y.L.; Mansour, M.; Moussaoui, A. Localization of thermal anomalies in electrical equipment using Infrared Thermography and support vector machine. Infrared Phys. Technol. 2017, 89, 120–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Yang, J.; Wang, K.; Wang, Z. Wind power prediction considering nonlinear atmospheric disturbances. Energies 2015, 8, 475–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehta, D.; Siddiqui, M.F.H.; Javaid, A.Y. Facial Emotion Recognition: A Survey and Real-World User Experiences in Mixed Reality. Sensors 2018, 18, 416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ran, L.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Yang, T. Convolutional neural network-based robot navigation using uncalibrated spherical images. Sensors 2017, 17, 1341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rundo, F.; Conoci, S.; Ortis, A.; Battiato, S. An Advanced Bio-Inspired PhotoPlethysmoGraphy (PPG) and ECG Pattern Recognition System for Medical Assessment. Sensors 2018, 18, 405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.-H.; Zhao, X.-P.; Wu, J.-X.; Xie, Y.-Y.; Zhang, Y.-H. Motor Fault Diagnosis Based on Short-time Fourier Transform and Convolutional Neural Network. Chin. J. Mech. Eng. 2017, 30, 1357–1368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Punch, S. Research with children: The same or different from research with adults? Childhood 2002, 9, 321–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeats, B. Factors that may influence the postural health of schoolchildren (K-12). Work 1997, 9, 45–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harreby, M.; Neergaard, K.; Hesselsøe, G.; Kjer, J. Are radiologic changes in the thoracic and lumbar spine of adolescents risk factors for low back pain in adults? A 25-year prospective cohort study of 640 school children. Spine 1995, 20, 2298–2302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boulay, B.; Brémond, F.; Thonnat, M. Posture Recognition with a 3d Human Model. In Proceedings of the IEE International Symposium on Imaging for Crime Detection and Prevention (ICDP), London, UK, 7–8 June 2005; pp. 135–138. [Google Scholar]
- Dunne, L.E.; Walsh, P.; Hermann, S.; Smyth, B.; Caulfield, B. Wearable monitoring of seated spinal posture. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Circuits Syst. 2008, 2, 97–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Knight, J.F.; Bristow, H.W.; Anastopoulou, S.; Baber, C.; Schwirtz, A.; Arvanitis, T.N. Uses of accelerometer data collected from a wearable system. Pers. Ubiquitous Comput. 2007, 11, 117–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foerster, F.; Smeja, M.; Fahrenberg, J. Detection of posture and motion by accelerometry: A validation study in ambulatory monitoring. Comput. Hum. Behav. 1999, 15, 571–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, W.; Huang, M.-C.; Amini, N.; He, L.; Sarrafzadeh, M. Ecushion: A textile pressure sensor array design and calibration for sitting posture analysis. IEEE Sens. J. 2013, 13, 3926–3934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, H.; Park, S. Estimation of sitting posture by using the combination of ground reaction force. J. Mech. Sci. Technol. 2015, 29, 1657–1662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, J.; Li, W.; Li, J.; Ge, Y.; Bao, C. Sitting Posture Recognition based on data fusion on pressure cushion. Indones. J. Electr. Eng. Comput. Sci. 2013, 11, 1769–1775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamiya, K.; Kudo, M.; Nonaka, H.; Toyama, J. Sitting Posture Analysis by Pressure Sensors. In Proceedings of the 19th International Conference on Pattern Recognition (ICPR 2008), Tampa, FL, USA, 8–11 December 2008; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, C.; Li, W.; Gravina, R.; Fortino, G. Activity Recognition and Monitoring for Smart Wheelchair Users. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE 20th International Conference on Computer Supported Cooperative Work in Design (CSCWD), Nanchang, China, 4–6 May 2016; pp. 664–669. [Google Scholar]
- Tan, H.Z.; Slivovsky, L.A.; Pentland, A. A sensing chair using pressure distribution sensors. IEEE/ASME Trans. Mech. 2001, 6, 261–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xu, L.; Chen, G.; Wang, J.; Shen, R.; Zhao, S. A Sensing Cushion Using Simple Pressure Distribution Sensors. In Proceedings of the 2012 IEEE Conference on Multisensor Fusion and Integration for Intelligent Systems (MFI), Hamburg, Germany, 13–15 September 2012; pp. 451–456. [Google Scholar]
- Roh, J.; Park, H.-J.; Lee, K.J.; Hyeong, J.; Kim, S.; Lee, B. Sitting Posture Monitoring System Based on a Low-Cost Load Cell Using Machine Learning. Sensors 2018, 18, 208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- LeCun, Y.; Bottou, L.; Bengio, Y.; Haffner, P. Gradient-based learning applied to document recognition. Proc. IEEE 1998, 86, 2278–2324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lee, D.D.; Seung, H.S. A neural network based head tracking system. In Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems; MIT Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 1998; pp. 908–914. [Google Scholar]
- Nowlan, S.J.; Platt, J.C. A convolutional neural network hand tracker. In Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems; MIT Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 1995; pp. 901–908. [Google Scholar]
- Fasel, B. Robust Face Analysis using Convolutional Neural Networks. In Proceedings of the 16th International Conference on Pattern Recognition (ICPR 2002), Quebec City, QC, Canada, 11–15 August 2002; pp. 40–43. [Google Scholar]
- McCallum, A.; Nigam, K. A Comparison of Event Models for Naive Bayes Text Classification. In Proceedings of the AAAI-98 Workshop on Learning for Text Categorization, Madison, WI, USA, 26–27 July 1998; pp. 41–48. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, H. The optimality of naive Bayes. In Proceedings of the Seventeenth International Florida Artificial Research Society Conference, Miami Beach, FL, USA, 17–19 May 2004. [Google Scholar]
- McFadden, D. Conditional logit analysis of qualitative choice behavior. In Frontiers in Economics; Zarembka, P., Ed.; Academic Press: Cambrisge, MA, USA, 1973; pp. 105–142. [Google Scholar]
- Tavakoli, H. A Dictionary of Research Methodology and Statistics in Applied Linguistics; Rahnama Press: Tehran, Iran, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Quinlan, J.R. Induction of decision trees. Mach. Learn. 1986, 1, 81–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kamiński, B.; Jakubczyk, M.; Szufel, P. A framework for sensitivity analysis of decision trees. Central Eur. J. Oper. Res. 2018, 26, 135–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zurada, J.M. Introduction to Artificial Neural Systems; West Publishing Co.: St. Paul, MN, USA, 1992; Volume 8. [Google Scholar]
- Haykin, S. Network: A comprehensive foundation. Neural Netw. 2004, 2, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, C.-C.; Lin, C.-J. LIBSVM: A library for support vector machines. ACM Trans. Intell. Syst. Technol. 2011, 2, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cortes, C.; Vapnik, V. Support-vector networks. Mach. Learn. 1995, 20, 273–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lin, S.; Cai, L.; Lin, X.; Ji, R. Masked face detection via a modified LeNet. Neurocomputing 2016, 218, 197–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarvadevabhatla, R.K.; Babu, R.V. Freehand sketch recognition using deep features. arXiv, 2015; arXiv:1502.00254. [Google Scholar]
- Eiben, A.E.; Schoenauer, M. Evolutionary computing. Inf. Process. Lett. 2002, 82, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, C.; Li, W.; Gravina, R.; Cao, J.; Li, Q.; Fortino, G. Activity Level Assessment Using a Smart Cushion for People with a Sedentary Lifestyle. Sensors 2017, 17, 2269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caponetto, R.; Fortuna, L.; Graziani, S.; Xibilia, M. Genetic algorithms and applications in system engineering: A survey. Trans. Inst. Meas. Control 1993, 15, 143–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| No. of Pressure Sensors and Location of Installation | No. of Participants | No. of Sitting Conditions | Algorithm | Accuracy | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Seat (5) | 10 | 8 | Density-based clustering | 94.2% familiar | Bao et al. [28] |
| Seat (8 × 8) | 10 | 9 | SVM | 93.9% unfamiliar; 98.9% familiar | Kamiya et al. [29] |
| Seat (16 × 16) | 25 | 7 | Dynamic Time Warping (DTW) | 85.90% | W. Xu et al. [26] |
| Seat (4) | 9 | 7 | SVM | 97.20% | Roh et. al. [33] |
| Seat (4) and Backrest (1) * Kinetic sensor (3) and temperature sensor (1) | 7 | 6 | kNN | 92.7% unfamiliar | Benocci et al. [8] |
| Seat (6 × 8) and Backrest (2 × 8) | 7 | 9 | combines several Naïve Bayes classifiers | 82.3% unfamiliar | L. Xu et al. [32] |
| Seat (2) and Backrest (1) | 20 | 6 | DT; SVM; Multilayer Perception | Decision tree (99.5%); SVM (81.5%); MLP (99.7%) | Ma et al. [30] |
| Customized device: Seat (240; a total of 96 out of 240 sensor elements have been preselected), Backrest (1); Commercial device: Seat (32 × 32), Backrest (1) | 9 | 11 | Naïve Bayes classifier | Customized: only seat sensor: 55%; (with back sensor: 81%); ComfortMat: only seat sensor: 56%; (with back sensor: 84%) | Meyer et al. [9] |
| Seat (42 × 48) and Backrest (42 × 48) | 1 (single); 30 (multi) | 14 | PCA-based Algorithms | single-user system: over 95%; multi-user system: 96% (familiar user), 79% (unfamiliar user) | Tan et al. [31] |
| Sitting Posture | Front and Side Views of Sitting Postures | Description | Heat Map Images of Body Pressure Distribution |
|---|---|---|---|
| Sitting straight |  | Sitting with the upper body straight comfortably and putting both feet flat on the floor. Placing the hip to the deepest side on the seat |  |
| Lean left |  | Leaning the upper body to the left and the center of gravity is shifted to the left hip |  |
| Lean right |  | Leaning the upper body to the right and the center of gravity is shifted to the right hip |  |
| Sitting at the front of the chair |  | Sitting the front edge of the seat with the upper body straight comfortably |  |
| Sitting crossed-legged on the chair |  | Bending both knees inward and placing each foot on the knee of the opposite leg |  |
| Actual Class | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Positive | Negative | ||
| Predicted class | Positive | True positive (TP) | False positive (FP) |
| Negative | False negative (FN) | True negative (TN) | |
| CNN | NB | MLR | DT | NN | SVM | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 0.995 (0.994) | 0.848 (0.900) | 0.776 (0.993) | 0.873 (0.974) | 0.938 (0.994) | 0.981 (0.986) |
| 2 | 0.950 (0.997) | 0.704 (0.922) | 0.740 (0.990) | 0.716 (0.978) | 0.839 (0.997) | 0.890 (0.989) |
| 3 | 0.908 (0.994) | 0.872 (0.931) | 0.800 (0.992) | 0.743 (0.979) | 0.912 (0.995) | 0.941 (0.990) |
| 4 | 0.916 (0.997) | 0.902 (0.914) | 0.835 (0.994) | 0.726 (0.970) | 0.895 (0.996) | 0.926 (0.990) |
| 5 | 0.986 (0.997) | 0.968 (0.928) | 0.894 (0.993) | 0.797 (0.980) | 0.983 (0.997) | 0.976 (0.989) |
| 6 | 0.934 (0.995) | 0.853 (0.934) | 0.737 (0.990) | 0.776 (0.972) | 0.888 (0.997) | 0.901 (0.982) |
| 7 | 0.902 (0.995) | 0.656 (0.942) | 0.795 (0.992) | 0.711 (0.981) | 0.835 (0.995) | 0.824 (0.991) |
| 8 | 0.981 (0.994) | 0.965 (0.917) | 0.977 (0.987) | 0.906 (0.972) | 0.968 (0.992) | 0.991 (0.985) |
| 9 | 0.958 (0.997) | 0.943 (0.921) | 0.952 (0.989) | 0.937 (0.972) | 0.968 (0.994) | 0.990 (0.988) |
| 10 | 1.000 (0.995) | 0.995 (0.912) | 0.948 (0.991) | 0.755 (0.968) | 0.986 (0.997) | 0.999 (0.986) |
| Ave. | 0.953 (0.995) | 0.871 (0.922) | 0.845 (0.991) | 0.794 (0.975) | 0.921 (0.995) | 0.942 (0.988) |
| Std. | 0.037 (0.001) | 0.113 (0.012) | 0.091 (0.002) | 0.083 (0.004) | 0.057 (0.002) | 0.057 (0.003) |
| 20 kg | 30 kg | 40 kg | ANOVA | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean | Std. | Mean | Std. | Mean | Std. | F | p | |
| Pa | 0.883 | 0.051 | 0.875 | 0.098 | 0.998 | 0.002 | 0.046 | 0.883 |
| Pb | 0.939 | 0.034 | 0.983 | 0.018 | 0.989 | 0.010 | 0.044 | 0.939 |
| Pc | 0.912 | 0.062 | 0.937 | 0.091 | 0.984 | 0.026 | 0.349 | 0.912 |
| Pd | 0.947 | 0.059 | 1.000 | 0.000 | 1.000 | 0.000 | 0.117 | 0.947 |
| Pe | 0.885 | 0.090 | 0.976 | 0.033 | 0.984 | 0.032 | 0.108 | 0.885 |
| Ra | 0.887 | 0.086 | 0.935 | 0.083 | 0.986 | 0.019 | 0.212 | 0.887 |
| Rb | 0.931 | 0.071 | 0.923 | 0.086 | 0.995 | 0.007 | 0.270 | 0.931 |
| Rc | 0.883 | 0.090 | 0.908 | 0.080 | 1.000 | 0.000 | 0.099 | 0.883 |
| Rd | 0.931 | 0.043 | 0.986 | 0.018 | 0.978 | 0.034 | 0.163 | 0.931 |
| Re | 0.912 | 0.067 | 0.985 | 0.027 | 0.993 | 0.008 | 0.060 | 0.912 |
| Accuracy | 0.909 | 0.007 | 0.947 | 0.012 | 0.991 | 0.009 | 0.000 | 0.909 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kim, Y.M.; Son, Y.; Kim, W.; Jin, B.; Yun, M.H. Classification of Children’s Sitting Postures Using Machine Learning Algorithms. Appl. Sci. 2018, 8, 1280. https://doi.org/10.3390/app8081280
Kim YM, Son Y, Kim W, Jin B, Yun MH. Classification of Children’s Sitting Postures Using Machine Learning Algorithms. Applied Sciences. 2018; 8(8):1280. https://doi.org/10.3390/app8081280
Chicago/Turabian StyleKim, Yong Min, Youngdoo Son, Wonjoon Kim, Byungki Jin, and Myung Hwan Yun. 2018. "Classification of Children’s Sitting Postures Using Machine Learning Algorithms" Applied Sciences 8, no. 8: 1280. https://doi.org/10.3390/app8081280
APA StyleKim, Y. M., Son, Y., Kim, W., Jin, B., & Yun, M. H. (2018). Classification of Children’s Sitting Postures Using Machine Learning Algorithms. Applied Sciences, 8(8), 1280. https://doi.org/10.3390/app8081280







