Microwave-Assisted Synthesis of SiC Nanoparticles for the Efficient Adsorptive Removal of Nitroimidazole Antibiotics from Aqueous Solution
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Preparation of SiC Nanoparticles
2.2. Characterization
2.3. Equilibrium Studies
2.4. Kinetic and Equilibrium Models
- (i)
- The pseudo-first order kinetic model is given as follows [30]:where qt is the amount of nitroimidazoles adsorbed (mg) per unit mass (g) of the adsorbent at time t, and k1 is the rate constant in (min−1) of the pseudo-first order kinetics.
- (ii)
- The pseudo-second order kinetic model is given as follows [31]:where k2 is the rate constant in (g/(mg min)) of the pseudo-second order kinetics.
- (iii)
- The intra-particle diffusion kinetic model is given as follows [32]:where C is the intercept and Ki is the intra-particle diffusion rate constant (mg/(g·min1/2)).
- (i)
- The Langmuir isotherm model is given as follows [33]:where Qm is the maximum adsorption capacity (mg/g) that corresponds to monolayer coverage, and KL is the Langmuir isotherm constant (L/mg).
- (ii)
- The Freundlich isotherm model is given as follows [34]:where qe (mg/g) is the equilibrium nitroimidazole concentration on SiC NPs, while KF and 1/n are constants of the isotherm model.
- (iii)
- The Flory–Huggins model is given as follows [35]:where θ is the degree of surface coverage, nFH is the number of nitroimidazole molecules that occupy the adsorption sites, and KFH is the equilibrium constant of adsorption.
3. Results and Discussion
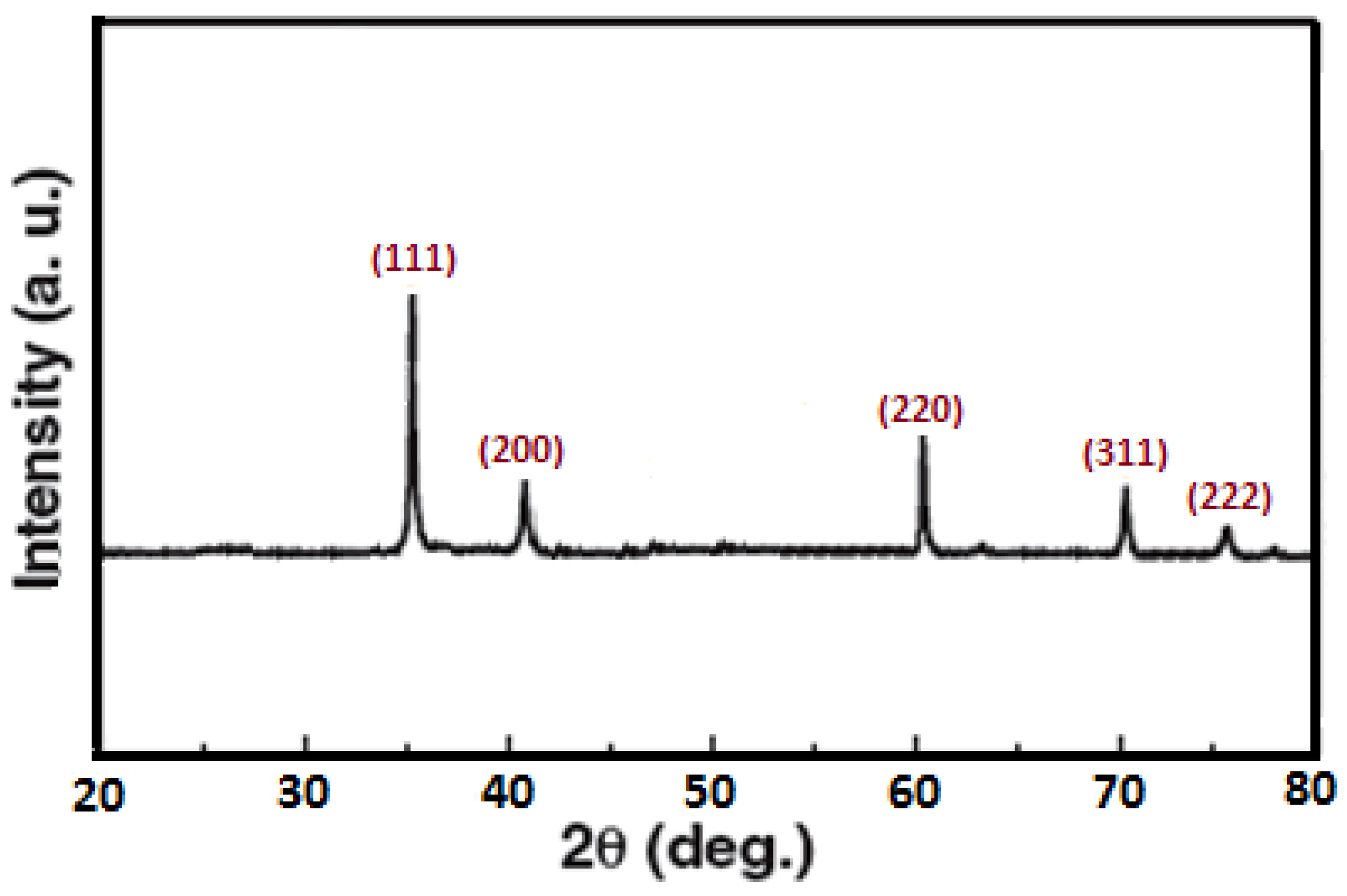
3.1. Characterization of SiC Nanoparticles
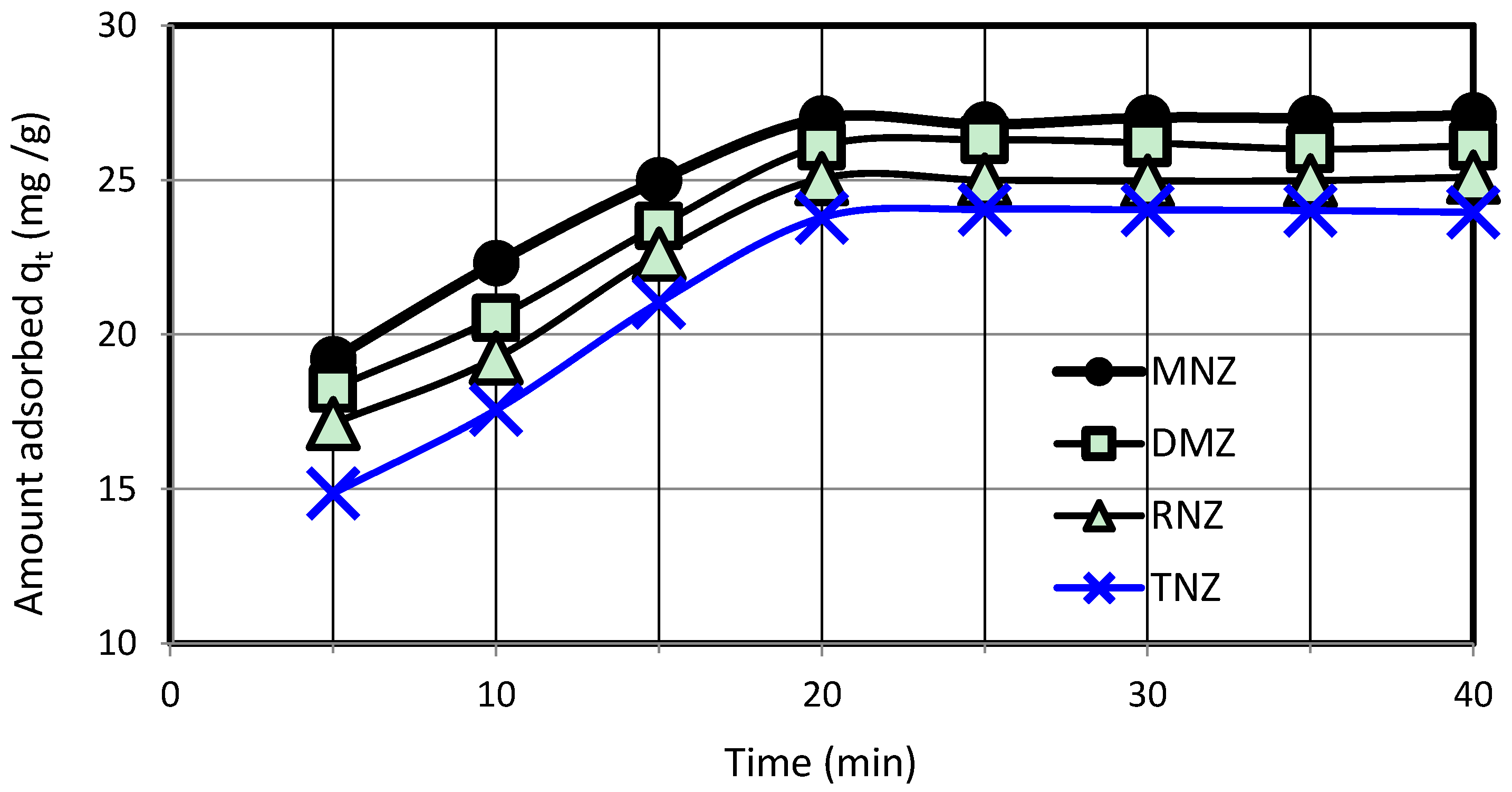
3.2. Adsorption Study
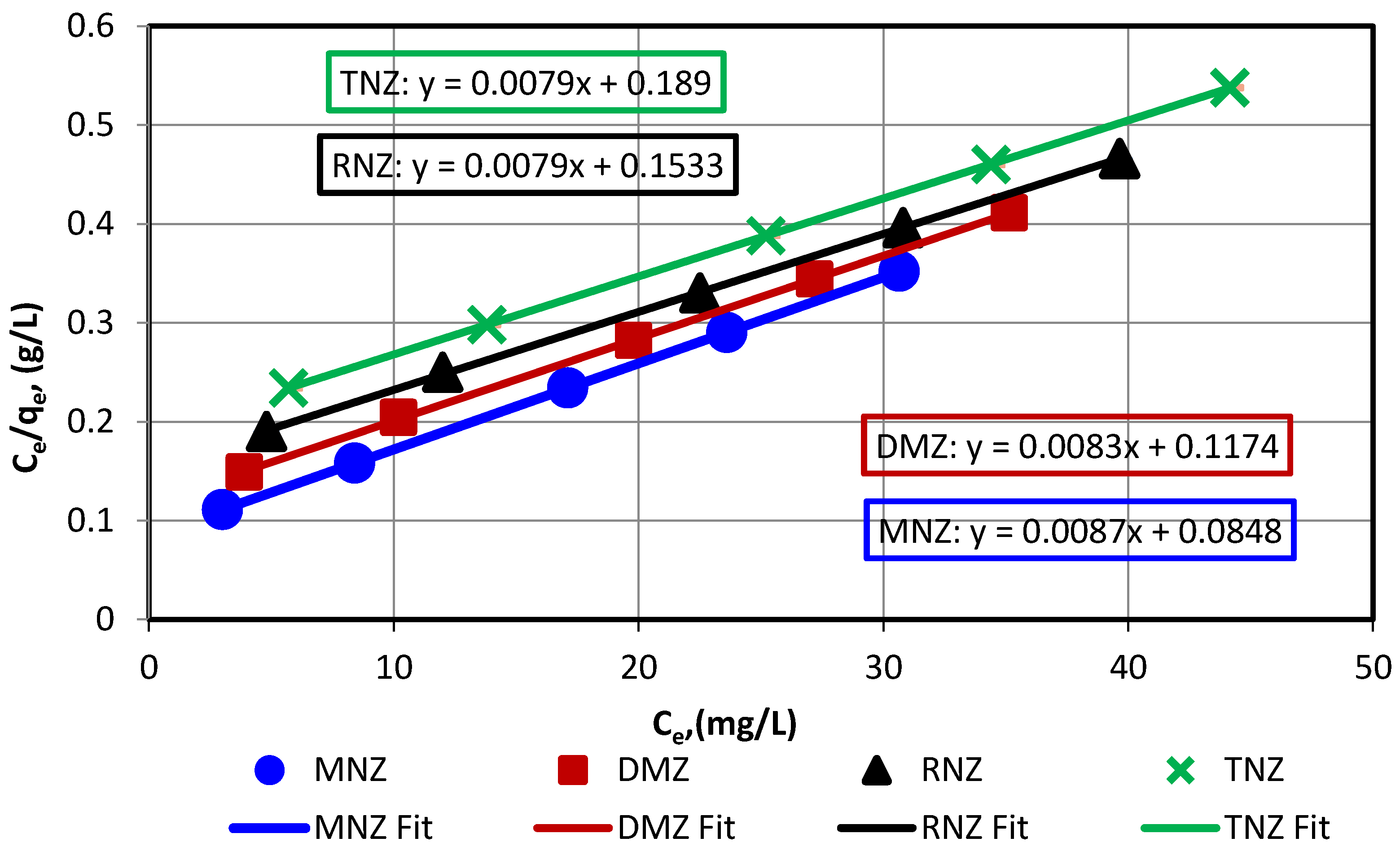
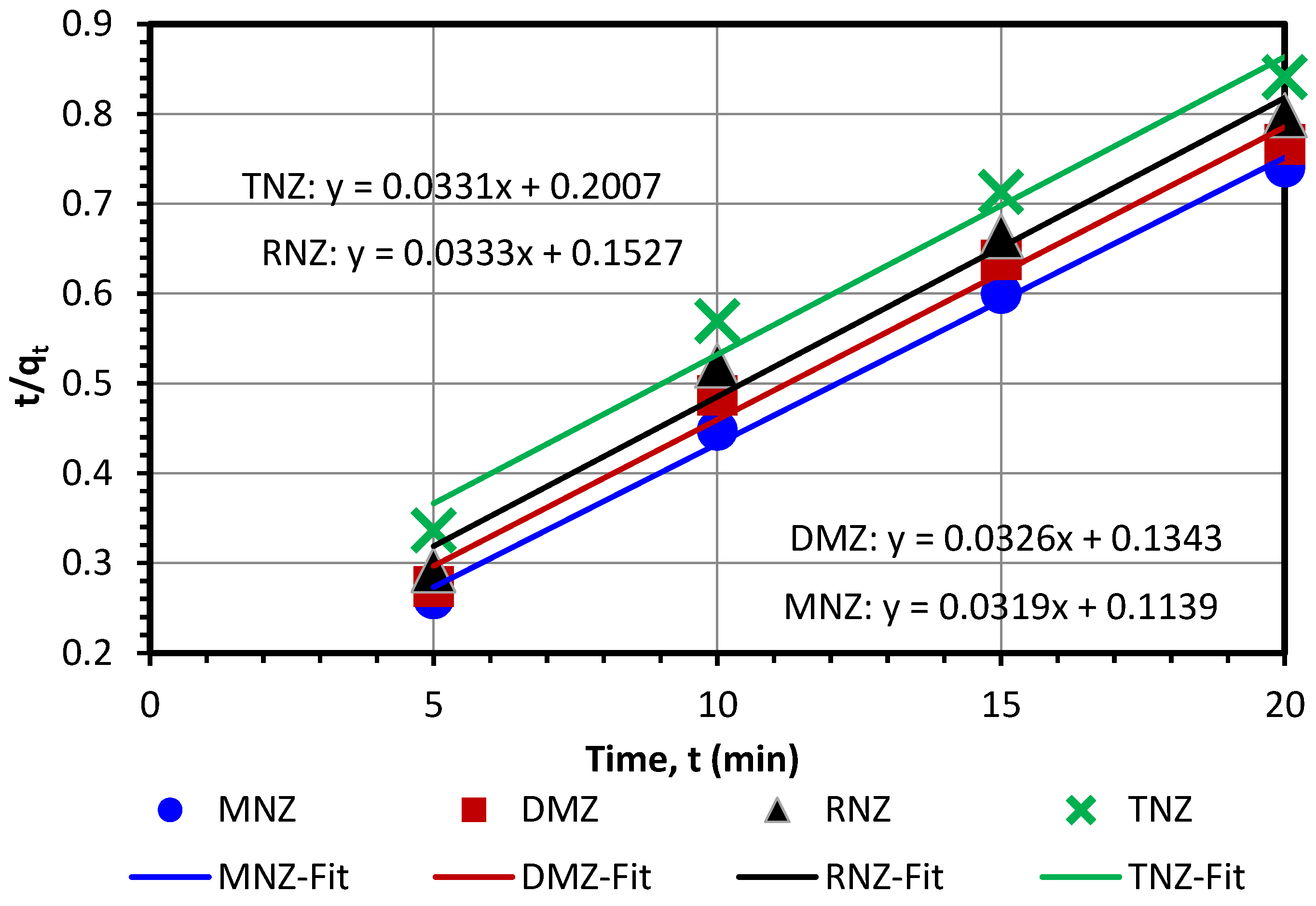
3.3. Investigation of Adsorption Isotherms and Kinetics
3.4. Comparison
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chang, X.; Meyer, M.T.; Liu, X.; Zhao, Q.; Chen, H.; Chen, J.-A.; Qiu, Z.; Yang, L.; Cao, J.; Shu, W. Determination of antibiotics in sewage from hospitals, nursery and slaughter house, wastewater treatment plant and source water in Chongqing region of three gorge reservoir in China. Environ. Pollut. 2010, 158, 1444–1450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Halling-Sørensen, B.; Nors Nielsen, S.; Lanzky, P.F.; Ingerslev, F.; Holten Lützhøft, H.C.; Jørgensen, S.E. Occurrence, fate and effects of pharmaceutical substances in the environment—A review. Chemosphere 1998, 36, 357–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aksu, Z.; Tunç, Ö. Application of biosorption for penicillin G removal: Comparison with activated carbon. Process Biochem. 2005, 40, 831–847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alcock, R.E.; Sweetman, A.; Jones, K.C. Assessment of organic contanhnant fate in waste water treatment plants I: Selected compounds and physicochemical properties. Chemosphere 1999, 38, 2247–2262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lau, A.H.; Lam, N.P.; Piscitelli, S.C.; Wilkes, L.; Danziger, L.H. Clinical pharmacokinetics of metronidazole and other nitroimidazole anti-infectives. Clin. Pharmacokinet. 1992, 23, 328–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tally, F.P.; Sullivan, C.E. Metronidazole: In vitro activity, pharmacology and efficacy in anaerobic bacterial infections. Pharmacother. J. Hum. Pharmacol. Drug Ther. 1981, 1, 28–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen, S.H.; Gerding, D.N.; Johnson, S.; Kelly, C.P.; Loo, V.G.; McDonald, L.C.; Pepin, J.; Wilcox, M.H. Clinical practice guidelines for clostridium difficile infection in adults: 2010 update by the society for healthcare epidemiology of America (SHEA) and the infectious diseases society of america (IDSA). Infect. Control Hosp. Epidemiol. 2010, 31, 431–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Olson, L.; Rodabaugh, D. Ronidazole in low concentrations in drinking water for treatment and development of immunity to swine dysentery. Am. J. Vet. Res. 1976, 37, 763–767. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Gunn-Moore, D.; Lalor, S. Treatment of diarrhoea in cats caused by Tritrichomonas foetus. Vet. Rec. 2011, 168, 56–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmed, M.J.; Theydan, S.K. Microwave assisted preparation of microporous activated carbon from siris seed pods for adsorption of metronidazole antibiotic. Chem. Eng. J. 2013, 214, 310–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, M.J.; Theydan, S.K. Microporous activated carbon from siris seed pods by microwave-induced koh activation for metronidazole adsorption. J. Anal. Appl. Pyrolysis 2013, 99, 101–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ocampo-Pérez, R.; Orellana-Garcia, F.; Sánchez-Polo, M.; Rivera-Utrilla, J.; Velo-Gala, I.; López-Ramón, M.V.; Alvarez-Merino, M.A. Nitroimidazoles adsorption on activated carbon cloth from aqueous solution. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2013, 401, 116–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Flores-Cano, J.V.; Sánchez-Polo, M.; Messoud, J.; Velo-Gala, I.; Ocampo-Pérez, R.; Rivera-Utrilla, J. Overall adsorption rate of metronidazole, dimetridazole and diatrizoate on activated carbons prepared from coffee residues and almond shells. J. Environ. Manag. 2016, 169, 116–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ding, H.; Bian, G. Adsorption of metronidazole in aqueous solution by fe-modified sepiolite. Desalin. Water Treat. 2015, 55, 1620–1628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rivera-Utrilla, J.; Prados-Joya, G.; Sánchez-Polo, M.; Ferro-García, M.A.; Bautista-Toledo, I. Removal of nitroimidazole antibiotics from aqueous solution by adsorption/bioadsorption on activated carbon. J. Hazard. Mater. 2009, 170, 298–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sánchez-Polo, M.; López-Peñalver, J.; Prados-Joya, G.; Ferro-García, M.A.; Rivera-Utrilla, J. Gamma irradiation of pharmaceutical compounds, nitroimidazoles, as a new alternative for water treatment. Water Res. 2009, 43, 4028–4036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johnson, M.B.; Mehrvar, M. Aqueous metronidazole degradation by UV/H2O2 process in single-and multi-lamp tubular photoreactors: Kinetics and reactor design. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2008, 47, 6525–6537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sánchez-Polo, M.; Rivera-Utrilla, J.; Prados-Joya, G.; Ferro-García, M.A.; Bautista-Toledo, I. Removal of pharmaceutical compounds, nitroimidazoles, from waters by using the ozone/carbon system. Water Res. 2008, 42, 4163–4171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shemer, H.; Kunukcu, Y.K.; Linden, K.G. Degradation of the pharmaceutical metronidazole via UV, fenton and photo-fenton processes. Chemosphere 2006, 63, 269–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ingerslev, F.; Halling-Sørensen, B. Biodegradability of metronidazole, olaquindox, and tylosin and formation of tylosin degradation products in aerobic soil–manure slurries. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2001, 48, 311–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Habib, M.J.; Asker, A.F. Complex formation between metronidazole and sodium urate: Effect on photodegradation of metronidazole. Pharm. Res. 1989, 6, 58–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Méndez-Díaz, J.D.; Prados-Joya, G.; Rivera-Utrilla, J.; Leyva-Ramos, R.; Sánchez-Polo, M.; Ferro-García, M.A.; Medellín-Castillo, N.A. Kinetic study of the adsorption of nitroimidazole antibiotics on activated carbons in aqueous phase. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2010, 345, 481–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, L.; Zhao, H.; Yan, Y.; Li, Z.; Tang, C. Synthesis and characterization of submicron silicon carbide powders with silicon and phenolic resin. Powder Technol. 2006, 169, 71–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raman, V.; Bahl, O.P.; Dhawan, U. Synthesis of silicon carbide through the sol-gel process from different precursors. J. Mater. Sci. 1995, 30, 2686–2693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larpkiattaworn, S.; Ngernchuklin, P.; Khongwong, W.; Pankurddee, N.; Wada, S. The influence of reaction parameters on the free si and c contents in the synthesis of nano-sized sic. Ceram. Int. 2006, 32, 899–904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.-J.; Chuang, C.-M. The effects of transition metals on carbothermal synthesis of β-sic powder. Ceram. Int. 2007, 33, 779–784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurtenbach, D.; Mitchell, B.S.; Zhang, H.; Ade, M.; Müller, E. Crystallization kinetics of amorphous silicon carbide derived from polymeric precursors. Thermochim. Acta 1999, 337, 155–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koc, R.; Glatzmaier, G.; Sibold, J. B-sic production by reacting silica gel with hydrocarbon gas. J. Mater. Sci. 2001, 36, 995–999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, R.; Rao, D.V.S.; Vankar, V.D. Growth of nanocrystalline β-silicon carbide and nanocrystalline silicon oxide nanoparticles by sol gel technique. Mater. Lett. 2008, 62, 3174–3177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fakhri, A.; Adami, S. Adsorption and thermodynamic study of cephalosporins antibiotics from aqueous solution onto mgo nanoparticles. J. Taiwan Inst. Chem. Eng. 2014, 45, 1001–1006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fakhri, A. Assessment of ethidium bromide and ethidium monoazide bromide removal from aqueous matrices by adsorption on cupric oxide nanoparticles. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2014, 104, 386–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fakhri, A. Utilization of tungsten trioxide nanoparticles and nickel oxide pillared montmorillonite nanocomposites for the adsorption of the drug dexamethasone from aqueous solutions. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 22199–22208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langmuir, I. The adsorption of gases on plane surfacesof glass, mica and platinum. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1918, 40, 1361–1403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freundlich, H. Uber die adsorption in l osungen (adsorption in solution). Z. Phys. Chem. 1906, 57, 384–470. [Google Scholar]
- Jnr, M.H.; Spiff, A.I. Equilibrium sorption study of Al3+, Co2+ and Ag+ in aqueous solutions by fluted pumpkin (telfairia occidentalis HOOK f) waste biomass. Acta Chim. Slov. 2005, 52, 174–181. [Google Scholar]
- Rajamohan, N. Equilibrium studies on sorption of an anionic dye onto acid activated water hyacinth roots. Afr. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2009, 3, 399–404. [Google Scholar]
- Özdemir, Y.; Doğan, M.; Alkan, M. Adsorption of cationic dyes from aqueous solutions by sepiolite. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2006, 96, 419–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Nitroimidazole | Molecular Formula | Molecular Weight (g·mol−1) | pKa | Melting Point (°C) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| DMZ | C5H7N3O2 | 141.13 | 2.81 | 138–141 |
| MNZ | C6H9N3O3 | 171.15 | 2.58 | 159–163 |
| RNZ | C6H8N4O4 | 200.15 | 1.32 | 168–169 |
| TNZ | C8H13N3O4S | 247.27 | 2.30 | 118–120 |
| Isotherm Model | Langmuir | Freundlich | Florry-Huggins | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Qm | KL | R2 | n | KF | R2 | KFH | nFH | R2 | |
| MNZ | 114.817 | 0.103 | 1.0000 | 1.971 | 16.481 | 0.9784 | 0.1125 | 2.065 | 0.9947 |
| DMZ | 119.786 | 0.071 | 0.9999 | 1.945 | 15.625 | 0.9866 | 0.0659 | 1.161 | 0.9980 |
| RNZ | 126.859 | 0.051 | 0.9999 | 1.722 | 10.655 | 0.9878 | 0.0513 | 1.165 | 0.9974 |
| TNZ | 126.755 | 0.042 | 1.0000 | 1.672 | 9.029 | 0.9879 | 0.0392 | 1.008 | 0.9979 |
| Kinetic Models | MNZ | DMZ | RNZ | TNZ |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| qexperimental (mg/g) | 27.04 ± 0.049 | 26.10 ± 0.100 | 25.02 ± 0.072 | 24.00 ± 0.042 |
| Pseudo-first-order | ||||
| qe (mg/g) | 23.19 | 21.97 | 21.74 | 21.72 |
| k1 (1/min) | 0.1651 | 0.1457 | 0.14650 | 0.1324 |
| R2 | 0.9723 | 0.9537 | 0.9579 | 0.9720 |
| Pseudo-second-order | ||||
| qe (mg/g) | 31.38 | 30.72 | 30.07 | 30.17 |
| k2 (g/(mg min)) | 0.0089 | 0.0079 | 0.0072 | 0.0055 |
| R2 | 0.9954 | 0.9862 | 0.9827 | 0.9784 |
| Intraparticle diffusion | ||||
| Ki (mg/g·min0.5) | 3.5283 | 3.1826 | 3.2955 | 3.7271 |
| C | 11.273 | 10.934 | 9.469 | 6.298 |
| R2 | 0.9989 | 0.9773 | 0.9583 | 0.9783 |
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license ( http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Fakhri, A.; Rashidi, S.; Asif, M.; Ibrahim, A.A. Microwave-Assisted Synthesis of SiC Nanoparticles for the Efficient Adsorptive Removal of Nitroimidazole Antibiotics from Aqueous Solution. Appl. Sci. 2017, 7, 205. https://doi.org/10.3390/app7020205
Fakhri A, Rashidi S, Asif M, Ibrahim AA. Microwave-Assisted Synthesis of SiC Nanoparticles for the Efficient Adsorptive Removal of Nitroimidazole Antibiotics from Aqueous Solution. Applied Sciences. 2017; 7(2):205. https://doi.org/10.3390/app7020205
Chicago/Turabian StyleFakhri, Ali, Sahar Rashidi, Mohammad Asif, and Ahmed A. Ibrahim. 2017. "Microwave-Assisted Synthesis of SiC Nanoparticles for the Efficient Adsorptive Removal of Nitroimidazole Antibiotics from Aqueous Solution" Applied Sciences 7, no. 2: 205. https://doi.org/10.3390/app7020205







