A Hospital Recommendation System Based on Patient Satisfaction Survey
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Literature Review
2.1. HCAHPS Hospital Survey Data
2.2. Review of Existing Studies on HCAHPS Dataset
2.3. Shortcomings of Existing Survey Analysis Methods
3. Analyzing HCAHPS Data
3.1. Data Preparation
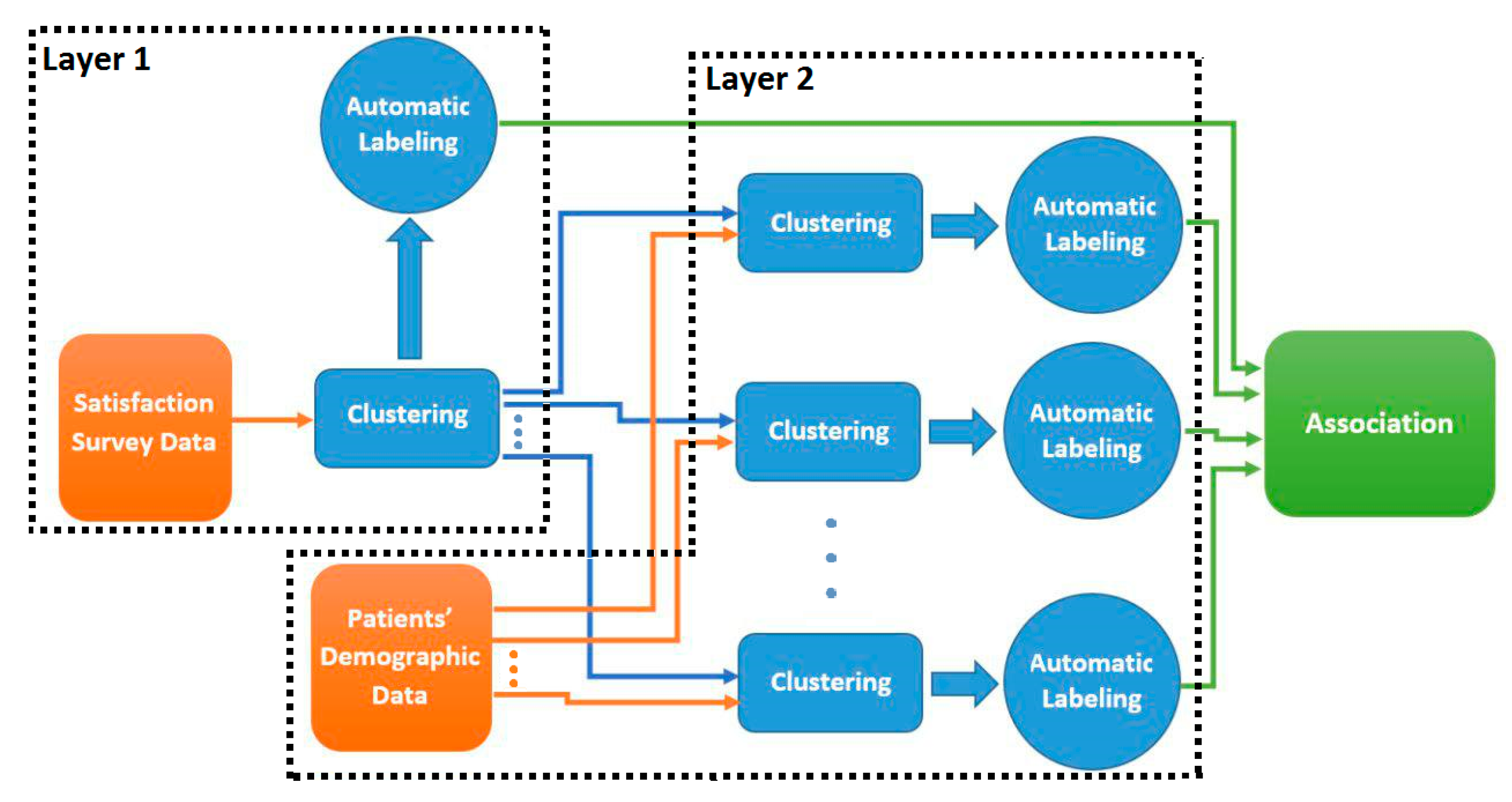
3.2. Two-Layer Cluster Analysis
| Algorithm 1. Optimal number of clusters using Calinski-Harabasz criterion. |
| Find Number of Clusters (data, minNumClusters = 1, maxNumClusters = 10 ) Fit ← cascadeKM (data, inf.gr = minNumClusters, sup.gr = maxNumClusters, iter = 100, criterion = “calinski”) calinski_best ← which.max (fit.results [2,]) Return calinski_best |
3.3. Salient Feature Extraction
- The centroid of a cluster k is computed as the average of the points in the cluster:where is the centroid of cluster k and is a point in cluster k.
- The Euclidean distance of each point to its cluster centroid is computed:
- The points in each cluster are divided into in-pattern and out-pattern records. The records whose distance lie within the range defined by (3) are called in-pattern records while all other records including the ones in other clusters are called out-pattern records.where and are the mean and standard deviation of the points in cluster k, respectively, and z is a constant factor. Smaller z results in more out-pattern records and larger z result in more in-pattern records.
- For each feature v and cluster k, the mean of all in-pattern records, and the mean of the out-pattern records, , are computed:where and are the set of in-pattern and out-pattern points in cluster k, respectively.
- A difference factor, , is calculated for each feature v in cluster k based on Equation (6):
- The mean and standard deviation of the difference factors for all features in cluster k are calculated as follows:where D is the number of features in the input space.
- A feature v is a salient feature in cluster k if its corresponding difference factor in k deviates considerably from . More formally, feature v is a salient feature in cluster k if:where z is a constant factor. The smaller the z the more salient features in each cluster. Salient feature extraction method is outlined in Algorithm 2.
| Algorithm 2. Salient features extraction. |
| FindingSalientFeatures (noc, clustered_data, z) Comment: calculating the center of each clustering by averaging records in the cluster. For i ← 0 to noc − 1 cluster_centers [i] ← average over columns(clustered_data[i]) Comment: calculating distance of records from their assigned cluster center. For i ← 0 to noc − 1 For j ← 0 to length(clustered_data[i]) − 1 distance_matrix[i][j] ← distance (clustered_data[i][j], cluster_centers [i]) Comment: calculating the average distance of each cluster from its center. For i ← 0 to noc − 1 average_distance[i] ← average over columns(distance_matrix[i]) Comment: calculating standard deviation of distances in each cluster. For i ← 0 to noc − 1 standard_deviation[i]←sqrt (average over j((distance_matrix[i][j] − Average_distance[i]) ^2)) Comment: Finding in pattern and out pattern records in each cluster counter ← 0 For i ← 0 to noc − 1 For j ← to length(clustered_data[i]) − 1 If (distance_matrix[i][j] < (average_distance[i] + (z * standard_deviation[i])) AND distance_matrix[i][j] > (average_distance[i] − (z * standard_deviation[i])) In_patterns[i][counter] ← j counter ++ Comment: Calculating the mean of each feature in each cluster for in-pattern neurons. For i ← 0 to noc-1 For j ← 0 to length (clustered_data[i]) − 1 If (j in In_patterns[i]) In_pattern_mean[i] ← In_pattern_mean[i] + clustered_data[i] else Out_pattern_mean[i] ← Out_pattern_mean[i] + clustered_data[i] In_pattern_mean[i] ← In_pattern_mean[i]/length(In_patterns[i]) Out_pattern_mean[i] ← Out_pattern_mean[i]/length(Out_patterns[i]) Comment: Calculating the difference factor of in and out pattern records. For i←0 to noc − 1 For j ← 0 to number_of _columns(clustered_data) − 1 difference_factor [i][j] ← In_pattern_mean[i][j] − Out_pattern_mean[i][j] Comment: Calculating the mean difference factor of each dimension. Mean_difference_factor ← average over row(difference_factor) Comment: Calculating the standard deviation difference factor of each cluster. For i←0 to noc − 1 For j←1 to number_of _columns(clustered_data) − 1 Difference_factor_SD[i] ← Difference_factor_SD[i] + difference_factor [i][j] − Mean_difference_factor [i])^2) Difference_factor_SD[i] ← sqrt(Difference_factor_SD[i]/ number_of _columns(clustered_data)) Comment: Calculating a matrix of salient dimentions. For i ← 0 to noc − 1 For j← number_of _columns(clustered_data) − 1 If (difference_factor [i][j]<= (Mean_difference_factor[i] − (z* Difference_factor_SD[i]))) Salient_dimension[i][j] = −1 else if (difference_factor [i][j]>= ( Mean_difference_factor[i] + (z* Difference_factor_SD[i]))) Salient_dimension[i][j] = 1 Return Salient_dimension |
4. Experiment
| Algorithm 3. Recommendation extraction. |
| Find Recommendations (data, split_index) Satisfaction_questions_data ← data [:] [0:split_index] noc ← FindNumberOfClusters (Satisfaction_questions_data ) Sq_clustered_data = kmeans (Satisfaction_questions_data) Sq_salient_dim ← FindingSalientFeatures (noc, Sq_clustered_data, z) For i ← 0 to noc For j in Sq_clustered_data[i] Demographic_data ← data[j] [split_index: number_of_columns(data)] D_clustered_data ← kmeans (Demographic_data) D_salient_dim ← FindingSalientFeatures (noc, D_clustered_data, z) For sq_salient in Sq_salient_dim[i]: If sq_salient != 0: For d_salient in D_salient_dim: If d_salient != 0: Recommendation [(col_name(sq_salient), sq_salient)]. Add ((col_name(d_salient), d_salient)) Return recommendation |
5. Validation
| Algorithm 4. Modified chi-square test. |
| Modified_chisquare(interaction_table): Comment: Adjusting interaction table not to have values less than five. Col ← 0 to num_col(interaction_table): If all(table[, col] < 5): table1 ← table [, -col] table ← table1 col ← col−1 numcol ← numcol−1 col ← col + 1 return chisq.test(table) |
| Algorithm 5. Validation function. |
| validate_relationships (recommendation) Interaction_table ← interact(recommendation) Chisqr ← Modifies_chisquare(Interaction_table) If Chisqr. P_value < 0.5: For row in interaction_table.rows: For col in interaction_table.cols: Odds_ratio ← Odds_ratio(interaction_table,row,col) If odds_ratio.p_value > 2 or odds_ratio.p_value < −2: Return True Return False |
6. Turning Associations into Recommendations for Hospitals
- The valid association can be simply transformed into a set of general applicable recommendations. For instance, based on the second association in Table 16, the system can make the recommendation that “Young ladies whose admission source is physician referral and their reason of admission is obstetrical, need more information about their symptoms when they are being discharged”. In this approach, one recommendation is generated for each correlation, although, the recommendations which are based on patients’ dissatisfaction are probably more useful than ones which are based on patients’ satisfaction.
- The associations can be used to produce target-based recommendations. Assume that a patient is being admitted to a hospital. The reception takes the patient’s information and relative recommendations would be popped out. For instance, suppose an old patient with physician referral is being admitted for surgical reason. Based on the 4th correlation in Table 4, a recommendation is shown to the health care provider asserting that this patient needs more information about her/his symptoms. This can be accomplished by a simple rule-based expert system.
7. Conclusions
- More extensive data collection: Our long-term goal is to assess how the recommendations produced by our system can improve patients’ loyalty and result in saving costs and time in the long run. Using the preliminary results outlined in this paper, our goal is to obtain a more comprehensive data set which includes data on whether the patients have come back to the hospital if medical services were needed, and to examine the relationship between customer loyalty and their satisfaction identifiers.
- Handling skip questions: In this study, a single imputation method based on K-nearest neighbor (KNN) is used to impute missing values. Other popular approaches, such as multiple imputations by chained equations (MICE) [19], should be explored in future for imputing both categorical and continues variables. Also, other approaches for handling skip questions should be examined to better distinguish between non-applicable and missing data.
- Alternative distance measures for K-means: In this study, we used Euclidean distance for clustering. Euclidean distance is typically used for continuous data where data are seen as points in the Euclidean space. Since HCAHPS data consist of mixed numeric and categorical variables, we should examine other types of distance measures such as cosine, Jaccard, Overlap, Occurrence Frequency, etc. [20] and compare the quality of recommendations produced by each measure. In addition, since there are two layers of clustering and the intrinsic characteristics of data points in each layer vary, and a different distance function can be used for each layer.
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A




References
- Lehtonen, R.; Pahkinen, E. Practical Methods for Design and Analysis of Complex Surveys; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Kenett, R.; Salini, S. Modern Analysis of Customer Surveys: With Applications Using R (Vol. 117); John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Giordano, L.A.; Elliott, M.N.; Goldstein, E.; Lehrman, W.G.; Spencer, P.A. Development, implementation, and public reporting of the HCAHPS survey. Med. Care Res. Rev. 2010, 67, 27–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stratford, N.J. Patient perception of pain care in the United States: A 5-year comparative analysis of hospital consumer assessment of health care providers and systems. Pain Phys. 2014, 17, 369–377. [Google Scholar]
- Sheetz, K.H.; Seth, A.W.; Micah, E.G.; Darrell, A.C., Jr.; Michael, J.E. Patients’ perspectives of care and surgical outcomes in Michigan: an analysis using the CAHPS hospital survey. Ann. Surg. 2014, 260, 5–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goldstein, E.; Marc, N.E.; William, G.L.; Katrin, H.; Laura, A.G. Racial/ethnic differences in patients’ perceptions of inpatient care using the HCAHPS survey. Med. Care Res. Rev. 2010, 67, 74–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elliott, M.N.; William, G.L.; Megan, K.B.; Elizabeth, G.; Katrin, H.; Laura, A.G. Gender differences in patients’ perceptions of inpatient care. Health Serv. Res. 2012, 47, 1482–1501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elliott, M.N.; William, G.L.; Elizabeth, G.; Katrin, H.; Megan, K.B.; Laura, A.G. Do hospitals rank differently on HCAHPS for different patient subgroups? Med. Care Res. Rev. 2010, 67, 56–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klinkenberg, W.; Dean, S.B.; Brian, M.W.; Koichiro, O.; Joe, M.I.; Jan, C.G.; Wm Claiborne, D. Inpatients’ willingness to recommend: a multilevel analysis. Health Care Manag. Rev. 2011, 36, 349–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kleinbaum, D.; Lawrence, K.; Azhar, N.; Eli, R. Applied Regression Analysis and Other Multivariable Methods; Nelson Education: Scarborough, ON, Canada, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Scholkopft, B.; Klaus-Robert, M. Fisher Discriminant Analysis with Kernels. In Proceedings of the Neural Networks for Signal Processing IX, Madison, WI, USA, 25 August 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Thurstone, L.L. Multiple factor analysis. Psychol. Rev. 1931, 38, 406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batista, G.E.; Monard, M.C. A Study of K-Nearest Neighbour as an Imputation Method. HIS 2002, 87, 251–260. [Google Scholar]
- Ailon, N.; Ragesh, J.; Claire, M. Streaming k-means approximation. In Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems; Columbia University: New York, NY, USA, 2009; pp. 10–18. [Google Scholar]
- Caliński, T.; Jerzy, H. A dendrite method for cluster analysis. Commun. Stat.-Theory Methods 1974, 3, 1–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azcarraga, A.P.; Hsieh, M.H.; Pan, S.L.; Setiono, R. Extracting salient dimensions for automatic SOM labeling. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man Cybern. Part C 2005, 35, 595–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McHugh, M.L. The chi-square test of independence. Biochem. Med. 2013, 23, 143–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bland, J.M.; Douglas, G.A. The odds ratio. BMJ 2000, 320, 1468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- White, I.R.; Patrick, R.; Angela, M.W. Multiple imputation using chained equations: Issues and guidance for practice. Stat. Med. 2011, 30, 377–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boriah, S.; Varun, C.; Vipin, K. Similarity measures for categorical data: A comparative evaluation. In Proceedings of the 2008 Society for Industrial and Applied Mathematics (SIAM) International Conference on Data Mining, Atlanta, GA, USA, 24–26 April 2008; pp. 243–254. [Google Scholar]


| Section | Number of Question in Each Section | Number of Choices for Each Question |
|---|---|---|
| Care from Nurses | 5 | 4 |
| Care from Doctors | 3 | 4 |
| Hospital Environment | 2 | 4 |
| Experience in Hospital | 5 | 4 |
| When You Left | 1 | 2 |
| Overall Rating | 1 | 2 |
| 1 | 11 |
| Questions | Number of Choices |
|---|---|
| Age | - |
| Discharge Date | - |
| State | 44 |
| Racial Category | 6 |
| Overall Health | 5 |
| Education | 6 |
| Ethnicity | 5 |
| Patient-Filled Race | 5 |
| Patient’s Language | 3 |
| Gender | 2 |
| Principal Reason | 3 |
| Admission Source | 10 |
| Survey Language | 2 |
| Features | Description |
|---|---|
| D1 | Communication with doctor |
| D2 | Communication with Nurse |
| D3 | Pain Management |
| D4 | Cleanliness |
| D5 | Quietness |
| Features | C1 | C2 | C3 |
|---|---|---|---|
| D1 | −0.0126243 | 0.97095961 | −0.9913867 |
| D2 | 0.03791055 | −0.07749729 | 0.02231231 |
| D3 | −1.1444478 | 0.8585494 | 0.8681821 |
| D4 | −1.1509251 | 0.8681547 | 0.8681547 |
| D5 | −0.00279281 | 0.009980126 | −0.0060900 |
| Records | C1 | C2 | C3 |
|---|---|---|---|
| R1 | 1.967133 | 0.7958750 | 1.3957300 |
| R2 | 2.121455 | 1.6483554 | 0.9116866 |
| R3 | 1.675209 | 1.5959835 | 1.7050408 |
| R4 | 1.518996 | 1.6174912 | 1.5210744 |
| R5 | 1.697462 | 1.0558556 | 2.1432977 |
| R6 | 1.843458 | 0.8124378 | 1.1173187 |
| R7 | 1.191784 | 2.2571117 | 1.3717867 |
| R8 | 2.266916 | 0.7501202 | 1.4390353 |
| R9 | 1.706186 | 1.6242395 | 1.7090141 |
| R10 | 1.107229 | 2.0101626 | 0.7544890 |
| µ | 1.687192 | 1.367895 | 1.367732 |
| σ | 0.3833892 | 0.4231975 | 0.4307547 |
| Features | C1 | C2 | C3 |
|---|---|---|---|
| D1 | −0.03037039 | 1.18199255 | −1.22503855 |
| D2 | 0.04416163 | −0.20817361 | −0.02380192 |
| D3 | −1.537553 | 1.033197 | 1.041475 |
| D4 | −1.554513 | 1.045382 | 1.047448 |
| D5 | −0.06825377 | −0.03673413 | −0.03182003 |
| µ | −0.6293057 | 0.6031327 | 0.1616524 |
| Σ | 0.7493974 | 0.5972044 | 0.8430252 |
| Cluster | Salient Features | |
|---|---|---|
| C1 | Pain Management | Low |
| Cleanliness | Low | |
| C2 | Communication with Nurse | Low |
| Quietness | Low | |
| C3 | Communication with doctor | Low |
| Pain Management | High | |
| Cleanliness | High | |
| Cluster | Salient Features |
|---|---|
| C1 |
|
| C2 |
|
| C3 |
|
| Cluster | C1 (1210 Observations) | |||
| Cluster Salient Features |
| |||
| Sub-cluster | SC1 (378 obs.) | SC2 (236 obs.) | SC3 (268 obs.) | SC4 (328) |
| Sub-cluster Salient Features |
|
|
|
|
| Cluster | C2 (602 Observations) | |||
| Cluster Salient Features |
| |||
| Sub-cluster | SC1 (141 obs.) | SC2 (224 obs.) | SC3 (237 obs.) | |
| Sub-cluster Salient Features |
|
|
| |
| Cluster | C3 (840 Observations) | |||
| Cluster Salient Features |
| |||
| Sub-cluster | SC1 (278 obs.) | SC2 (296 obs.) | SC3 (266 obs.) | |
| Sub-cluster Salient Features |
|
|
| |
| 1 | Patients who have high Satisfaction with Help After Discharge, have these qualities: Mostly Physician Referral Admission Source, Mostly not Medical Principal Reason of Admission |
| 2 | Patients who have high Satisfaction with Symptoms Info, have these qualities: Mostly Physician Referral Admission Source, Rarely Medical Principal Reason of Admission |
| 3 | Patients who have high Satisfaction with Help After Discharge, have these qualities: Rarely White Race |
| 4 | Patients who have high Satisfaction with Symptoms Info, have these qualities: Rarely White Race |
| 5 | Patients who have high Satisfaction with Help After Discharge, have these qualities: Mostly Old, Mostly Emergency Room Admission Source, Mostly Medical Principal Reason of Admission |
| 6 | Patients who have high Satisfaction with Symptoms Info, have these qualities: Mostly Old, Mostly Emergency Room Admission Source, Mostly Medical Principal Reason of Admission |
| 7 | Patients who have low Satisfaction with Help After Discharge, have these qualities: Mostly Old, Mostly Physician Referral Admission Source, Mostly Surgical Principal Reason of Admission |
| 8 | Patients who have low Satisfaction with Symptoms Info, have these qualities: Mostly Old, Mostly Physician Referral Admission Source, Mostly Surgical Principal Reason of Admission |
| 9 | Patients who have low Satisfaction with Help After Discharge, have these qualities: Mostly Young, Mostly Female, Mostly Physician Referral Admission Source, Mostly Obstetric Principal Reason of Admission |
| 10 | Patients who have low Satisfaction with Symptoms Info, have these qualities: Mostly Young, Mostly Female, Mostly Physician Referral Admission Source, Mostly Obstetric Principal Reason of Admission |
| 11 | Patients who have low Satisfaction with Help After Discharge, have these qualities: Mostly Old, Mostly Emergency Room Admission Source, Mostly Medical Principal Reason of Admission |
| 12 | Patients who have low Satisfaction with Symptoms Info, have these qualities: Mostly Old, Mostly Emergency Room Admission Source, Mostly Medical Principal Reason of Admission |
| 13 | Patients who have high Satisfaction with Help After Discharge, have these qualities: Mostly Physician Referral Admission Source, Mostly Obstetric Principal Reason of Admission |
| 14 | Patients who have high Satisfaction with Symptoms Info, have these qualities: Mostly Physician Referral Admission Source, Mostly Obstetric Principal Reason of Admission |
| 15 | Patients who have high Satisfaction with Help After Discharge, have these qualities: Rarely not Spanish/Hispanic/Latino Ethnicity, Rarely English Language |
| 16 | Patients who have high Satisfaction with Help After Discharge, have these qualities: Rarely not Spanish/Hispanic/Latino Ethnicity, Rarely English Language |
| 17 | Patients who have high Satisfaction with Help After Discharge, have these qualities: Mostly Old, Mostly Emergency Room Admission Source |
| 18 | Patients who have high Satisfaction with Symptoms Info, have these qualities: Mostly Old, Mostly Emergency Room Admission Source |
| 19 | Patients who have high Overall health, have these qualities: Mostly Old, Mostly Emergency Room Admission Source |
| Satisfaction with Symptoms Info | Rarely Not Spanish/Hispanic/Latino Ethnicity Spanish Language | |||
| 0.0 | 1.0 | 0.1 | 1.1 | |
| 1 | 3 | 180 | 1710 | 249 |
| 2 | 1 | 32 | 521 | 63 |
| 3 | 0 | 6 | 94 | 7 |
| 4 | 0 | 5 | 72 | 5 |
| Satisfaction with Symptoms Info | Rarely Not Spanish/Hispanic/Latino Ethnicity Spanish Language | |||
| 0.0 | 1.0 | 0.1 | 1.1 | |
| Low | 4 | 212 | 2231 | 256 |
| High | 0 | 11 | 166 | 12 |
| Satisfaction with Symptoms Info | Rarely Not Spanish/Hispanic/Latino Ethnicity Spanish Language | ||
| X.0 | 0.1 | 1.1 | |
| Low | 216 | 2231 | 256 |
| High | 11 | 166 | 12 |
| Satisfaction with Symptoms Info | Condition: Rarely Not Spanish/Hispanic/Latino Ethnicity High Spanish Language | |
|---|---|---|
| Meet Condition | Do Not Meet Conditions | |
| Low | 2447 | 256 |
| High | 177 | 12 |
| 1 | Chi-square | X-squared = 28.104 | p-value = 3.455 × 10−6 |
| z-test | p-value = 5.00891912614554 | ||
| 2 | Chi-square | X-squared = 7.084 | p-value = 0.06927 |
| z-test | p-value = 0.0183582852328812 | ||
| 3 | Chi-square | X-squared = 1.5969 | p-value = 0.2063 |
| z-test | p-value = 1.31385601104743 | ||
| 4 | Chi-square | X-squared = 0.50012 | p-value = 0.4794 |
| z-test | p-value = −0.760696016958917 | ||
| 5 | Chi-square | X-squared = 30.14 | p-value = 0.001506 |
| z-test | p-value = −2.9118314808416 | ||
| 6 | Chi-square | X-squared = 43.594 | p-value = 8.558 × 10−6 |
| z-test | p-value = −0.212828628801027 | ||
| 7 | Chi-square | X-squared = 26.86 | p-value = 0.004825 |
| z-test | p-value = −1.97247635563556 | ||
| 8 | Chi-square | X-squared = 63.926 | p-value = 1.715 × 10−9 |
| z-test | p-value = 3.59338301942709 | ||
| 9 | Chi-square | X-squared = 25.48 | p-value = 0.01271 |
| z-test | p-value = −3.39514132553282 | ||
| 10 | Chi-square | X-squared = 61.28 | p-value = 1.315 × 10−8 |
| z-test | p-value = −5.48685043800752 | ||
| 11 | Chi-square | X-squared = 30.14 | p-value = 0.001506 |
| z-test | p-value = 2.9118314808416 | ||
| 12 | Chi-square | X-squared = 43.594 | p-value = 8.558 × 10−6 |
| z-test | p-value = 0.212828628801027 | ||
| 13 | Chi-square | X-squared = 20.061 | p-value = 0.0001649 |
| z-test | p-value = 3.50130627065847 | ||
| 14 | Chi-square | X-squared = 43.489 | p-value = 1.937 × 10−9 |
| z-test | p-value = 5.57545804293131 | ||
| 15 | Chi-square | X-squared = 8.8791 | p-value = 0.03094 |
| z-test | p-value = 2.45951143035353 | ||
| 16 | Chi-square | X-squared = 0.9116 | p-value = 0.8226 |
| z-test | p-value = −0.774093020800148 | ||
| 17 | Chi-square | X-squared = 18.715 | p-value = 0.002172 |
| z-test | p-value = −2.85471982135127 | ||
| 18 | Chi-square | X-squared = 27.572 | p-value = 4.413 × 10−5 |
| z-test | p-value = −1.47076729692434 | ||
| 19 | Chi-square | X-squared = 24.691 | p-value = 0.0001599 |
| z-test | p-value = −0.231962167837976 | ||
| 1 | Patients who have high Satisfaction with Symptoms Info, have these qualities: Mostly Physician Referral Admission Source, Mostly Obstetric Principal Reason of Admission | |
| z-test | p-value = 5.57545804293131 | |
| 2 | Patients who have low Satisfaction with Symptoms Info, have these qualities: Mostly Young, Mostly Female, Mostly Physician Referral Admission Source, Mostly Obstetric Principal Reason of Admission | |
| z-test | p-value = −5.48685043800752 | |
| 3 | Patients who have high Satisfaction with Help After Discharge, have these qualities: Mostly Physician Referral Admission Source, Rarely Medical Principal Reason of Admission | |
| z-test | p-value = 5.00891912614554 | |
| 4 | Patients who have low Satisfaction with Symptoms Info, have these qualities: Mostly Old, Mostly Physician Referral Admission Source, Mostly Surgical Principal Reason of Admission | |
| z-test | p-value = 3.59338301942709 | |
| 5 | Patients who have high Satisfaction with Help After Discharge, have these qualities: Mostly Physician Referral Admission Source, Mostly Obstetric Principal Reason of Admission | |
| z-test | p-value = 3.50130627065847 | |
| 6 | Patients who have low Satisfaction with Help After Discharge, have these qualities: Mostly Young, Mostly Female, Mostly Physician Referral Admission Source, Mostly Obstetric Principal Reason of Admission | |
| z-test | p-value = −3.39514132553282 | |
| 7 | Patients who have high Satisfaction with Help After Discharge, have these qualities: Mostly Old, Mostly Emergency Room Admission Source, Mostly Medical Principal Reason of Admission | |
| z-test | p-value = −2.9118314808416 | |
| 8 | Patients who have high Satisfaction with Help After Discharge, have these qualities: Mostly Old, Mostly Emergency Room Admission Source | |
| z-test | p-value = −2.85471982135127 | |
| 9 | Patients who have high Satisfaction with Help After Discharge, have these qualities: Rarely not Spanish/Hispanic/Latino Ethnicity, Rarely English Language | |
| z-test | p-value = 2.45951143035353 | |
| 10 | Patients who have high Satisfaction with Symptoms Info, have these qualities: Mostly Old, Mostly Emergency Room Admission Source, Mostly Medical Principal Reason of Admission | |
| z-test | p-value = −0.212828628801027 | |
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Khoie, M.R.; Sattari Tabrizi, T.; Khorasani, E.S.; Rahimi, S.; Marhamati, N. A Hospital Recommendation System Based on Patient Satisfaction Survey. Appl. Sci. 2017, 7, 966. https://doi.org/10.3390/app7100966
Khoie MR, Sattari Tabrizi T, Khorasani ES, Rahimi S, Marhamati N. A Hospital Recommendation System Based on Patient Satisfaction Survey. Applied Sciences. 2017; 7(10):966. https://doi.org/10.3390/app7100966
Chicago/Turabian StyleKhoie, Mohammad Reza, Tannaz Sattari Tabrizi, Elham Sahebkar Khorasani, Shahram Rahimi, and Nina Marhamati. 2017. "A Hospital Recommendation System Based on Patient Satisfaction Survey" Applied Sciences 7, no. 10: 966. https://doi.org/10.3390/app7100966




