Influence of Workpiece Material on Tool Wear Performance and Tribofilm Formation in Machining Hardened Steel
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Experimental Work
2.1. Workpiece Material
2.2. Cutting Tool and Turning Tests
2.3. Characterization
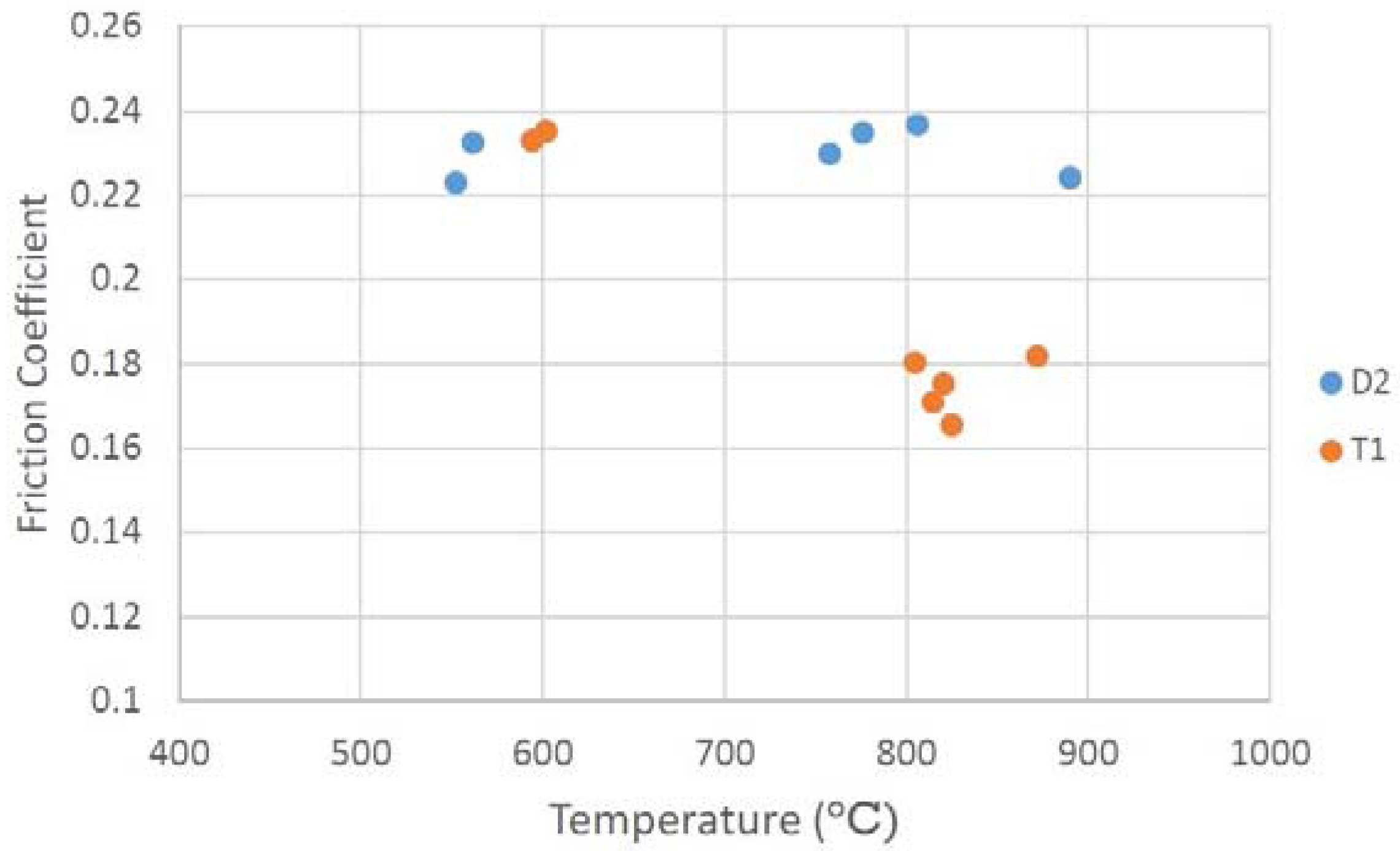
2.4. Friction Tests in Tribometer
3. Results and Discussion
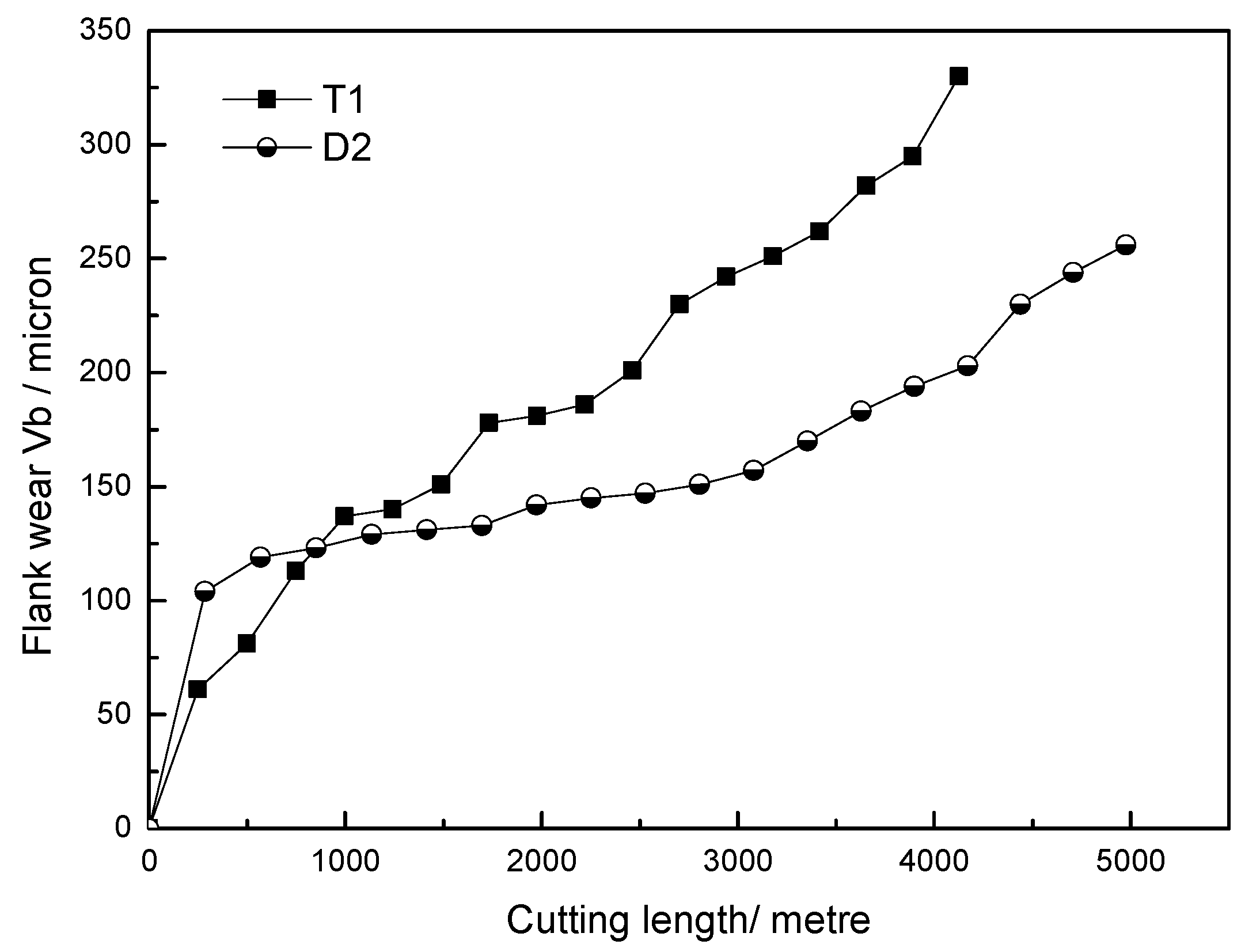
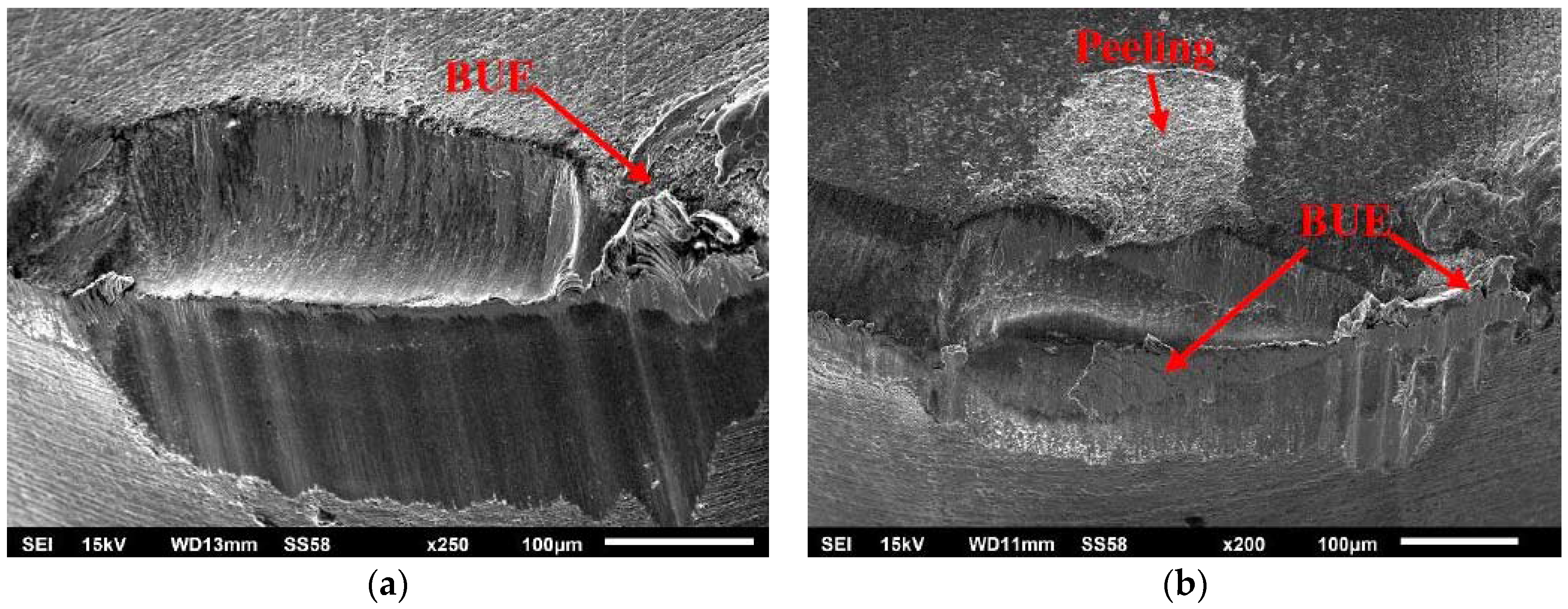
3.1. Tool Life and Tool Wear
3.2. Adaptive Behaviour
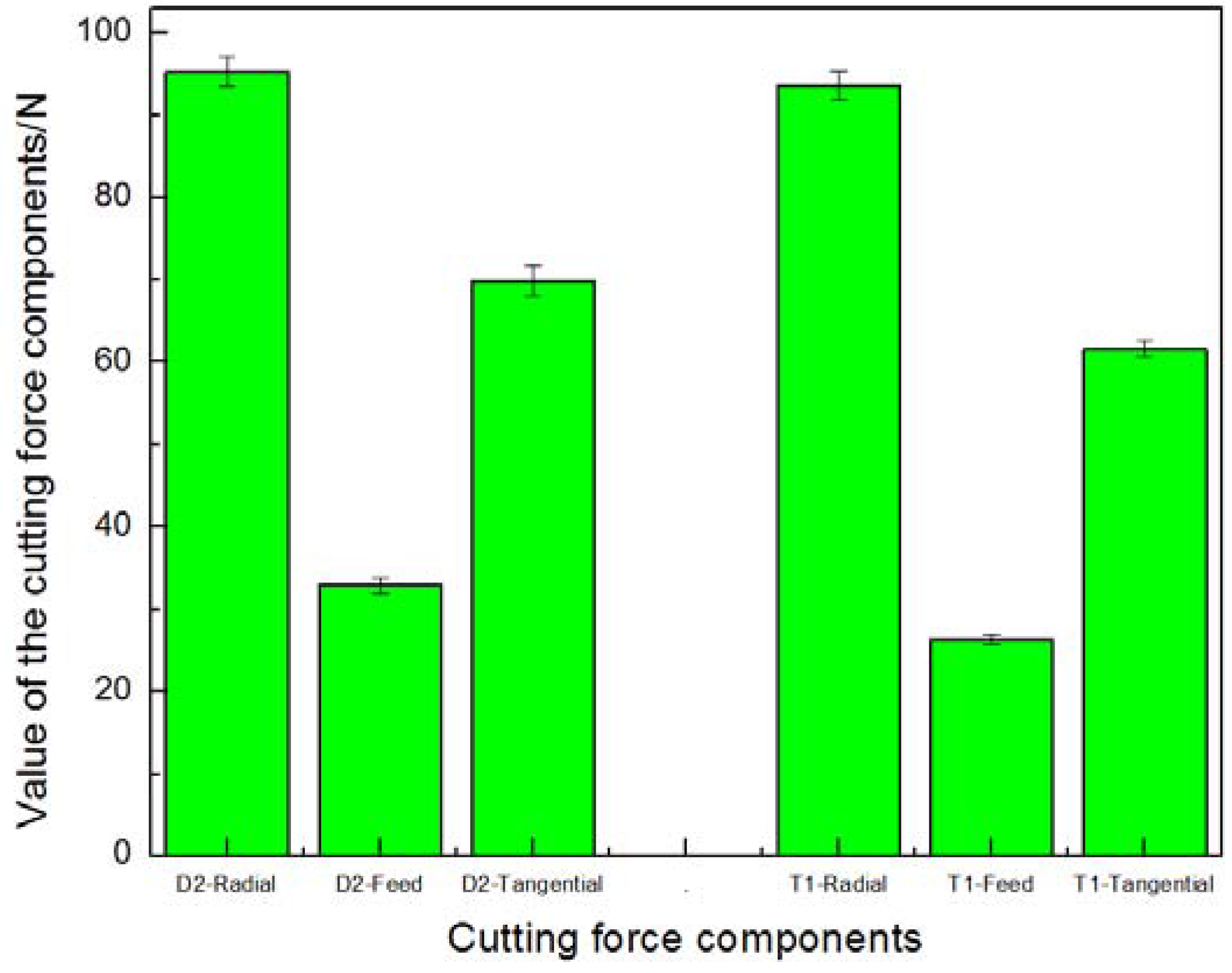
3.3. Cutting Performance During Early Stages of Tool Wear
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Byrne, G.; Dornfeld, D.; Denkena, B. Advancing cutting technology. CIRP Ann. Manuf. Technol. 2003, 52, 483–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sreejith, P.; Ngoi, B. Dry machining: Machining of the future. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 2000, 101, 287–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dudzinski, D.; Devillez, A.; Moufki, A.; Larrouquère, D.; Zerrouki, V.; Vigneau, J. A review of developments towards dry and high speed machining of Inconel 718 alloy. Int. J. Mach. Tools Manuf. 2004, 44, 439–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davim, J.P. Machining of Hard Materials; Springer-Verlag: London, UK, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Hashimoto, F.; Guo, Y.; Warren, A. Surface integrity difference between hard turned and ground surfaces and its impact on fatigue life. CIRP Ann. Manuf. Technol. 2006, 55, 81–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chou, Y.K.; Evans, C.J. White layers and thermal modeling of hard turned surfaces. Int. J. Mach. Tools Manuf. 1999, 39, 1863–1881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsumoto, Y.; Hashimoto, F.; Lahoti, G. Surface integrity generated by precision hard turning. CIRP Ann. Manuf. Technol. 1999, 48, 59–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ezugwu, E.; Bonney, J.; Yamane, Y. An overview of the machinability of aeroengine alloys. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 2003, 134, 233–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Claudin, C.; Rech, J.; Grzesik, W.; Zalisz, S. Characterization of the frictional properties of various coatings at the tool/chip/workpiece interfaces in dry machining of AISI 4140 steel. Int. J. Mater. Form. 2008, 1, 511–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trent, E.M.; Wright, P.K. Metal Cutting; Butterworth-Heinemann: Boston, MA, USA, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Lahiff, C.; Gordon, S.; Phelan, P. PCBN tool wear modes and mechanisms in finish hard turning. Robot. Comput. Integr. Manuf. 2007, 23, 638–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barry, J.; Byrne, G. Cutting tool wear in the machining of hardened steels: Part II: Cubic boron nitride cutting tool wear. Wear 2001, 247, 152–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richards, N.; Aspinwall, D. Use of ceramic tools for machining nickel based alloys. Int. J. Mach. Tools Manuf. 1989, 29, 575–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barry, J.; Byrne, G. Cutting tool wear in the machining of hardened steels: Part I: Alumina/TiC cutting tool wear. Wear 2001, 247, 139–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayas, E.; Kara, A. Pressureless Sintering of Al2O3-TiCN Composites. Key Eng. Mater. 2004, 264, 849–852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fox-Rabinovich, G.; Totten, G.E. Self-organization During Friction: Advanced Surface-engineered Materials and Systems Design; CRC Press: Hamilton, Canada, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Franz, R.; Neidhardt, J.; Sartory, B.; Kaindl, R.; Tessadri, R.; Polcik, P.; Derflinger, V.H.; Mitterer, C. High-temperature low-friction properties of vanadium-alloyed AlCrN coatings. Tribol. Lett. 2006, 23, 101–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fox-Rabinovich, G.S.; Gershman, I.; Hakim, M.A.E.; Shalaby, M.A.; Krzanowski, J.E.; Veldhuis, S.C. Tribofilm Formation As a Result of Complex Interaction at the Tool/Chip Interface during Cutting. Lubricants 2014, 2, 113–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fox-Rabinovich, G.S.; Yamomoto, K.; Veldhuis, S.C.; Kovalev, A.I.; Dosbaeva, G.K. Tribological adaptability of TiAlCrN PVD coatings under high performance dry machining conditions. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2005, 200, 1804–1813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fox-Rabinovich, G.S.; Yamomoto, K.; Veldhuis, S.C.; Kovalev, A.I.; Shuster, L.S.; Ning, L. Self-adaptive wear behavior of nano-multilayered TiAlCrN/WN coatings under severe machining conditions. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2006, 201, 1852–1860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shalaby, M.; El Hakim, M.; Abdelhameed, M.M.; Krzanowski, J.; Veldhuis, S.; Dosbaeva, G. Wear mechanisms of several cutting tool materials in hard turning of high carbon–chromium tool steel. Tribol. Int. 2014, 70, 148–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Hakim, M.; Abad, M.; Abdelhameed, M.; Shalaby, M.; Veldhuis, S. Wear behavior of some cutting tool materials in hard turning of HSS. Tribol. Int. 2011, 44, 1174–1181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arsecularatne, J.; Zhang, L.; Montross, C.; Mathew, P. On machining of hardened AISI D2 steel with PCBN tools. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 2006, 171, 244–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geller, Y. Tool Steels; Mashinostroenie: Moscow, Russia, 1979. [Google Scholar]
- Ning, Y.; Rahman, M.; Wong, Y. Investigation of chip formation in high speed end milling. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 2001, 113, 360–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boyd, J.M.; Hosseinkhani, K.; Veldhuis, S.C.; Ng, E. Improved prediction of cutting forces via finite element simulations using novel heavy-load, high-temperature tribometer friction data. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biksa, A. Tribological Characterization of Surface Engineered Tooling for Metal Cutting Applications. Master’s Thesis, University of Toronto, Toronto, Canada, August 2010. [Google Scholar]
- International Organization for Standardization. Tool Life Testing with Single-point Turning Tools; American Society of Mechanical Engineers: New York, NY, USA, 1986. [Google Scholar]
- Jacobson, S.; Hogmark, S. Tribofilms—On the crucial importance of tribologically induced surface modifications, Recent developments in wear prevention. Frict. Lubr. 2010, 661, 197–225. [Google Scholar]
- Bouzakis, K.D.; Michailidis, N.; Skordaris, G.; Bouzakis, E.; Biermann, D.; M'Saoubi, R. Cutting with coated tools: Coating technologies, characterization methods and performance optimization. CIRP Ann. Manuf. Technol. 2012, 61, 703–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lehn, J.M. Toward self-organization and complex matter. Science 2002, 295, 2400–2403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fox-Rabinovich, G.; Kovalev, A.; Veldhuis, S.; Yamamoto, K.; Endrino, J.; Gershman, I.; Rashkovskiy, A.; Aguirre, M.; Wainstein, D. Spatio-temporal behaviour of atomic-scale tribo-ceramic films in adaptive surface engineered nano-materials. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kovalev, A.; Wainstein, D.; Fox-Rabinovich, G.; Veldhuis, S.; Yamamoto, K. Features of self-organization in nanostructuring PVD coatings on a base of polyvalent metal nitrides under severe tribological conditions. Surf. Interface Anal. 2008, 40, 881–884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fox-Rabinovich, G.; Kovalev, A.; Aguirre, M.; Yamamoto, K.; Veldhuis, S.; Gershman, I.; Rashkovskiy, A.; Endrino, J.; Beake, B.; Dosbaeva, G. Evolution of self-organization in nano-structured PVD coatings under extreme tribological conditions. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2014, 297, 22–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, J.; Yamamoto, K.; Covelli, D.; Tauhiduzzaman, M.; Arif, T.; Gershman, I.S.; Veldhuis, S.C.; Fox-Rabinovich, G.S. Tribo-films control in adaptive TiAlCrSiYN/TiAlCrN multilayer PVD coating by accelerating the initial machining conditions. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2016, 294, 54–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| wt% | C | Si | Mn | S | P | Ni+Cu | Cr | Mo | V | W | N |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| T1 | 0.74 | 0.37 | 0.25 | 0.001 | 0.03 | 0 | 4.1 | 0 | 1.03 | 18.1 | 0 |
| D2 | 1.52 | 0.32 | 0.28 | 0.001 | 0.026 | 0.3 | 11.54 | 0.73 | 0.58 | 0 | 0 |
| Austenitization Temperature/°C | Tempering Temperature/°C | Hardness/HRC | |
|---|---|---|---|
| T1 HSS | 1250–1260 | 560–570, twice | 59.0(±0.5) |
| D2 tool steel | 1000–1040 | 430–450, twice | 58.7(±0.5) |
| Inserts Material | Chemical Compositions | Hardness | Nose Radius | Tool Holder |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mixed Alumina | 70%Al2O3 + 30%TiC | 2000 HV | 0.313 inch | rake angle −5°; clearance angle +5°; setting angle 95° |
| Workpiece Material | Surface Roughness | |
|---|---|---|
| Ra (µm) | PV (µm) | |
| T1 | 0.40 ± 0.01 | 3.23 ± 0.18 |
| D2 | 0.79 ± 0.01 | 4.92 ± 0.38 |
© 2016 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yuan, J.; Boyd, J.M.; Covelli, D.; Arif, T.; Fox-Rabinovich, G.S.; Veldhuis, S.C. Influence of Workpiece Material on Tool Wear Performance and Tribofilm Formation in Machining Hardened Steel. Lubricants 2016, 4, 10. https://doi.org/10.3390/lubricants4020010
Yuan J, Boyd JM, Covelli D, Arif T, Fox-Rabinovich GS, Veldhuis SC. Influence of Workpiece Material on Tool Wear Performance and Tribofilm Formation in Machining Hardened Steel. Lubricants. 2016; 4(2):10. https://doi.org/10.3390/lubricants4020010
Chicago/Turabian StyleYuan, Junfeng, Jeremy M. Boyd, Danielle Covelli, Taib Arif, German S. Fox-Rabinovich, and Stephen C. Veldhuis. 2016. "Influence of Workpiece Material on Tool Wear Performance and Tribofilm Formation in Machining Hardened Steel" Lubricants 4, no. 2: 10. https://doi.org/10.3390/lubricants4020010







