Stability toward High Energy Radiation of Non-Proteinogenic Amino Acids: Implications for the Origins of Life
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Experimental Section
2.1. Materials and Equipment
2.2. Irradiation Procedure with γ Rays
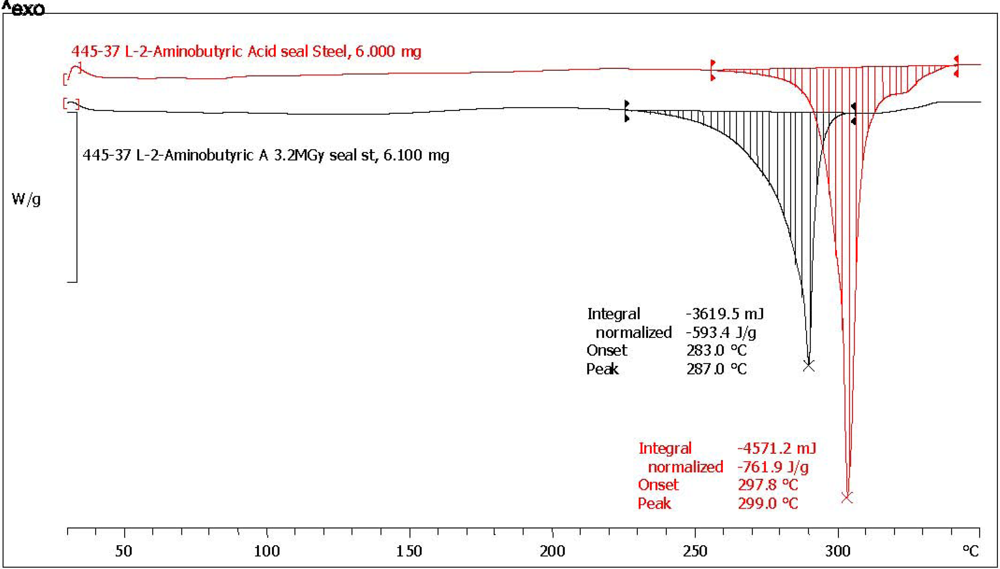
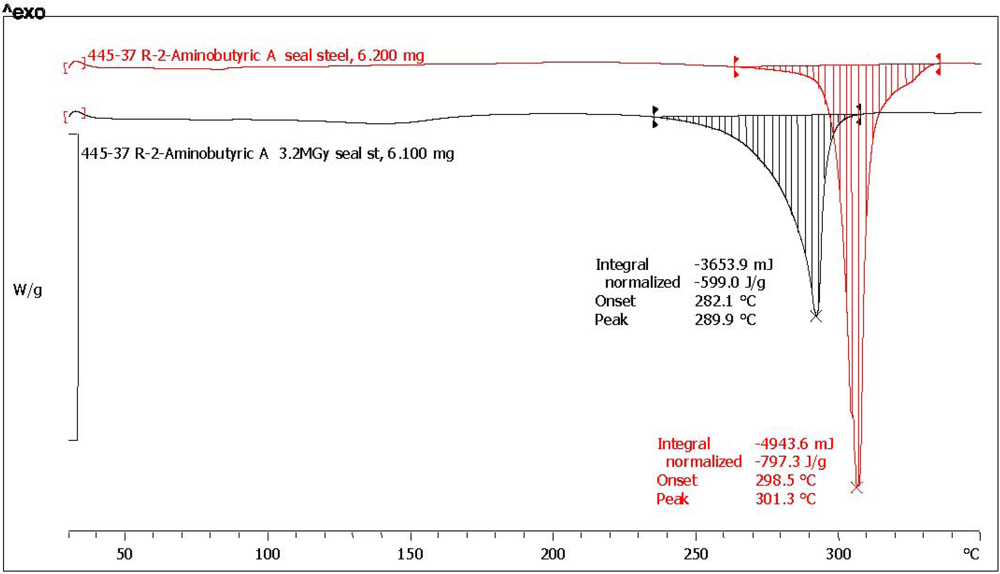
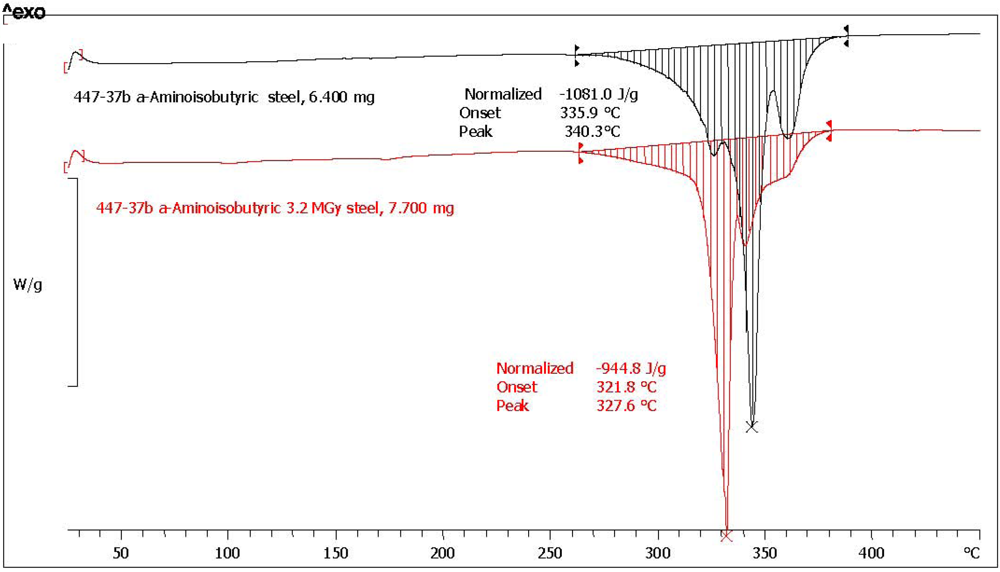
2.3. Analysis with Differential Scanning Calorimetry
| Equation 3 | Equation 2 | Pristine | 3.2 MGy | Equation 1 | σ | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Amino Acid | Rα | Rγ | ΔH0 melt. (J/g) | ΔHγ melt. (J/g) | Nγ% | Standard deviation 3 × 3 measu-rement | Residual weight after radiolysis (%) | Notes after radiolysis |
| (*)2-Aminoisobutyric acid [α-AIB] | n.a. | n.a. | 1081.0 | 944.8 | 87.4 | 1.1 | 97.6 | yellow, aminic and fatty odor |
| (*) dl-3-aminoisobutyric a. [dl-3-AIB] | n.a. | n.a. | 180.3 | 153.5 | 85.1 | 1.5 | 95.4 | pale yellow aminic odor |
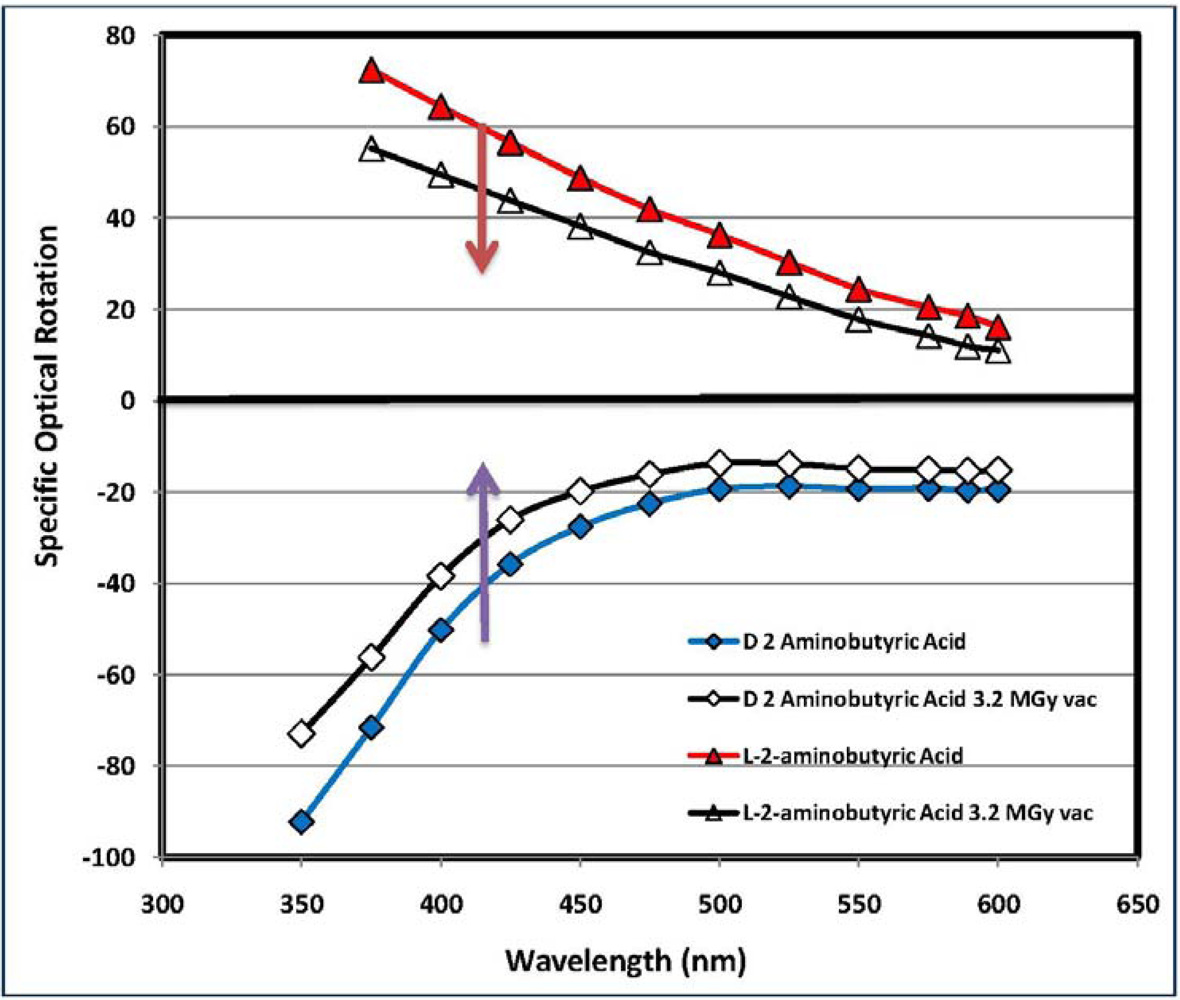
| (*) d-2-aminobutyric acid [d-ABA] | 78.6 | 75.0 | 796.3 | 601.0 | 75.5 | 0.5 | 97.2 | dark yellow, aminic and fatty odor |
| (*) l-2-aminobutyric acid [l-ABA] | 64.3 | 73.7 | 752.1 | 543.1 | 72.2 | 4.6 | 92.8 | yellow, aminic and fatty odor |
| (*) l-β-homoalanine HCl [β-Ala] | 84.2 | 86.4 | 476.0 | 365.0 | 76.7 | n.d. | 95.9 | brown, sweet odor; DSC shows melting with decomposition |
| l-β-homoglutamic acid HCl [β-Glu] | 91.3 | 93.4 | 180.2 | 134.8 | 74.8 | n.d. | 94.0 | cream color; DSC only melting peak considered |
| (*) l-norleucine [Nle] | 63.6 | 70.8 | 681.4 | 488.5 | 71.7 | n.d. | 93.0 | light yellow, weak aminic odor |
| (*) l-norvaline [Nvl] | 81.0 | 84.0 | 782.1 | 549.0 | 70.2 | n.d. | 96.8 | pale yellow, distinctive aminic odor |
| S(−)-α-Methylvaline [α-MV] | 88.7 | 92.8 | 850.9 | 595.2 | 69.9 | n.d. | 95.8 | pale yellow, pungent odor |
| l-β-leucine HCl [β-Leu] | 74.3 | 79.9 | 138.9 | 74.2 | 53.4 | n.d. | 94.5 | cream color, sweet odor; DSC only melting peak considered |
2.4. Analysis of the Radioracemization Degree by Optical Rotatory Dispersion Spectroscopy
2.5. FT-IR Analysis of the Amino Acids
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Amino Acids Selection
3.2. Non-Proteinaceous Amino Acids Radiolysis: Infrared Difference Spectroscopy
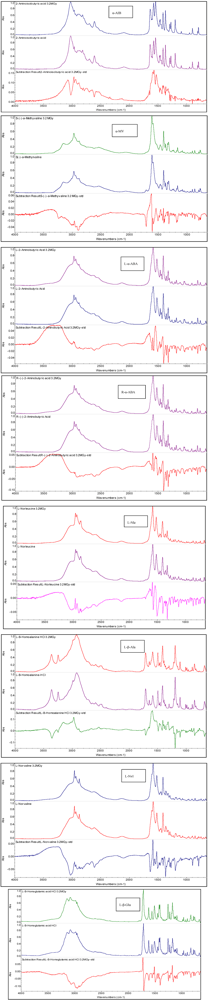

3.3. Amino Acids Weight Loss after 3.2 MGy Radiolysis
3.4. Residual Purity Measurement of Amino Acids after 3.2 MGy Radiolysis
| Amino Acid | Abbreviation | Melting point °C pristine reference | Melting point °C after radiolysis | Melting point shift after radiolysis |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2-Aminoisobutyric acid (*) | α-AIB | 340.3 | 327.7 | −12.0 |
| dl-3-aminoisobutyric a. (*) | dl-3-AIB | 172.1 | 171.2 | −0.9 |
| d-2-aminobutyric acid (*) | d-ABA | 301.3 | 290.0 | −11.3 |
| l-2-aminobutyric acid (*) | l-ABA | 302.9 | 290.2 | −12.7 |
| l-β-Homolanine HCl (*) | l-β-Ala | 244.5 | 243.5 | −1.0 |
| l-β-homoglutamic acid HCl | l-β-Glu | 190.8 | 182.7 | −8.1 |
| l-norleucine (*) | l-Nle | 322.9 | 297.4 | −25.5 |
| l-norvaline (*) | l-Nvl | 321.2 | 302.6 | −18.6 |
| S(−)-α-Methylvaline | α-MV | 306.1 | 298.8 | −7.3 |
| l-β-leucine HCl | l-β-Leu | 176.3 | 159.8 | −16.5 |
3.5. Measurement of the Optical Activity and Optical Rotatory Dispersion (ORD)
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Conflict of Interest
References
- Anders, E. Organic matter in meteorites: Possible origins. Space Sci. Rev. 1991, 56, 157–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sephton, M.A. Organic compounds in carbonaceous meteorites. Nat. Prod. Rep. 2002, 19, 292–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cronin, J.R.; Pizzarello, S. Chirality of meteoritic organic matter: A brief review. In Perspective in Amino Acid and Protein Geochemistry; Goodfriend, G.A., Collins, M.J., Fogel, M.L., Macko, S.A., Wehmiller, J.F., Eds.; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 2000; Chapter 2. [Google Scholar]
- Pizzarello, S.; Cronin, J.R. Non-racemic amino acids in the Murray and Murchison meteorites. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2000, 64, 329–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pizzarello, S.; Huang, Y.; Alexandre, M.R. Molecular asymmetry in extraterrestrial chemistry: Insights from a pristine meteorite. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 3700–3704. [Google Scholar]
- Meierhenrich, U.J. Amino Acids and the Asymmetry of Life; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Martins, Z.; Sephton, M.A. Extraterrestrial amino acids. In Amino Acids, Peptides and Proteins in Organic Chemistry; Hughes, A.W., Ed.; Wiley-VCH: Weinheim, Germany, 2009; Chapter 1. [Google Scholar]
- Pizzarello, S.; Groy, T.L. Molecular asymmetry in extraterrestrial organic chemistry: An analytical perspective. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2011, 75, 645–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pizzarello, S.; Schrader, D.L.; Monroe, A.A.; Lauretta, D.S. Large enantiomeric excesses in primitive meteorites and the diverse effects of water in cosmochemical evolution. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 11949–11954. [Google Scholar]
- Martins, Z.; Alexander, C.M.O.; Orzechowska, G.E.; Fogel, M.I.; Ehrenfreund, P. Indigenous amino acids in primitive CR meteorites. Meteorit. Planet. Sci. 2007, 42, 2125–2136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pizzarello, S.; Shock, E. The organic composition of carbonaceous meteorites: The evolutionary story ahead of biochemistry. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2010, 2, a00210. [Google Scholar]
- Schmitt-Kopplin, P.; Gabelic, Z.; Gougeon, R.D.; Fekete, A.; Kanawati, B.; Harir, M.; Gebefuegi, I.; Eckel, G.; Hertkorn, N. High molecular diversity of extraterrestrial organic matter in Murchison meteorite revealed 40 years after its fall. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 2763–2768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glavin, D.P.; Callahan, M.P.; Dworkin, J.P.; Elsila, J.E. The effects of parent body processes on amino acids in carbonaceous chondrites. Meteorit. Planet. Sci. 2010, 45, 1948–1972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burton, A.S.; Stern, J.C.; Elsila, J.E.; Glavin, D.P.; Dworkin, J.P. Understanding prebiotic chemistry through the analysis of extraterrestrial amino acids and nucleobases in meteorites. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2012, 41, 5459–5472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elsila, J.E.; Charnley, S.B.; Burton, A.S.; Glavin, D.P.; Dworkin, J.P. Compound-specific carbon, nitrogen, and hydrogen isotopic ratios for amino acids in CM and CR chondrites and their use in evaluating potential formation pathways. Meteorit. Planet. Sci. 2012, 47, 1517–1536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, H.S.; Martins, Z.; Sephton, M.A. Amino acid analyses of type 3 chondrites colony, ornans, chainpur, and bishunpur. Meteorit. Planet. Sci. 2012, 47, 1502–1516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burton, A.S.; Elsila, J.E.; Hein, J.E.; Glavin, D.P.; Dworkin, J.P. Extraterrestrial amino acids identified in metal-rich CH and CB carbonaceous chondrites from Antarctica. Meteorit. Planet. Sci. 2013, 48, 390–402. [Google Scholar]
- Miller, S.L. The endogenous synthesis of organic compounds. In The Molecular Origin of Life: Assembling the Pieces of a Puzzle; Brack, A., Ed.; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2000; Chapter 3. [Google Scholar]
- Sagan, C.; Khare, B.N. Long wavelength ultraviolet photoproduction of amino acids on the primitive earth. Science 1971, 173, 417–420. [Google Scholar]
- Takano, Y.; Takahashi, J.; Kaneko, T.; Marumo, K.; Kobayashi, K. Asymmetric synthesis of amino acid precursors in interstellar complex organics by circularly polarized light. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 2007, 254, 106–114. [Google Scholar]
- Bonner, W.A.; Rubenstein, E. Supernovae, neutron stars and biomolecular chirality. BioSystems 1987, 20, 99–111. [Google Scholar]
- Jorissen, A.; Cerf, C. Asymmetric photoreactions as the origin of the biomolecular homochirality: A critical review. Orig. Life Evol. Biosph. 2002, 32, 129–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meierhenrich, U.J.; Nahon, L.; Alcaraz, C.; Bredehoft, J.H.; Hoffmann, S.V.; Barbier, B.; Brack, A. Asymmetric photolysis of the amino acid leucine in the solid state. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2005, 44, 2–5. [Google Scholar]
- Kwok, S. Organic matter in space: From star dust to the Solar System. Astrophys. Space Sci. 2009, 319, 5–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwok, S. Organic Matter in the Universe; Wiley: Weinheim, Germany, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Urey, H.C. On the early chemical history of the earth and the origin of life. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1952, 38, 351–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Urey, H.C. The cosmic abundances of potassium, uranium and thorium and the heat balance of the earth the moon and mars. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1955, 41, 127–144. [Google Scholar]
- Urey, H.C. The cosmic abundances of potassium, uranium and thorium and the heat balance of the earth, the moon and mars. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1956, 42, 889–891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Navarro-Gonzalez, R.; Romero, A. On the survivability of an enantiomeric excess of amino acids in comet nuclei during the decay of 26Al and other radionuclides. Astrophys. Space Sci. 1996, 236, 49–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cataldo, F.; Ursini, O.; Angelini, G.; Iglesias-Groth, S.; Manchado, A. Radiolysis and radioracemization of 20 amino acids from the beginning of the Solar System. Rend. Fis. Acc. Lincei 2011, 22, 81–94. [Google Scholar]
- Kohman, T.P. Aluminium-26 a radionuclide for all seasons. J. Radioanal. Nucl. Chem. 1997, 219, 165–176. [Google Scholar]
- Cataldo, F.; Angelini, G.; Iglesias-Groth, S.; Manchado, A. Solid state radiolysis of amino acids in an astrochemical perspective. Radiat. Phys. Chem. 2010, 80, 57–65. [Google Scholar]
- Cataldo, F.; Ragni, P.; Iglesias-Groth, S.; Manchado, A. Solid state radiolysis of sulphur-containing amino acids: Cysteine, cystine and methionine. J. Radioanal. Nucl. Chem. 2010, 287, 573–580. [Google Scholar]
- Cataldo, F.; Ragni, P.; Iglesias-Groth, S.; Manchado, A. A detailed analysis of the properties of radiolyzed proteinaceous amino acids. J. Radioanal. Nucl. Chem. 2010, 287, 903–911. [Google Scholar]
- Iglesias-Groth, S.; Cataldo, F.; Ursini, O.; Manchado, A. Amino acids in comets and meteorites: Stability under gamma radiation and preservation of the enantiomeric excess. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2011, 210, 1447–1453. [Google Scholar]
- Cataldo, F.; Angelini, G.; Hafez, Y.; Iglesias-Groth, S. Solid state radiolysis of non-proteinaceous amino acids in vacuum: Astrochemical implications. J. Radioanal. Nucl. Chem. 2012, 295, 1235–1243. [Google Scholar]
- Cataldo, F. Gamma radiolysis of chiral terpenes: A(+)pinene and a(−)pinene. J. Radioanal. Nucl. Chem. 2007, 272, 82–90. [Google Scholar]
- Cataldo, F. Radiation-induced racemization and amplification of chirality: Implications for comets and meteorites. Int. J. Astrobiol. 2007, 6, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cataldo, F.; Angelini, G.; Capitani, D.; Gobbino, M.; Ursini, O.; Forlini, F. Determination of the Chemical Structure of Poly-(−)-pinene by NMR Spectroscopy. J. Macromol. Sci. Pure Appl. Chem. 2008, 45, 839–849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cataldo, F.; Ursini, O.; Angelini, G. Radioracemization and radiation-induced chiral amplification of chiral terpenes measured by optical rotatory dispersion (ORD) spectroscopy. Radiat. Phys. Chem. 2008, 77, 961–967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cataldo, F.; Ursini, O.; Angelini, G.; Ragni, P. Radiation-induced inclusion polymerization of (−)pinene in deoxycholic acid. J. Macromol. Sci. Pure Appl. Chem. 2009, 46, 493–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cataldo, F.; Ursini, O.; Angelini, G. Synthesis and study of the thermal and chiro-optical properties of polyacetylenes with bulky side groups: Poly(1-ethynyl-4-biphenyl), Poly(1-ethynyl-4-phenoxybenzene) and Poly(1-ethynyl-4-pentylbenzene). J. Macromol. Sci. Pure Appl. Chem. 2009, 46, 860–869. [Google Scholar]
- Cataldo, F.; Ursini, O.; Angelini, G. Asymmetric radiation-induced inclusion polymerization of 3-methyl-1,4-pentadiene in deoxycholic acid. Radiat. Phys. Chem. 2010, 79, 57–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cataldo, F.; Lilla, E.; Ursini, O. Radiation-induced polymerization of B(+)-pinene and synthesis of optically active B(+)/B(−)pinene polymers and copolymers. Radiat. Phys. Chem. 2011, 80, 723–730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Djerassi, C. Optical Rotatory Dispersion Applications to Organic Chemistry; McGraw-Hill: New York, NY, USA, 1960. [Google Scholar]
- Freeland, S. Terrestrial amino acids and their evolution. In Amino Acids, Peptides and Proteins in Organic Chemistry; Hughes, A.W., Ed.; Wiley-VCH: Weinheim, Germany, 2009; Volume 1. [Google Scholar]
- Gargaud, M. Encyclopedia of Astrobiology; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2011; Volume 1, p. 39. [Google Scholar]
- Gejvall, T.; Lofroth, G. Radiation induced degradation of some crystalline amino acids. Radiat. Eff. 1975, 25, 187–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garrison, W.M. The radiation chemistry of amino acids, peptides and proteins in relation to the radiation sterilization of high-protein foods. Radiat. Eff. 1981, 54, 29–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raffi, J.; Talbi, S.; Dolo, J.M.; Garcia, T.; Kister, J. Advances in solid alanine radiolysis understanding. Spectrochim. Acta Part A 2008, 69, 904–910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kushelevsky, A.P.; Slifkin, M.A. The effect of crystal structure on the stability, amino acids and dipeptides yield and shape of ESR spectra of gamma-irradiated. Radiat. Eff. 1972, 15, 175–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Başkan, M.H. EPR of γ-irradiated l-glutamine, glycyl-l-glutamine and N-glycyl-l-valine. Radiat. Eff. Defects Solids 2008, 163, 35–39. [Google Scholar]
- Aydin, M.; Başkan, M.H.; Yakar, S.; Ulak, F.S.; Aydinol, M.; Aydinol, B.; Büyüm, M. EPR studies of gamma-irradiated l-alanine ethyl ester hydrochloride, l-arginine and alanyl-l-glutamine. Radiat.Eff. Defects Solids 2008, 163, 41–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Başkan, M.H.; Osmanoglu, S.; Diclec, I.Y. Radiation damage produced in powder of α-(methylamino)isobutyric acid, α-aminoisobutyric acid methyl ester hydrochloride and diethylmalonic acid. Radiat. Eff. Defects Solids 2009, 164, 673–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Başkan, M.H.; Aydın, M.; Osmanoğlu, S.; Topkaya, R. Electron paramagnetic resonance characterization of gamma irradiation damage centers in powder of l-(+)-tartaric acid, N-acetyl-l-alanine and 1-methyl-l-histidine. Radiat. Eff. Defects Solids 2010, 165, 938–943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonner, W.; Lemmon, R.M. Radiolysis, racemization and the origin o molecular asymmetry in the biosphere. J. Mol. Evol. 1978, 11, 95–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonner, W.; Lemmon, R.M. Radiolysis, racemization, and the origin of optical activity. Bioorg. Chem. 1987, 7, 175–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonner, W.A.; Blair, N.E.; Lemmon, R.M. The radioracemization of amino acids by ionizing radiation: Geochemical and cosmochemical implications. Orig. Life Evol. Biosph. 1979, 9, 279–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonner, W.; Liang, Y. β-Decay, Bremsstrahlen, and the Origin of Molecular Chirality. J. Mol. Evol. 1984, 21, 84–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonner, W.A. The radiolysis and radioracemization of poly-l-leucines. Radiat. Res. 1999, 152, 83–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kminek, G.; Bada, J.L. The effect of ionizing radiation on the preservation of amino acids on Mars. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 2006, 245, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zscherp, C.; Barth, A. Reaction-induced infrared difference spectroscopy for the study of protein reaction mechanism. Biochemistry 2001, 40, 1875–1883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avram, M.; Mateescu, G.D. Infrared Spectroscopy Applications to Organic Chemistry; Wiley-Interscience: New York, NY, USA, 1972; p. 479. [Google Scholar]
- Colthup, N.B.; Daly, L.H.; Wiberley, S.E. Introduction to Infrared and Raman Spectroscopy, 3rd ed.; Academic Press, Inc.: San Diego, CA, USA, 1990; p. 318. [Google Scholar]
- Barth, A. The infrared absorption spectra of amino acids side chains. Progr. Biophys. Mol. Biol. 2000, 74, 141–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hohne, G.; Hemminger, W.; Flammersheim, H.J. Differential Scanning Calorimetry. An Introduction for Practictioners; Springer-Verlag: Berlin, Germany, 2001; p. 176. [Google Scholar]
- Marciniec, B.; Kozak, M.; Ogrodowczyk, M. DSC study of radiostability of 1,4-dihydropyridine derivatives. J. Thermal Anal. Calorim. 2004, 77, 581–596. [Google Scholar]
© 2013 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Cataldo, F.; Iglesias-Groth, S.; Angelini, G.; Hafez, Y. Stability toward High Energy Radiation of Non-Proteinogenic Amino Acids: Implications for the Origins of Life. Life 2013, 3, 449-473. https://doi.org/10.3390/life3030449
Cataldo F, Iglesias-Groth S, Angelini G, Hafez Y. Stability toward High Energy Radiation of Non-Proteinogenic Amino Acids: Implications for the Origins of Life. Life. 2013; 3(3):449-473. https://doi.org/10.3390/life3030449
Chicago/Turabian StyleCataldo, Franco, Susana Iglesias-Groth, Giancarlo Angelini, and Yaser Hafez. 2013. "Stability toward High Energy Radiation of Non-Proteinogenic Amino Acids: Implications for the Origins of Life" Life 3, no. 3: 449-473. https://doi.org/10.3390/life3030449





