Ex-Vivo Preservation with the Organ Care System in High Risk Heart Transplantation
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Material and Methods
2.1. Exclusion Criteria
2.2. Statistical Analysis
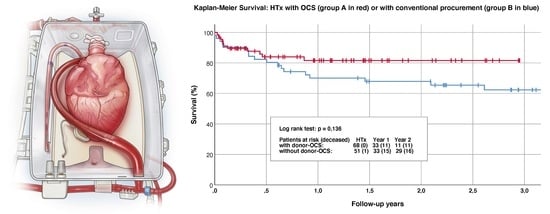
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| BIVAD | Biventricular assist device |
| DBD | Donation after brainstem death |
| DCD | Donation after cardiac death |
| ET | Eurotransplant |
| ECMO | Extracorporeal membrane oxygenation (VA = veno-arterial) |
| HU | High urgency |
| ICU | Intensive care unit |
| LV | Left ventricle |
| LVAD | Left ventricular assist device |
| LV-EF | Left ventricular ejection fraction |
| MACE | Major adverse cerebrovascular event |
| OCS | The Organ Care System |
| VAD | Ventricular assist device |
References
- Fuchs, M.; Schibilsky, D.; Zeh, W.; Berchtold-Herz, M.; Beyersdorf, F.; Siepe, M. Does the heart transplant have a future? Eur. J. Cardiothorac. Surg. 2019, 55, i38–i48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tarabeih, M.; Bokek-Cohen, Y.; Azuri, P. Health-related quality of life of transplant recipients: A comparison between lung, kidney, heart, and liver recipients. Qual. Life Res. 2020, 29, 1631–1639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vistarini, N.; Nguyen, A.; White, M.; Racine, N.; Perrault, L.P.; Ducharme, A.; Bouchard, D.; Demers, P.; Pellerin, M.; Lamarche, Y.; et al. Changes in patient characteristics following cardiac transplantation: The Montreal Heart Institute experience. Can. J. Surg. 2017, 60, 305–310. [Google Scholar]
- Khush, K.K.; Potena, L.; Cherikh, W.S.; Chambers, D.C.; Harhay, M.O.; Hayes, D.; Hsich, E.; Sadavarte, A.; Singh, T.P.; Zuckermann, A.; et al. The International Thoracic Organ Transplant Registry of the International Society for Heart and Lung Transplantation: 37th adult heart transplantation report-2020; focus on deceased donor characteristics. J. Heart Lung Transplant. 2020, 39, 1003–1015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shudo, Y.; Cohen, J.E.; Lingala, B.; He, H.; Zhu, Y.; Woo, Y.J. Impact of “increased-risk” donor hearts on transplant outcomes: A propensity-matched analysis. J. Thorac. Cardiovasc. Surg. 2019, 157, 603–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia-Saez, D.; Zych, B.; Sabashnikov, A.; Bowles, C.T.; De Robertis, F.; Mohite, P.N.; Popov, A.F.; Maunz, O.; Patil, N.P.; Weymann, A.; et al. Evaluation of the organ care system in heart transplantation with an adverse donor/recipient profile. Ann. Thorac. Surg. 2014, 98, 2099–2105, 2105–2106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monteagudo Vela, M.; Garcia-Saez, D.; Simon, A.R. Current approaches in retrieval and heart preservation. Ann. Cardiothorac. Surg. 2018, 7, 67–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Morshuis, M.; Rojas, S.V.; Hakim Meibodi, K.; Razumov, A.; Gummert, J.F.; Schramm, R. Heart transplantation after SynCardia® total artificial heart implantation. Ann. Cardiothorac. Surg. 2020, 9, 98–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mogaldea, A.; Rojas, S.V.; Ius, F.; Kaufeld, T.; Sommer, W.; Avsar, M.; Bara, C.; Haverich, A.; Warnecke, G.; Kuehn, C. Upper-body cannulation for midterm mechanical circulatory support: A novel bridging strategy to cardiac retransplantation. Int. J. Artif. Organs 2020, 43, 743–747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Southerland, K.W.; Milano, C.A. Heart Transplantation after Left Ventricular Assist Device. Oper. Tech. Thorac. Cardiovasc. Surg. 2014, 19, 47–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Axtell, A.L.; Fiedler, A.G.; Lewis, G.; Melnitchouk, S.; Tolis, G.; D’Alessandro, D.A.; Villavicencio, M.A. Reoperative sternotomy is associated with increased early mortality after cardiac transplantation. Eur. J. Cardiothorac. Surg. 2019, 55, 1136–1143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rajagopalan, N.; Shafii, A.E.; Dennis, D.R.; Charnigo, R.; Sekela, M.E. Increasing Heart Transplant Volume by Expansion of Donor Heart Selection Criteria: A Single-Center Analysis. Transplant. Proc. 2020, 52, 949–953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chan, J.L.; Kobashigawa, J.A.; Reich, H.J.; Ramzy, D.; Thottam, M.M.; Yu, Z.; Aintablian, T.L.; Liou, F.; Patel, J.K.; Kittleson, M.M.; et al. Intermediate outcomes with ex-vivo allograft perfusion for heart transplantation. J. Heart Lung Transplant. 2017, 36, 258–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Van Raemdonck, D.; Rega, F.; Rex, S.; Neyrinck, A. Machine perfusion of thoracic organs. J. Thorac. Dis. 2018, 10, S910–S923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Verzelloni Sef, A.; Sef, D.; Garcia-Saez, D.; Trkulja, V.; Walker, C.; Mitchell, J.; McGovern, I.; Stock, U. Heart Transplantation in Adult Congenital Heart Disease with the Organ Care System Use: A 4-Year Single-Center Experience. ASAIO J. 2021, 67, 862–868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ardehali, A.; Esmailian, F.; Deng, M.; Soltesz, E.; Hsich, E.; Naka, Y.; Mancini, D.; Camacho, M.; Zucker, M.; Leprince, P.; et al. Ex-vivo perfusion of donor hearts for human heart transplantation (PROCEED II): A prospective, open-label, multicentre, randomised non-inferiority trial. Lancet 2015, 385, 2577–2584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loor, G.; Warnecke, G.; Villavicencio, M.A.; Smith, M.A.; Kukreja, J.; Ardehali, A.; Hartwig, M.; Daneshmand, M.A.; Hertz, M.I.; Huddleston, S.; et al. Portable normothermic ex-vivo lung perfusion, ventilation, and functional assessment with the Organ Care System on donor lung use for transplantation from extended-criteria donors (EXPAND): A single-arm, pivotal trial. Lancet Respir. Med. 2019, 7, 975–984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warnecke, G.; Van Raemdonck, D.; Smith, M.A.; Massard, G.; Kukreja, J.; Rea, F.; Loor, G.; De Robertis, F.; Nagendran, J.; Dhital, K.K.; et al. Normothermic ex-vivo preservation with the portable Organ Care System Lung device for bilateral lung transplantation (INSPIRE): A randomised, open-label, non-inferiority, phase 3 study. Lancet Respir. Med. 2018, 6, 357–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warnecke, G.; Moradiellos, J.; Tudorache, I.; Kühn, C.; Avsar, M.; Wiegmann, B.; Sommer, W.; Ius, F.; Kunze, C.; Gottlieb, J.; et al. Normothermic perfusion of donor lungs for preservation and assessment with the Organ Care System Lung before bilateral transplantation: A pilot study of 12 patients. Lancet 2012, 380, 1851–1858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehta, V.; Taylor, M.; Hasan, J.; Dimarakis, I.; Barnard, J.; Callan, P.; Shaw, S.; Venkateswaran, R.V. Establishing a heart transplant programme using donation after circulatory-determined death donors: A United Kingdom based single-centre experience. Interact. CardioVascular Thorac. Surg. 2019, 29, 422–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chew, H.C.; Iyer, A.; Connellan, M.; Scheuer, S.; Villanueva, J.; Gao, L.; Hicks, M.; Harkness, M.; Soto, C.; Dinale, A.; et al. Outcomes of Donation After Circulatory Death Heart Transplantation in Australia. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2019, 73, 1447–1459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Messer, S.J.; Axell, R.G.; Colah, S.; White, P.A.; Ryan, M.; Page, A.A.; Parizkova, B.; Valchanov, K.; White, C.W.; Freed, D.H.; et al. Functional assessment and transplantation of the donor heart after circulatory death. J. Heart Lung Transplant. 2016, 35, 1443–1452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dhital, K.K.; Iyer, A.; Connellan, M.; Chew, H.C.; Gao, L.; Doyle, A.; Hicks, M.; Kumarasinghe, G.; Soto, C.; Dinale, A.; et al. Adult heart transplantation with distant procurement and ex-vivo preservation of donor hearts after circulatory death: A case series. Lancet 2015, 385, 2585–2591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehra, M.R. Challenges, diligence, and a breakthrough in donation after circulatory death in heart transplantation. J. Heart Lung Transplant. 2017, 36, 1319–1321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jawitz, O.K.; Raman, V.; DeVore, A.D.; Mentz, R.J.; Patel, C.B.; Rogers, J.; Milano, C. Increasing the United States heart transplant donor pool with donation after circulatory death. J. Thorac. Cardiovasc. Surg. 2020, 159, e307–e309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rojas, S.V.; Haverich, A. [Heart failure: Ventricular assist devices and cardiac transplantation: A review of current surgical innovations]. Chirurg 2019, 90, 110–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Potapov, E.V.; Antonides, C.; Crespo-Leiro, M.G.; Combes, A.; Färber, G.; Hannan, M.M.; Kukucka, M.; de Jonge, N.; Loforte, A.; Lund, L.H.; et al. 2019 EACTS Expert Consensus on long-term mechanical circulatory support. Eur. J. Cardiothorac. Surg. 2019, 56, 230–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirklin, J.K.; Goldstein, D.J.; Atluri, P.; Arabia, F.A.; Cheung, A.; Holman, W.; Hoopes, C.; Jeevanandam, V.; John, R.; Jorde, U.P.; et al. American Association for Thoracic Surgery/International Society for Heart and Lung Transplantation guidelines on selected topics in mechanical circulatory support. J. Thorac. Cardiovasc. Surg. 2020, 159, 865–896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruiz-Cano, M.J.; Ramazyan, L.; Schramm, R.; Lauenroth, V.; Paluszkiewicz, L.; Rojas, S.; Gummert, J.; Morshuis, M. Clinical implications of late-onset right ventricular failure after implantation of a continuous-flow left ventricular assist device as bridge to transplantation. Eur. J. Cardiothorac. Surg. 2021, 60, 177–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, M.Y.; Wever-Pinzon, O.; Mehra, M.R.; Selzman, C.H.; Toll, A.E.; Cherikh, W.S.; Nativi-Nicolau, J.; Fang, J.C.; Kfoury, A.G.; Gilbert, E.M.; et al. Post-transplant outcome in patients bridged to transplant with temporary mechanical circulatory support devices. J. Heart Lung Transplant. 2019, 38, 858–869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Stehlik, J.; Mehra, M.R. Secular changes in organ donor profiles and impact on heart and lung transplantation. J. Heart Lung Transplant. 2020, 39, 997–1002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| Group A (OCS) | Group B (Non OCS) | p | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age (y) M (SD) | 49.4 (12.6) | 58.6 (13.1) | 0.72 |
| Gender (male) (%) | 76.5 | 78.4 | 0.83 |
| Weight (kg) M (SD) | 81.0 (13.8) | 81.5 (17.1) | 0.85 |
| Height (cm) M (SD) | 177 (8) | 176 (10) | 0.85 |
| BMI M (SD) | 26.0 (4.2) | 26.1 (4.4) | 0.84 |
| Cardiac index M (SD) | 2.3 (0.6) | 2.4 (0.7) | 0.68 |
| PVR (dyn/s/cm2) M (SD) | 142 (60) | 146 (92) | 0.83 |
| HU grade (%) | 86.8 | 87.7 | 1.00 |
| Waiting-list period (days) M [IQR] | 137 [607] | 239 [903] | 0.47 |
| Dialysis pre HTx (%) | 5.9 | 6.0 | 0.83 |
| Stroke pre HTx (%) | 14.7 | 22.0 | 0.34 |
| Previous cardiac surgery (%) | 89.7 | 78.4 | 0.67 |
| Presence of durable VAD (%) | 77.9 | 74.5 | 0.67 |
| Previous VAD exchange (%) | 20.8 | 27.0 | 0.61 |
| Heart failure etiology | |||
| ICM n (%) | 22.1 | 35.3 | * |
| DCM n (%) | 57.4 | 43.1 | * |
| Congenital heart disease (%) | 4.4 | 3.9 | * |
| Other (%) | 4.4 | 5.9 | * |
| Group A (OCS) | Group B (Non OCS) | p | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Donor age (y) M [IQR] | 37 [25] | 44.5 [16] | 0.45 |
| Donor height (cm) M (SD) | 176 (9.0) | 178 (9.3) | 0.30 |
| Donor weight (kg) M (SD) | 81.0 (14.0) | 80.8 (15.3) | 0.93 |
| Donor BMI M (SD) | 26.2 (3.5) | 25.5 (4.1) | 0.39 |
| Donor LV-EF (%) M [IQR] | 60 [5] | 60 [3] | 0.38 |
| Donor gender (male) (%) | 63.2 | 58.8 | 0.71 |
| Donor LV-hypertrophy (%) | 19.1 | 8.3 | 0.119 |
| Donor coronary sclerosis (%) | 2.9 | 2.2 | 0.119 |
| Donor cardiac arrest (%) | 32.4 | 22.2 | 0.029 |
| Donor cardiac arrest period (min) M (SD) | 22.4 (14.2) | 14.6 (7.3) | 0.155 |
| CAUSE OF DEATH | |||
| Cerebral hemorrhage (%) | 48.5 | 47.1 | * |
| Cerebral ischemia (%) | 23.5 | 17.6 | * |
| Head Trauma (%) | 7.4 | 25.5 | * |
| Other (%) | 20.6 | 9.8 | * |
| Group A | Group B | p | |
|---|---|---|---|
| ISCHEMIA | |||
| Pre OCS ischemia (min) M (SD) | 42.4 (15.8) | ||
| OCS running-time (min) M (SD) | 267 (54.3) | ||
| Post OCS ischemia (min) M (SD) | 76.6 (33.6) | ||
| Pre & Post OCS ischemia (min) M (SD) | 115 (43.1) | ||
| OCS Ex-situ-time (min) M (SD) | 381 (74.0) | ||
| Ischemia non-OCS patients (min) M (SD) | 228 (43) | ||
| SURGERY | |||
| Operation time (min) M (SD) | 489 (94) | 458 (131) | 0.165 |
| GENDER-MATCH | |||
| Recipient:donor = male:male (%) | 60.3 | 54.9 | |
| Recipient:donor = female:female (%) | 20.6 | 17.6 | |
| Recipient:donor = male:female (%) | 16.2 | 23.5 | |
| Recipient:donor = female:male (%) | 2.9 | 3.9 |
| Group A | Group B | p | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Ventilation time (d) M [IQR] | 22 [37.8] | 47.4 [105] | 0.057 |
| ECMO postop. n (%) | 25.0 | 39.2 | 0.112 |
| Duration ECMO (d) M [IQR] | 6.8 [7.3] | 6.7 [5.8] | 0.27 |
| ICU stay (d) M [IQR] | 36 [48] | 70 [118] | 0.53 |
| Total postoperative stay (d) M [IQR] | 96 [71] | 111 [106] | 0.49 |
| Bleeding requiring surgery (%) | 19.1 | 25.5 | 0.50 |
| Dialysis (acute) (%) | 52.9 | 70.6 | 0.060 |
| Dialysis (permanent) (%) | 4.4 | 27.5 | 0.001 |
| Myocardial infarction (%) | 0 | 0 | - |
| Pulmonary embolism (%) | 1.5 | 3.9 | 1.00 |
| Stroke (%) | 4.4 | 5.6 | 1.00 |
| Rejection grade (>1R) (%) | 23.5 | 25.5 | 0.83 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Rojas, S.V.; Avsar, M.; Ius, F.; Schibilsky, D.; Kaufeld, T.; Benk, C.; Maeding, I.; Berchtold-Herz, M.; Bara, C.; Beyersdorf, F.; et al. Ex-Vivo Preservation with the Organ Care System in High Risk Heart Transplantation. Life 2022, 12, 247. https://doi.org/10.3390/life12020247
Rojas SV, Avsar M, Ius F, Schibilsky D, Kaufeld T, Benk C, Maeding I, Berchtold-Herz M, Bara C, Beyersdorf F, et al. Ex-Vivo Preservation with the Organ Care System in High Risk Heart Transplantation. Life. 2022; 12(2):247. https://doi.org/10.3390/life12020247
Chicago/Turabian StyleRojas, Sebastian V., Murat Avsar, Fabio Ius, David Schibilsky, Tim Kaufeld, Christoph Benk, Ilona Maeding, Michael Berchtold-Herz, Christoph Bara, Friedhelm Beyersdorf, and et al. 2022. "Ex-Vivo Preservation with the Organ Care System in High Risk Heart Transplantation" Life 12, no. 2: 247. https://doi.org/10.3390/life12020247
APA StyleRojas, S. V., Avsar, M., Ius, F., Schibilsky, D., Kaufeld, T., Benk, C., Maeding, I., Berchtold-Herz, M., Bara, C., Beyersdorf, F., Haverich, A., Warnecke, G., & Siepe, M. (2022). Ex-Vivo Preservation with the Organ Care System in High Risk Heart Transplantation. Life, 12(2), 247. https://doi.org/10.3390/life12020247