Selective RNA Labeling by RNA-Compatible Type II Restriction Endonuclease and RNA-Extending DNA Polymerase
Abstract
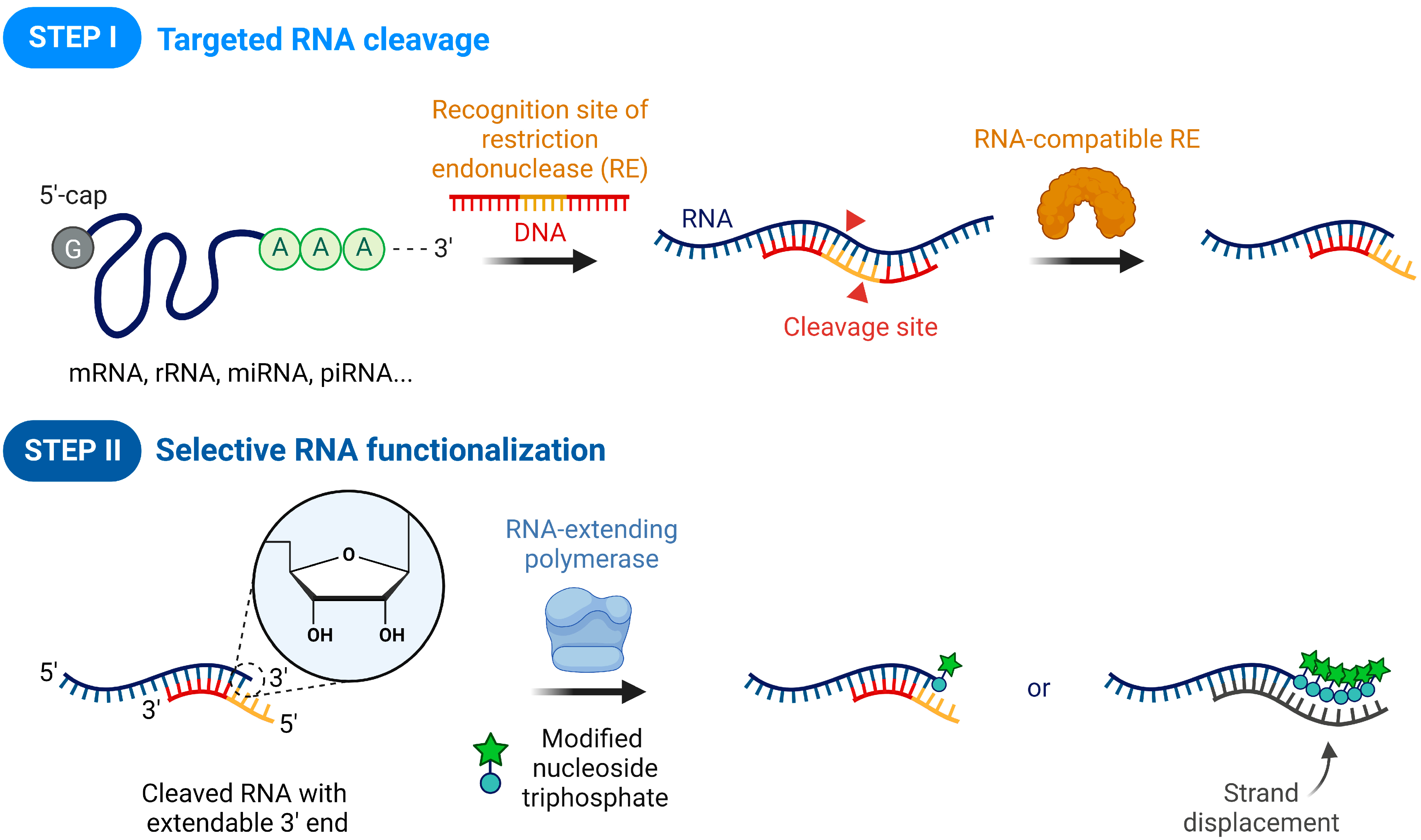
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. In Vitro RNA Transcription
2.3. Restriction Endonuclease Activity Assay Using RNA-DNA Heteroduplex
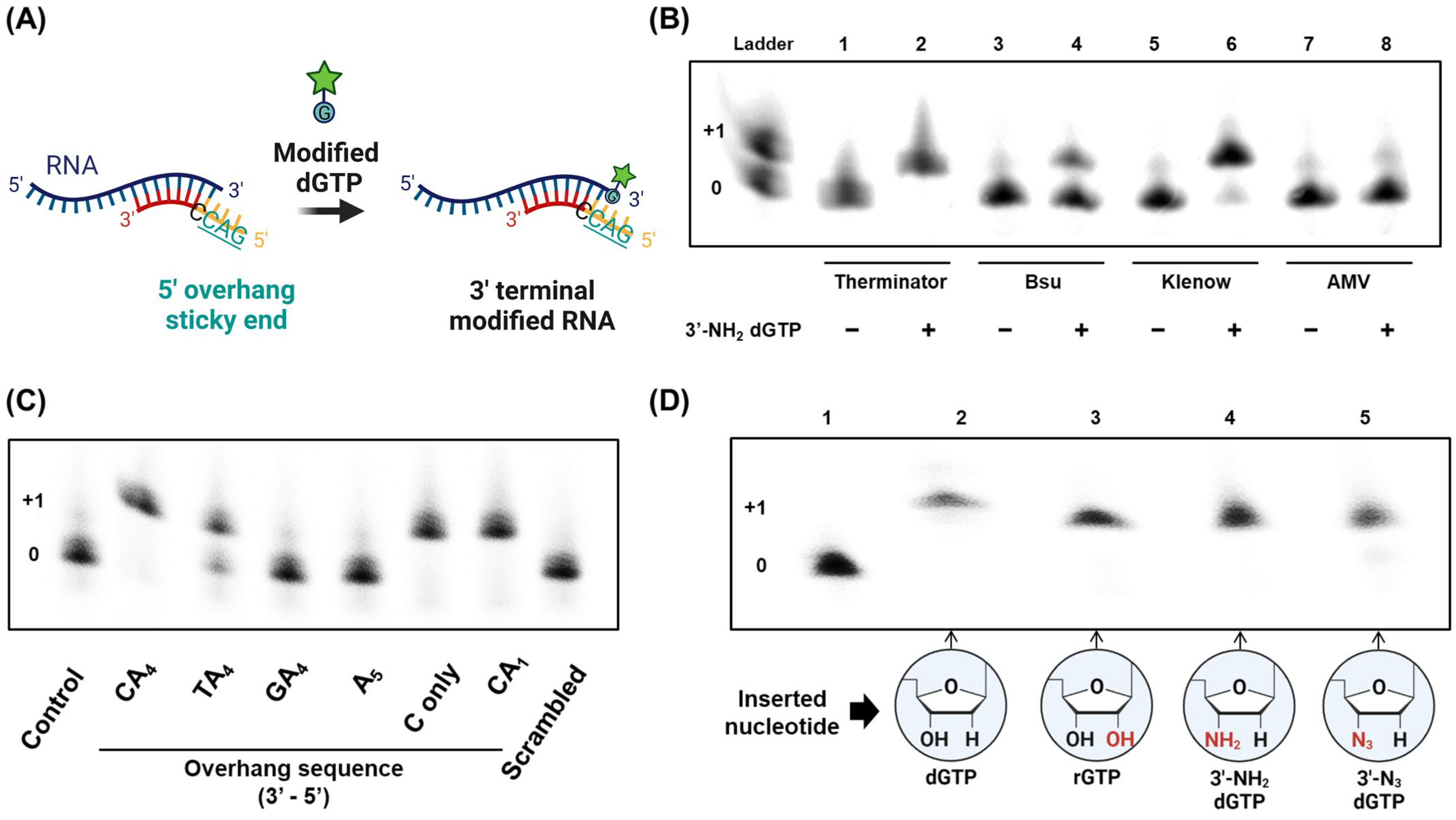
2.4. Modified Nucleotide Insertion Using Polymerases
2.5. Denaturing Gel Electrophoresis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Site-Specific Cleavage of RNA-DNA Heteroduplexes
3.2. Sequence-Specific RNA Labeling Based on RNA-DNA Hybrid Sticky Ends
3.3. Selective Labeling of Target RNA and RNA Functionalization
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zong, D.; Oberdoerffer, P.; Batista, P.J.; Nussenzweig, A. RNA: A double-edged sword in genome maintenance. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2020, 21, 651–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Statello, L.; Guo, C.-J.; Chen, L.-L.; Huarte, M. Gene regulation by long non-coding RNAs and its biological functions. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2021, 22, 96–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, M.; Beon, J.; Lee, J.Y.; Oh, S.S. Systematic combination of oligonucleotides and synthetic polymers for advanced therapeutic applications. Macromol. Res. 2021, 29, 665–680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ouyang, T.; Liu, Z.; Han, Z.; Ge, Q. MicroRNA Detection specificity: Recent advances and future perspective. Anal. Chem. 2019, 91, 3179–3186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Paillasson, S.; van de Corput, M.; Dirks, R.W.; Tanke, H.J.; Robert-Nicoud, M.; Ronot, X. In situ hybridization in living cells: Detection of RNA molecules. Exp. Cell Res. 1997, 231, 226–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, G.; Kang, B.; Park, S.V.; Lee, D.; Oh, S.S. A unified computational view of DNA duplex, triplex, quadruplex and their donor-acceptor interactions. Nucleic Acids Res. 2021, 49, 4919–4933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoo, H.; Jo, H.; Oh, S.S. Detection and beyond: Challenges and advances in aptamer-based biosensors. Mater. Adv. 2020, 1, 2663–2687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sawai, T.; Uzuki, M. In situ hybridization for RNA: Radioactive DNA probe. In Molecular Histochemical Techniques; Koji, T., Ed.; Springer: Tokyo, Japan, 2000; pp. 100–114. [Google Scholar]
- Unger, E.R. In situ hybridization: Principles and practice. Clin. Immunol. Newsl. 1990, 10, 120–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Ridzon, D.A.; Broomer, A.J.; Zhou, Z.; Lee, D.H.; Nguyen, J.T.; Barbisin, M.; Xu, N.L.; Mahuvakar, V.R.; Andersen, M.R.; et al. Real-time quantification of microRNAs by stem-loop RT-PCR. Nucleic Acids Res. 2005, 33, e179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tyagi, S.; Kramer, F.R. Molecular beacons: Probes that fluoresce upon hybridization. Nat. Biotechnol. 1996, 14, 303–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ried, T.; Baldini, A.; Rand, T.C.; Ward, D.C. Simultaneous visualization of seven different DNA probes by in situ hybridization using combinatorial fluorescence and digital imaging microscopy. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1992, 89, 1388–1392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Arvey, A.; Hermann, A.; Hsia, C.C.; Ie, E.; Freund, Y.; McGinnis, W. Minimizing off-target signals in RNA fluorescent in situ hybridization. Nucleic Acids Res. 2010, 38, e115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yang, H.; Wanner, I.B.; Roper, S.D.; Chaudhari, N. An optimized method for in situ hybridization with signal amplification that allows the detection of rare mRNAs. J. Histochem. Cytochem. 1999, 47, 431–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cui, S.; Yu, J.; Kühner, F.; Schulten, K.; Gaub, H.E. Double-stranded DNA dissociates into single strands when dragged into a poor solvent. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2007, 129, 14710–14716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Necsulea, A.; Soumillon, M.; Warnefors, M.; Liechti, A.; Daish, T.; Zeller, U.; Baker, J.C.; Grützner, F.; Kaessmann, H. The evolution of lncRNA repertoires and expression patterns in tetrapods. Nature 2014, 505, 635–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hezroni, H.; Koppstein, D.; Schwartz, M.G.; Avrutin, A.; Bartel, D.P.; Ulitsky, I. Principles of long noncoding RNA evolution derived from direct comparison of transcriptomes in 17 Species. Cell Rep. 2015, 11, 1110–1122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chen, J.; Shishkin, A.A.; Zhu, X.; Kadri, S.; Maza, I.; Guttman, M.; Hanna, J.H.; Regev, A.; Garber, M. Evolutionary analysis across mammals reveals distinct classes of long non-coding RNAs. Genome Biol. 2016, 17, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ruan, X.; Li, P.; Chen, Y.; Shi, Y.; Pirooznia, M.; Seifuddin, F.; Suemizu, H.; Ohnishi, Y.; Yoneda, N.; Nishiwaki, M.; et al. In vivo functional analysis of non-conserved human lncRNAs associated with cardiometabolic traits. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Clark, D.P.; Pazdernik, N.J.; McGehee, M.R. Basic genetics. In Molecular Biology; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2019; pp. 38–62. [Google Scholar]
- Murray, I.A.; Stickel, S.K.; Roberts, R.J. Sequence-specific cleavage of RNA by type II restriction enzymes. Nucleic Acids Res. 2010, 38, 8257–8268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Breslow, R. Kinetics and mechanism in RNA cleavage. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1993, 90, 1208–1211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shigematsu, M.; Kawamura, T.; Kirino, Y. Generation of 2′,3′-cyclic phosphate-containing RNAs as a hidden layer of the transcriptome. Front. Genet. 2018, 9, 562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, H.; Yu, X.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, J.; Wu, B.; Zheng, L.; Haruehanroengra, P.; Wang, R.; Li, S.; Lin, J.; et al. Crystal structure of an RNA-cleaving DNAzyme. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 2006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yoo, H.; Lee, J.Y.; Park, K.S.; Oh, S.S. Lead-start isothermal polymerase amplification controlled by DNAzymatic switches. Nanoscale 2022, 14, 7828–7836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, S.V.; Yang, J.-S.; Jo, H.; Kang, B.; Oh, S.S.; Jung, G.Y. Catalytic RNA, ribozyme, and its applications in synthetic biology. Biotechnol. Adv. 2019, 37, 107452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Watanabe, T. Chapter 4—The Cell. In Biophysical Basis of Physiology and Calcium Signaling Mechanism in Cardiac and Smooth Muscle; Watanabe, T., Ed.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2018; pp. 99–137. [Google Scholar]
- Gardner, A.F.; Jackson, K.M.; Boyle, M.M.; Buss, J.A.; Potapov, V.; Gehring, A.M.; Zatopek, K.M.; Corrêa, I.R.; Ong, J.L.; Jack, W.E. Therminator DNA polymerase: Modified nucleotides and unnatural substrates. Front. Mol. Biosci. 2019, 6, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- McKenzie, L.K.; El-Khoury, R.; Thorpe, J.D.; Damha, M.J.; Hollenstein, M. Recent progress in non-native nucleic acid modifications. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2021, 50, 5126–5164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coulther, T.A.; Stern, H.R.; Beuning, P.J. Engineering polymerases for new functions. Trends Biotechnol. 2019, 37, 1091–1103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jo, H.; Beon, J.; Oh, S.S. Selective RNA Labeling by RNA-Compatible Type II Restriction Endonuclease and RNA-Extending DNA Polymerase. Life 2022, 12, 1674. https://doi.org/10.3390/life12101674
Jo H, Beon J, Oh SS. Selective RNA Labeling by RNA-Compatible Type II Restriction Endonuclease and RNA-Extending DNA Polymerase. Life. 2022; 12(10):1674. https://doi.org/10.3390/life12101674
Chicago/Turabian StyleJo, Hyesung, Jiyun Beon, and Seung Soo Oh. 2022. "Selective RNA Labeling by RNA-Compatible Type II Restriction Endonuclease and RNA-Extending DNA Polymerase" Life 12, no. 10: 1674. https://doi.org/10.3390/life12101674




