Host Cell Proteins in Biologics Manufacturing: The Good, the Bad, and the Ugly
Abstract
:1. Introduction
- Impurities, which can be separated easily from the main component, are considered “the Good.” They possess physicochemical properties significantly different from the protein of interest (i.e., pI, MW, hydrophobicity). As a result, they may be separated by only one unit operation in an efficient way (ion exchange in terms of charge differences).
- Side components showing more similarity to the product are more difficult to separate or are persistent throughout (i.e., not separable from the product) and thus are considered as “the Bad” or “the Ugly.”
2. Results and Discussion
3. Materials and Methods
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
| # | Gel MW | Gel pI | MW (UniProt) | pI (UniProt) | Primary Accession Number (UniProt) | Number of Unique Peptides | Protein |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 25 | 7.2 | 25.76 | 6.45 | A0A061HUZ2 | 9 | Platelet-activating factor |
| 81.56 | 5.69 | A0A061IN16 | 11 | Glutathione S-transferase Mu 7-like protein | |||
| 25.88 | 6.43 | A0A061HYZ1 | 9 | Peroxiredoxin-6-like protein | |||
| 2 | 25 | 7.9 | 30.28 | 7.22 | A0A061IFC9 | 4 | Carbonic anhydrase |
| 89.52 | 6.23 | A0A061IJC4 | 4 | Glutathione S-transferase Mu 1-like protein | |||
| 81.56 | 5.69 | A0A061IN16 | 4 | Glutathione S-transferase Mu 7-like protein | |||
| 3 | 30 | 7.6 | 72.13 | 7.23 | A0A098KXF7 | 8 | Pyruvate kinase |
| 38.03 | 6.08 | A0A061ILE8 | 6 | Purine nucleoside phosphorylase-like protein | |||
| 32.23 | 9.11 | A0A061IAK4 | 5 | l-lactate dehydrogenase A chain | |||
| 4 | 50 | 9.6 | 45.28 | 8.48 | A0A061IB69 | 7 | Fructose-bisphosphate aldolase |
| 72.13 | 7.23 | A0A098KXF7 | 15 | Pyruvate kinase | |||
| 102.7 | 6.02 | A0A069C7Y3 | 5 | Actin, cytoplasmic 1 | |||
| 5 | 25 | 6.6 | 27.39 | 6.34 | A0A061I2E1 | 8 | Proteasome subunit |
| 89.52 | 6.23 | A0A061IJC4 | 8 | Glutathione S-transferase Mu 1-like protein | |||
| 81.56 | 5.69 | A0A061IN16 | 8 | Glutathione S-transferase Mu 7-like protein | |||
| 6 | 45 | 6.7 | 50.57 | 5.93 | G3GR73 | 11 | Rab GDP diss. inhib. |
| 52.79 | 6 | A0A098KXB1 | 10 | Cytosol aminopeptidase-like protein | |||
| 44.67 | 7.54 | A0A061IJI8 | 9 | Alpha-enolase | |||
| 7 | 50 | 6.1 | 52.79 | 6 | A0A098KXB1 | 20 | Aminopeptidase |
| 72.13 | 7.23 | A0A098KXF7 | 29 | Pyruvate kinase | |||
| 145.1 | 8.37 | A0A061HU29 | 15 | Glucose-6-phosphate 1-dehydrogenase | |||
| 8 | 57 | 6 | 73.86 | 5.56 | A0A061I5D1 | 22 | Heat shock protein |
| 74.72 | 5.29 | A0A061HWC7 | 9 | Plastin-3 | |||
| 69.64 | 5.57 | A0A061I5U1 | 9 | Heat shock-related protein 2 | |||
| 9 | 80 | 6.1 | 72.13 | 7.23 | A0A098KXF7 | 11 | Pyruvate kinase |
| 117.7 | 5.42 | G3IBG3 | 8 | Ubiquitin activating enzyme E1 | |||
| 73.86 | 5.56 | A0A061I5D1 | 7 | Heat shock protein | |||
| 10 | 70 | 5.6 | 73.86 | 5.56 | A0A061I5D1 | 9 | Heat shock protein |
| 68.43 | 5.55 | A0A061I1Q2 | 5 | Vitamin K-dependent protein S | |||
| 85.71 | 5.2 | A0A061IAX6 | 5 | Dipeptidyl peptidase 3 | |||
| 11 | 25 | 6 | 25.88 | 6.43 | A0A061HYZ1 | 9 | Peroxiredoxin |
| 89.52 | 6.23 | A0A061IJC4 | 19 | Glutathione S-transferase Mu 1-like protein | |||
| 81.56 | 5.69 | A0A061IN16 | 14 | Glutathione S-transferase Mu 7-like protein | |||
| 12 | 55 | 7.8 | 72.13 | 7.23 | A0A098KXF7 | 37 | Pyruvate kinase |
| 52.79 | 6 | A0A098KXB1 | 10 | Cytosol aminopeptidase-like protein | |||
| 73.86 | 5.56 | A0A061I5D1 | 4 | Heat shock protein | |||
| 13 | 50 | 8.6 | 52.79 | 6 | A0A098KXB1 | 4 | Cytosol aminopeptidase-like protein |
| 72.13 | 7.23 | A0A098KXF7 | 19 | Pyruvate kinase | |||
| 145.1 | 8.37 | A0A061HU29 | 2 | Glucose-6-phosphate 1-dehydrogenase | |||
| 14 | 50 | 9.2 | 72.13 | 7.23 | A0A098KXF7 | 20 | Pyruvate kinase |
| 44.67 | 7.54 | A0A061IJI8 | 3 | Alpha-enolase | |||
| 42.69 | 8.78 | A0A061HV36 | 3 | Eukaryotic translation initiation factor 2 subunit 3-like protein |
| # | Gel MW | Gel pI | MW (UniProt) | pI (UniProt) | Primary accession number (UniProt) | Number of Unique Peptides | Protein |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 25 | 7 | 26.96 | 5.38 | A0A061I6A0 | 5 | Glutathione S-transferase A4-like protein |
| 81.56 | 5.69 | A0A061IN16 | 8 | Glutathione S-transferase Mu 7-like protein | |||
| 38.03 | 6.08 | A0A061ILE8 | 8 | Purine nucleoside phosphorylase-like protein | |||
| 2 | 25 | 7.5 | 38.03 | 6.08 | A0A061ILE8 | 6 | Purine nucleoside phosphorylase |
| 102.7 | 6.02 | A0A069C7Y3 | 2 | Actin, cytoplasmic 1 | |||
| 43.35 | 6.48 | A0A061IJG8 | 2 | Prostaglandin reductase 1-like protein | |||
| 3 | 30 | 7.4 | 45.28 | 8.48 | A0A061IB69 | 1 | Fructose-bisphosphate aldolase |
| 4 | 50 | 9.4 | 89.52 | 6.23 | A0A061IJC4 | 2 | Glutathione S-transferase |
| 5 | 25 | 6.6 | 38.03 | 6.08 | A0A061ILE8 | 7 | Purine nucleoside phosphorylase |
| 89.52 | 6.23 | A0A061IJC4 | 5 | Glutathione S-transferase | |||
| 6 | 37 | 9.4 | 45.28 | 8.48 | A0A061IB69 | 4 | Fructose-bisphosphate aldolase |
| 43.35 | 6.48 | A0A061IJG8 | 2 | Prostaglandin reductase 1-like protein | |||
| 361.89 | 4.81 | A0A061IH02 | 2 | Desmoglein-4-like protein | |||
| 7 | 30 | 7 | 38.03 | 6.08 | A0A061ILE8 | 4 | Purine nucleoside phosphorylase |
| 128.68 | 6.78 | A0A061IK77 | 3 | Exosome component 10 isoform 1 | |||
| 11.37 | 11.36 | G3H2T6 | 2 | Histone H4 | |||
| 8 | 30 | 6.8 | 27.79 | 4.7 | A0A061IGS6 | 4 | Protein sigma |
| 102.7 | 6.02 | A0A069C7Y3 | 5 | Actin, cytoplasmic 1 | |||
| 361.89 | 4.81 | A0A061IH02 | 4 | Desmoglein-4-like protein | |||
| 9 | 17 | 6.6 | 11.37 | 11.36 | G3H2T6 | 4 | Histone H4 |
| 14.99 | 10.2 | A0A061IP52 | 2 | Histone H2B | |||
| 10 | 30 | 5.6 | 52.25 | 5.35 | A0A061IML2 | 13 | Annexin |
| 268.7 | 5.69 | A0A061IP39 | 10 | Filamin-B isoform 4 | |||
| 50.99 | 6.94 | A0A061I8I4 | 4 | Cathepsin F | |||
| 11 | 30 | 4.5 | 52.25 | 5.35 | A0A061IML2 | 2 | Annexin |
| 14.73 | 9.87 | A0A061IQB8 | 3 | Ubiquitin-60S | |||
| 12 | 30 | 2.8 | 38.03 | 6.08 | A0A061ILE8 | 8 | Purine nucleoside phosphorylase |
| 89.52 | 6.23 | A0A061IJC4 | 8 | Glutathione S-transferase | |||
| 101.51 | 5.12 | A0A061IRD9 | 5 | AP complex subunit beta | |||
| 13 | 15 | 6.7 | 38.03 | 6.08 | A0A061ILE8 | 4 | Purine nucleoside phosphorylase |
| 89.52 | 6.23 | A0A061IJC4 | 4 | Glutathione S-transferase | |||
| 38.31 | 5.33 | A0A061IEW1 | 3 | Nuclear migration protein nudC-like protein | |||
| 14 | 15 | 6.1 | 38.31 | 5.33 | A0A061IEW1 | 5 | Nuclear migration protein nudC-like protein |
| 89.52 | 6.23 | A0A061IJC4 | 4 | Glutathione S-transferase | |||
| 54.11 | 5.01 | A0A061IDB2 | 3 | Prelamin-A/C-like isoform 1 | |||
| 15 | 12 | 5.6 | 17.16 | 7.8 | A0A061I0I3 | 4 | SH3 binding protein |
| 17.19 | 5.94 | G3HBD4 | 3 | Nucleoside diphosphate kinase | |||
| 16 | 17 | 6.6 | 23.42 | 5.1 | G3GXB0 | 3 | Rho GDP |
| 89.52 | 6.23 | A0A061IJC4 | 8 | Glutathione S-transferase | |||
| 102.7 | 6.02 | A0A069C7Y3 | 2 | Actin, cytoplasmic 1 | |||
| 17 | 16 | 9.2 | 14.73 | 9.87 | A0A061IQB8 | 3 | Ubiquitin-60S |
| 102.7 | 6.02 | A0A069C7Y3 | 3 | Actin, cytoplasmic 1 | |||
| 23.42 | 5.1 | G3GXB0 | 3 | Rho GDP |
| # | Gel MW | Gel pI | MW (UniProt) | pI (UniProt) | Primary Accession Number (UniProt) | Number of Unique Peptides | Protein |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 25 | 6.9 | - | - | - | - | - |
| 2 | 25 | 7.6 | 11.37 | 11.36 | G3H2T6 | 2 | Histone H4 |
| 102.7 | 6.02 | A0A069C7Y3 | 2 | Actin, cytoplasmic 1 | |||
| 3 | 30 | 7.6 | 38.03 | 6.08 | A0A061ILE8 | 2 | Purine nucleoside |
| 102.7 | 6.02 | A0A069C7Y3 | 1 | Actin, cytoplasmic 1 | |||
| 4 | 50 | 8.4 | 44.67 | 7.54 | A0A061IJI8 | 8 | Alpha-enolase |
| 72.13 | 7.23 | A0A098KXF7 | 8 | Pyruvate kinase | |||
| 38.03 | 6.08 | A0A061ILE8 | 2 | Purine nucleoside | |||
| 5 | 25 | 6.3 | 38.03 | 6.08 | A0A061ILE8 | 6 | Purine nucleoside |
| 6 | 25 | 8.4 | 38.03 | 6.08 | A0A061ILE8 | 4 | Purine nucleoside |
| 7 | 50 | 8 | 44.67 | 7.54 | A0A061IJI8 | 1 | Alpha-enolase |
| 8 | 47 | 7.6 | 44.67 | 7.54 | A0A061IJI8 | 5 | Alpha-enolase |
| 102.7 | 6.02 | A0A069C7Y3 | 3 | Actin, cytoplasmic 1 | |||
| 72.13 | 7.23 | A0A098KXF7 | 2 | Pyruvate kinase | |||
| 9 | 50 | 7.2 | 59.76 | 9.22 | A0A061ICE4 | 4 | ATP synthase subunit |
| 14.73 | 9.87 | A0A061IQB8 | 2 | Ubiquitin-60S ribosomal protein L40-like isoform 2 | |||
| 102.7 | 6.02 | A0A069C7Y3 | 2 | Actin, cytoplasmic 1 | |||
| 10 | 25 | 5.1 | - | - | - | - | - |
| 11 | 50 | 4.8 | 211.66 | 5.42 | A0A061I4N6 | 1 | CAP-Gly domain-containing linker protein 1 |
| 12 | 52 | 4 | - | - | - | - | - |
References
- EvaluatePharma. World Preview 2016, Outlook to 2022; EvaluatePharma: London, UK, 2016; pp. 1–39. [Google Scholar]
- EvaluatePharma. World Preview 2015, Outlook to 2020; EvaluatePharma: London, UK, 2015; pp. 1–39. [Google Scholar]
- Li, F.; Vijayasankaran, N.; Shen, A.; Kiss, R.; Amanullah, A. Cell culture processes for monoclonal antibody production. mAbs 2010, 2, 466–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gronemeyer, P.; Ditz, R.; Strube, J. Trends in Upstream and Downstream Process Development for Antibody Manufacturing. Bioengineering 2014, 1, 188–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sommerfeld, S.; Strube, J. Challenges in biotechnology production—Generic processes and process optimization for monoclonal antibodies. Chem. Eng. Process. Process Intensif. 2005, 44, 1123–1137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Birch, J.R.; Racher, A.J. Antibody production. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2006, 58, 671–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, H.F.; Ma, J.; Winter, C.; Bayer, R. Recovery and purification process development for monoclonal antibody production. mAbs 2010, 2, 480–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shukla, A.A.; Thömmes, J. Recent advances in large-scale production of monoclonal antibodies and related proteins. Trends Biotechnol. 2010, 28, 253–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jain, E.; Kumar, A. Upstream processes in antibody production: Evaluation of critical parameters. Biotechnol. Adv. 2008, 26, 46–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Strube, J.; Grote, F.; Josch, J.P.; Ditz, R. Process development and design of downstream processes. Chemie-Ingenieur-Technik 2011, 83, 1044–1065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gagnon, P. Technology trends in antibody purification. J. Chromatogr. A 2012, 1221, 57–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kelley, B. Industrialization of mAb production technology: The bioprocessing industry at a crossroads. mAbs 2009, 1, 440–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chon, J.H.; Zarbis-Papastoitsis, G. Advances in the production and downstream processing of antibodies. New Biotechnol. 2011, 28, 458–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, J.H.; Jin, J.H.; Lim, M.S.; An, H.J.; Kim, J.W.; Lee, G.M. Proteomic Analysis of Host Cell Protein Dynamics in the Culture Supernatants of Antibody-Producing CHO Cells. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 44246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reinhart, D.; Damjanovic, L.; Kaisermayer, C.; Kunert, R. Benchmarking of commercially available CHO cell culture media for antibody production. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2015, 4645–4657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Strube, J.; Sommerfeld, S.; Lohrmann, M. Process Development and Optimization for Biotechnology Production—Monoclonal Antibodies. In Bioseparation and Bioprocessing, 2nd ed.; Subramanian, G., Ed.; Wiley-VCH: Weinheim, Germany, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Strube, J.; Grote, F.; Ditz, R. Bioprocess Design and Production Technology for the Future. In Biopharmaceutical Production Technology; Subramanian, G., Ed.; Wiley-VCH: Weinheim, Germany, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- GE Healthcare. Strategies for Protein Purification. Handbook; GE Healthcare: Little Chalfont, UK, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Levy, N.E.; Valente, K.N.; Choe, L.H.; Lee, K.H.; Lenhoff, A.M. Identification and Characterization of Host Cell Protein Product-Associated Impurities in Monoclonal Antibody Bioprocessing. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 2014, 111, 904–912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Del Val, I.J.; Kontoravdi, C.; Nagy, J.M. Towards the implementation of quality by design to the production of therapeutic monoclonal antibodies with desired glycosylation patterns. Biotechnol. Prog. 2010, 26, 1505–1527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hinz, D.C. Process analytical technologies in the pharmaceutical industry: The FDA’s PAT initiative. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2006, 384, 1036–1042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mercier, S.M.; Rouel, P.M.; Lebrun, P.; Diepenbroek, B.; Wijffels, R.H.; Streefland, M. Process analytical technology tools for perfusion cell culture. Eng. Life Sci. 2016, 16, 25–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hakemeyer, C.; McNight, N.; St. John, R.; Meier, S.; Trexler-Schmidt, M.; Kelley, B.; Zettl, F.; Puskeiler, R.; Kleinjans, A.; Lim, F.; et al. Process characterization and Design Space definition. Biologicals 2016, 44, 306–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frenzel, A.; Hust, M.; Schirrmann, T. Expression of recombinant antibodies. Front. Immunol. 2013, 4, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shields, R.L.; Lai, J.; Keck, R.; O’Connell, L.Y.; Hong, K.; Gloria Meng, Y.; Weikert, S.H.A.; Presta, L.G. Lack of fucose on human IgG1 N-linked oligosaccharide improves binding to human Fc\gammaRIII and antibody-dependent cellular toxicity. J. Biol. Chem. 2002, 277, 26733–26740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Richter, V.; Kwiatkowski, M.; Omidi, M.; Omidi, A.; Robertson, W.D.; Schlüter, H. Mass spectrometric analysis of protein species of biologics. Pharm. Bioprocess. 2013, 1, 381–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hakemeyer, C.; Pech, M.; Lipok, G.; Herrmann, A. Characterization of the influence of cultivation parameters on extracellular modifications of antibodies during fermentation. BMC Proc. 2013, 7, P85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kunert, R.; Reinhart, D. Advances in recombinant antibody manufacturing. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2016, 100, 3451–3461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jefferis, R. Glycosylation as a strategy to improve antibody-based therapeutics. Nature reviews. Drug Discovery 2009, 8, 226–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alt, N.; Zhang, T.Y.; Motchnik, P.; Taticek, R.; Quarmby, V.; Schlothauer, T.; Beck, H.; Emrich, T.; Harris, R.J. Determination of critical quality attributes for monoclonal antibodies using quality by design principles. Biologicals 2016, 44, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brunner, M.; Fricke, J.; Kroll, P.; Herwig, C. Investigation of the interactions of critical scale-up parameters (pH, pO2 and pCO2) on CHO batch performance and critical quality attributes. Bioprocess Biosyst. Eng. 2016, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chee Furng Wong, D.; Tin Kam Wong, K.; Tang Goh, L.; Kiat Heng, C.; Gek Sim Yap, M. Impact of dynamic online fed-batch strategies on metabolism, productivity and N-glycosylation quality in CHO cell cultures. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 2005, 89, 164–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, S.X.; Zhang, Y.; Stansberry-Perkins, K.; Buko, A.; Bai, S.; Nguyen, V.; Brader, M.L. Fragmentation of a highly purified monoclonal antibody attributed to residual CHO cell protease activity. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 2011, 108, 977–982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gramer, M.J.; Goochee, C.F. Glycosidase activities of the 293 and NS0 cell lines, and of an antibody-producing hybridoma cell line. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 1994, 43, 423–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Robert, F.; Bierau, H.; Rossi, M.; Agugiaro, D.; Soranzo, T.; Broly, H.; Mitchell-Logean, C. Degradation of an Fc-fusion recombinant protein by host cell proteases: Identification of a CHO cathepsin D protease. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 2009, 104, 1132–1141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tait, A.S.; Hogwood, C.E.M.; Smales, C.M.; Bracewell, D.G. Host cell protein dynamics in the supernatant of a mAb producing CHO cell line. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 2012, 109, 971–982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hogwood, C.E.M.; Tait, A.S.; Koloteva-Levine, N.; Bracewell, D.G.; Smales, C.M. The dynamics of the CHO host cell protein profile during clarification and protein A capture in a platform antibody purification process. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 2013, 110, 240–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, N.; Arunkumar, A.; Chollangi, S.; Tan, Z.G.; Borys, M.; Li, Z.J. Clarification technologies for monoclonal antibody manufacturing processes: Current state and future perspectives. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 2016, 113, 698–716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valente, K.N.; Lenhoff, A.M.; Lee, K.H. Expression of difficult-to-remove host cell protein impurities during extended Chinese hamster ovary cell culture and their impact on continuous bioprocessing. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 2015, 112, 1232–1242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Hunter, A.K.; Mozier, N.M. Host cell proteins in biologics development: Identification, quantitation and risk assessment. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 2009, 103, 446–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eggersgluess, J.K.; Richter, M.; Dieterle, M.; Strube, J. Multi-stage aqueous two-phase extraction for the purification of monoclonal antibodies. Chem. Eng. Technol. 2014, 37, 675–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gronemeyer, P.; Ditz, R.; Strube, J. Implementation of aqueous two-phase extraction combined with precipitation in a monoclonal antibody manufacturing process. Chimica Oggi/Chem. Today 2016, 34, 66–70. [Google Scholar]
- Eggersgluess, J.A.N.K.; Both, S.; Strube, J. Process Development for the Extraction of Biomolecules. Chimica Oggi/Chem. Today 2012, 30, 4. [Google Scholar]
- Asenjo, J.A.; Andrews, B.A. Aqueous two-phase systems for protein separation: A perspective. J. Chromatogr. A 2011, 1218, 8826–8835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Azevedo, A.M.; Gomes, A.G.; Rosa, P.A.J.; Ferreira, I.F.; Pisco, A.M.M.O.; Aires-Barros, M.R. Partitioning of human antibodies in polyethylene glycol-sodium citrate aqueous two-phase systems. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2009, 65, 14–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zobel, S.; Helling, C.; Ditz, R.; Strube, J. Design and operation of continuous countercurrent chromatography in biotechnological production. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2014, 53, 9169–9185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gronemeyer, P.; Ditz, R.; Strube, J. DoE based integration approach of upstream and downstream processing regarding HCP and ATPE as harvest operation. Biochem. Eng. J. 2016, 113, 158–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, U.; Saunders, G. The Effect of NaCl Concentration on Protein Size Exclusion Chromatography. Application Note. Available online: http://cn.agilent.com/cs/library/applications/SI-02416.pdf (accessed on 17 July 2017).
- Roch, P.; Mandenius, C.-F. On-line monitoring of downstream bioprocesses. Curr. Opin. Chem. Eng. 2016, 14, 112–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
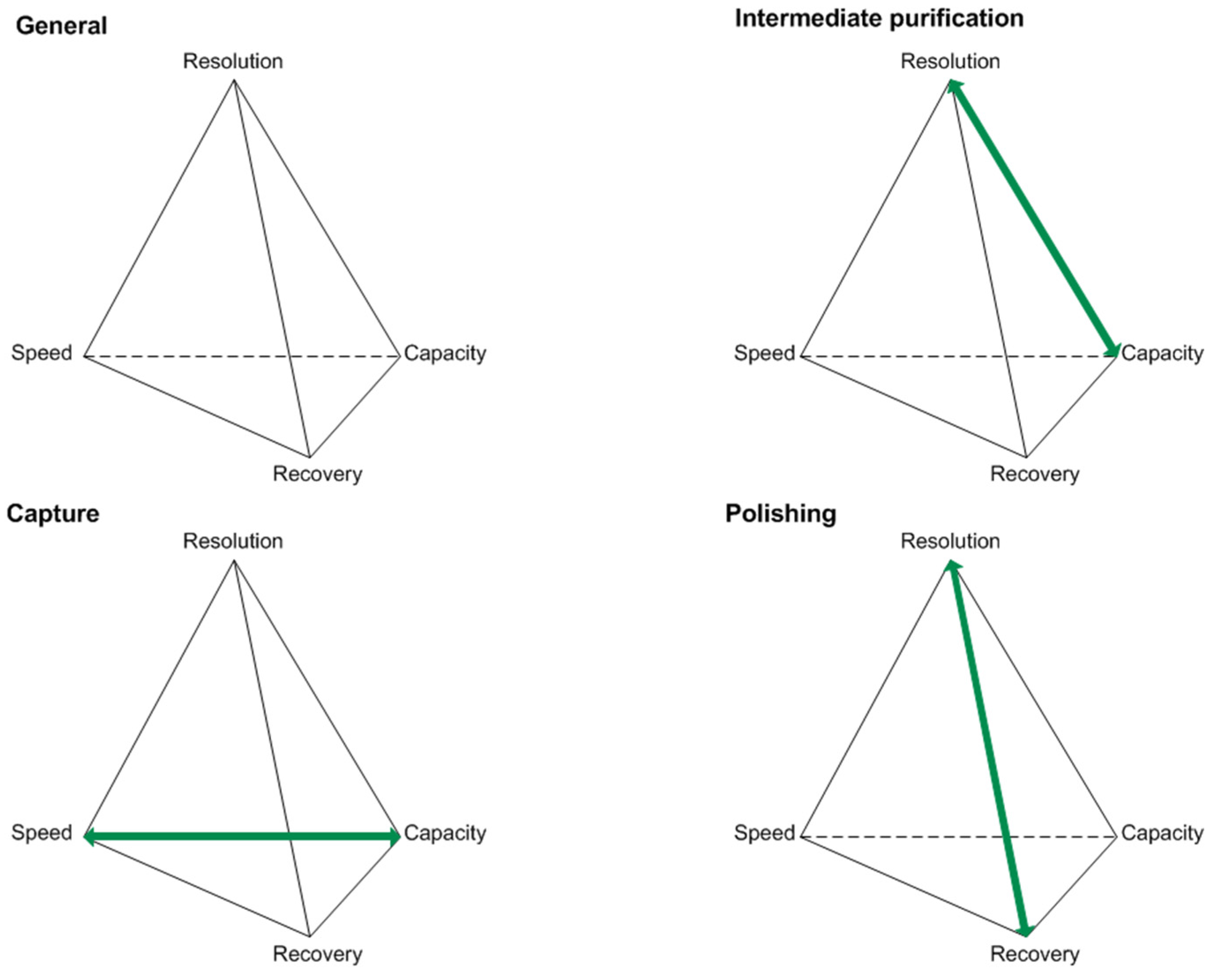
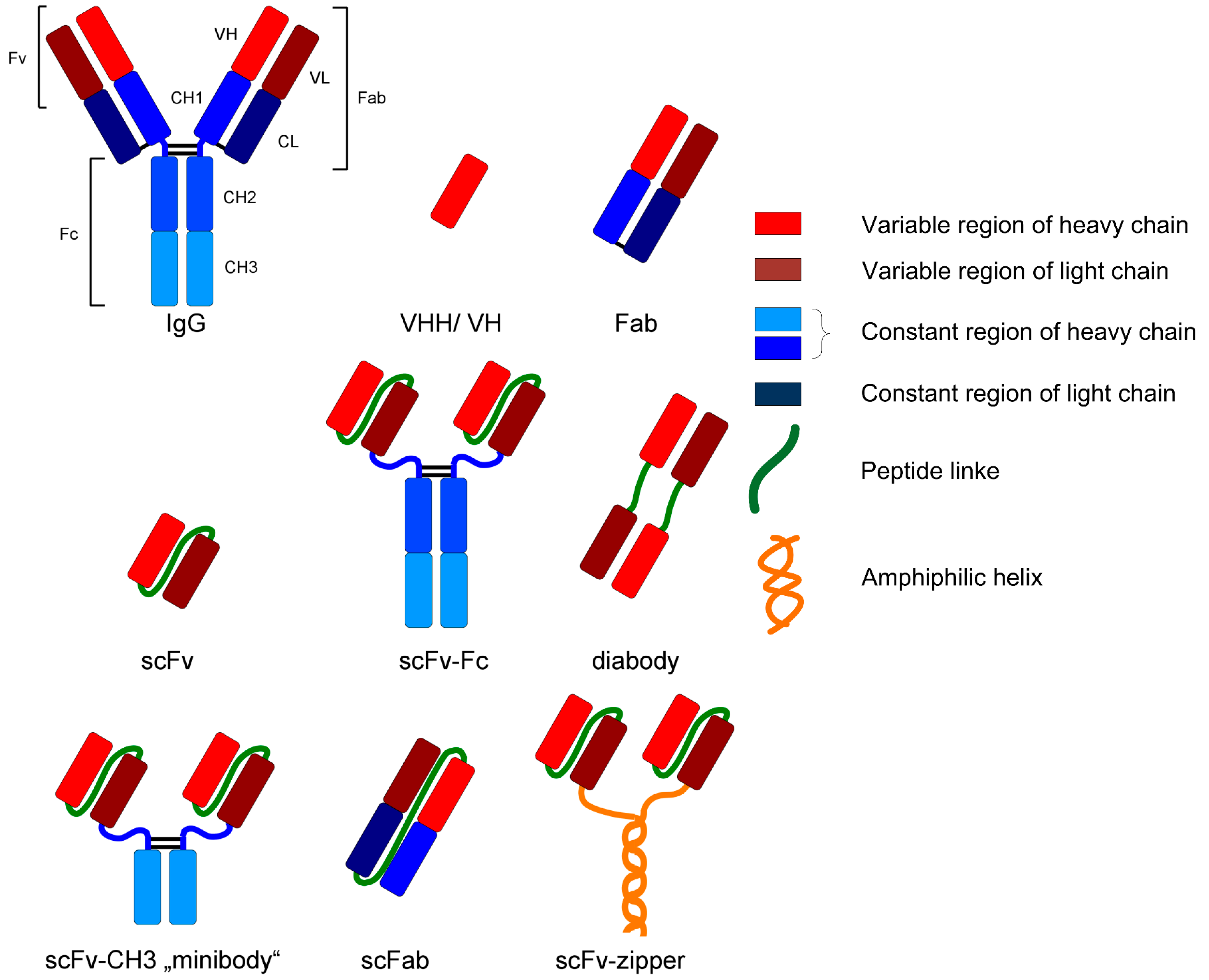
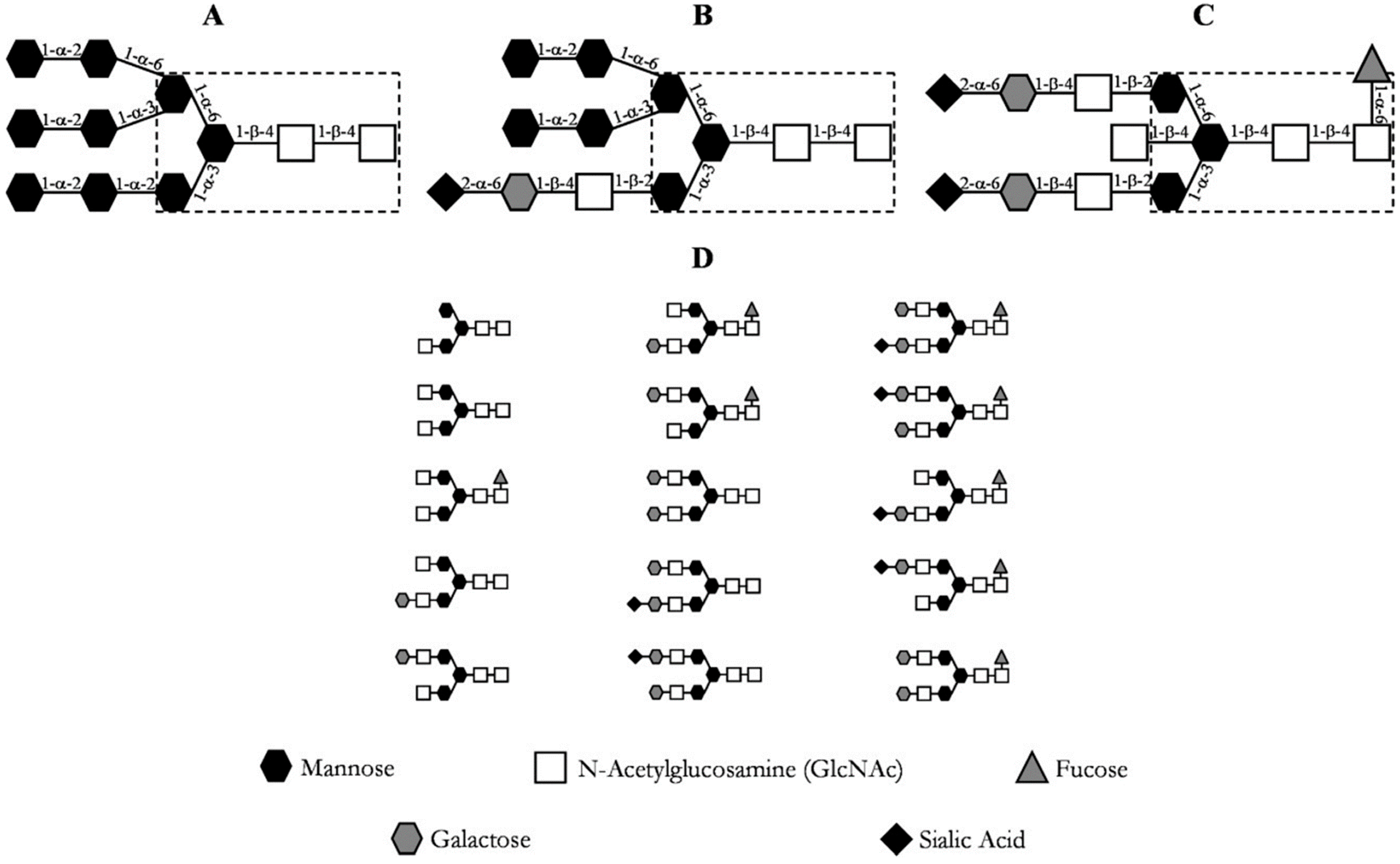
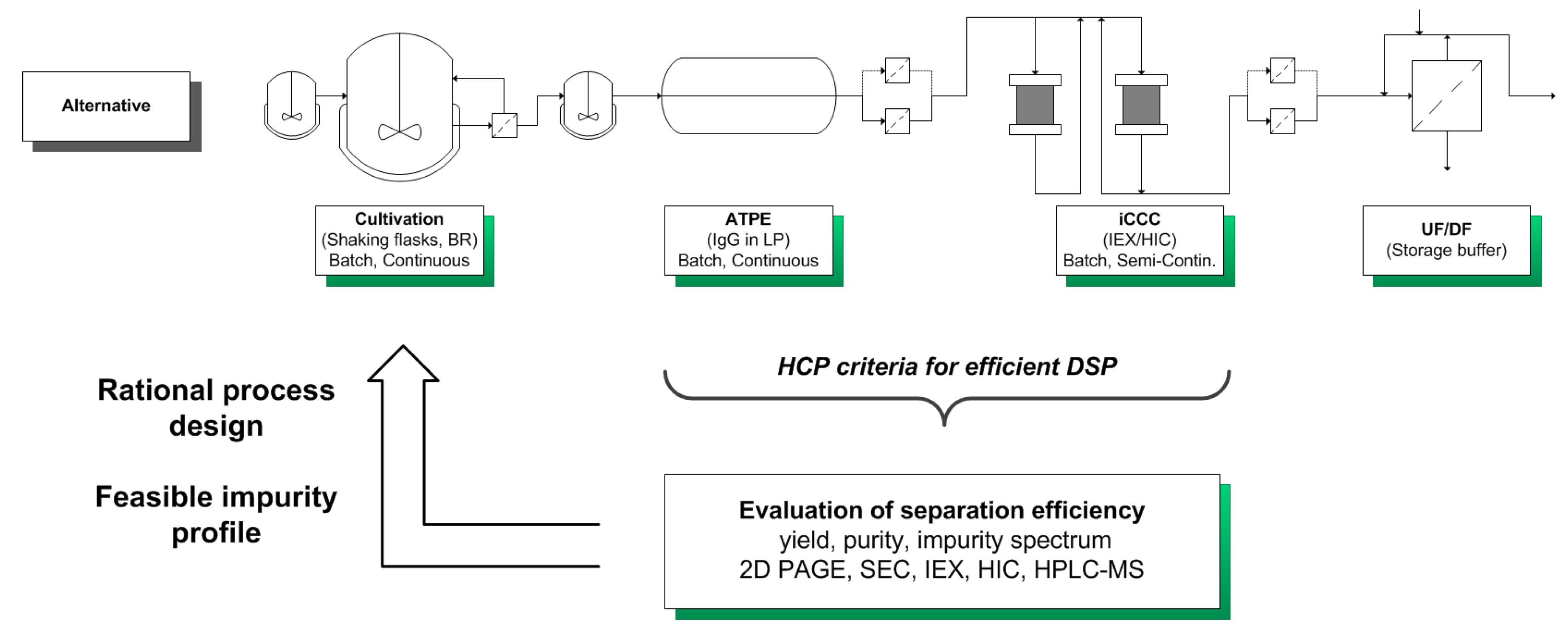
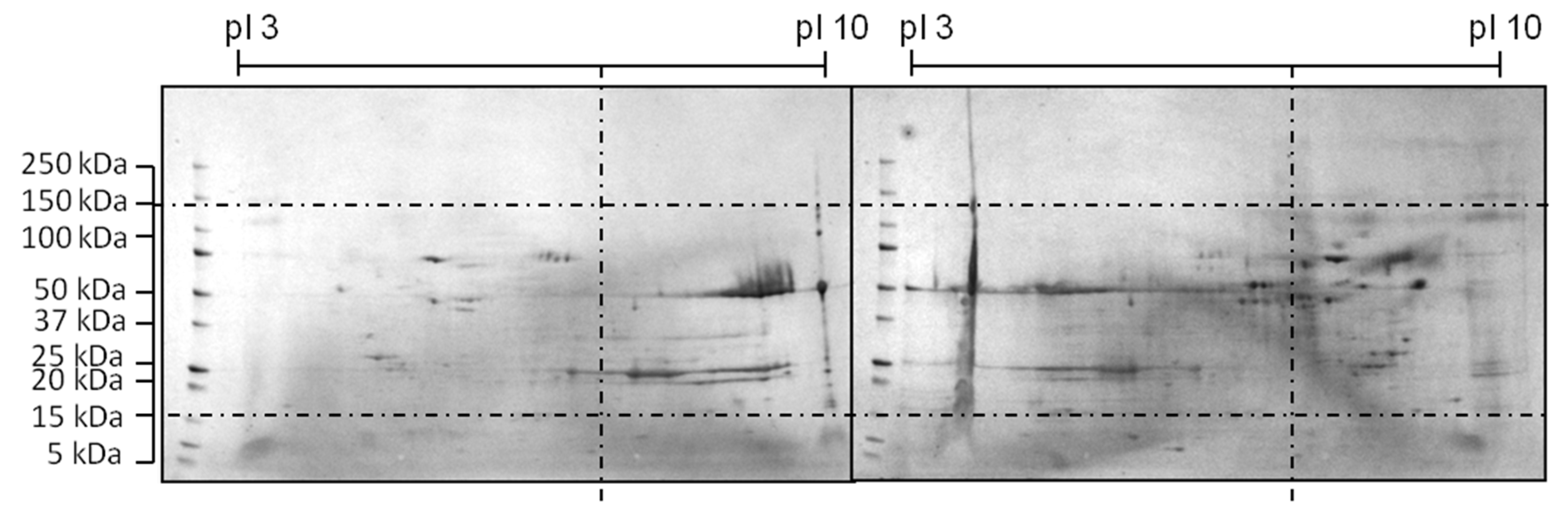
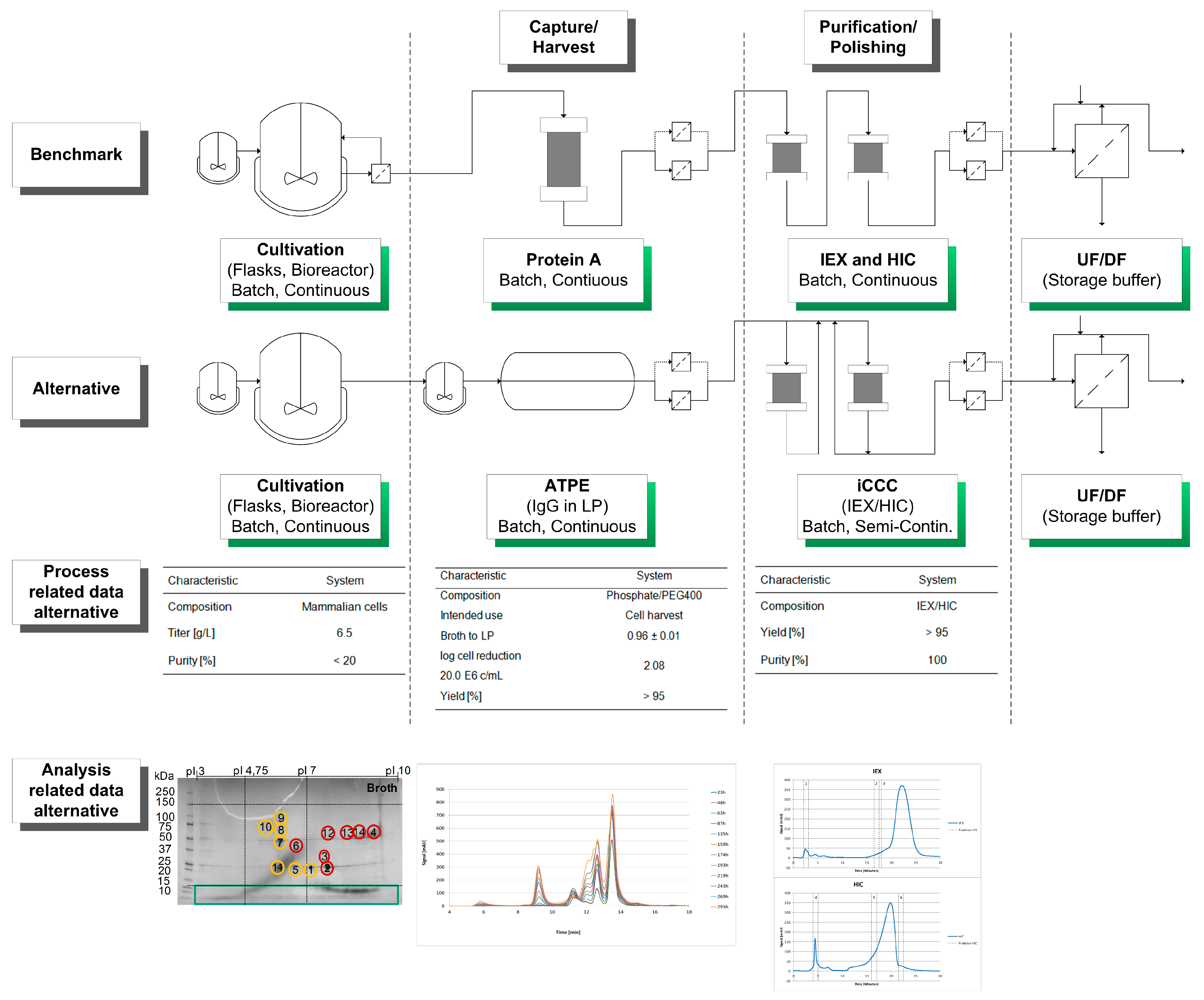

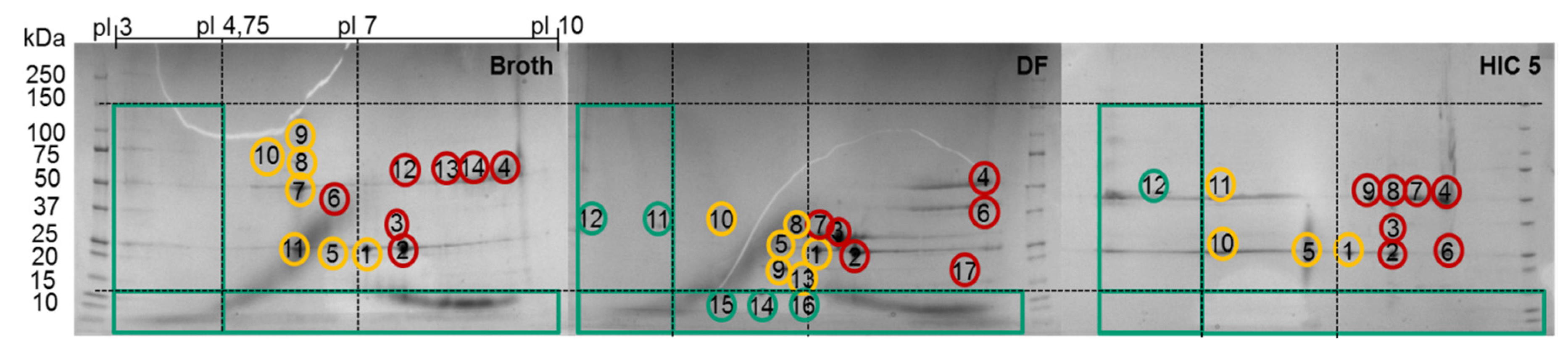
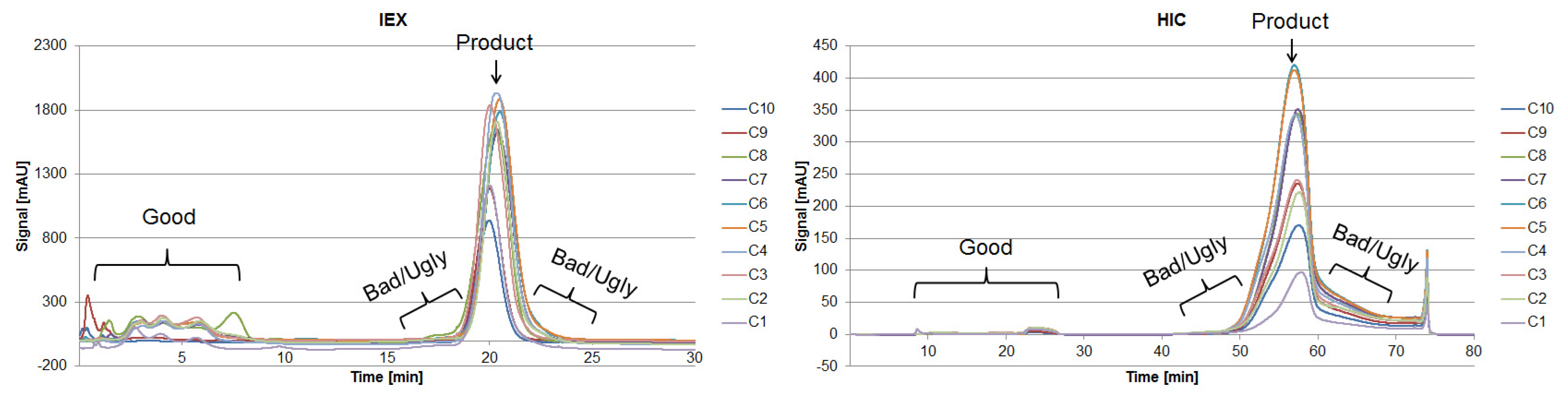

| Class | pI | MW (kDa) | Hydrophobicity | Origin | Cause |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HCP | 2–11 | 10–200 | Variable | Host cells | Secretion, lysis |
| hDNA | 2–3 | 90–1000 | Low | Host cells | Lysis |
| Insulin | 5.3–5.5 | 5.8 | Low | Media | Supplement |
| Virus | 4–7.5 | 200–7200 | Variable | Host cells, media | Contamination |
| Endotoxins | 1–4 | 3–40 | Variable | Media, contamination | Contamination |
| Characteristic | Method | Orthogonal Method |
|---|---|---|
| Isoelectric point | 2D-SDS PAGE | IEX; HPLC-MS/MS |
| Molecular weight | SEC | 2D-SDS PAGE; HPLC-MS/MS |
| Hydrophobicity | HIC | - |
| Parameter | Optimized medium |
|---|---|
| Titer increase | Factor 2.5 |
| Cell growth | Factor 2–2.3 |
| IgG/HCP | 65% |
| HCP profile | Shift |
| Cultivation | ATPE | iCCC | |
|---|---|---|---|
| System | Mammalian cells | PEG400/40 wt% PO4 | IEX/HIC combination |
| Titer/yield | 6.5 g/L | >95% | >95% |
| Log cell reduction 20.0 E6 cells/mL | - | 2.08 | - |
| Purity | <20% | up to 80% * | 100% |
| Characteristic | mAb | Good | Bad | Ugly |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| MW [kDa] | 144.2 | <15 | >15 | >15 |
| pI [−] | 8.30 | <4.75 >10.00 | 4.75–7.30 9.30–10.00 | 7.30–9.30 |
| Spot Gel | MW Gel | pI Gel | Class Gel | MW 1 | pI 2 | Class MS | Protein | UniProt Accession Number |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 25 | 7.0 | Bad | 81.56 | 5.69 | Bad | Glutathione S-transferase Mu7-like protein | A0A061IN16 |
| 2 | 25 | 7.5 | Ugly | 102.7 | 6.02 | Bad | Actin, cytoplasmic 1 | A0A069C7Y3 |
| 3 | 30 | 7.6 | Ugly | 38.03 | 6.08 | Bad | Purine nucleoside phosphorylase-like protein | A0A061ILE8 |
| 4 | 50 | 9.4 | Bad | 72.13 | 7.23 | Ugly | Pyruvate kinase | A0A098KXF7 |
| 5 | 25 | 6.3 | Bad | 38.03 | 6.08 | Bad | Purine nucleoside phosphorylase-like protein | A0A061ILE8 |
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kornecki, M.; Mestmäcker, F.; Zobel-Roos, S.; Heikaus de Figueiredo, L.; Schlüter, H.; Strube, J. Host Cell Proteins in Biologics Manufacturing: The Good, the Bad, and the Ugly. Antibodies 2017, 6, 13. https://doi.org/10.3390/antib6030013
Kornecki M, Mestmäcker F, Zobel-Roos S, Heikaus de Figueiredo L, Schlüter H, Strube J. Host Cell Proteins in Biologics Manufacturing: The Good, the Bad, and the Ugly. Antibodies. 2017; 6(3):13. https://doi.org/10.3390/antib6030013
Chicago/Turabian StyleKornecki, Martin, Fabian Mestmäcker, Steffen Zobel-Roos, Laura Heikaus de Figueiredo, Hartmut Schlüter, and Jochen Strube. 2017. "Host Cell Proteins in Biologics Manufacturing: The Good, the Bad, and the Ugly" Antibodies 6, no. 3: 13. https://doi.org/10.3390/antib6030013
APA StyleKornecki, M., Mestmäcker, F., Zobel-Roos, S., Heikaus de Figueiredo, L., Schlüter, H., & Strube, J. (2017). Host Cell Proteins in Biologics Manufacturing: The Good, the Bad, and the Ugly. Antibodies, 6(3), 13. https://doi.org/10.3390/antib6030013








