Formic Acid Modified Co3O4-CeO2 Catalysts for CO Oxidation
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
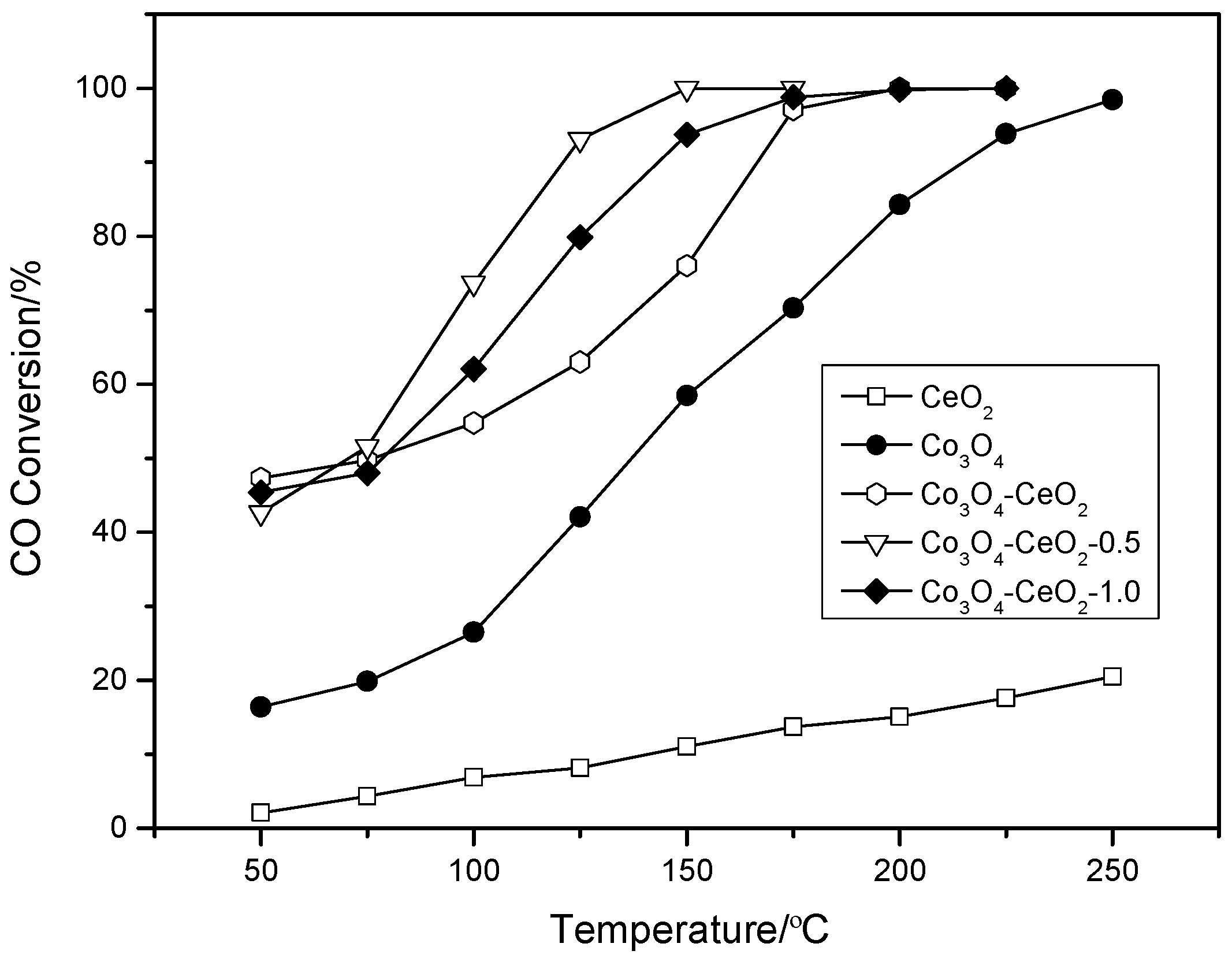
2.1. Catalytic Performance Tests
2.2. Characterizations
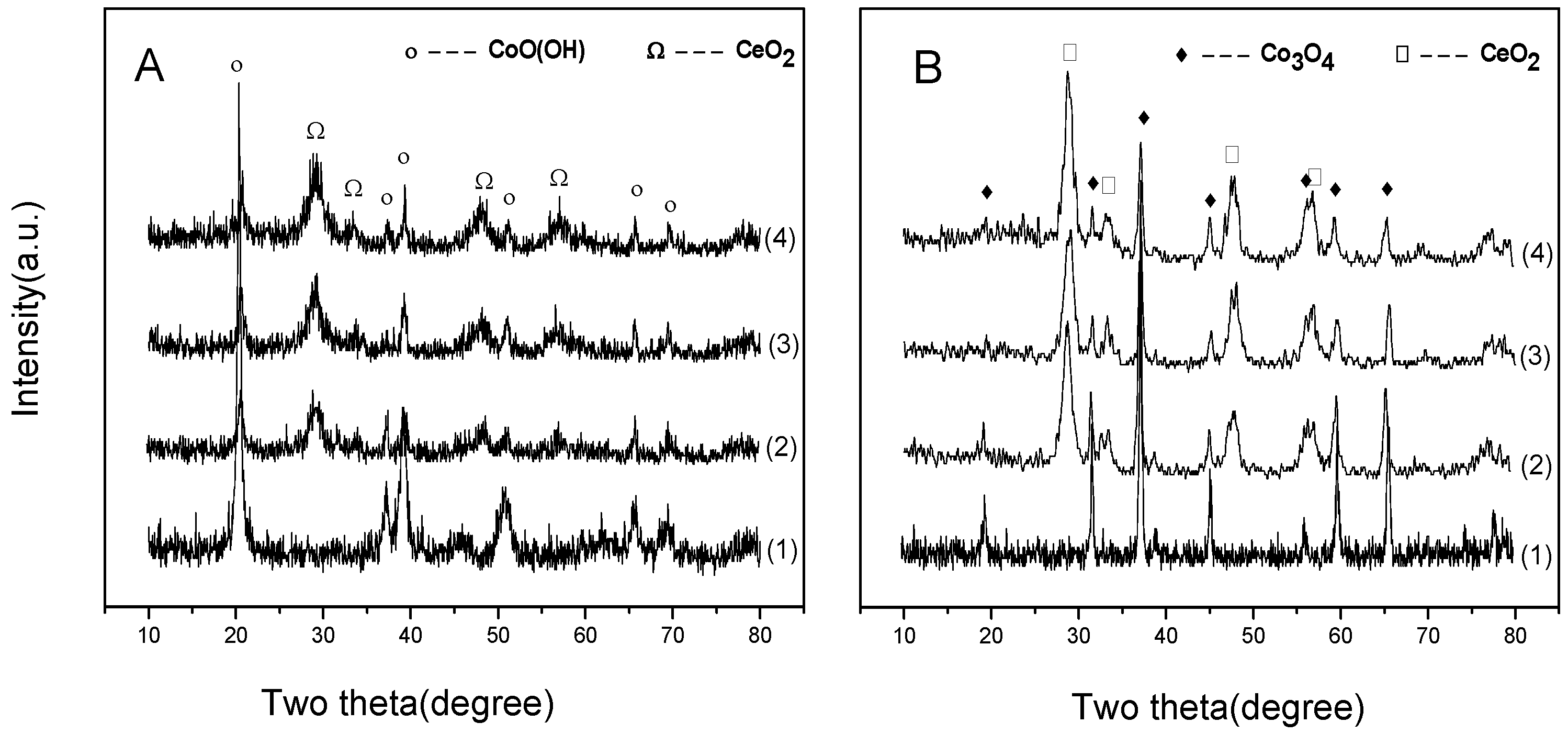
2.2.1. XRD
2.2.2. HRTEM
2.2.3. ICP-AES
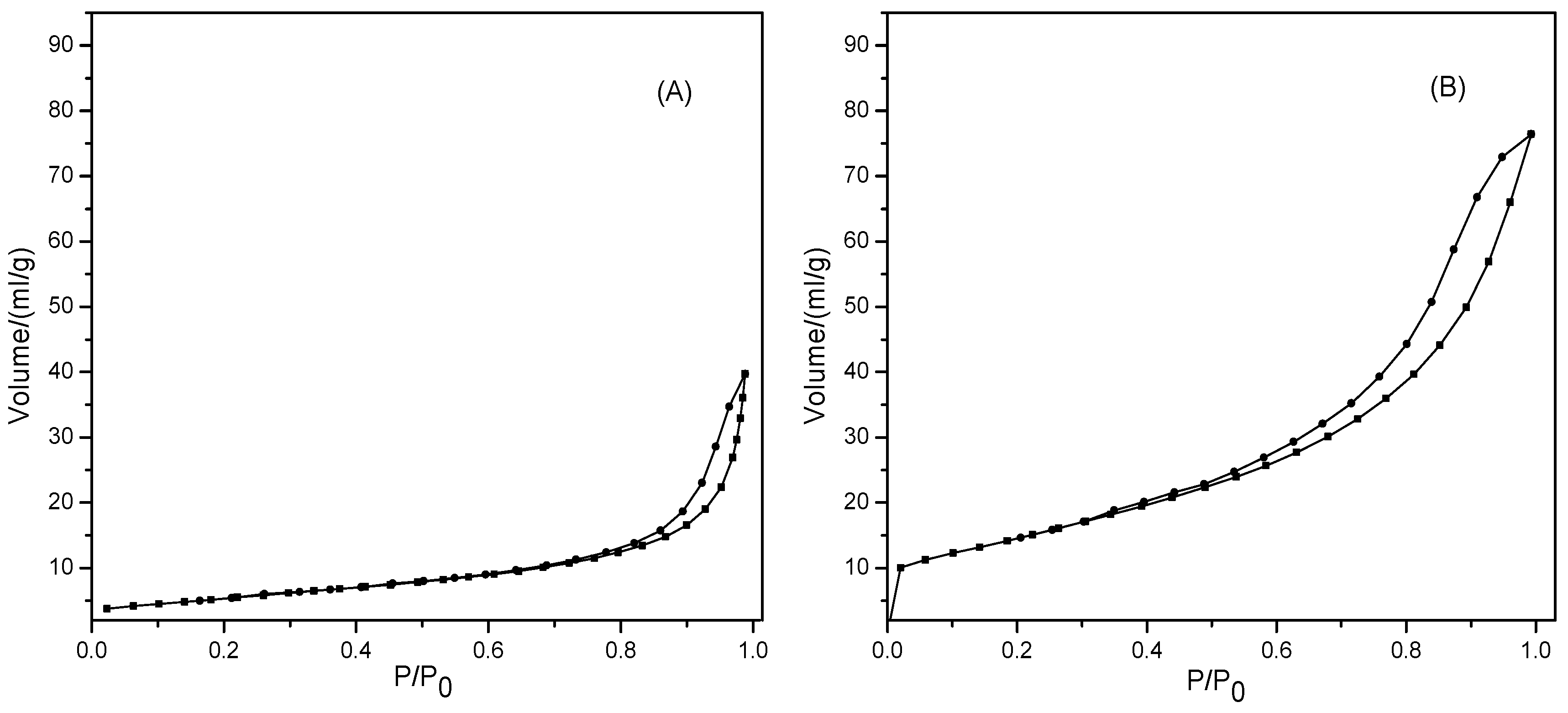
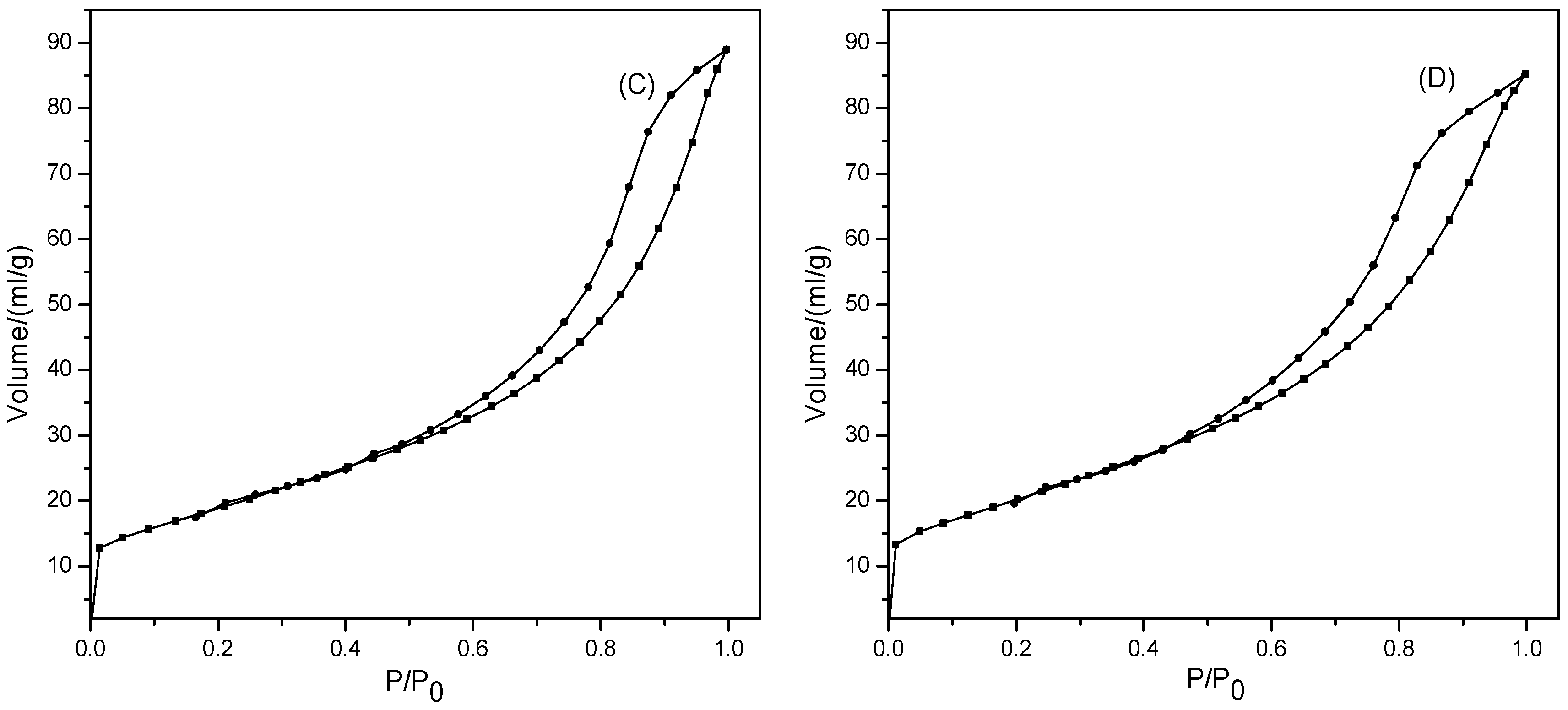
2.2.4. N2 Physisorption
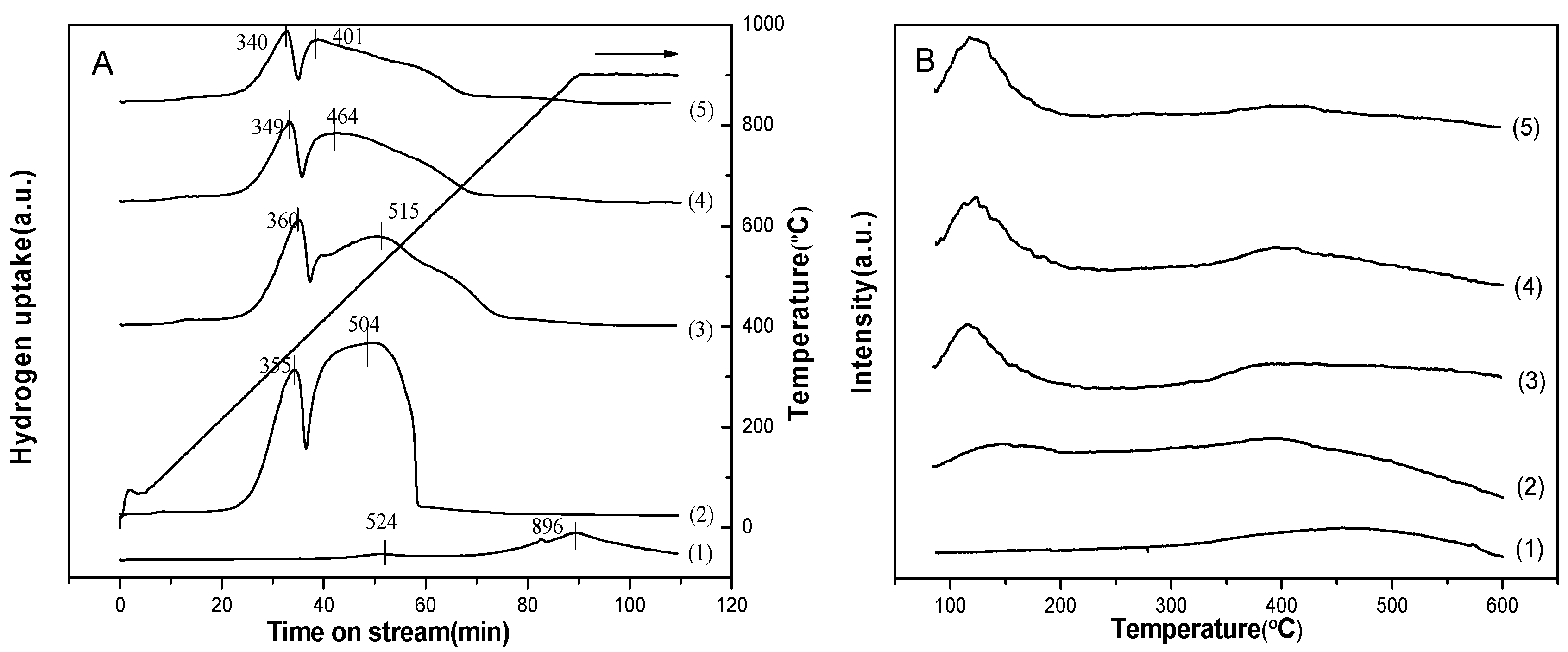
2.2.5. Temperature-Programmed Reduction (TPR)
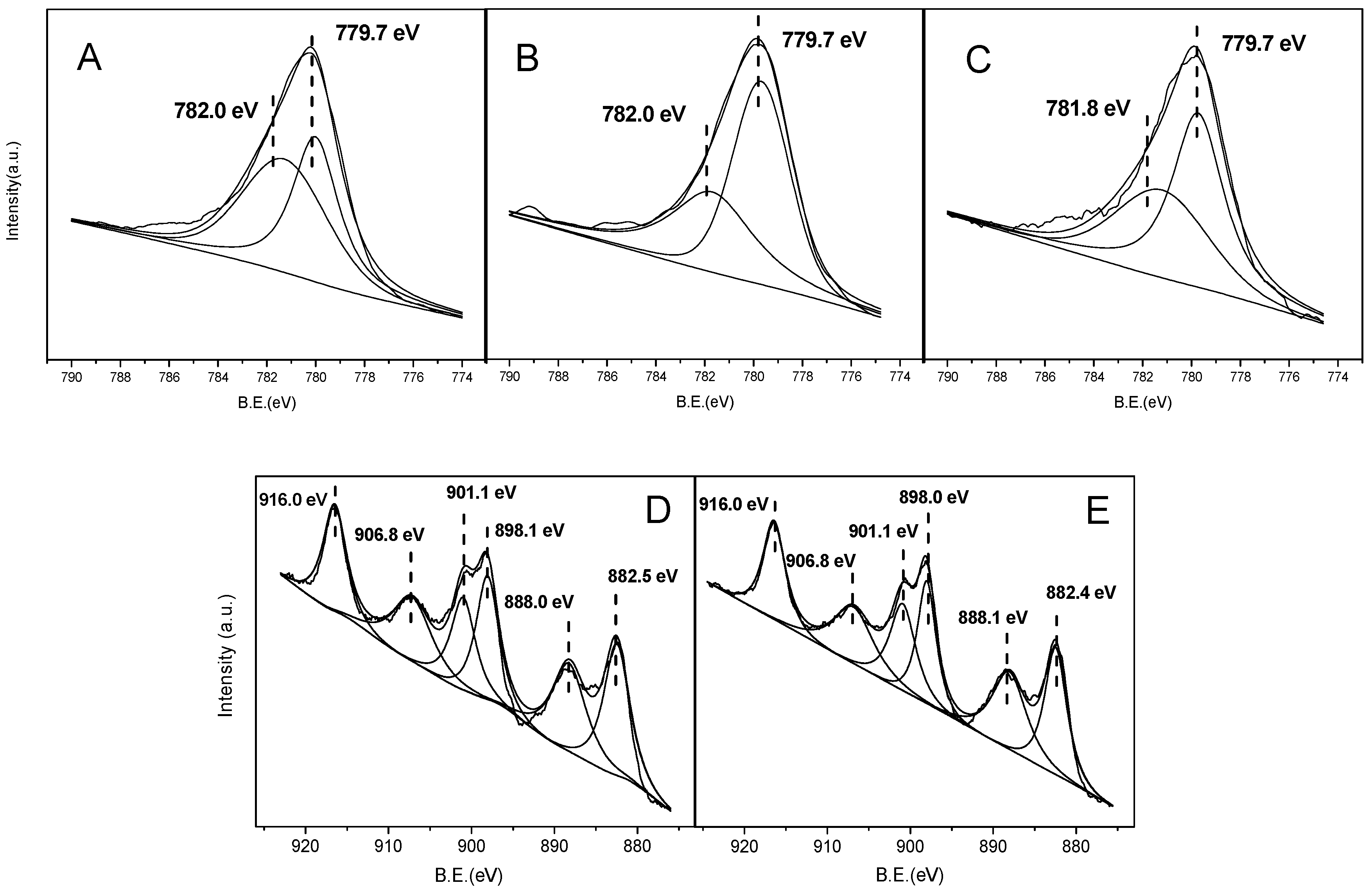
2.2.6. X-ray Photoelectron Spectra (XPS)
2.2.7. Temperature-Programmed Desorption (TPD) of CO
2.2.8. Temperature-Programmed Desorption (TPD) of H2
2.3. Discussion
3. Experimental Section
3.1. Catalysts Preparation
3.1.1. Synthesis of Co3O4
3.1.2. Synthesis of CeO2
3.1.3. Synthesis of Co3O4-CeO2
3.1.4. Treatment with Formic Acid
3.2. Catalytic Performance Evaluation
3.3. Characterizations
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Do, Y.; Cho, I.; Park, Y.; Pradhan, D.; Sohn, Y. CO Oxidation Activities of Ni and Pd-TiO2@SiO2 Core-Shell Nanostructures. Bull. Korean Chem. Soc. 2013, 34, 3635–3640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhen, J.; Wang, X.; Liu, D.; Song, S.; Wang, Z.; Wang, Y.; Li, J.; Wang, F.; Zhang, H. Co3O4@CeO2 core@shell cubes: Designed synthesis and optimization of catalytic properties. Chemistry 2014, 20, 4469–4473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iablokov, V.; Frey, K.; Geszti, O.; Kruse, N. Kruse. High Catalytic Activity in CO Oxidation over MnOx Nanocrystals. Catal. Lett. 2009, 134, 210–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wojciech, G. Acid-base properties of Ni-MgO-Al2O3 materials. Appl. Surface Sci. 2011, 257, 2875–2880. [Google Scholar]
- Sasirekha, N.; Sangeetha, P.; Chen, Y.-W. Bimetallic Au-Ag/CeO2 Catalysts for Preferential Oxidation of CO in Hydrogen-Rich Stream: Effect of Calcination Temperature. J. Phys. Chem. C 2014, 118, 15226–15233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gil, S.; Garcia-Vargas, J.; Liotta, L.; Pantaleo, G.; Ousmane, M.; Retailleau, L.; Giroir-Fendler, A. Catalytic Oxidation of Propene over Pd Catalysts Supported on CeO2, TiO2, Al2O3 and M/Al2O3 Oxides (M = Ce, Ti, Fe, Mn). Catalysts 2015, 5, 671–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, C.-F.; Chen, H.; Hu, R.-R.; Huang, S.; Luo, W.; Guo, C.; Li, M.; Li, W. Synthesis of mesoporous Co-Ce oxides catalysts by glycine-nitrate combustion approach for CO preferential oxidation reaction in excess H2. Int. J. Hydrogen. Energy 2014, 39, 18695–18701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, W.; Zhao, Y.F.; Chen, H.R.; Chen, H.; Li, Y.W.; He, S.; Zhang, Y.K.; Wei, M.; Evans, D.G.; Duan, X. Core-shell Cu@(CuCo-alloy)/Al2O3 catalysts for the synthesis of higher alcohols from syngas. Green Chem. 2015, 17, 1525–1534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schuh, K.; Kleist, W.; Høj, M.; Trouillet, V.; Beato, P.; Jensen, A.D.; Grunwaldt, J.D. Bismuth molybdate catalysts prepared by mild hydrothermal synthesis: Influence of pH on the selective oxidation of propylene. Catalysts 2015, 5, 1554–1573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Velu, S.; Suzuki, K.; Vijayaraj, M.; Barman, S.; Gopinath, C.S. In situ XPS investigations of Cu1-x Nix ZnAl-mixed metal oxide catalysts used in the oxidative steam reforming of bio-ethanol. Appl. Catal. B 2005, 5, 287–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guil-López, R.; Navarro, R.M.; Peña, M.A.; Fierro, J.L.G. Hydrogen production by oxidative ethanol reforming on Co, Ni and Cu ex-hydrotalcite catalysts. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2011, 36, 1512–1523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sesis, A.; Hodnett, M.; Memoli, G.; Wain, A.J.; Jurewicz, I.; Dalton, A.B.; Carey, J.D.; Hinds, G. Influence of acoustic cavitation on the controlled ultrasonic dispersion of carbon nanotubes. J. Phys. Chem. B 2013, 117, 15141–15150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, F.; Wang, X.; Liu, D.; Zhen, J.; Li, J.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, H. High-performance ZnCo2O4@CeO2 core@shell microspheres for catalytic CO oxidation. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2014, 6, 22216–22223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuo, C.H.; Li, W.; Song, W.; Luo, Z.; Poyraz, A.S.; Guo, Y.; Ma, A.W.; Suib, S.L.; He, J. Facile synthesis of Co3O4@CNT with high catalytic activity for CO oxidation under moisture-rich conditions. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2014, 6, 11311–11317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.; Lu, G.; Qiao, D.; Wang, Y.; Guo, Y.; Guo, Y. Catalytic Methane Combustion over Co3O4/CeO2 Composite Oxides Prepared by Modified Citrate Sol-Gel Method. Catal. Lett. 2010, 141, 452–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, L.; Zhang, C.; He, H.; Teraoka, Y. Teraoka. Catalytic decomposition of N2O over CeO2 promoted Co3O4 spinel catalyst. Appl. Catal. B 2007, 75, 167–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, Z.; Gao, K.; Fu, Q.; Qin, Y. Low-temperature catalytic oxidation of toluene over nanocrystal-like Mn-Co oxides prepared by two-step hydrothermal method. Catal. Commun. 2014, 52, 31–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, L.; Liu, Q.; Chen, R.; Chu, D.; Hsu, A.T. Layered double hydroxide derived Co0.3 Mg2.7Al1−xFexO4.5±δ catalysts for hydrogen production via auto-thermal reforming of bio-ethanol. Catal. Commun. 2010, 12, 40–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baek, J.H.; Park, J.Y.; Hwang, A.R.; Kang, Y.C. Spectroscopic and Morphological Investigation of Co3O4 Microfibers Produced by Electrospinning Process. Bull. Korean Chem. Soc. 2012, 33, 1242–1246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Zhu, H.; Qin, Z.; Wang, G.; Zhang, Y.; Wu, Z.; Li, Z.; Chen, G.; Dong, W.; Wu, Z.; et al. Morphologic effects of nano CeO2-TiO2 on the performance of Au/CeO2-TiO2 catalysts in low-temperature CO oxidation. Appl. Catal. B 2014, 144, 498–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, L.; Yu, Q.; Dai, Y.; Tang, C.; Liu, L.; Zhang, H.; Gao, F.; Dong, L.; Chen, Y. Influence of cerium precursors on the structure and reducibility of mesoporous CuO-CeO2 catalysts for CO oxidation. Appl. Catal. B 2012, 119–120, 308–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Ding, Y.; Lü, Y.; Zhu, H.; Lin, L. Influence of lanthanum on the performance of Zr-Co/activated carbon catalysts in Fischer-Tropsch synthesis. J. Nat. Gas Chem. 2008, 17, 153–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, W.; Cheng, H.; He, L.; Yu, Y.; Zhao, F. High performance of Ir-promoted Ni/TiO2 catalyst toward the selective hydrogenation of cinnamaldehyde. J. Catal. 2013, 303, 110–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Catalysts | Surface Area, m2/g | Average Pore Volume, mL/g | Average Pore Size, nm | Particle Size Estimated by XRD, nm | Co3O4 Content, wt % c | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Precursors a | Calcined b | |||||
| CeO2 | 79.8 | 0.087 | 4.4 | 26.2 | 20.7 | - |
| Co3O4 | 19.3 | 0.064 | 12.7 | 19.4 | 29.0 | - |
| Co3O4-CeO2 | 53.0 | 0.126 | 8.9 | 16.4 | 23.9 | 52.00 |
| Co3O4-CeO2-0.5 | 68.3 | 0.146 | 8.1 | 15.8 | 23.6 | 42.74 |
| Co3O4-CeO2-1.0 | 73.4 | 0.142 | 7.2 | 16.6 | 23.8 | 37.56 |
© 2016 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons by Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Shang, R.; Duan, Y.; Zhong, X.; Xie, W.; Luo, Y.; Huang, L. Formic Acid Modified Co3O4-CeO2 Catalysts for CO Oxidation. Catalysts 2016, 6, 48. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal6030048
Shang R, Duan Y, Zhong X, Xie W, Luo Y, Huang L. Formic Acid Modified Co3O4-CeO2 Catalysts for CO Oxidation. Catalysts. 2016; 6(3):48. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal6030048
Chicago/Turabian StyleShang, Ruishu, Yiping Duan, Xinyan Zhong, Wei Xie, Yan Luo, and Lihong Huang. 2016. "Formic Acid Modified Co3O4-CeO2 Catalysts for CO Oxidation" Catalysts 6, no. 3: 48. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal6030048






