NF-κB Signaling Regulates Epstein–Barr Virus BamHI-Q-Driven EBNA1 Expression
Abstract
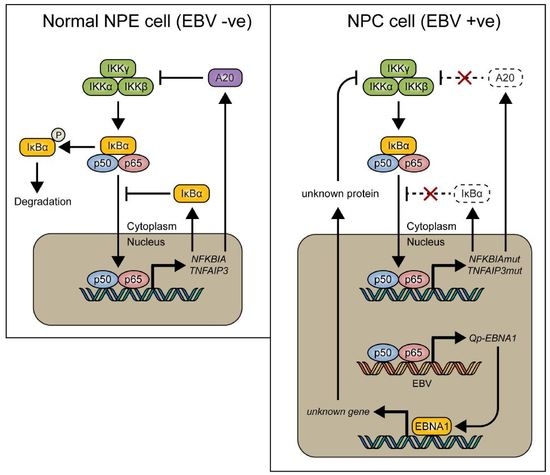
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. NF-κB p65 Upregulates Qp Activity
2.2. Mutations in the Putative NF-κB Binding Site Attenuate Qp Activation by NF-κB p65
2.3. Binding of NF-κB to Qp
2.4. NF-κB Activation in EBV-Positive Epithelial Cells Upregulates Qp-EBNA1 Expression
2.5. Nuclear Localization of NF-κB p65 in an EBV-Positive NPC Cell Line
2.6. Inhibition of NF-κB Signaling Downregulates Qp-EBNA1 Expression in C666-1 Cells
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Cell Lines and Cell Culture Conditions
4.2. Plasmid Constructs
4.3. ChIP Assay
4.4. EMSA Analysis
4.5. Luciferase Reporter Assay
4.6. Immunoblotting
4.7. Quantitative RT-PCR (RT-qPCR)
4.8. Indirect Immunofluorescence
4.9. Statistics
5. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Rickinson, A.B.; Kieff, E.D. Epstein-Barr Virus. In Fields Virology, 5th ed.; Knipe, D.M., Howley, P.M., Eds.; Lippincott Williams & Wilkins: Philadephia, PA, USA, 2007; Volume 2, pp. 2603–2654. [Google Scholar]
- Speck, S.H.; Ganem, D. Viral latency and its regulation: lessons from the gamma-herpesviruses. Cell. Host Microbe 2010, 8, 100–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kieff, E.D.; Rickinson, A.B. Epstein-Barr Virus and Its Replication. In Fields Virology, 5th ed.; Knipe, D.M., Howley, P.M., Eds.; Lippincott Williams & Wilkins: Philadephia, PA, USA, 2007; Volume 2, pp. 2655–2700. [Google Scholar]
- Young, L.S.; Murray, P.G. Epstein-Barr virus and oncogenesis: from latent genes to tumours. Oncogene 2003, 22, 5108–5121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abbott, R.J.; Quinn, L.L.; Leese, A.M.; Scholes, H.M.; Pachnio, A.; Rickinson, A.B. CD8+ T cell responses to lytic EBV infection: Late antigen specificities as subdominant components of the total response. J. Immunol. 2013, 191, 5398–5409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schaefer, B.C.; Strominger, J.L.; Speck, S.H. Redefining the Epstein-Barr virus-encoded nuclear antigen EBNA-1 gene promoter and transcription initiation site in group I Burkitt lymphoma cell lines. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1995, 92, 10565–10569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nonkwelo, C.; Skinner, J.; Bell, A.; Rickinson, A.; Sample, J. Transcription start sites downstream of the Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) Fp promoter in early-passage Burkitt lymphoma cells define a fourth promoter for expression of the EBV EBNA-1 protein. J. Virol. 1996, 70, 623–627. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Robertson, K.D.; Manns, A.; Swinnen, L.J.; Zong, J.C.; Gulley, M.L.; Ambinder, R.F. CpG methylation of the major Epstein-Barr virus latency promoter in Burkitt’s lymphoma and Hodgkin’s disease. Blood 1996, 88, 3129–3136. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Schaefer, B.C.; Strominger, J.L.; Speck, S.H. Host-cell-determined methylation of specific Epstein-Barr virus promoters regulates the choice between distinct viral latency programs. Mol. Cell. Biol. 1997, 17, 364–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Minarovits, J.; Hu, L.F.; Imai, S.; Harabuchi, Y.; Kataura, A.; Minarovits-Kormuta, S.; Osato, T.; Klein, G. Clonality, expression and methylation patterns of the Epstein-Barr virus genomes in lethal midline granulomas classified as peripheral angiocentric T cell lymphomas. J. Gen. Virol. 1994, 75 Pt 1, 77–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, F.W.; Wu, X.R.; Liu, W.J.; Liao, Y.J.; Lin, S.; Zong, Y.S.; Zeng, M.S.; Zeng, Y.X.; Mai, S.J.; Xie, D. Heat shock factor 1 upregulates transcription of Epstein-Barr Virus nuclear antigen 1 by binding to a heat shock element within the BamHI-Q promoter. Virology 2011, 421, 184–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.; Pagano, J.S. IRF-7, a new interferon regulatory factor associated with Epstein-Barr virus latency. Mol. Cell. Biol. 1997, 17, 5748–5757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.; Pagano, J.S. Interferon regulatory factor 2 represses the Epstein-Barr virus BamHI Q latency promoter in type III latency. Mol. Cell. Biol. 1999, 19, 3216–3223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, H.; Lee, J.M.; Wang, Y.; Huang, D.P.; Ambinder, R.F.; Hayward, S.D. The Epstein-Barr virus latency BamHI-Q promoter is positively regulated by STATs and Zta interference with JAK/STAT activation leads to loss of BamHI-Q promoter activity. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1999, 96, 9339–9344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sample, J.; Henson, E.B.; Sample, C. The Epstein-Barr virus nuclear protein 1 promoter active in type I latency is autoregulated. J. Virol. 1992, 66, 4654–4661. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Sung, N.S.; Wilson, J.; Davenport, M.; Sista, N.D.; Pagano, J.S. Reciprocal regulation of the Epstein-Barr virus BamHI-F promoter by EBNA-1 and an E2F transcription factor. Mol. Cell. Biol. 1994, 14, 7144–7152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schaefer, B.C.; Paulson, E.; Strominger, J.L.; Speck, S.H. Constitutive activation of Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) nuclear antigen 1 gene transcription by IRF1 and IRF2 during restricted EBV latency. Mol. Cell. Biol. 1997, 17, 873–886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valentine, R.; Dawson, C.W.; Hu, C.; Shah, K.M.; Owen, T.J.; Date, K.L.; Maia, S.P.; Shao, J.; Arrand, J.R.; Young, L.S.; O’Neil, J.D. Epstein-Barr virus-encoded EBNA1 inhibits the canonical NF-kappaB pathway in carcinoma cells by inhibiting IKK phosphorylation. Mol. Cancer 2010, 9, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johansson, P.; Jansson, A.; Ruetschi, U.; Rymo, L. Nuclear factor-kappaB binds to the Epstein-Barr Virus LMP1 promoter and upregulates its expression. J. Virol. 2009, 83, 1393–1401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verhoeven, R.J.A.; Tong, S.; Zhang, G.H.; Zong, J.F.; Chen, Y.X.; Jin, D.Y.; Chen, M.R.; Pan, J.J.; Chen, H.L. NF-kappa B Signaling Regulates Expression of Epstein-Barr Virus BART MicroRNAs and Long Noncoding RNAs in Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma. J. Virol. 2016, 90, 6475–6488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scott, M.L.; Fujita, T.; Liou, H.C.; Nolan, G.P.; Baltimore, D. The p65 subunit of NF-kappa B regulates I kappa B by two distinct mechanisms. Genes Dev. 1993, 7, 1266–1276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vallabhapurapu, S.D.; Noothi, S.K.; Pullum, D.A.; Lawrie, C.H.; Pallapati, R.; Potluri, V.; Kuntzen, C.; Khan, S.; Plas, D.R.; Orlowski, R.Z.; et al. Transcriptional repression by the HDAC4-RelB-p52 complex regulates multiple myeloma survival and growth. Nat. Commun. 2015, 6, 8428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, G.; Zong, J.; Lin, S.; Verhoeven, R.J.; Tong, S.; Chen, Y.; Ji, M.; Cheng, W.; Tsao, S.W.; Lung, M.; et al. Circulating Epstein-Barr virus microRNAs miR-BART7 and miR-BART13 as biomarkers for nasopharyngeal carcinoma diagnosis and treatment. Int. J. Cancer 2015, 136, E301–E312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raab-Traub, N. Epstein-Barr virus in the pathogenesis of NPC. Semin. Cancer Biol. 2002, 12, 431–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kube, D.; Vockerodt, M.; Weber, O.; Hell, K.; Wolf, J.; Haier, B.; Grasser, F.A.; Muller-Lantzsch, N.; Kieff, E.; Diehl, V.; et al. Expression of epstein-barr virus nuclear antigen 1 is associated with enhanced expression of CD25 in the Hodgkin cell line L428. J. Virol. 1999, 73, 1630–1636. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Baumforth, K.R.; Birgersdotter, A.; Reynolds, G.M.; Wei, W.; Kapatai, G.; Flavell, J.R.; Kalk, E.; Piper, K.; Lee, S.; Machado, L.; et al. Expression of the Epstein-Barr virus-encoded Epstein-Barr virus nuclear antigen 1 in Hodgkin’s lymphoma cells mediates Up-regulation of CCL20 and the migration of regulatory T cells. Am. J. Pathol. 2008, 173, 195–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Neil, J.D.; Owen, T.J.; Wood, V.H.; Date, K.L.; Valentine, R.; Chukwuma, M.B.; Arrand, J.R.; Dawson, C.W.; Young, L.S. Epstein-Barr virus-encoded EBNA1 modulates the AP-1 transcription factor pathway in nasopharyngeal carcinoma cells and enhances angiogenesis in vitro. J. Gen. Virol. 2008, 89, 2833–2842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wood, V.H.; O’Neil, J.D.; Wei, W.; Stewart, S.E.; Dawson, C.W.; Young, L.S. Epstein-Barr virus-encoded EBNA1 regulates cellular gene transcription and modulates the STAT1 and TGFbeta signaling pathways. Oncogene 2007, 26, 4135–4147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baud, V.; Karin, M. Is NF-kappaB a good target for cancer therapy? Hopes and pitfalls. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2009, 8, 33–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- DiDonato, J.A.; Mercurio, F.; Karin, M. NF-kappaB and the link between inflammation and cancer. Immunol. Rev. 2012, 246, 379–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thornburg, N.J.; Pathmanathan, R.; Raab-Traub, N. Activation of nuclear factor-kappaB p50 homodimer/Bcl-3 complexes in nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Cancer Res. 2003, 63, 8293–8301. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Chung, G.T.; Lou, W.P.; Chow, C.; To, K.F.; Choy, K.W.; Leung, A.W.; Tong, C.Y.; Yuen, J.W.; Ko, C.W.; Yip, T.T.; Busson, P.; Lo, K.W. Constitutive activation of distinct NF-kappaB signals in EBV-associated nasopharyngeal carcinoma. J. Pathol. 2013, 231, 311–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brown, H.J.; Song, M.J.; Deng, H.; Wu, T.T.; Cheng, G.; Sun, R. NF-kappaB inhibits gammaherpesvirus lytic replication. J. Virol. 2003, 77, 8532–8540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tao, Q.; Robertson, K.D.; Manns, A.; Hildesheim, A.; Ambinder, R.F. The Epstein-Barr virus major latent promoter Qp is constitutively active, hypomethylated, and methylation sensitive. J. Virol. 1998, 72, 7075–7083. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Takacs, M.; Banati, F.; Koroknai, A.; Segesdi, J.; Salamon, D.; Wolf, H.; Niller, H.H.; Minarovits, J. Epigenetic regulation of latent Epstein-Barr virus promoters. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2010, 1799, 228–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tempera, I.; Klichinsky, M.; Lieberman, P.M. EBV latency types adopt alternative chromatin conformations. PLoS Pathog. 2011, 7, e1002180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, H.; Lee, J.M.; Zong, Y.; Borowitz, M.; Ng, M.H.; Ambinder, R.F.; Hayward, S.D. Linkage between STAT regulation and Epstein-Barr virus gene expression in tumors. J. Virol. 2001, 75, 2929–2937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seitz, C.S.; Deng, H.; Hinata, K.; Lin, Q.; Khavari, P.A. Nuclear factor kappaB subunits induce epithelial cell growth arrest. Cancer Res. 2000, 60, 4085–4092. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Chen, H.; Huang, J.; Wu, F.Y.; Liao, G.; Hutt-Fletcher, L.; Hayward, S.D. Regulation of expression of the Epstein-Barr virus BamHI-A rightward transcripts. J. Virol. 2005, 79, 1724–1733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]






| Oligo | Sequence (5′–3′) |
|---|---|
| BCL2L11-F | CAAGAGTTGCGGCGTATTGGAG |
| BCL2L11-R | ACACCAGGCGGACAATGTAACG |
| ChIP-Qp-F | GACAGAAATTGGGTGACCACTGAGGG |
| ChIP-Qp-R | CGCCATCCGGTAGCGCAC |
| ChIP-Control-F | TCCCTAAGTCACTTTCTTCAAGTTGC |
| ChIP-Control-R | CGTGCATTTAATTGTGTCTTGTGG |
| EBV-BLLF1-F | TGTGCTGATAGAGGCTGGTG |
| EBV-BLLF1-R | TGACACCAAGTCCATCTCCA |
| EBV-BMRF1-F | AGGAGTGCTGCAGGTAAACC |
| EBV-BMRF1-R | GCTCTGGTGATTCTGCCACT |
| EBV-BZLF1-F | AAATTTAAGAGATCCTCGTGTAAAACATC |
| EBV-BZLF1-R | CGCCTCCTGTTGAAGCAGAT |
| EBV-LMP1-F | AATTTGCACGGACAGGCATT |
| EBV-LMP1-R | AAGGCCAAAAGCTGCCAGAT |
| EBV-Qp-EBNA1-F | GTGCGCTACCGGATGGC |
| EBV-Qp-EBNA1-R | CATGATTCACACTTAAAGGAGACGG |
| EBV-RPMS1-F | GAAAAGCTTGGGATTAATGCCTGGACCCTCACCAG |
| EBV-RPMS1-R | AGGGGATCCCCCGCCACCACGGTGCAGCCTAC |
| GAPDH-F | GAAGGTGAAGGTCGGAGTA |
| GAPDH-R | GAAGATGGTGATGGGATTTC |
| NFKBIA-F | CCCTACACCTTGCCTGTGAG |
| NFKBIA-R | CGTGTGGCCATTGTAGTTGG |
| Qp-KpnI-F | CGGGGTACCGACAGAAATTGGGTGACCAC |
| Qp-HindIII-R | ATCCCAAGCTTCGCCATCCGGTAGCGCAC |
| Qp-mut1-F | GGTGACCACTGAAAAAGTGTTCCACAG |
| Qp-mut1-R | CTGTGGAACACTTTTTCAGTGGTCACC |
| Qp-mut2-F | CTGAGGGAGTGAAAAACAGTAATGTTG |
| Qp-mut2-R | CAACATTACTGTTTTTCACTCCCTCAG |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Verhoeven, R.J.A.; Tong, S.; Zong, J.; Chen, Y.; Tsao, S.-W.; Pan, J.; Chen, H. NF-κB Signaling Regulates Epstein–Barr Virus BamHI-Q-Driven EBNA1 Expression. Cancers 2018, 10, 119. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers10040119
Verhoeven RJA, Tong S, Zong J, Chen Y, Tsao S-W, Pan J, Chen H. NF-κB Signaling Regulates Epstein–Barr Virus BamHI-Q-Driven EBNA1 Expression. Cancers. 2018; 10(4):119. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers10040119
Chicago/Turabian StyleVerhoeven, Rob J. A., Shuang Tong, Jingfeng Zong, Yixin Chen, Sai-Wah Tsao, Jianji Pan, and Honglin Chen. 2018. "NF-κB Signaling Regulates Epstein–Barr Virus BamHI-Q-Driven EBNA1 Expression" Cancers 10, no. 4: 119. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers10040119
APA StyleVerhoeven, R. J. A., Tong, S., Zong, J., Chen, Y., Tsao, S.-W., Pan, J., & Chen, H. (2018). NF-κB Signaling Regulates Epstein–Barr Virus BamHI-Q-Driven EBNA1 Expression. Cancers, 10(4), 119. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers10040119