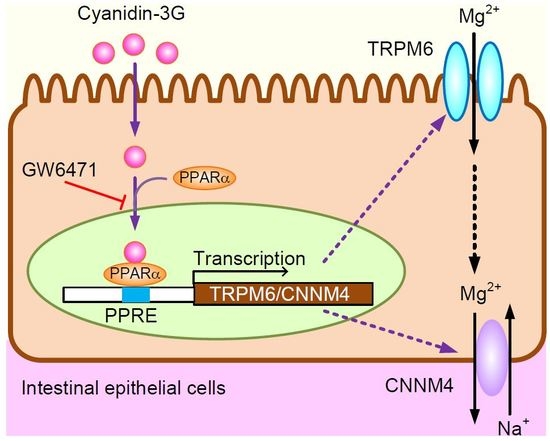
Cyanidin Increases the Expression of Mg2+ Transport Carriers Mediated by the Activation of PPARα in Colonic Epithelial MCE301 Cells
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Experimental Section
2.1. Materials
2.2. Cell Culture
2.3. RNA Isolation and Quantitative Real-Time Reverse-Transcription Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR)
2.4. Preparation of Cytoplasmic Extracts and Western Blotting
2.5. Immunocytochemistry
2.6. Luciferase Reporter Assay
2.7. ChIP Assay
2.8. Mg2+ Transport Assay
2.9. Statistics
3. Results
3.1. Increase in TRPM6 and CNNM4 mRNA Expression by Cyanidin
3.2. Effect of Cyanidin on the Expression and Localization of TRPM6 and CNNM4 Proteins
3.3. Increase in Nuclear Localization of PPARα by Cyanidin
3.4. Effects of Cyanidin and Inhibitors on TRPM6 and CNNM4 Promoter Activities
3.5. Association of PPARα with the TRPM6 and CNNM4 Promoter Regions
3.6. Increase in Mg2+ Transport by Cyanidin
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ChIP | Chromatin immunoprecipitation |
| CNNM4 | Cyclin M4 |
| Ct | Threshold cycle |
| Cyanidin-3G | Cyanidin-3-O-glucoside |
| DAPI | 4′,6-Diamidino-2-phenylindole |
| DMSO | Dimethyl sulfoxide |
| EGF | Epidermal growth factor |
| GLUT | Sodium-independent glucose transporter |
| HBSS | Hank’s balanced salt solution |
| Mg2+ | Magnesium ion |
| [Mg2+]i, | Intracellular free Mg2+ concentration |
| PCR | Polymerase chain reaction |
| PKA | Protein kinase A |
| PPAR | Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor |
| SGLT | Sodium-dependent glucose transporter |
| TER | Transepithelial electrical resistance |
| TRPM6 | Transient receptor potential melastatin 6 |
| XB-1 | Xylidyl blue-I |
References
- Takayanagi, K.; Shimizu, T.; Tayama, Y.; Ikari, A.; Anzai, N.; Iwashita, T.; Asakura, J.; Hayashi, K.; Mitarai, T.; Hasegawa, H. Downregulation of transient receptor potential M6 channels as a cause of hypermagnesiuric hypomagnesemia in obese type 2 diabetic rats. Am. J. Physiol. Ren. Physiol. 2015, 308, F1386–F1397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- De Leeuw, I.H.; van Gaal, L.; Vanroelen, W. Magnesium and obesity: Effects of treatment on magnesium and other parameters. Magnesium 1987, 6, 40–47. [Google Scholar]
- Dousdampanis, P.; Trigka, K.; Fourtounas, C. Hypomagnesemia, chronic kidney disease and cardiovascular mortality: Pronounced association but unproven causation. Hemodial. Int. 2014, 18, 730–739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zieba, A.; Kata, R.; Dudek, D.; Schlegel-Zawadzka, M.; Nowak, G. Serum trace elements in animal models and human depression: Part III. Magnesium. Relationship with copper. Hum. Psychopharmacol. 2000, 15, 631–635. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Golf, S.W.; Bender, S.; Gruttner, J. On the significance of magnesium in extreme physical stress. Cardiovasc. Drugs Ther. 1998, 12 (Suppl. 2), 197–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schweigel, M.; Martens, H. Magnesium transport in the gastrointestinal tract. Front. Biosci. 2000, 5, D666–D677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graham, L.A.; Caesar, J.J.; Burgen, A.S. Gastrointestinal absorption and excretion of Mg 28 in man. Metabolism 1960, 9, 646–659. [Google Scholar]
- De Baaij, J.H.; Hoenderop, J.G.; Bindels, R.J. Magnesium in man: Implications for health and disease. Physiol. Rev. 2015, 95, 1–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Voets, T.; Nilius, B.; Hoefs, S.; van der Kemp, A.W.; Droogmans, G.; Bindels, R.J.; Hoenderop, J.G. TRPM6 forms the Mg2+ influx channel involved in intestinal and renal Mg2+ absorption. J. Biol. Chem. 2004, 279, 19–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schlingmann, K.P.; Weber, S.; Peters, M.; Niemann Nejsum, L.; Vitzthum, H.; Klingel, K.; Kratz, M.; Haddad, E.; Ristoff, E.; Dinour, D.; et al. Hypomagnesemia with secondary hypocalcemia is caused by mutations in TRPM6, a new member of the TRPM gene family. Nat. Genet. 2002, 31, 166–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Walder, R.Y.; Landau, D.; Meyer, P.; Shalev, H.; Tsolia, M.; Borochowitz, Z.; Boettger, M.B.; Beck, G.E.; Englehardt, R.K.; Carmi, R.; et al. Mutation of TRPM6 causes familial hypomagnesemia with secondary hypocalcemia. Nat. Genet. 2002, 31, 171–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamazaki, D.; Funato, Y.; Miura, J.; Sato, S.; Toyosawa, S.; Furutani, K.; Kurachi, Y.; Omori, Y.; Furukawa, T.; Tsuda, T.; et al. Basolateral Mg2+ extrusion via CNNM4 mediates transcellular Mg2+ transport across epithelia: A mouse model. PLoS Genet. 2013, 9, e1003983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meyer, T.E.; Verwoert, G.C.; Hwang, S.J.; Glazer, N.L.; Smith, A.V.; van Rooij, F.J.; Ehret, G.B.; Boerwinkle, E.; Felix, J.F.; Leak, T.S.; et al. Genome-wide association studies of serum magnesium, potassium, and sodium concentrations identify six Loci influencing serum magnesium levels. PLoS Genet. 2010, 6, e1001045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schuchardt, J.P.; Hahn, A. Intestinal Absorption and Factors Influencing Bioavailability of Magnesium-An Update. Curr. Nutr. Food Sci. 2017, 13, 260–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoenderop, J.G.; Bindels, R.J. Calciotropic and magnesiotropic TRP channels. Physiology 2008, 23, 32–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elin, R.J. Magnesium metabolism in health and disease. Dis. Mon. 1988, 34, 161–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanai, M.; Esashi, T. Bioavailability of magnesium contained in roasted and ground soybean (kinako) as evaluated by serum and bone magnesium contents, kidney calcification, and magnesium absorption. J. Nutr. Sci. Vitaminol. 1998, 44, 437–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsuda, T.; Horio, F.; Osawa, T. Absorption and metabolism of cyanidin 3-O-beta-d-glucoside in rats. FEBS Lett. 1999, 449, 179–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olivas-Aguirre, F.J.; Rodrigo-Garcia, J.; Martinez-Ruiz, N.D.; Cardenas-Robles, A.I.; Mendoza-Diaz, S.O.; Alvarez-Parrilla, E.; Gonzalez-Aguilar, G.A.; de la Rosa, L.A.; Ramos-Jimenez, A.; Wall-Medrano, A. Cyanidin-3-O-glucoside: Physical-Chemistry, Foodomics and Health Effects. Molecules 2016, 21, 1264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tabuchi, Y.; Ohta, S.; Arai, Y.; Kawahara, M.; Ishibashi, K.; Sugiyama, N.; Horiuchi, T.; Furusawa, M.; Obinata, M.; Fuse, H.; et al. Establishment and characterization of a colonic epithelial cell line MCE301 from transgenic mice harboring temperature-sensitive simian virus 40 large T-antigen gene. Cell Struct. Funct. 2000, 25, 297–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Furukawa, C.; Ishizuka, N.; Hayashi, H.; Fujii, N.; Manabe, A.; Tabuchi, Y.; Matsunaga, T.; Endo, S.; Ikari, A. Up-regulation of claudin-2 expression by aldosterone in colonic epithelial cells of mice fed with NaCl-depleted diets. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 12223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Furukawa, C.; Fujii, N.; Manabe, A.; Matsunaga, T.; Endo, S.; Hasegawa, H.; Ito, Y.; Yamaguchi, M.; Yamazaki, Y.; Ikari, A. Up-regulation of transient receptor potential melastatin 6 channel expression by tumor necrosis factor-alpha in the presence of epidermal growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitor. J. Cell. Physiol. 2017, 232, 2841–2850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manabe, A.; Furukawa, C.; Endo, S.; Marunaka, K.; Nishiyama, T.; Fujii, N.; Tabuchi, Y.; Matsunaga, T.; Ikari, A. Chlorpheniramine Increases Paracellular Permeability to Marker Fluorescein Lucifer Yellow Mediated by Internalization of Occludin in Murine Colonic Epithelial Cells. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 2017, 40, 1299–1305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhu, W.; Jia, Q.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Xia, M. The anthocyanin cyanidin-3-O-beta-glucoside, a flavonoid, increases hepatic glutathione synthesis and protects hepatocytes against reactive oxygen species during hyperglycemia: Involvement of a cAMP-PKA-dependent signaling pathway. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2012, 52, 314–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, Y.; Kim, J.Y.; Jun, H.J.; Kim, S.J.; Lee, J.H.; Hoang, M.H.; Kim, H.S.; Chang, H.I.; Hwang, K.Y.; Um, S.J.; et al. Cyanidin is an agonistic ligand for peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-alpha reducing hepatic lipid. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2013, 1831, 698–708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Z.; Ding, L.; Lu, Q.; Chen, Y.H. Claudins in intestines: Distribution and functional significance in health and diseases. Tissue Barriers 2013, 1, e24978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kopf-Bolanz, K.A.; Schwander, F.; Gijs, M.; Vergeres, G.; Portmann, R.; Egger, L. Validation of an in vitro digestive system for studying macronutrient decomposition in humans. J. Nutr. 2012, 142, 245–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, T.B.; Feng, D.; Song, G.; Li, H.W.; Tang, H.W.; Ling, W.H. The role of sodium-dependent glucose transporter 1 and glucose transporter 2 in the absorption of cyanidin-3-o-beta-glucoside in Caco-2 cells. Nutrients 2014, 6, 4165–4177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walton, M.C.; McGhie, T.K.; Reynolds, G.W.; Hendriks, W.H. The flavonol quercetin-3-glucoside inhibits cyanidin-3-glucoside absorption in vitro. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2006, 54, 4913–4920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braissant, O.; Foufelle, F.; Scotto, C.; Dauca, M.; Wahli, W. Differential expression of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptors (PPARs): Tissue distribution of PPAR-alpha, -beta, and -gamma in the adult rat. Endocrinology 1996, 137, 354–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ikari, A.; Sanada, A.; Okude, C.; Sawada, H.; Yamazaki, Y.; Sugatani, J.; Miwa, M. Up-regulation of TRPM6 transcriptional activity by AP-1 in renal epithelial cells. J. Cell. Physiol. 2010, 222, 481–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manabe, A.; Furukawa, C.; Hasegawa, H.; Matsunaga, T.; Endo, S.; Ikari, A. Upregulation of transient receptor potential melastatin 6 channel expression by rosiglitazone and all-trans-retinoic acid in erlotinib-treated renal tubular epithelial cells. J. Cell. Physiol. 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thebault, S.; Alexander, R.T.; Tiel Groenestege, W.M.; Hoenderop, J.G.; Bindels, R.J. EGF increases TRPM6 activity and surface expression. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2009, 20, 78–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirata, Y.; Funato, Y.; Miki, H. Basolateral sorting of the Mg2+ transporter CNNM4 requires interaction with AP-1A and AP-1B. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2014, 455, 184–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]









| Drugs | Mode of Action |
|---|---|
| GW9662 | PPARγ antagonist |
| GSK3787 | PPARδ antagonist |
| GW6471 | PPARα antagonist |
| H-89 | PKA inhibitor |
| TRPM6 | Sense | 5′-ACCACCTAAGGCAGATGCAA-3′ |
| Antisense | 5′-CAACTTCATTTGGGCTTCTTG-3′ | |
| TRPM7 | Sense | 5′-AACCAACACTCTGGAAGAGATCA-3′ |
| Antisense | 5′-TCAGTCAAGTTTTCTCCCACAC-3′ | |
| CNNM4 | Sense | 5′-TGATGGAGATGTTGAAGGTGAC-3′ |
| Antisense | 5′-CCTCCACAGTTTTGGTCCTTAG-3′ | |
| β-Actin | Sense | 5′-CCAACCGTGAAAAGATGACC-3′ |
| Antisense | 5′-CCAGAGGCATACAGGGACAG-3′ |
| TRPM6 | Sense | 5′-GACTGAAGGATGCAGTGAGCCATGATCCTGC-3′ |
| Antisense | 5′-CCCAGGCTCAAGTGATCCTTCCACT-3′ | |
| CNNM4 | Sense | 5′-GAATTCTTGCCCCAATTCTCTGGTTAGCAAG-3′ |
| Antisense | 5′-TTACCTCTTACGGCCTTGGTTTCTC-3′ |
| TRPM6 | Sense | 5′-CCAGGTTTTATGGCTACTGGAC-3′ |
| Antisense | 5′-GACGTATGACTACGGGCTTCTC-3′ | |
| CNNM4 | Sense | 5′-CTGCCATTTTTCTGATGATAGG-3′ |
| Antisense | 5′-TCTGACCTAGGTTTTTCACCTG-3′ |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Takashina, Y.; Manabe, A.; Tabuchi, Y.; Ikari, A. Cyanidin Increases the Expression of Mg2+ Transport Carriers Mediated by the Activation of PPARα in Colonic Epithelial MCE301 Cells. Nutrients 2019, 11, 641. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu11030641
Takashina Y, Manabe A, Tabuchi Y, Ikari A. Cyanidin Increases the Expression of Mg2+ Transport Carriers Mediated by the Activation of PPARα in Colonic Epithelial MCE301 Cells. Nutrients. 2019; 11(3):641. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu11030641
Chicago/Turabian StyleTakashina, Yui, Aya Manabe, Yoshiaki Tabuchi, and Akira Ikari. 2019. "Cyanidin Increases the Expression of Mg2+ Transport Carriers Mediated by the Activation of PPARα in Colonic Epithelial MCE301 Cells" Nutrients 11, no. 3: 641. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu11030641