Dynamic Range Compression Self-Adaption Method for SAR Image Based on Deep Learning
Abstract
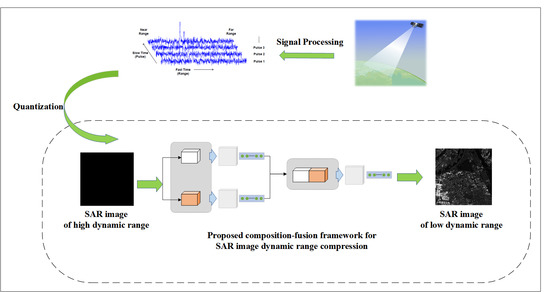
:1. Introduction
2. Proposed Method
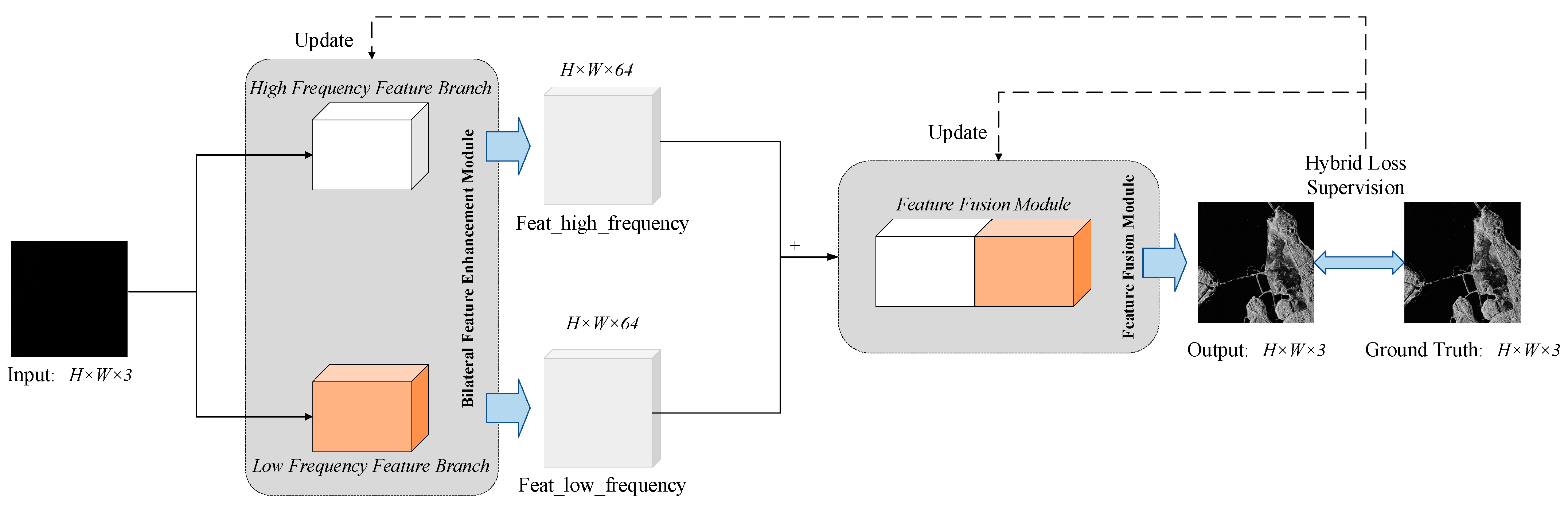
2.1. Overview of Proposed Decomposition-Fusion Framework
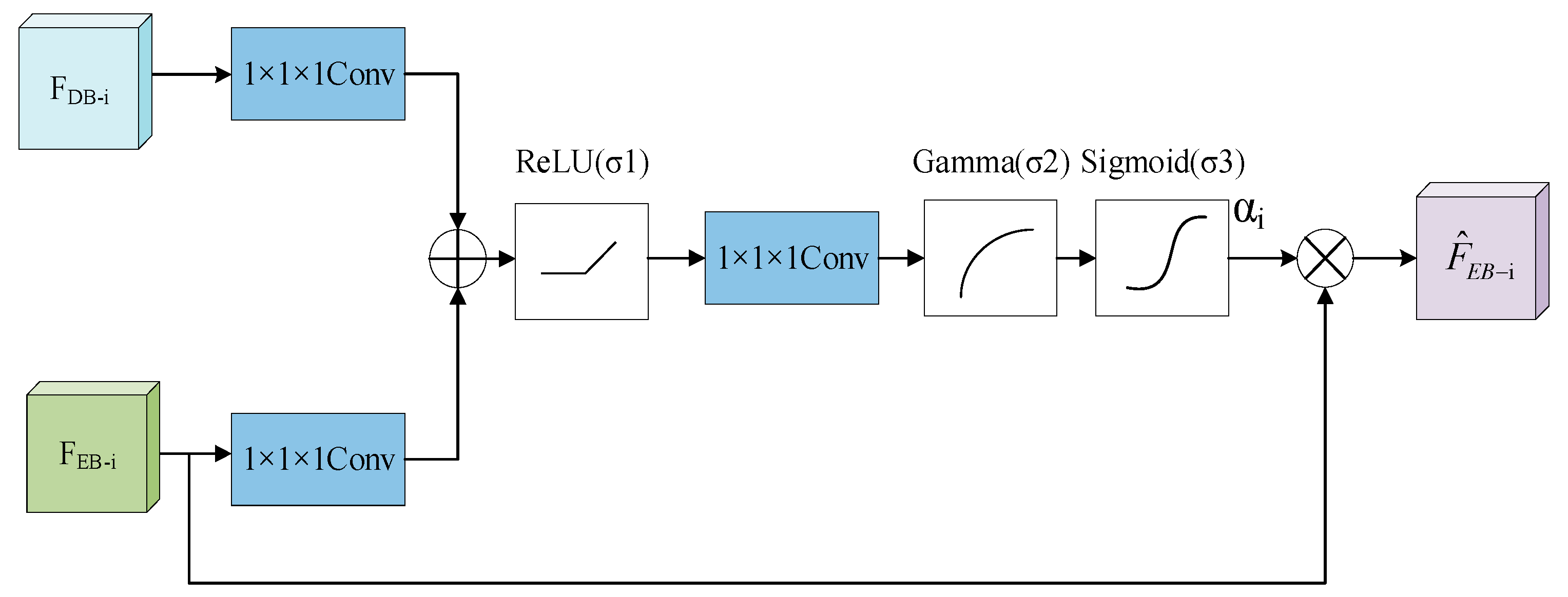
2.2. Bilateral Feature Enhancement Module
2.2.1. High Frequency Feature Branch
2.2.2. Low Frequency Feature Branch
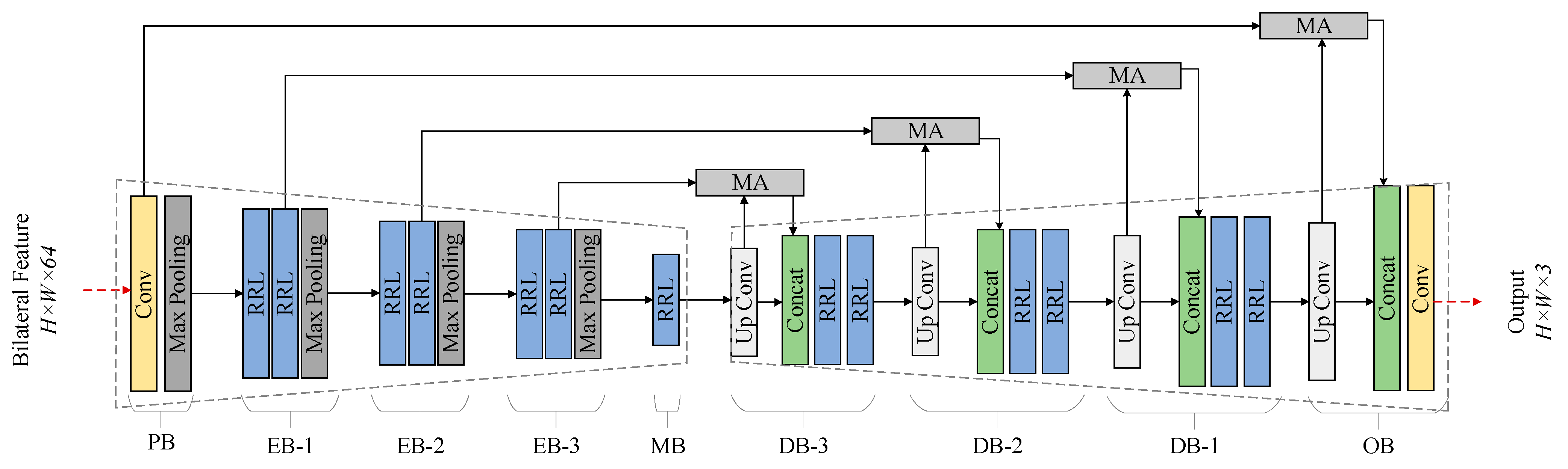
2.3. Feature Fusion Module
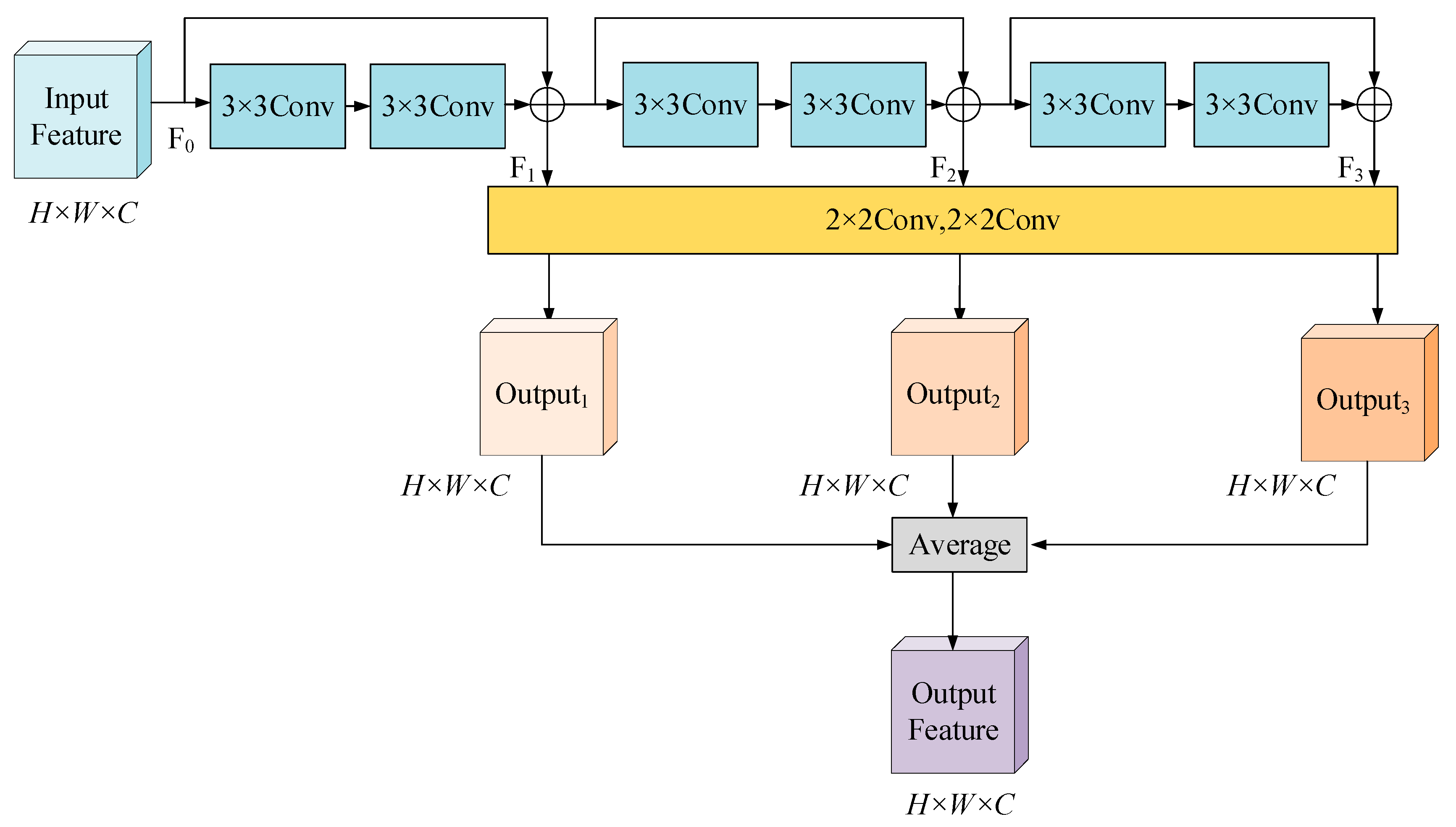
2.3.1. Residual Recursive Learning Unit
2.3.2. Multi-Scale Attention Mechanism
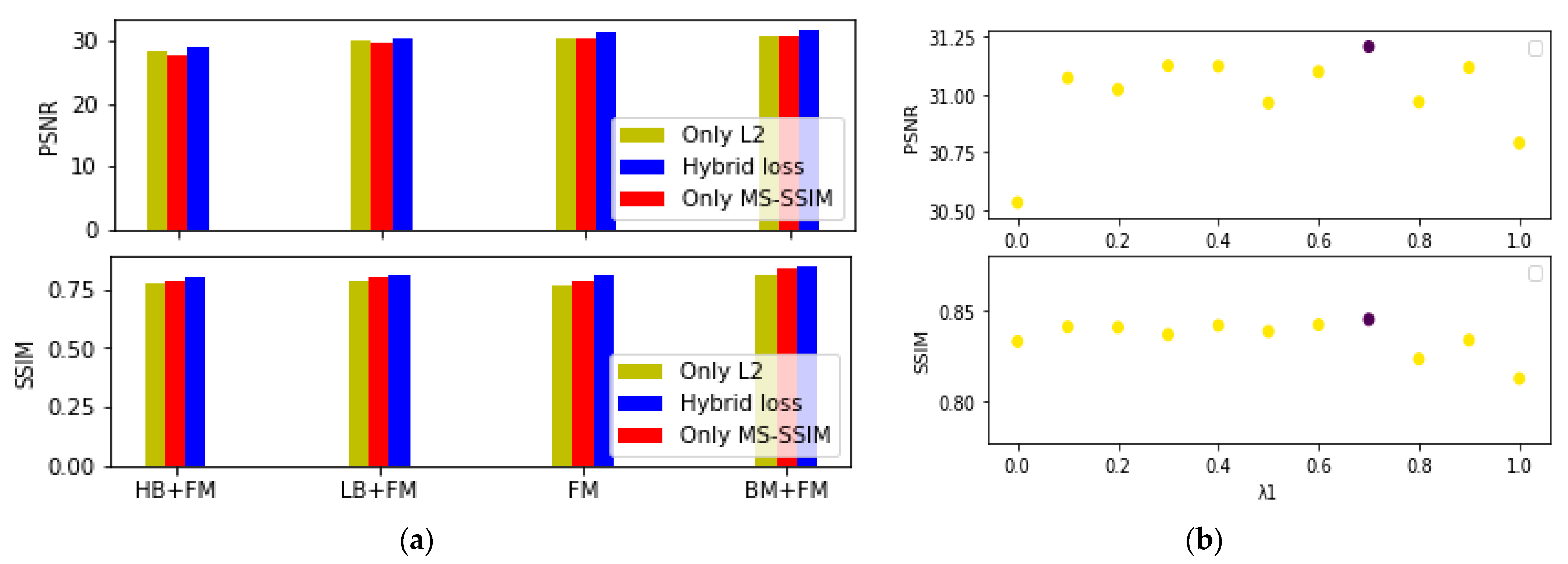
2.4. Loss Function
3. Experiments and Analysis
3.1. Implementation Details
3.2. Evaluation Metrics
3.3. Results and Analysis
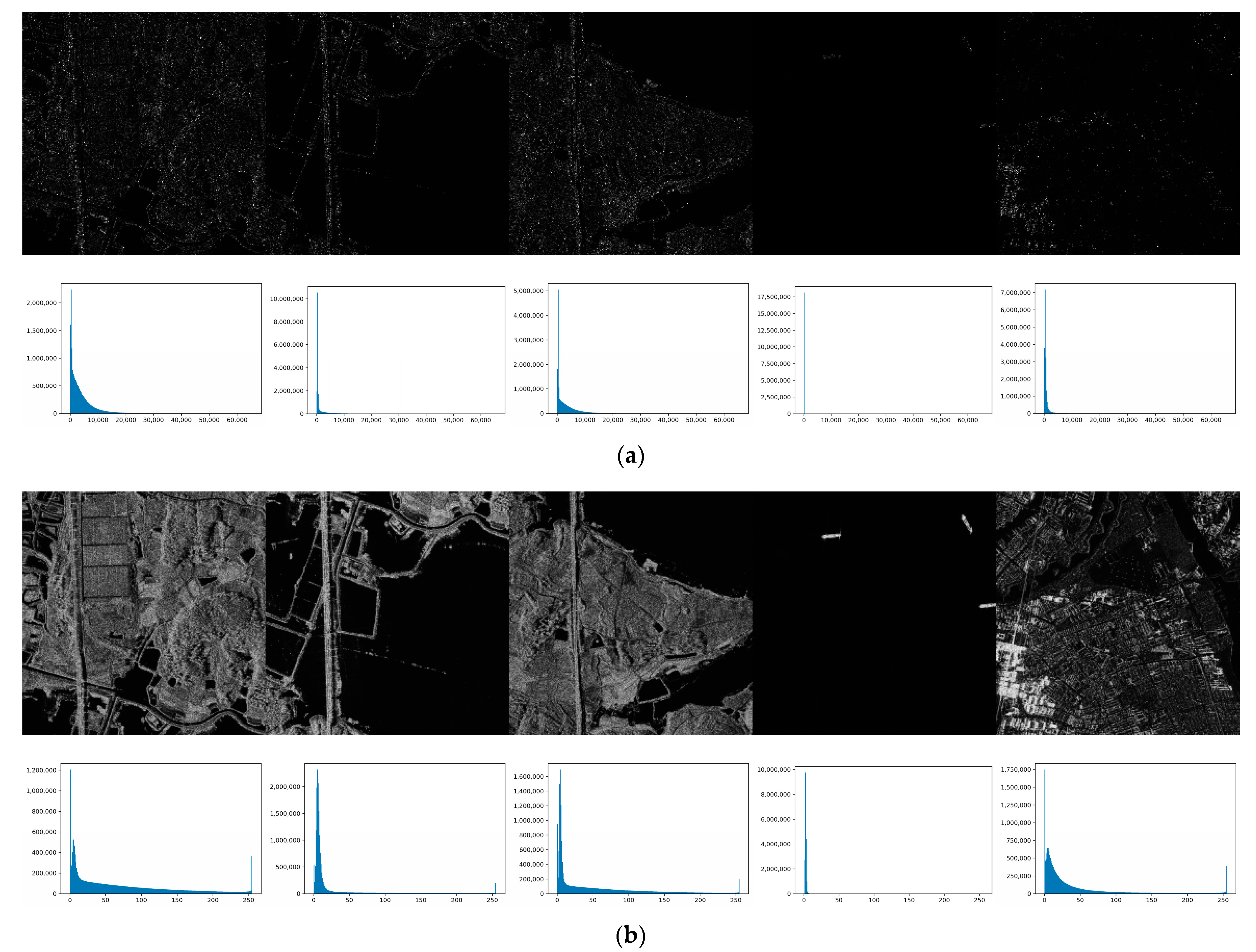
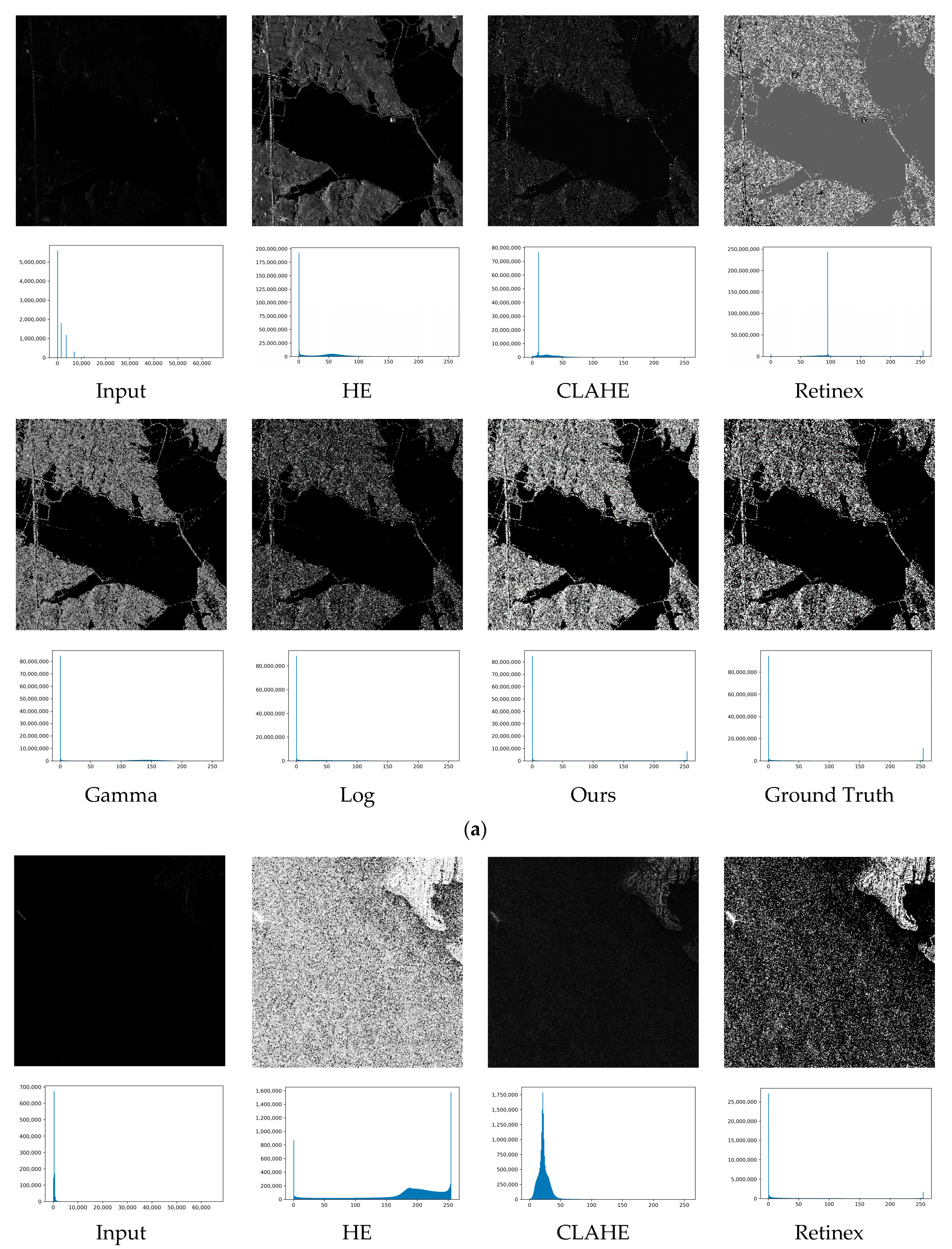
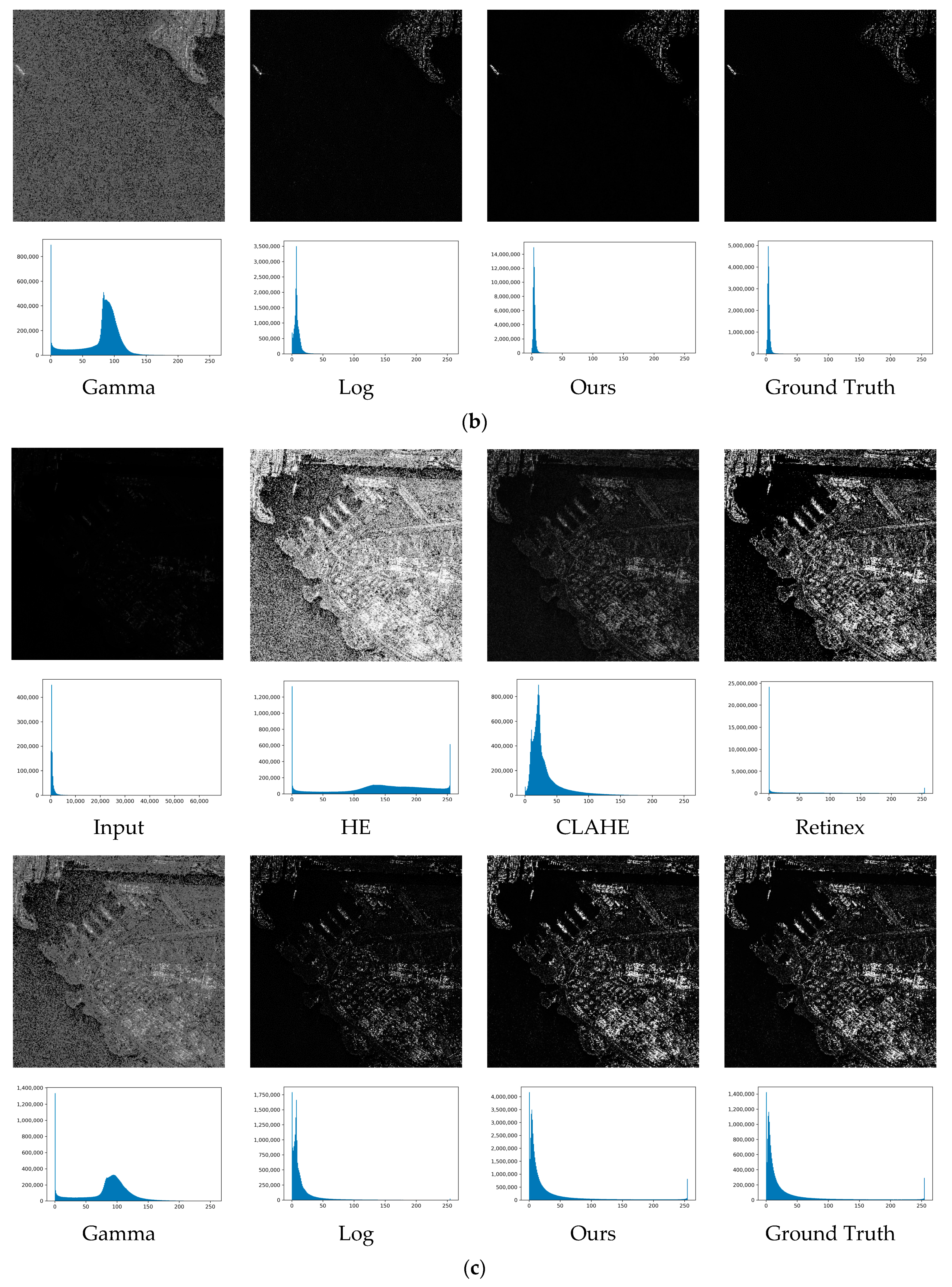
3.3.1. Experiments on Synthesized SAR Images
3.3.2. Experiments on Real-world SAR Images
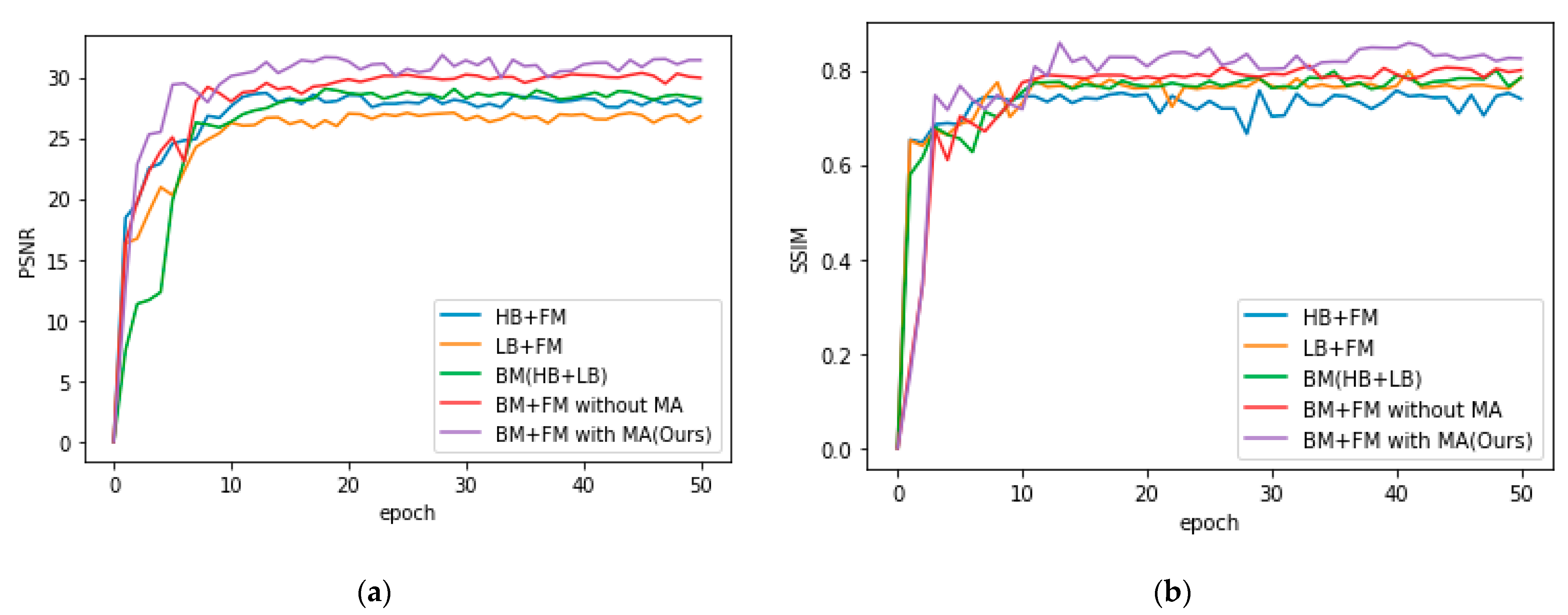
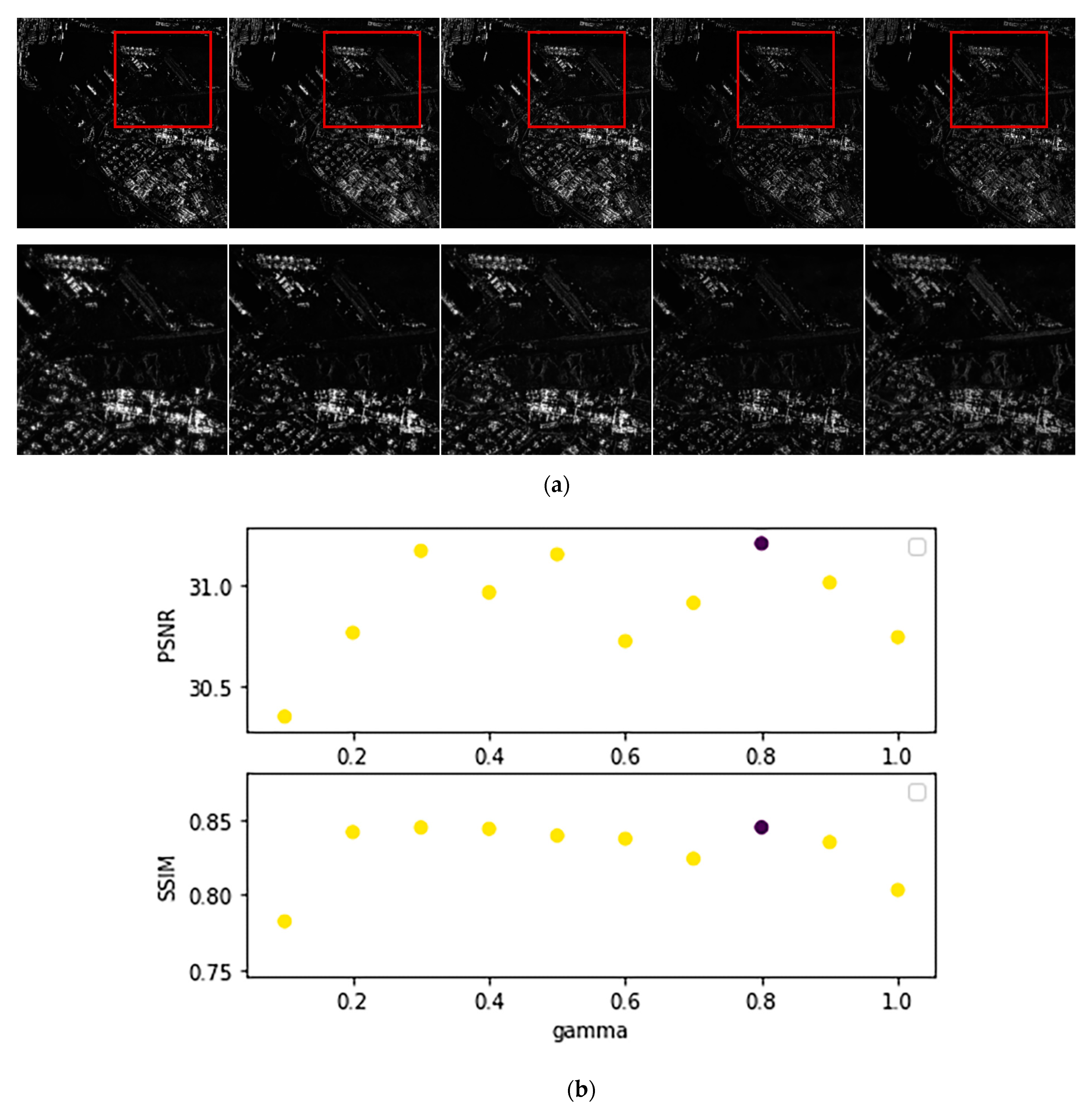
3.4. Ablation and Analysis
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviation
| Abbreviation | Definition |
| SAR | Synthetic Aperture Radar |
| HDR | High Dynamic Range |
| LDR | Low Dynamic Range |
| CAM | Channel Attention Module |
| RRL | Residual Recursive Learning Unit |
| MA | Multi-scale Attention Module |
| HB | High frequency feature Branch |
| LB | Low frequency feature Branch |
| BM | Bilateral feature enhancement Module |
| FM | Feature fusion Module |
| PB | Preprocessing Block |
| EB | Encoder Block |
| MB | Middle Block |
| DB | Decoder Block |
| OB | Output Block |
| PSNR | Peak Signal-to-Noise Ratio |
| SSIM | Structural Similarity Index |
| HE | Histogram Equalization |
| CLAHE | Contrast Adaptive Limitation Histogram Equalization |
References
- Moreira, A.; Prats-Iraola, P.; Younis, M.; Krieger, G.; Hajnsek, I.; Papathanassiou, K.P. A tutorial on synthetic aperture radar. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Mag. 2013, 1, 6–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pizer, S.M.; Amburn, E.P.; Austin, J.D.; Cromartie, R.; Geselowitz, A.; Greer, T.; ter Haar Romeny, B.; Zimmerman, J.B.; Zuiderveld, K. Adaptive histogram equalization and its variations. Comput. Vis. Graph. Image Process. 1987, 39, 355–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stark, J.A. Adaptive Image Contrast Enhancement Using Generalizations of Histogram Equalization. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2000, 9, 889–896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Reza, A.M. Realization of the contrast limited adaptive histogram equalization (CLAHE) for real-time image enhancement. J. VLSI Signal Process. Syst. Signal Image Video Technol. 2004, 38, 35–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Land, E.H.; McCann, J.J. Lightness and retinex theory. J. Opt. Soc. Am. 1971, 61, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jobson, D.; Rahman, Z.; Woodell, G. Properties and performance of a center/surround retinex. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 1997, 6, 451–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, Z.; Jobson, D.J.; Woodell, G. Multiscale retinex for color image enhancement. In Proceedings of the 3rd IEEE International Conference on Image Processing, Lausanne, Switzerland, 19 September 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Farid, H. Blind inverse gamma correction. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2001, 10, 1428–1433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drago, F.; Myszkowski, K.; Annen, T.; Chiba, N. Adaptive Logarithmic Mapping for Displaying High Contrast Scenes. In Computer Graphics Forum; Blackwell Publishing, Inc.: Oxford, UK, 2003; Volume 22. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Z.; Liu, J.; Huang, J. Dynamic range compression and pseudo-color presentation based on Retinex for SAR images. In Proceedings of the 2008 International Conference on Computer Science and Software Engineering, Wuhan, China, 12–14 December 2008; Volume 6, pp. 257–260. [Google Scholar]
- Hisanaga, S.; Wakimoto, K.; Okamura, K. Tone mapping and blending method to improve SAR image visibility. IAENG Int. J. Comput. Sci. 2011, 38, 289–294. [Google Scholar]
- Hisanaga, S.; Wakimoto, K.; Okamura, K. Compression method for high dynamic range intensity to improve sar image visibility. In Proceedings of the International MultiConference of Engineers and Computer Scientists, Hong Kong, 16–18 March 2011; Volume 1. [Google Scholar]
- Upadhyay, A.; Mahapatra, S. Adaptive enhancement of compressed SAR images. Signal Image Video Process. 2016, 10, 1335–1342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, R.; Guan, J.; Yang, Y.; Xiong, A. Spatiotemporal adaptive nonuniformity correction based on BTV regularization. IEEE Access 2018, 7, 753–762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tirandaz, Z.; Akbarizadeh, G. A two-phase algorithm based on kurtosis curvelet energy and unsupervised spectral regression for segmentation of SAR images. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2015, 9, 1244–1264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Wang, S.; Jiao, L.; Li, K. SAR image despeckling based on sparse representation. In MIPPR 2007: Multispectral Image Processing. International Society for Optics and Photonics. Proceedings of the International Symposium on Multispectral Image Processing and Pattern Recognition, Wuhan, China, 15–17 November 2007; SPIE: Bellingham, WA, USA, 2007; Volume 6787, p. 67872I. [Google Scholar]
- Dabov, K.; Foi, A.; Katkovnik, V.; Egiazarian, K. Image denoising with block-matching and 3D filtering. In Image Processing: Algorithms and Systems, Neural Networks, and Machine Learning. International Society for Optics and Photonics. Proceedings of the Electronic Imaging 2006, San Jose, CA, USA, 16–19 January 2006; SPIE: Bellingham, WA, USA, 2006; Volume 6064, p. 606414. [Google Scholar]
- Bioucas-Dias, J.M.; Figueiredo, M.A.T. Multiplicative noise removal using variable splitting and constrained optimization. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2010, 19, 1720–1730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chierchia, G.; Cozzolino, D.; Poggi, G.; Verdoliva, L. SAR image despeckling through convolutional neural networks. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium (IGARSS), Fort Worth, TX, USA, 23–28 July 2017; pp. 5438–5441. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Q.; Yuan, Q.; Li, J.; Yang, Z.; Ma, X. Learning a dilated residual network for SAR image despeckling. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, J.; Li, Y.; Xiao, Y.; Bai, Y. Hdranet: Hybrid dilated residual attention network for SAR image despeckling. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 2921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, K.; Zuo, W.; Chen, Y.; Meng, D.; Zhang, L. Beyond a gaussian denoiser: Residual learning of deep CNN for image denoising. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2017, 26, 3142–3155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ronneberger, O.; Fischer, P.; Brox, T. U-net: Convolutional networks for biomedical image segmentation. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention, Munich, Germany, 5–9 October 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Gharbi, M.; Chen, J.; Barron, J.T.; Hasinoff, S.W.; Durand, F. Deep bilateral learning for real-time image enhancement. ACM Trans. Graph. 2017, 36, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ignatov, A.; Kobyshev, N.; Timofte, R.; Vanhoey, K. DSLR-quality photos on mobile devices with deep convolutional networks. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Venice, Italy, 22–29 October 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Goodfellow, I.; Pouget-Abadie, J.; Mirza, M.; Xu, B.; Warde-Farley, D.; Ozair, S.; Courville, A.; Bengio, Y. Generative adversarial nets. In Proceedings of the Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems 27 (NIPS 2014), Montreal, QC, Canada, 8–13 December 2014; Volume 27.
- Caballero, J.; Ledig, C.; Aitken, A.; Acosta, A.; Totz, J.; Wang, Z.; Shi, W. Real-time video super-resolution with spatio-temporal networks and motion compensation. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017; pp. 4778–4787. [Google Scholar]
- Ledig, C.; Theis, L.; Huszár, F.; Caballero, J.; Cunningham, A.; Acosta, A.; Aitken, A.; Tejani, A.; Totz, J.; Wang, Z.; et al. Photo-realistic single image super-resolution using a generative adversarial network. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017; pp. 4681–4690. [Google Scholar]
- Remez, T.; Litany, O.; Giryes, R.; Bronstein, A.M. Deep class-aware image denoising. In Proceedings of the 2017 International Conference on Sampling Theory and Applications (SampTA), Tallinn, Estonia, 3–7 July 2017; pp. 138–142. [Google Scholar]
- Isola, P.; Zhu, J.Y.; Zhou, T.; Efros, A.A. Image-to-image translation with conditional adversarial networks. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017; pp. 1125–1134. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, J.Y.; Park, T.; Isola, P.; Efros, A.A. Unpaired image-to-image translation using cycle-consistent adversarial networks. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017; pp. 2223–2232. [Google Scholar]
- Yan, Z.; Zhang, H.; Wang, B.; Paris, S.; Yu, Y. Automatic photo adjustment using deep neural networks. ACM Trans. Graph. 2016, 35, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, L.; Zhu, C.; Xiang, G.; Li, Y.; Jia, H.; Xie, X. LLCNN: A convolutional neural network for low-light image enhancement. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE Visual Communications and Image Processing (VCIP), St. Petersburg, FL, USA, 10–13 December 2017; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Lore, K.G.; Akintayo, A.; Sarkar, S. LLNet: A deep autoencoder approach to natural low-light image enhancement. Pattern Recognit. 2017, 61, 650–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- He, K.; Zhang, X.; Ren, S.; Sun, J. Delving deep into rectifiers: Surpassing human-level performance on imagenet classification. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Santiago, Chile, 11–18 December 2015; pp. 1026–1034. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, F.; Koltun, V.; Funkhouser, T. Dilated residual networks. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017; pp. 472–480. [Google Scholar]
- Kingma, D.; Ba, J. Adam: A Method for Stochastic Optimization. arXiv 2014, arXiv:1412.6980. [Google Scholar]
- Lattari, F.; Gonzalez Leon, B.; Asaro, F.; Rucci, A.; Prati, C.; Matteucci, M. Deep learning for SAR image despeckling. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 1532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, Z.; Bovik, A.C.; Sheikh, H.R.; Simoncelli, E.P. Image quality assessment: From error visibility to structural similarity. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2004, 13, 600–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Watson, A.B.; Borthwick, R.; Taylor, M. Image quality and entropy masking. In Human Vision and Electronic Imaging II. International Society for Optics and Photonics. Proceedings of the Electronic Imaging’97, San Jose, CA, USA, 8–14 February 1997; SPIE: Bellingham, WA, USA, 1997; Volume 3016, pp. 2–12. [Google Scholar]
- Sundaram, M.; Ramar, K.; Arumugam, N.; Prabin, G. Histogram modified local contrast enhancement for mammogram images. Appl. Soft Comput. 2011, 11, 5809–5816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xian, S.; Zhirui, W.; Yuanrui, S.; Wenhui, D.; Yue, Z.; Kun, F. AIR-SARShip–1.0: High resolution SAR ship detection dataset. Radars 2019, 8, 852–862. [Google Scholar]


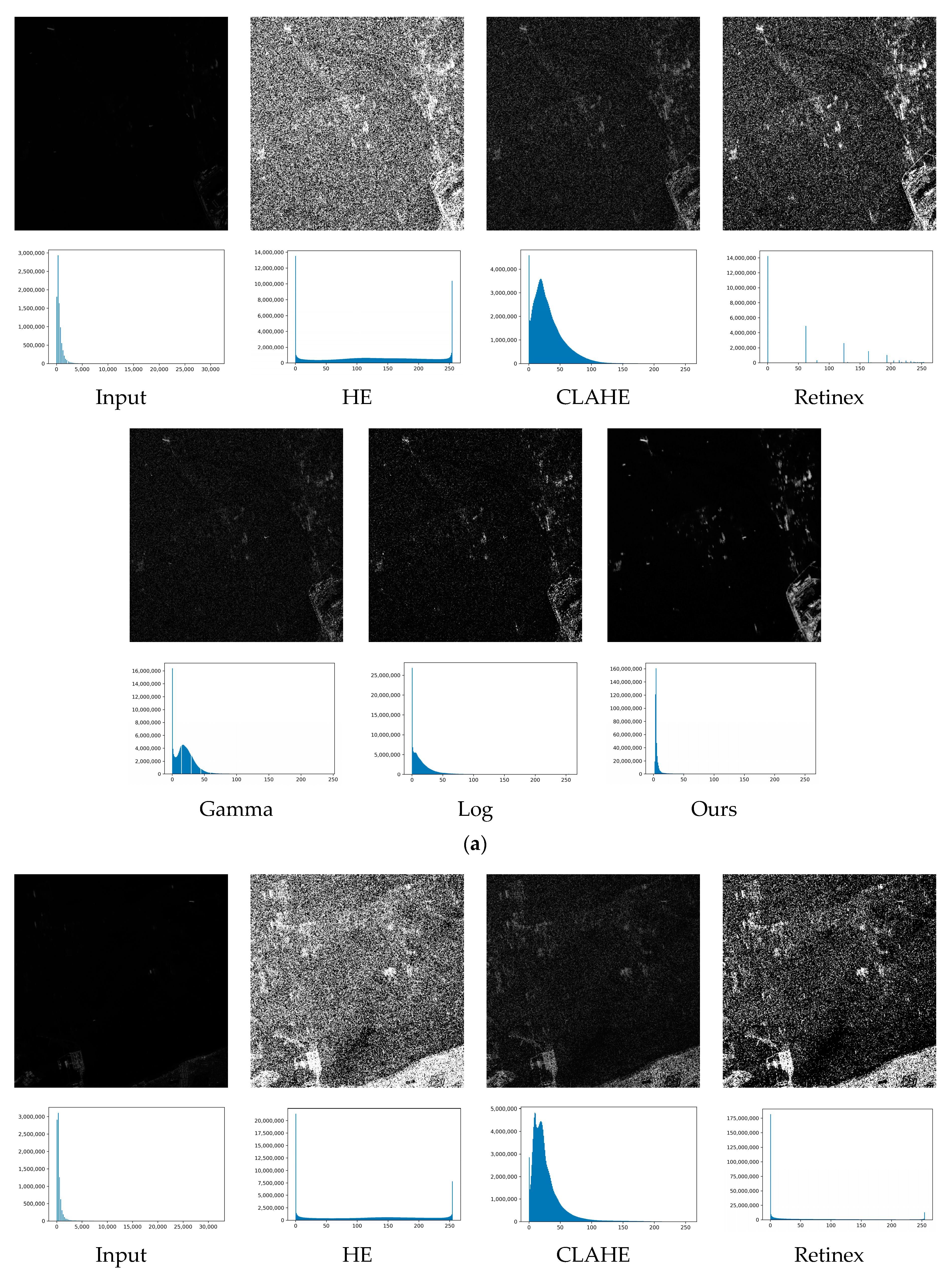
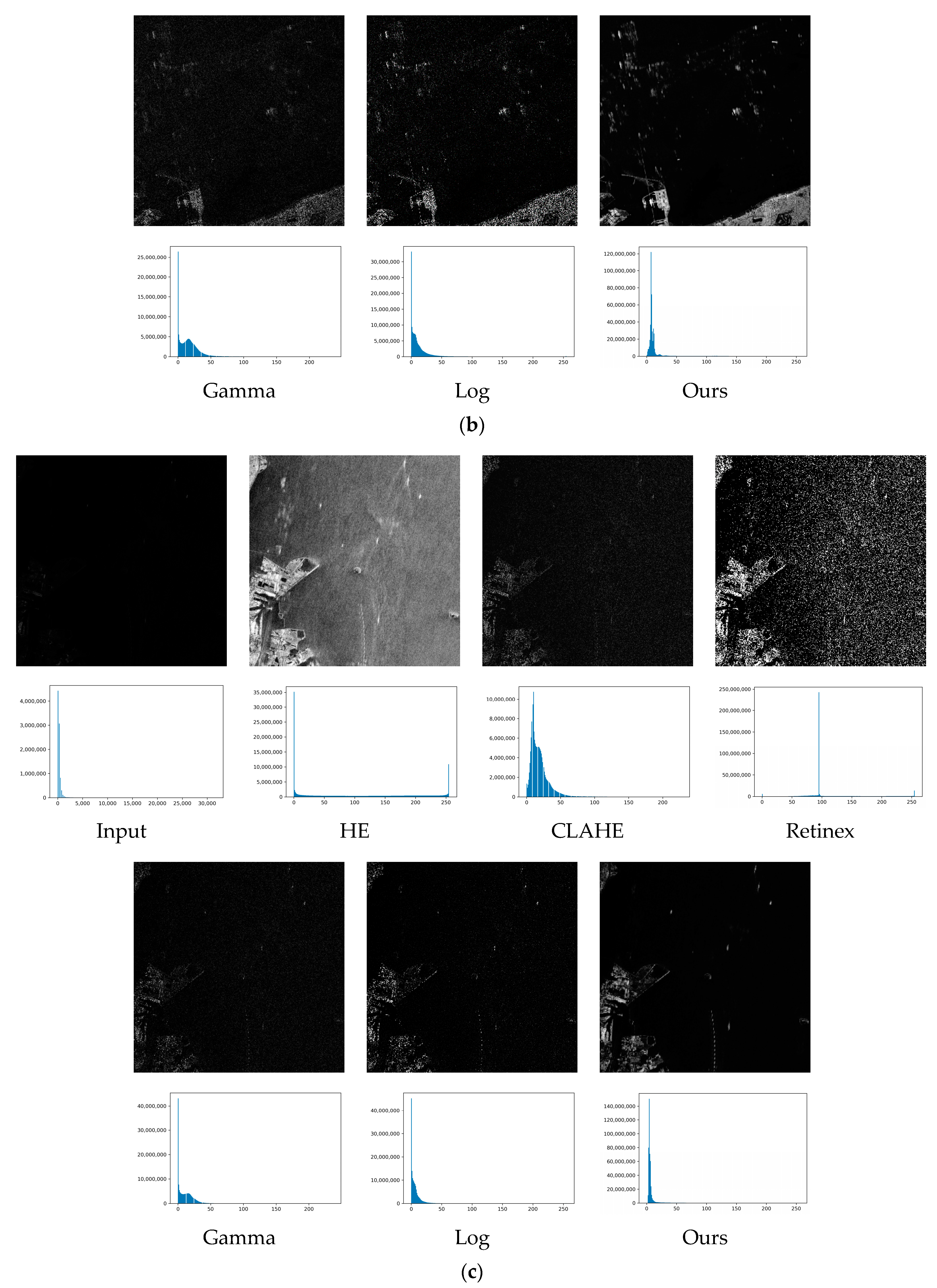
| Image 1 | Image 2 | Image 3 | Image 4 | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PSNR | SSIM | PSNR | SSIM | PSNR | SSIM | PSNR | SSIM | |
| HE | 6.572 | 0.527 | 7.397 | 0.493 | 7.324 | 0.490 | 6.721 | 0.587 |
| CLAHE | 25.293 | 0.584 | 25.431 | 0.572 | 25.445 | 0.571 | 25.240 | 0.589 |
| Retinex | 20.663 | 0.753 | 20.675 | 0.781 | 20.142 | 0.774 | 20.146 | 0.745 |
| Gamma | 21.193 | 0.538 | 21.690 | 0.574 | 21.031 | 0.576 | 21.832 | 0.508 |
| Log | 23.162 | 0.531 | 23.532 | 0.585 | 23.043 | 0.581 | 23.849 | 0.517 |
| Proposed | 31.308 | 0.845 | 31.774 | 0.890 | 31.866 | 0.894 | 31.267 | 0.838 |
| Image 1 | Image 2 | Image 3 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Entropy | EME | Entropy | EME | Entropy | EME | |
| HE | 6.195895 | 0.922171 | 5.493693 | 0.920750 | 3.406962 | 0.921220 |
| CLAHE | 8.533201 | 0.791921 | 8.103221 | 0.778417 | 4.734564 | 0.741041 |
| Retinex | 5.172613 | 0.858365 | 4.164617 | 0.829591 | 1.321904 | 0.798544 |
| Gamma | 3.707392 | 0.7473 | 3.059469 | 0.7421 | 0.874383 | 0.7116 |
| Log | 3.695861 | 0.8301 | 3.034859 | 0.8188 | 0.870504 | 0.8031 |
| Proposed | 7.779042 | 0.921855 | 10.72357 | 0.920489 | 8.081626 | 0.920724 |
| PSNR | SSIM | Entropy | EME | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| HB + FM | 28.554 | 0.757 | 2.938 | 0.644 |
| LB + FM | 27.058 | 0.799 | 4.068 | 0.843 |
| BM (HB + LB) | 28.983 | 0.808 | 4.417 | 0.828 |
| BM + FM without MA | 30.341 | 0.810 | 5.081 | 0.887 |
| BM + FM with MA(Ours) | 31.817 | 0.848 | 5.497 | 0.899 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Shi, H.; Sheng, Q.; Wang, Y.; Yue, B.; Chen, L. Dynamic Range Compression Self-Adaption Method for SAR Image Based on Deep Learning. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 2338. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14102338
Shi H, Sheng Q, Wang Y, Yue B, Chen L. Dynamic Range Compression Self-Adaption Method for SAR Image Based on Deep Learning. Remote Sensing. 2022; 14(10):2338. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14102338
Chicago/Turabian StyleShi, Hao, Qingqing Sheng, Yupei Wang, Bingying Yue, and Liang Chen. 2022. "Dynamic Range Compression Self-Adaption Method for SAR Image Based on Deep Learning" Remote Sensing 14, no. 10: 2338. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14102338
APA StyleShi, H., Sheng, Q., Wang, Y., Yue, B., & Chen, L. (2022). Dynamic Range Compression Self-Adaption Method for SAR Image Based on Deep Learning. Remote Sensing, 14(10), 2338. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14102338