Influencing Factors of the Adoption of Agricultural Irrigation Technologies and the Economic Returns: A Case Study in Chaiyaphum Province, Thailand
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
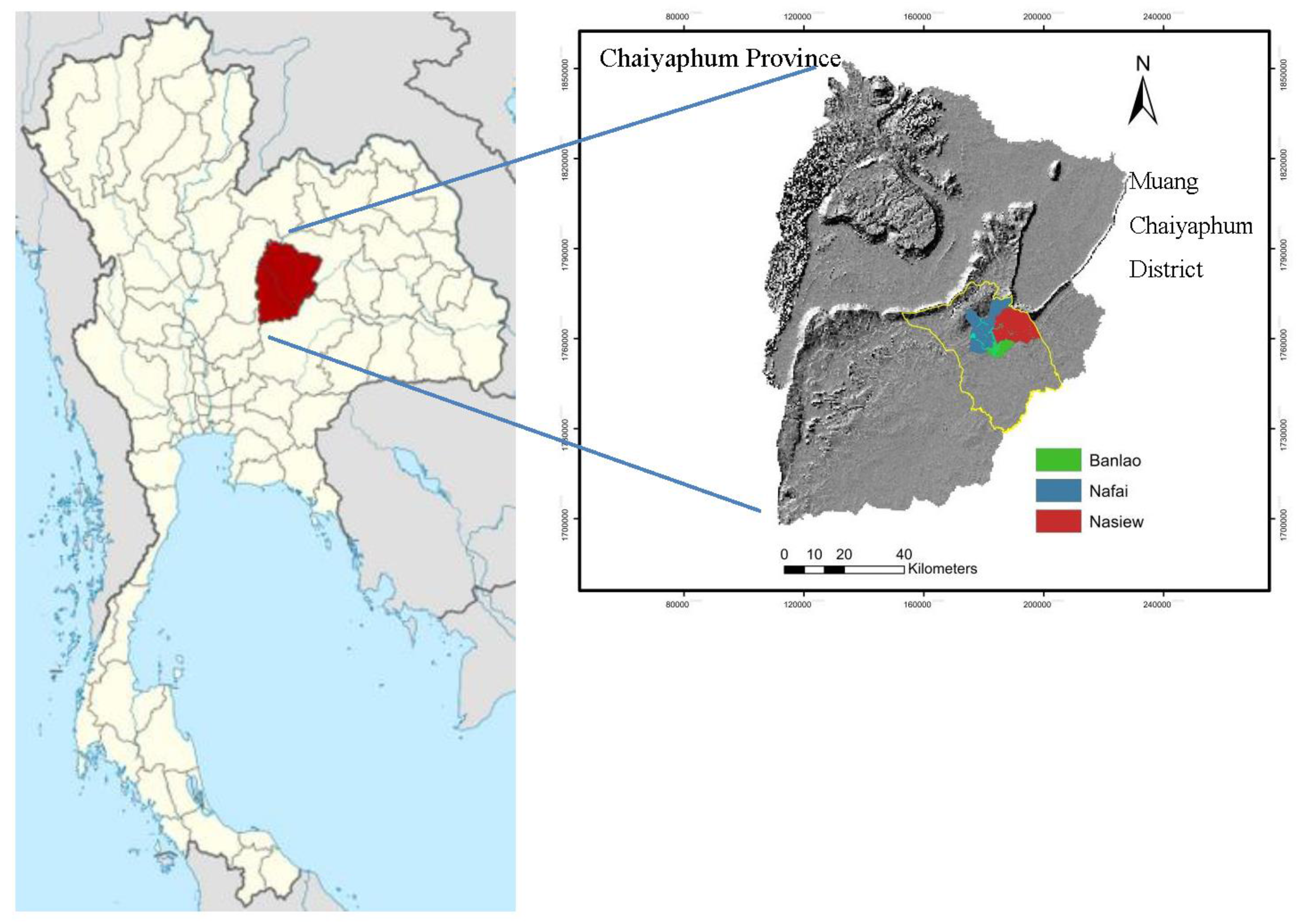
2.1. Study Area and Data Collection
2.2. Data Analysis
2.2.1. Household Characteristics
2.2.2. Factors Influencing Technology Adoption
2.2.3. Economic Returns from Technology Adoption
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Demographic and Socioeconomic Factors
3.1.1. Gender
3.1.2. Education Level
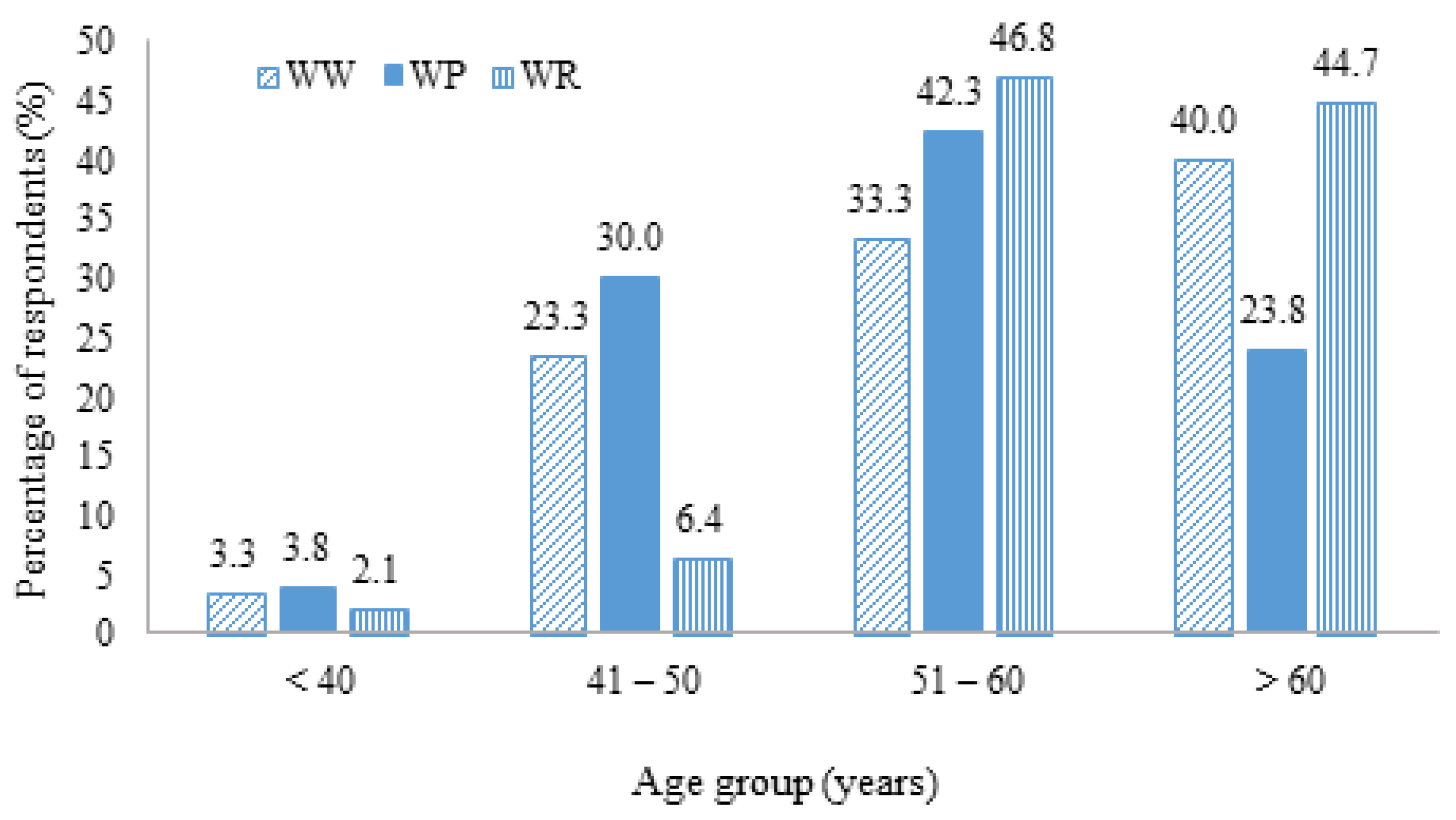
3.1.3. Age
3.1.4. Rice Farming Experience
3.1.5. Number of Farm Laborers
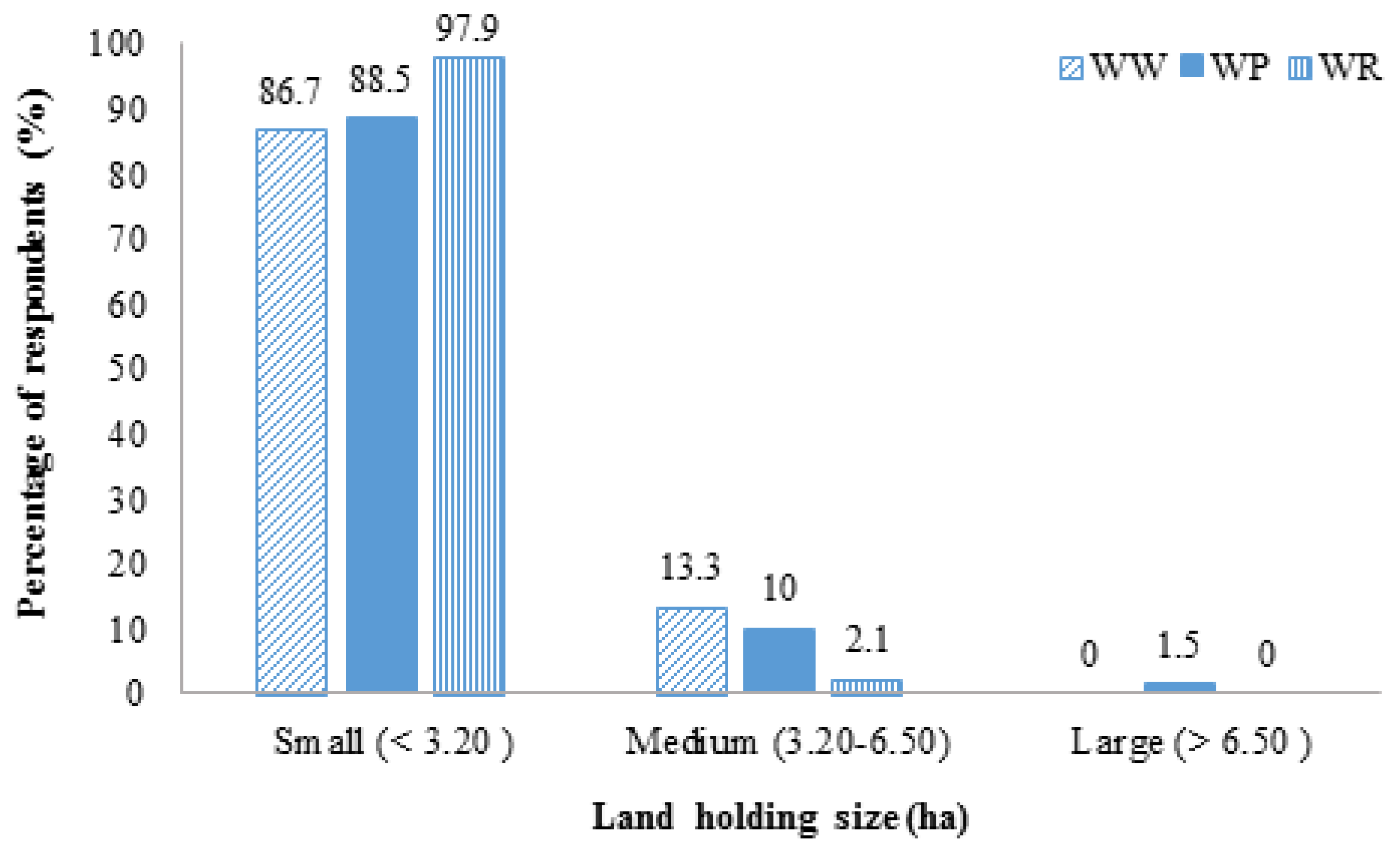
3.1.6. Land Holding Size
3.2. Influencing Factors of the Adoption of Variable Irrigation Technologies
3.2.1. Age
3.2.2. Land Holding Size
3.2.3. Farm Income
3.2.4. Farmland Location (Upstream)
3.2.5. Proximity to Water Source
3.2.6. Training on Agricultural Practices
3.2.7. WUA Membership
3.2.8. Group Participation
3.3. Economic Returns under Variable Irrigation Schemes
4. Conclusions and Recommendations
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gregg, N.S. Integrated water resources management: Balancing views and improving practice. Water Int. 2008, 33, 272–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lenton, R.; Muller, M. Integrated Water Resources Management in Practice: Better Water Management for Development; Earthscan Publication Ltd.: London, UK, 2009; Volume 38, p. 249. [Google Scholar]
- Davivongs, V.; Yokohari, M.; Hara, Y. Neglected canals: Deterioration of indigenous irrigation system by urbanization in the West Peri-Urban area of Bangkok Metropolitan Region. Water 2012, 4, 12–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kitchaicharoen, J.; Ekasingh, B.; Dithaprayoon, S.; Chaiwinit, W. Linkages between access to irrigation water and livelihood strategies using. In Proceedings of the The 4th National Agricultural Conference Agriculture for the Environment and the Environment and Recognization Global Warming, Chiang Mai, Thailand, 27–28 May 2008; Research Center for Agricultural Productivity: Chiang Mai, Thailand, 2008; pp. 225–235. [Google Scholar]
- Namara, R.; Awulachew, S.B.; Merrey, D.J. Review of agricultural water management technologies and practices. In Best Practices and Technologies for Small Scale Agricultural Water Management in Ethiopia, Proceedings of the MoARD/MoWR/USAID/IWMI Symposium and Exhibition, Addis Ababa, Ethiopia, 7–9 March, 2006; Awulachew, S.B., Menker, M., Abesha, D., Atnafe, T., Wondimkum, Y., Eds.; International Water Management Institute: Colombo, Sri Lanka, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Sethaputra, S.; Thanopanuwat, S.; Kumpa, L.; Pattanee, S. Thailand’s water vision: A case study. In From Vision to Action: A synthesis of Experiences in Southeast Asia; FAO—Office of the National Water Resources Committee, ESCAP: Bangkok, Thailand, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Senanarong, N.; Cheuwchoom, P.; Lusanandana, C.; Tangpoonpol, S.; Atichart, S.; Pongkanjana, A.; Srihaban, P.; Singhapong, T.; Patanothai, A.; Toomsan, B.; et al. Improving management of natural resources for sustainable rainfed agriculture in northeastern Thailand. In Proceedings of the ADB-ICRISAT-IWMI Project Review and Planning Meeting, Hanoi, Vietnam, 10–14 December 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Samian, M.; Mahdei, K.N.; Saadi, H.; Movahedi, R. Identifying factors affecting optimal management of agricultural water. J. Saudi Soc. Agric. Sci. 2014, 14, 11–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forrest, T.I. Principles of On-Form Water Management; University of Florida: Gainesville, FL, USA, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Pandy, R.K.; Maranville, J.W.; Admou, A. Deficit irrigation and nitrogen effects on maize in a Sahelian environment. I. Grain yield and yield components. Agric. Water Manag. 2000, 46, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panda, R.K.; Behera, S.K.; Kashyap, P.S. Effective management of irrigation water for maize under stressed conditions. Agric. Water Manag. 2004, 66, 181–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Hu, X.; Zhang, Q.; Zheng, M. Improving agricultural water use efficiency: A quantitative study of Zhangye City using the static CGE model with a CES water-land resources account. Sustainability 2017, 9, 308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srichaiwong, P.; Kwawjai, L.; Kroeksakul, P. Guidelines for natural food conservation for the community around the upstream forest of the Chi River Basin. Asian Soc. Sci. 2014, 10, 132–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dandedjrohoun, L.; Diagne, A.; Biaou, G. Determinants of diffusion and adoption of improved technology for rice parboiling in Benin. Rev. Agric. Environ. Stud. 2012, 93, 171–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oladeji, O.O.; Okoruwa, V.O.; Ojehomon, V.E.T.; Diagne, A.; Obasoro, O.A. Determinants of awareness and adoption of improved rice varieties in north central, Nigeria. Rice Genom. Genet. 2015, 6, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tetteh Anang, B. Factors influencing pesticide use in smallholder rice production in northern Ghana. Agric. For. Fish. 2015, 4, 77–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, X.; Cao, H.; Li, F. Econometric analysis of the determinants of adoption of rainwater harvesting and supplementary irrigation technology (RHSIT) in the semiarid Loess Plateau of China. Agric. Water Manag. 2007, 89, 243–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mittal, S.; Mehar, M. Socio-economic factors affecting adoption of modern informationand communication technology by farmers in India: Analysis using multivariate probit model. J. Agric. Educ. Ext. 2016, 22, 199–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, D.R. Agricultural sustainability and technology adoption: Issues and Policies for Developing Countries. Am. J. Agric. Econ. 2005, 87, 1325–1334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gebregziabher, G.; Giordano, M.A.; Langan, S.; Namara, R.E. Economic analysis of factors influencing adoption of motor pumps in Ethiopia. J. Dev. Agric. Econ. 2014, 6, 490–500. [Google Scholar]
- Mourshed, M. Rethinking Irrigation Technology Adoption: Lessons from the Egiptian Desert: Working No. 23, Program in Sciency, Technology and Society; Massachusetts Institute of Technology Moyo: Cambridge, MA, USA, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Mutambara, S.; Darkoh, M.B.K.; Atlhopheng, J.R. A comparative review of water management sustainability challenges in smallholder irrigation schemes in Africa and Asia. Agric. Water Manag. 2016, 171, 63–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bastakoti, R.C.; Shivakoti, G.P. Context and Institutions in Irrigation Management: Applicability of Design Principles in Nepal and Thailand; Chiang Mai University: Chiang Mai, Thailand, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Sithole, N.L.; Lagat, J.K.; Masuku, M.B. Factors influencing farmers participation in smallholder irrigation schemes: The case of Ntfonjeni rural development area. J. Econ. Sustain. Dev. 2014, 5, 159–168. [Google Scholar]
- Aseyehegu, K.; Yirga, C.; Rajan, S. Effect of small-scale irrigation on the income of rural farm households: The case of Laelay Maichew District, Central Tigray, Ethiopia. J. Agric. Sci. 2012, 7, 208–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panahi, F.; Malek-Mohammadi, I.; Chizari, M.; Samani, J. The role of optimizing agricultural water resource management to livelihood poverty abolition in rural Iran. Aust. J. Basic Appl. Sci. 2009, 3, 3841–3849. [Google Scholar]
- Rezadoost, B.; Allahyari, M.S. Farmers’ opinions regarding effective factors on optimum agricultural water management. J. Saudi Soc. Agric. Sci. 2014, 13, 15–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammadi, Y.; Shabanali Fami, H.; Asadi, A. Analysis of effective components on agricultural water management in Zarin- dasht County from farmers viewpoint. J. Agric. Sci. Nat. Resour. 2009, 16, 9–18. [Google Scholar]
- Buyukcangaz, H.; Korukcu, A. Integrated approach for water resources and irrigation management in Turkey. Water Int. 2007, 32, 710–719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, M.; Munoz, G. Irrigation Advisory Services for Effective Water Use: A Review of Experiences; FAO–ICID: Montreal, QC, Canada, 2002; pp. 1–16. [Google Scholar]
- Abdulai, A.; Owusu, V.; Bakang, J.A. Adoption of safer irrigation technologies and cropping patterns: Evidence from Southern Ghana. Ecol. Econ. 2011, 70, 1415–1423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ndunda, E.N.; Mungatana, E.D. Determinants of farmers’ choice of innovative risk-reduction interventions to wastewater-irrigated agriculture. Afr. J. Agric. Res. 2013, 8, 119–128. [Google Scholar]
- Willy, D.K.; Holm-Müller, K. Social influence and collective action effects on farm level soil conservation effort in rural Kenya. Ecol. Econ. 2013, 90, 94–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, S.; Herzfeld, T.; Glauben, T.; Zhang, Y.; Hu, B. Factors affecting Chinese farmers’ decisions to adopt a water-saving technology. Can. J. Agric. Econ. 2008, 56, 51–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lampayan, R.M.; Bouman, B.A.; de Dios, J.L.; Lactaoen, A.T.; Espiritu, A.J.; Norte, T.M. Adoption of Water Saving Technologies in Rice Production in the Philippines. Available online: http://agnet.org/htmlarea_file/library/20110808151231/eb548.pdf (accessed on 27 February 2017).
- Masuki, K.; Mutabazi, K.; Mattee, A.; Tumbo, S.; Rwehumbiza, F.; Mowo, J. Factors influencing intensity of adoption of integrated water management innovation in the semi-arid areas of Northeastern Tanzania. Int. J. Environ. Eng. Nat. Resour. 2014, 1, 227–234. [Google Scholar]
- Sidibé, A. Farm-level adoption of soil and water conservation techniques in northern Burkina Faso. Agric. Water Manag. 2005, 71, 211–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azizi Khalkheili, T.; Zamani, G.H. Farmer participation in irrigation management: The case of Doroodzan Dam Irrigation Network, Iran. Agric. Water Manag. 2009, 96, 859–865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Getacher, T.; Mesfin, A.; Gebre-Egziahber, G. Adoption and impacts of an irrigation technology: Evidence from household-level data in Tigray, Northern Ethiopia. Afr. J. Agric. Res. 2013, 8, 4766–4772. [Google Scholar]
- Namara, R.E.; Uphadyay, B.; Nagar, R.K. Adoption and Impacts of Microirrigation Technologies: Empirical Results from Selected Localities of Maharashtra and Gujarat States of India; Research Report No. 93; International Water Management Institute: Colombo, Sri Lanka, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Kay, D.R.; Edwards, W.M. Farm Management, 4th ed.; McGraw-Hill Companies: New York, NY, USA, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Greaves, G.E.; Wang, Y.M. Identifying irrigation strategies for improved agricultural water productivity in irrigated maize production through crop simulation modelling. Sustainability 2017, 9, 630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Notation | Variable Name | Description | Variable Type/Criteria |
|---|---|---|---|
| Y | Adoption (Dependent variable) | Farmer’s adoption of irrigation technology | Dummy: 1 if adopted, 0 otherwise |
| X1 | Gender | Respondent’s gender | Dummy: 1 = male, 0 = otherwise |
| X2 | Age | Respondent’s age | Continuous variable |
| X3 | Education | Level of formal education | Independent variable: 1 = Primary, 2 = Secondary, 3 = Tertiary |
| X4 | Farming experience | Years of rice farming experience | Continuous variable |
| X5 | Land holding size | Total rice cultivation area in hectare (ha) | Continuous variable |
| X6 | Farm income | Amount of rice farming income (Thai Baht/ha) | Continuous variable |
| X7 | Labor | Number of farm workers | Continuous variable |
| X8 | Farmland location | Location of farmland (upstream or downstream) | Dummy: 1 if upstream, 0 otherwise |
| X9 | Proximity to water source | Proximity to the irrigation system | Dummy: 1 if ≤1 km, 0 otherwise |
| X10 | Training | Famer’s training in agricultural practices | Dummy: 1 if yes, 0 otherwise |
| X11 | WUA membership | Member of the community’s water use association (WUA) | Dummy: 1 if yes, 0 otherwise |
| X12 | Information access | Frequency of information access | A 5-point Likert scale, ranging from rarely to constantly. |
| X13 | Degree of participation | Active participation in community projects and activity (other than WUA) | A 5-point Likert scale, ranging from rarely to constantly. |
| X14 | Perceived equality | The level of perceived fairness of the water allocation | A 5-point Likert scale, ranging from very low to very high. |
| Water Wheel (n = 30) | Water Pump (n = 130) | Weir (n = 47) | Total (n = 207) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| f | (%) | f | (%) | f | (%) | f | (%) | |
| Gender | ||||||||
| Male | 23 | (76.7) | 75 | (57.7) | 26 | (55.3) | 124 | (59.9) |
| Female | 7 | (23.3) | 55 | (42.3) | 21 | (44.7) | 83 | (40.1) |
| χ2 = 4.186, df = 2, Sig = 0.123 | ||||||||
| Education Level | ||||||||
| Primary | 28 | (93.3) | 116 | (89.2) | 44 | (93.6) | 188 | (90.8) |
| Secondary | 2 | (6.7) | 10 | (7.7) | 1 | (2.1) | 13 | (6.3) |
| Tertiary | - | - | 4 | (3.1) | 2 | (4.3) | 6 | (2.9) |
| χ2 = 2.990, df = 4, Sig = 0.559 | ||||||||
| Age (Year) | ||||||||
| <40 | 1 | (3.3) | 5 | (3.8) | 1 | (2.1) | 7 | (3.4) |
| 41–50 | 7 | (23.3) | 39 | (30.0) | 3 | (6.4) | 49 | (23.7) |
| 51–60 | 10 | (33.3) | 55 | (42.3) | 22 | (46.8) | 87 | (42.0) |
| >60 | 12 | (40.0) | 31 | (23.8) | 21 | (44.7) | 64 | (30.9) |
| Mean (SD) | 58.07 (9.71) | 55.38 (9.04) | 61.1 (8.67) | 57.08 (9.33) | ||||
| F = 7.241, Sig = 0.001 ** | ||||||||
| Rice Farming Experience (Year) | ||||||||
| <10 | - | - | 5 | (3.8) | 1 | (2.1) | 6 | (2.9) |
| 10–20 | 5 | (16.7) | 33 | (25.4) | 8 | (17.0) | 46 | (22.2) |
| 21–30 | 8 | (26.7) | 41 | (31.5) | 19 | (40.4) | 68 | (32.9) |
| 31–40 | 11 | (36.7) | 29 | (22.3) | 15 | (31.9) | 55 | (26.6) |
| >40 | 6 | (20.0) | 22 | (16.9) | 4 | (8.5) | 32 | (15.5) |
| Mean (SD) | 36.16 (11.57) | 32.68 (12.37) | 32.76 (9.76) | 33.21 (11.73) | ||||
| F = 1.118, Sig = 0.329 | ||||||||
| Number of farm workers | ||||||||
| 1–2 | 16 | (53.3) | 52 | (40.0) | 23 | (48.9) | 91 | (44.0) |
| 3–4 | 12 | (40.0) | 69 | (53.1) | 21 | (44.7) | 102 | (49.3) |
| >4 | 2 | (6.7) | 9 | (6.9) | 3 | (6.4) | 14 | (6.8) |
| Mean (SD) | 2.90 (1.06) | 2.86 (0.99) | 2.72 (0.88) | 2.84 (0.97) | ||||
| F = 0.423, Sig = 0.655 | ||||||||
| Land Holding Size (ha) | ||||||||
| Small (<3.20 ha) | 26 | (86.7) | 115 | (88.5) | 46 | (97.9) | 187 | (90.3) |
| Medium (3.20–6.50) | 4 | (13.3) | 13 | (10.0) | 1 | (2.1) | 18 | (8.7) |
| Large (>6.50 ha) | - | - | 2 | (1.5) | - | - | 2 | (1.0) |
| Mean (SD) | 2.48 (1.10) | 1.98 (1.32) | 1.54 (0.84) | 1.95 (1.23) | ||||
| F = 5.695, Sig = 0.004 ** | ||||||||
| Factors | Water Wheel (WW) | Water Pump (WP) | Weir (WR) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Coefficient | Std. Err. | Coefficient | Std. Err. | Coefficient | Std. Err. | |
| Gender | 0.491 | 0.551 | −0.587 | 0.416 | 0.280 | 0.456 |
| Age | −0.032 | 0.046 | −0.089 ** | 0.035 | 0.105 ** | 0.044 |
| Education | 1.764 | 1.038 | −0.084 | 0.710 | –0.373 | 0.901 |
| Experience | 0.027 | 0.037 | 0.018 | 0.026 | –0.021 | 0.037 |
| Land holding size | 0.556 *** | 0.197 | 0.143 | 0.162 | –0.608 *** | 0.229 |
| Farm income | 0.002 *** | 0.000 | −0.001 *** | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 |
| Labor | 0.388 | 0.221 | −0.312 | 0.179 | 0.116 | 0.226 |
| Location | −0.651 | 0.767 | 3.089 *** | 0.641 | –3.043 *** | 0.600 |
| Proximity to water | −0.169 | 0.697 | 2.017 *** | 0.597 | –3.587 | 1.867 |
| Training | 1.131 | 0.777 | −1.382 ** | 0.680 | - | - |
| WUA membership | 2.437 *** | 0.678 | −3.524 *** | 0.677 | 0.834 | 0.557 |
| Information access | 0.433 | 0.721 | −0.862 | 0.607 | 1.283 | 0.720 |
| Participation | 2.137 | 4.547 | 0.975 | 0.577 | –2.802 ** | 1.245 |
| Perceived fairness of water allocation | −0.274 | 0.664 | −0.884 | 0.722 | - | - |
| Constant | −16.260 | 6.474 | 11.676 | 3.018 | –1.152 | 2.702 |
| Log likelihood | −27.635 | −36.488 | −26.694 | |||
| LR (likelihood ratio) test Chi2 | 115.73 | 199.33 | 167.87 | |||
| Prob > Chi2 | 0.0000 | 0.0000 | 0.0000 | |||
| Pseudo R-squared | 0.6768 | 0.7320 | 0.7587 | |||
| Item | Water Wheel | Water Pump | Weir | Overall Average | F-Test (Sig) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1. Farm revenue | 28,007.50 a | 21,264.38 c | 25,262.50 b | 23,149.38 | 0.000 ** |
| 2. Total variable cost | 9985.63 c | 13,649.38 a | 12,127.50 b | 12,772.50 | 0.000 ** |
| 2.1 Seed | 1525.00 a,b | 1551.25 a | 1520.00 b | 1540.00 | 0.012 * |
| 2.2 Fertilizer | 1795.63 b | 2412.50 a | 2516.88 a | 2346.88 | 0.000 ** |
| 2.3 Pesticide | 574.38 b | 841.88 a | 992.50 a | 837.50 | 0.027 * |
| 2.4 Fuel | - | 2499.38 | - | - | - |
| 2.5 Hired labor | 6090.00 b | 6343.75 a,b | 7097.50 a | 6478.13 | 0.083 |
| 3. Fixed cost (Depreciation) | 601.88 b | 968.75 a | 651.88 b | 843.13 | 0.000 ** |
| 4. Total cost = (2) + (3) | 10,588.13 c | 14,617.50 a | 12,778.75 b | 13,616.25 | 0.000 ** |
| 5. Yield (kg/ha) | 2306.88 a | 1772.31 c | 2105.19 b | 1925.36 | 0.000 ** |
| 6. Gross margin = (1) − (2) | 18,021.88 a | 7435.00 c | 13,135.00 b | 10,263.13 | 0.000 ** |
| 7. Net farm income (crop value per ha) = (1) − (4) | 17,419.38 a | 6646.88 c | 12,483.13 b | 11,103.13 | 0.000 ** |
| 8. Operating expense ratio = (2)/(1) × 100 | 35.7 | 64.2 | 48.0 | 48.4 | |
| 9. Depreciation expense ratio = (3)/(1) × 100 | 2.1 | 4.6 | 2.6 | 3.6 | |
| 10. Net farm income ratio = (7)/(1) × 100 | 62.2 | 31.3 | 49.4 | 48.0 | |
| 11. Benefit-to-cost ratio = (1)/(4) | 2.6 | 1.5 | 2.0 | 1.9 |
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chuchird, R.; Sasaki, N.; Abe, I. Influencing Factors of the Adoption of Agricultural Irrigation Technologies and the Economic Returns: A Case Study in Chaiyaphum Province, Thailand. Sustainability 2017, 9, 1524. https://doi.org/10.3390/su9091524
Chuchird R, Sasaki N, Abe I. Influencing Factors of the Adoption of Agricultural Irrigation Technologies and the Economic Returns: A Case Study in Chaiyaphum Province, Thailand. Sustainability. 2017; 9(9):1524. https://doi.org/10.3390/su9091524
Chicago/Turabian StyleChuchird, Ratchaneewan, Nophea Sasaki, and Issei Abe. 2017. "Influencing Factors of the Adoption of Agricultural Irrigation Technologies and the Economic Returns: A Case Study in Chaiyaphum Province, Thailand" Sustainability 9, no. 9: 1524. https://doi.org/10.3390/su9091524






