Potential Antiviral Properties of Industrially Important Marine Algal Polysaccharides and Their Significance in Fighting a Future Viral Pandemic
Abstract
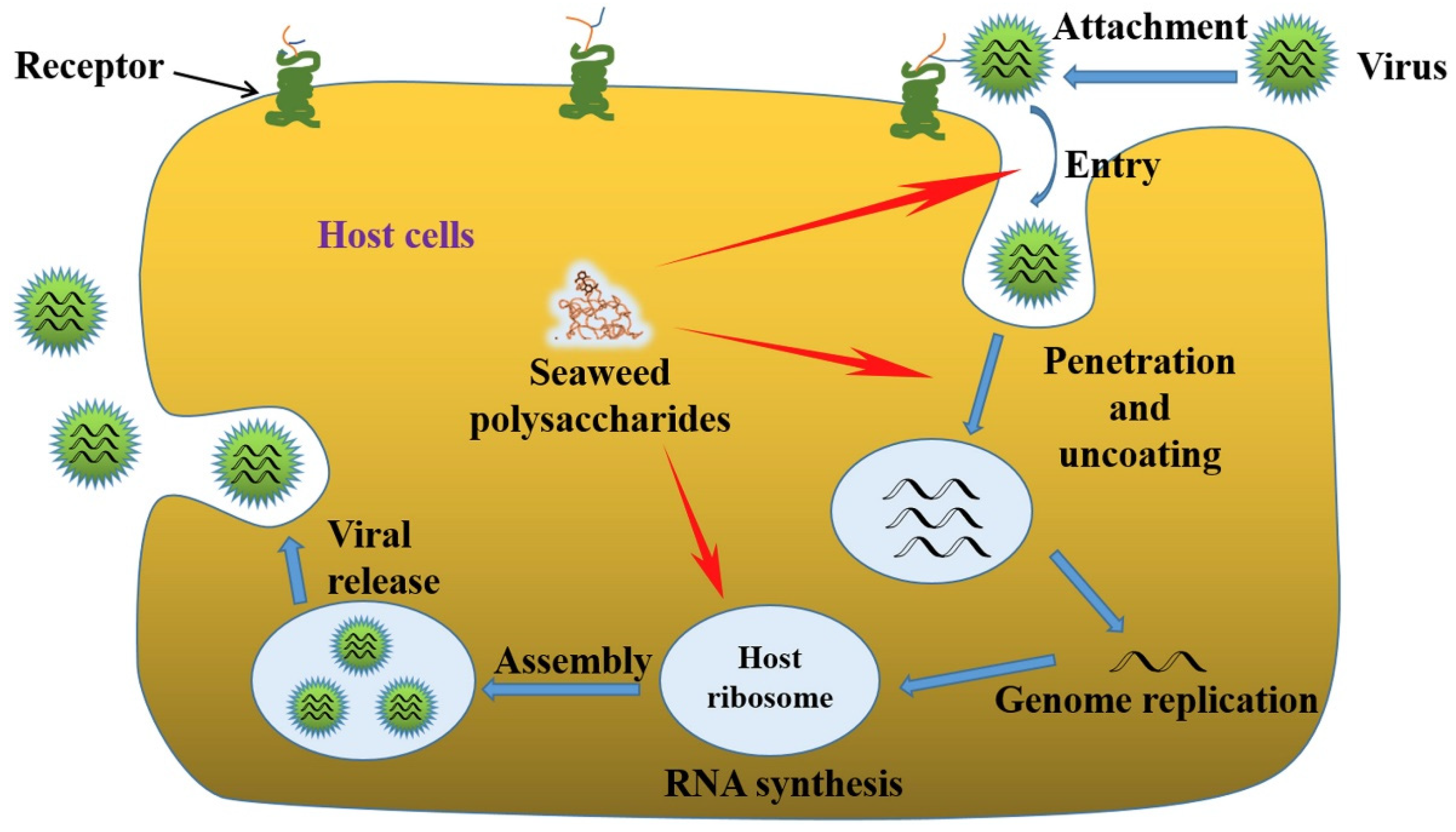
:1. Introduction
1.1. Biological Properties of Algal Polysaccharides
1.2. Significance of Antiviral Activities of Algal Polysaccharides
2. Industrially Important Polysaccharides from Marine Algae
2.1. Agar
2.2. Porphyran
2.3. Carrageenans
2.4. Alginate
2.5. Fucoidan
2.6. Ulvan
2.7. Laminaran
3. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Jha, R.K.; Zi-Rong, X. Biomedical compounds from marine organisms. Mar. Drugs 2004, 2, 123–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- König, G.M.; Kehraus, S.; Seibert, S.F.; Abdel-Lateff, A.; Müller, D. Natural products from marine organisms and their associated microbes. ChemBioChem 2005, 7, 229–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burgess, J.G. New and emerging analytical techniques for marine biotechnology. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 2012, 23, 29–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radmer, R.J. Algal diversity and commercial algal products. Bioscience 1996, 46, 263–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kraan, S. Algal Polysaccharides, novel applications and outlook. In Carbohydrates—Comprehensive Studies on Glycobiology and Glycotechnology; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- El Gamal, A.A. Biological importance of marine algae. Saudi Pharm. J. 2010, 18, 1–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Usman, A.; Khalid, S.; Usman, A.; Hussain, Z.; Wang, Y. Algal polysaccharides, novel application, and outlook. In Algae Based Polymers, Blends, and Composites; Elsevier BV: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2017; pp. 115–153. [Google Scholar]
- Wahlström, N.; Edlund, U.; Pavia, H.; Toth, G.; Jaworski, A.; Pell, A.; Choong, F.X.; Shirani, H.; Nilsson, K.P.R.; Richter-Dahlfors, A. Cellulose from the green macroalgae Ulva lactuca: Isolation, characterization, optotracing, and production of cellulose nanofibrils. Cellulose 2020, 27, 3707–3725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dumitriu, S. Polysaccharides in Medicinal Applications; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Van Regenmortel, M. Antigenicity and immunogenicity of viral proteins. Encycl. Virol. 2008, 17, 137–142. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, Y.; Shen, M.; Song, Q.; Xie, J. Biological activities and pharmaceutical applications of polysaccharide from natural re-sources: A review. Carbohydr. Polym. 2018, 183, 91–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fishman, J.M.; Wiles, K.; Wood, K.J. The acquired immune system response to biomaterials, including both naturally occur-ring and synthetic biomaterials. In Host Response to Biomaterials; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2015; pp. 151–187. [Google Scholar]
- Shi, Q.; Wang, A.; Lu, Z.; Qin, C.; Hu, J.; Yin, J. Overview on the antiviral activities and mechanisms of marine polysaccharides from seaweeds. Carbohydr. Res. 2017, 453–454, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Wang, S.-X.; Guan, H.-S. The antiviral activities and mechanisms of marine polysaccharides: An overview. Mar. Drugs 2012, 10, 2795–2816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diogo, J.V.; Novo, S.G.; González, M.J.; Ciancia, M.; Bratanich, A.C. Antiviral activity of lambda-carrageenan prepared from red seaweed (Gigartina skottsbergii) against BoHV-1 and SuHV-1. Res. Veter. Sci. 2015, 98, 142–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Talarico, L.B.; Damonte, E.B. Interference in dengue virus adsorption and uncoating by carrageenans. Virology 2007, 363, 473–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Liu, C.; Zhou, Q.; Li, Y.; Garner, L.V.; Watkins, S.P.; Carter, L.J.; Smoot, J.; Gregg, A.C.; Daniels, A.D.; Jervey, S. Research and development on therapeutic agents and vaccines for covid-19 and related human coronavirus diseases. ACS Cent. Sci. 2020, 6, 3, 315–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Yang, C.; Xu, X.-f.; Xu, W.; Liu, S.-w. Structural and functional properties of SARS-CoV-2 spike protein: Potential antivirus drug development for COVID-19. Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 2020, 41, 1141–1149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Peng, F.; Wang, R.; Guan, K.; Jiang, T.; Xu, G.; Sun, J.; Chang, C. The deadly coronaviruses: The 2003 SARS pandemic and the 2020 novel coronavirus epidemic in China. J. Autoimmun. 2020, 109, 102434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoffmann, M.; Kleine-Weber, H.; Schroeder, S.; Krüger, N.; Herrler, T.; Erichsen, S.; Schiergens, T.S.; Herrler, G.; Wu, N.-H.; Nitsche, A. SARS-CoV-2 cell entry depends on ACE2 and TMPRSS2 and is blocked by a clinically proven protease inhibitor. Cell 2020, 181, 271–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Belouzard, S.; Chu, V.C.; Whittaker, G.R. Activation of the SARS coronavirus spike protein via sequential proteolytic cleavage at two distinct sites. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 5871–5876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kim, S.Y.; Zhao, J.; Liu, X.; Fraser, K.; Lin, L.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, F.; Dordick, J.S.; Linhardt, R.J. Interaction of Zika virus envelope protein with glycosaminoglycans. Biochemistry 2017, 56, 1151–1162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coutard, B.; Valle, C.; De Lamballerie, X.; Canard, B.; Seidah, N.; Decroly, E. The spike glycoprotein of the new coronavirus 2019-nCoV contains a furinlike cleavage site absent in CoV of the same clade. Antivir. Res. 2020, 176, 104742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.Y.; Jin, W.; Sood, A.; Montgomery, D.W.; Grant, O.C.; Fuster, M.M.; Fu, L.; Dordick, J.S.; Woods, R.J.; Zhang, F. Characteri-zation of heparin and severe acute respiratory syndrome-related coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) spike glycoprotein binding interactions. Antivir. Res. 2020, 181, 104873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, S.; Peng, H.; Wang, Q.; Liu, Z.; Dong, X.; Wen, C.; Ai, C.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, Z.; Zhu, B. Inhibitory activities of marine sulfated polysaccharides against SARS-CoV-2. Food Funct. 2020, 11, 7415–7420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fitton, J.H.; Park, A.Y.; Karpiniec, S.S.; Stringer, D.N. Fucoidan and lung function: Value in viral infection. Mar. Drugs 2020, 19, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Armisen, R.; Galatas, F. Production, properties and uses of agar. In Production and Utilization of Products from Commercial Seaweeds; FAO Fish. Technical Paper; FAO: Rome, Italy, 1987; Volume 288, pp. 1–57. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, W.-K.; Lim, Y.-Y.; Leow, A.; Thean, C.; Namasivayam, P.; Abdullah, J.O.; Ho, C.-L. Biosynthesis of agar in red seaweeds: A review. Carbohydr. Polym. 2017, 164, 23–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Usov, A.I. Polysaccharides of the red algae. In Advances in Carbohydrate Chemistry and Biochemistry; Elsevier BV: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2011; Volume 65, pp. 115–217. [Google Scholar]
- Usov, A. Structural analysis of red seaweed galactans of agar and carrageenan groups. Food Hydrocoll. 1998, 12, 301–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alba, K.; Kontogiorgos, V. Seaweed Polysaccharides (Agar, Alginate Carrageenan). Encycl. Food Chem. 2018, 240–250. [Google Scholar]
- Stanley, N. Production, properties and uses of carrageenan. In Production and Utilization of Products from Commercial Seaweeds; FAO Fish. Technical Paper; FAO: Rome, Italy, 1987; Volume 288, pp. 116–146. [Google Scholar]
- Renn, D.W. Agar and agarose: Indispensable partners in biotechnology. Ind. Eng. Chem. Prod. Res. Dev. 1984, 23, 17–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Margel, S. Agarose-polyaldehyde microsphere beads: Synthesis and biomedical applications. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 1983, 8, 523–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miguel, S.P.; Ribeiro, M.P.; Brancal, H.; Coutinho, P.; Correia, I.J. Thermoresponsive chitosan–agarose hydrogel for skin re-generation. Carbohydr. Polym. 2014, 111, 366–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ninan, N.; Forget, A.; Shastri, V.P.; Voelcker, N.H.; Blencowe, A. Antibacterial and anti-inflammatory pH-responsive tannic acid-carboxylated agarose composite hydrogels for wound healing. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2016, 8, 28511–28521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazumder, S.; Ghosal, P.K.; Pujol, C.A.; Carlucci, M.J.; Damonte, E.B.; Ray, B. Isolation, chemical investigation and antiviral activity of polysaccharides from Gracilaria corticata (Gracilariaceae, Rhodophyta). Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2002, 31, 87–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agol, V.; Chumakova, M.Y. An agar polysaccharide and d marker of poliovirus. Virology 1962, 17, 221–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerber, P.; Dutcher, J.D.; Adams, E.V.; Sherman, J.H. Protective effect of seaweed extracts for chicken embryos infected with influenza B or mumps virus. Exp. Biol. Med. 1958, 99, 590–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schulze, I.T. Reversible inhibition of type 2 dengue virus by agar polysaccharide. Virology 1964, 22, 79–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stim, T.B. Dengue virus plaque development in simian cell systems. I. Factors influencing virus adsorption and variables in the agar overlay medium. Appl. Microbiol. 1970, 19, 751–756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takemoto, K.; Liebhaber, H. Virus-polysaccharide interactions: I. An agar polysaccharide determining plaque morphology of EMC virus. Virology 1961, 14, 456–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colón, J.I.; Idoine, J.B.; Brand, O.M.; Costlow, R.D. Mode of action of an inhibitor from agar on growth and hemagglutination of group A arboviruses. J. Bacteriol. 1965, 90, 172–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Borden, E.C.; Gary, G.W.; Murphy, F.A. Comparison of agar and agarose preparations for mengovirus plaque formation. Appl. Microbiol. 1970, 20, 289–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Colter, J.S.; Davies, M.A.; Campbell, J.B. Studies of three variants of Mengo encephalomyelitis virus II. Inhibition of interaction with L cells by an agar inhibitor and by protamine. Virology 1964, 24, 578–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blouin, N.A.; Brodie, J.A.; Grossman, A.C.; Xu, P.; Brawley, S.H. Porphyra: A marine crop shaped by stress. Trends Plant Sci. 2011, 16, 29–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duckworth, M.; Turvey, J.R. The action of a bacterial agarase on agarose, porphyran and alkali treated porphyran. Biochem. J. 1969, 113, 687–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Praiboon, J.; Chirapart, A.; Soisarp, N. Principle and biological properties of sulfated polysaccharides from seaweed. Mar. Glycobiol. 2016, 85–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishihara, K.; Oyamada, C.; Matsushima, R.; Murata, M.; Muraoka, T. Inhibitory effect of porphyran, prepared from dried “nori”, on contact hypersensitivity in mice. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 2005, 69, 1824–1830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhatia, S.; Sharma, A.; Sharma, K.; Kavale, M.; Chaugule, B.; Dhalwal, K.; Namdeo, A.; Mahadik, K. Novel algal polysaccharides from marine source: Porphyran. Pharmacogn. Rev. 2008, 2, 271. [Google Scholar]
- Isaka, S.; Cho, K.; Nakazono, S.; Abu, R.; Ueno, M.; Kim, D.; Oda, T. Antioxidant and anti-inflammatory activities of porphyran isolated from discolored nori (Porphyra yezoensis). Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2015, 74, 68–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Z.; Gao, T.; Yang, Y.; Meng, F.; Zhan, F.; Jiang, Q.; Sun, X. Anti-cancer activity of porphyran and carrageenan from red seaweeds. Molecules 2019, 24, 4286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kwon, M.-J.; Nam, T.-J. Porphyran induces apoptosis related signal pathway in AGS gastric cancer cell lines. Life Sci. 2006, 79, 1956–1962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, D.; Wu, S.; Yan, L.; Zuo, J.; Cheng, Y.; Wang, H.; Liu, J.; Zhang, X.; Wu, M.; Choi, J.i. Antitumor bioactivity of porphyran extracted from Pyropia yezoensis Chonsoo2 on human cancer cell lines. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2019, 99, 6722–6730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Hou, Y.; Duan, D.; Zhang, Q. The structure and nephroprotective activity of oligo-porphyran on glycerol-induced acute renal failure in rats. Mar. Drugs 2017, 15, 135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Santos, S.; Ferreira, T.; Almeida, J.; Pires, M.J.; Colaço, A.; Lemos, S.; Gil Da Costa, R.M.; Medeiros, R.; Bastos, M.M.S.M.; Neuparth, M.J.; et al. Dietary supplementation with the red seaweed porphyra umbilicalis protects against DNA damage and pre-malignant dysplastic skin lesions in HPV-transgenic mice. Mar. Drugs 2019, 17, 615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dixon, D.W.; Gill, A.F.; Giribabu, L.; Vzorov, A.; Alam, A.B.; Compans, R. Sulfonated naphthyl porphyrins as agents against HIV-1. J. Inorg. Biochem. 2005, 99, 813–821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Debnath, A.K.; Jiang, S.; Strick, N.; Lin, K.; Haberfield, P.; Neurath, A.R. Three-dimensional structure-activity analysis of a series of porphyrin derivatives with anti-HIV-1 activity targeted to the V3 loop of the gp120 envelope glycoprotein of the human im-munodeficiency virus type 1. J. Med. Chem. 1994, 37, 1099–1108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meitian, X.; Junling, Y.; Haiying, L.; Fengxiang, T.; Chun, M.; Xianai, S.; Yanghao, G. Extraction of Porphyra haitanensis polysac-charides and its anti-influenza virus activity. J. Fuzhou Univ. 2003, 5, 631–635. [Google Scholar]
- Blauvelt, A. Hepatitis C virus and human immunodeficiency virus infection can alter porphyrin metabolism and lead to por-phyria cutanea tarda. Arch. Dermatol. 1996, 32, 1503–1504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cunha, L.; Grenha, A. Sulfated seaweed polysaccharides as multifunctional materials in drug delivery applications. Mar. Drugs 2016, 14, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knutsen, S.H.; Myslabodski, D.E.; Larsen, B.; Usov, A.I. A modified system of nomenclature for red algal galactans. Bot. Mar. 1994, 37, 163–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van de Velde, F.; Knutsen, S.H.; Usov, A.; Rollema, H.; Cerezo, A. 1H and 13C high resolution NMR spectroscopy of carrageenans: Application in research and industry. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2002, 13, 73–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qureshi, D.; Nayak, S.K.; Maji, S.; Kim, D.; Banerjee, I.; Pal, K. Carrageenan: A wonder polymer from marine algae for potential drug delivery applications. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2019, 25, 1172–1186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Campo, V.L.; Kawano, D.F.; da Silva, D.B., Jr.; Carvalho, I. Carrageenans: Biological properties, chemical modifications and structural analysis—A review. Carbohydr. Polym. 2009, 77, 167–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Ni, R.; Shao, Y.; Mao, S. Carrageenan and its applications in drug delivery. Carbohydr. Polym. 2014, 103, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Zhan, X.; Wan, J.-B.; Wang, Y.; Wang, C. Review for carrageenan-based pharmaceutical biomaterials: Favourable physical features versus adverse biological effects. Carbohydr. Polym. 2015, 121, 27–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khotimchenko, Y.S.; Khozhaenko, E.V.; Khotimchenko, M.Y.; Kolenchenko, E.A.; Kovalev, V.V. Carrageenans as a new source of drugs with metal binding properties. Mar. Drugs 2010, 8, 1106–1121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gonzalez, M.E.; Alarcón, B.; Carrasco, L. Polysaccharides as antiviral agents: Antiviral activity of carrageenan. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 1987, 31, 1388–1393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zacharopoulos, V.R.; Phillips, D.M. Vaginal formulations of carrageenan protect mice from herpes simplex virus infection. Clin. Diagn. Lab. Immunol. 1997, 4, 465–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Carlucci, M.; Ciancia, M.; Matulewicz, M.; Cerezo, A.; Damonte, E. Antiherpetic activity and mode of action of natural carra-geenans of diverse structural types. Antivir. Res. 1999, 43, 93–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carlucci, M.; Scolaro, L.; Noseda, M.; Cerezo, A.; Damonte, E. Protective effect of a natural carrageenan on genital herpes sim-plex virus infection in mice. Antivir. Res. 2004, 64, 137–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buck, C.B.; Thompson, C.D.; Roberts, J.N.; Müller, M.; Lowy, D.R.; Schiller, J.T. Carrageenan is a potent inhibitor of papilloma-virus infection. PLoS Pathog 2006, 2, e69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Derby, N.; Lal, M.; Aravantinou, M.; Kizima, L.; Barnable, P.; Rodriguez, A.; Lai, M.; Wesenberg, A.; Ugaonkar, S.; Levendosky, K.; et al. Griffithsin carrageenan fast dissolving inserts prevent SHIV HSV-2 and HPV infections in vivo. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levendosky, K.; Mizenina, O.; Martinelli, E.; Jean-Pierre, N.; Kizima, L.; Rodriguez, A.; Kleinbeck, K.; Bonnaire, T.; Robbiani, M.; Zydowsky, T.M.; et al. Griffithsin and carrageenan combination to target herpes simplex virus 2 and human papillomavirus. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2015, 59, 7290–7298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- De Sf-Tischer, P.C.; Talarico, L.B.; Noseda, M.D.; Guimarães, S.M.P.B.; Damonte, E.B.; Duarte, M.E.R. Chemical structure and antiviral activity of carrageenans from Meristiella gelidium against herpes simplex and dengue virus. Carbohydr. Polym. 2006, 63, 459–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomaa, H.H.; Elshoubaky, G.A. Antiviral activity of sulfated polysaccharides carrageenan from some marine seaweeds. Int. J. Curr. Pharm. Rev. Res. 2016, 7, 34–42. [Google Scholar]
- Yamada, T.; Ogamo, A.; Saito, T.; Watanabe, J.; Uchiyama, H.; Nakagawa, Y. Preparation and anti-HIV activity of low-molecular-weight carrageenans and their sulfated derivatives. Carbohydr. Polym. 1997, 32, 51–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vlieghe, P.; Clerc, T.; Pannecouque, C.; Witvrouw, M.; De Clercq, E.; Salles, J.-P.; Kraus, J.-L. Synthesis of new covalently bound κ-carrageenan−AZT conjugates with improved anti-HIV activities. J. Med. Chem. 2002, 45, 1275–1283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leibbrandt, A.; Meier, C.; König-Schuster, M.; Weinmüllner, R.; Kalthoff, D.; Pflugfelder, B.; Graf, P.; Frank-Gehrke, B.; Beer, M.; Fazekas, T.; et al. Iota-carrageenan is a potent inhibitor of influenza A virus infection. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e14320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, W.; Zhang, P.; Hao, C.; Zhang, X.-E.; Cui, Z.-Q.; Guan, H.-S. In vitro inhibitory effect of carrageenan oligosaccharide on influenza A H1N1 virus. Antivir. Res. 2011, 92, 237–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morokutti-Kurz, M.; König-Schuster, M.; Koller, C.; Graf, C.; Graf, P.; Kirchoff, N.; Reutterer, B.; Seifert, J.-M.; Unger, H.; Grassauer, A.; et al. The intranasal application of zanamivir and carrageenan is synergistically active against influenza A virus in the murine model. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0128794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wang, W.; Zhang, P.; Yu, G.-L.; Li, C.-X.; Hao, C.; Qi, X.; Zhang, L.-J.; Guan, H.-S. Preparation and anti-influenza A virus activity of κ-carrageenan oligosaccharide and its sulphated derivatives. Food Chem. 2012, 133, 880–888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, F.; Chen, F.; Li, F. Preparation and potential in vivo anti-influenza virus activity of low molecular-weight κ-carrageenans and their derivatives. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2013, 127, 2110–2115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, Q.; Guo, Q.; Ping, X.W.; Li, Z.; Tong, Z.T. Specific inhibitory effect of κ-carrageenan polysaccharide on swine pandemic 2009 H1N1 influenza virus. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0126577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smidsrød, O.; Skja, G. Alginate as immobilization matrix for cells. Trends Biotechnol. 1990, 8, 71–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smidsrod, O.; Draget, K. Chemistry and physical properties of alginates. Chemistry 1996, 14, 6–13. [Google Scholar]
- Szekalska, M.; Puciłowska, A.; Szymańska, E.; Ciosek, P.; Winnicka, K. Alginate: Current use and future perspectives in pharmaceutical and biomedical applications. Int. J. Polym. Sci. 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lee, K.Y.; Mooney, D.J. Alginate: Properties and biomedical applications. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2012, 37, 106–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tønnesen, H.H.; Karlsen, J. Alginate in drug delivery systems. Drug Dev. Ind. Pharm. 2002, 28, 621–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fabra, M.J.; Falcó, I.; Randazzo, W.; Sánchez, G.; López-Rubio, A. Antiviral and antioxidant properties of active alginate edible films containing phenolic extracts. Food Hydrocoll. 2018, 81, 96–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tran, N.-M.; Dufresne, M.; Helle, F.; Hoffmann, T.W.; Francois, C.; Brochot, E.; Paullier, P.; Legallais, C.; Duverlie, G.; Castelain, S. Alginate hydrogel protects encapsulated hepatic HuH-7 cells against hepatitis C virus and other viral infections. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e109969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xianliang, X.; Hua, D.; Meiyu, G.; Pingfang, L.; Yingxia, L.; Huashi, G. Studies of the anti-AIDS effects of marine polysaccharide drug 911 and its related mechanisms of action. Zhongguo Hai Yang Yao Wu Chin. J. Mar. Drugs 2000, 19, 4–8. [Google Scholar]
- Xianliang, X.; Meiyu, G.; Guiling, L.; Huashi, G.; Zelin, L. Effects of marine polysaccharide 911 on HIV-1 proliferation in vitro. Zhongguo Hai Yang Yao Wu Chin. J. Mar. Drugs 2000, 19, 8–11. [Google Scholar]
- Xianliang, X.; Meiyu, G.; Huashi, G.; Zelin, L. Study on the mechanism of inhibitory action of 911 on replication of HIV-1 in vitro. Zhongguo Hai Yang Yao Wu Chin. J. Mar. Drugs 2000, 19, 15–18. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, B.; Xu, X.; Li, L.; Yuan, W. Study on-911‖ anti-HBV effect in HepG2. 2.15 cells culture. Mod. Prev. Med. 2003, 30, 517–518. [Google Scholar]
- Joshy, K.; George, A.; Jose, J.; Kalarikkal, N.; Pothen, L.A.; Thomas, S. Novel dendritic structure of alginate hybrid nanoparticles for effective anti-viral drug delivery. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2017, 103, 1265–1275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fong, K.; Smith, T.J. Citrate-mediated release of aurintricarboxylic acid from a calcium alginate complex: Implications for intravaginal HIV chemoprophylaxis and related applications. Pharm. Dev. Technol. 2009, 14, 341–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joshy, K.; Susan, M.A.; Snigdha, S.; Nandakumar, K.; Laly, A.P.; Sabu, T. Encapsulation of zidovudine in PF-68 coated alginate conjugate nanoparticles for anti-HIV drug delivery. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2018, 107, 929–937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, J.; Agrahari, V.; Ezoulin, M.J.; Purohit, S.S.; Zhang, T.; Molteni, A.; Dim, D.; Oyler, N.A.; Youan, B.-B.C. Spray-dried thiolated chitosan-coated sodium alginate multilayer microparticles for vaginal HIV microbicide delivery. AAPS J. 2017, 19, 692–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.-H.; Hsu, Y.-S.; Peng, C.-A. Quantum dots encapsulated with amphiphilic alginate as bioprobe for fast screening anti-dengue virus agents. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2008, 24, 1012–1019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lim, G.-P.; Ahmad, M.S. Development of Ca-alginate-chitosan microcapsules for encapsulation and controlled release of imidacloprid to control dengue outbreaks. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2017, 56, 382–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, J.-Y.; Sun, X.-Q.; Chen, X.-G. Formation and oral administration of alginate microspheres loaded with pDNA coding for lymphocystis disease virus (LCDV) to Japanese flounder. Fish. Shellfish. Immunol. 2008, 24, 592–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nallamuthu, N.; Braden, M.; Oxford, J.; Williams, D.; Patel, M. Modification of pH conferring virucidal activity on dental alginates. Materials 2015, 8, 1966–1975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Son, E.-W.; Rhee, D.-K.; Pyo, S. Antiviral and tumoricidal activities of alginate-stimulated macrophages are mediated by different mechanisms. Arch. Pharmacal Res. 2003, 26, 960–966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, A.B.A.; Adel, M.; Karimi, P.; Peidayesh, M. Pharmaceutical, cosmeceutical, and tratitional applications of marine carbohydrates. In Advances in Food and Nutrition Research; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2014; Volume 73, pp. 197–220. [Google Scholar]
- Fitton, J.H. Therapies from fucoidan; multifunctional marine polymers. Mar. Drugs 2011, 9, 1731–1760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiao, G.; Yu, G.; Zhang, J.; Ewart, H.S. Chemical structures and bioactivities of sulfated polysaccharides from marine algae. Mar. Drugs 2011, 9, 196–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Morya, V.; Kim, J.; Kim, E.-K. Algal fucoidan: Structural and size-dependent bioactivities and their perspectives. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2012, 93, 71–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dörschmann, P.; Bittkau, K.S.; Neupane, S.; Roider, J.; Alban, S.; Klettner, A. Effects of fucoidans from five different brown algae on oxidative stress and VEGF interference in ocular cells. Mar. Drugs 2019, 17, 258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Byon, Y.-Y.; Kim, M.-H.; Yoo, E.-S.; Hwang, K.-K.; Jee, Y.; Shin, T.; Joo, H.-G. Radioprotective effects of fucoidan on bone marrow cells: Improvement of the cell survival and immunoreactivity. J. Vet. Sci. 2008, 9, 359–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, M.-H.; Joo, H.-G. Immunostimulatory effects of fucoidan on bone marrow-derived dendritic cells. Immunol. Lett. 2008, 115, 138–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Araya, N.; Takahashi, K.; Sato, T.; Nakamura, T.; Sawa, C.; Hasegawa, D.; Ando, H.; Aratani, S.; Yagishita, N.; Fujii, R.; et al. Fucoidan therapy decreases the proviral load in patients with human T-lymphotropic virus type-1-associated neurological disease. Antivir. Ther. 2011, 16, 89–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mandal, P.; Mateu, C.G.; Chattopadhyay, K.; Pujol, C.A.; Damonte, E.B.; Ray, B. Structural features and antiviral activity of sulphated fucans from the brown seaweed Cystoseira indica. Antivir. Chem. Chemother. 2007, 18, 153–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- McClure, M.O.; Moore, J.P.; Blanc, D.F.; Scotting, P.; Cook, G.M.; Keynes, R.J.; Weber, J.N.; Davies, D.; Weiss, R.A. In-vestigations into the mechanism by which sulfated polysaccharides inhibit HIV infection in vitro. AIDS Res. Hum. Retro-Viruses 1992, 8, 19–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Witvrouw, M.; De Clercq, E. Sulfated polysaccharides extracted from sea algae as potential antiviral drugs. Gen. Pharmacol. Vasc. Syst. 1997, 29, 497–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dinesh, S.; Menon, T.; Hanna, L.E.; Suresh, V.; Sathuvan, M.; Manikannan, M. In vitro anti-HIV-1 activity of fucoidan from Sargassum swartzii. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2016, 82, 83–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.-B.; Takeshita, A.; Hayashi, K.; Hayashi, T. Structures and antiviral activities of polysaccharides from Sargassum trichophyllum. Carbohydr. Polym. 2011, 86, 995–999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rabanal, M.; Ponce, N.M.; Navarro, D.A.; Gomez, R.; Stortz, C.A. The system of fucoidans from the brown seaweed Dictyota dichotoma: Chemical analysis and antiviral activity. Carbohydr. Polym. 2014, 101, 804–811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narayanan, K.B.; Park, G.T.; Han, S.S. Electrospun poly(vinyl alcohol)/reduced graphene oxide nanofibrous scaffolds for skin tissue engineering. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2020, 191, 110994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Queiroz, K.; Medeiros, V.; Queiroz, L.; Abreu, L.; Rocha, H.A.; Ferreira, C.; Jucá, M.; Aoyama, H.; Leite, E. Inhibition of reverse transcriptase activity of HIV by polysaccharides of brown algae. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2008, 62, 303–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krylova, N.V.; Ermakova, S.P.; Lavrov, V.F.; Leneva, I.A.; Kompanets, G.G.; Iunikhina, O.V.; Nosik, M.N.; Ebralidze, L.K.; Falynskova, I.N.; Silchenko, A.S.; et al. The comparative analysis of antiviral activity of native and modified fucoidans from brown algae Fucus evanescens in vitro and in vivo. Mar. Drugs 2020, 18, 224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lee, J.-B.; Hayashi, K.; Hashimoto, M.; Nakano, T.; Hayashi, T. Novel antiviral fucoidan from sporophyll of Undaria pinnatifida (Mekabu). Chem. Pharm. Bull. 2004, 52, 1091–1094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hayashi, K.; Nakano, T.; Hashimoto, M.; Kanekiyo, K.; Hayashi, T. Defensive effects of a fucoidan from brown alga Undaria pinnatifida against herpes simplex virus infection. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2008, 8, 109–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Synytsya, A.; Bleha, R.; Synytsya, A.; Pohl, R.; Hayashi, K.; Yoshinaga, K.; Nakano, T.; Hayashi, T. Mekabu fucoidan: Structural complexity and defensive effects against avian influenza A viruses. Carbohydr. Polym. 2014, 111, 633–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayashi, K.; Lee, J.-B.; Nakano, T.; Hayashi, T. Anti-influenza A virus characteristics of a fucoidan from sporophyll of Undaria pinnatifida in mice with normal and compromised immunity. Microbes Infect. 2013, 15, 302–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lahaye, M.; Robic, A. Structure and functional properties of ulvan, a polysaccharide from green seaweeds. Biomacromolecules 2007, 8, 1765–1774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robic, A.; Bertrand, D.; Sassi, J.-F.; Lerat, Y.; Lahaye, M. Determination of the chemical composition of ulvan, a cell wall polysaccharide from Ulva spp. (Ulvales, Chlorophyta) by FT-IR and chemometrics. Environ. Boil. Fishes 2008, 21, 451–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robic, A.; Gaillard, C.; Sassi, J.-F.; Lerat, Y.; Lahaye, M. Ultrastructure of ulvan: A polysaccharide from green seaweeds. Biopolymers 2009, 91, 652–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaulneau, V.; Lafitte, C.; Jacquet, C.; Fournier, S.; Salamagne, S.; Briand, X.; Esquerré-Tugayé, M.-T.; Dumas, B. Ulvan, a sulfated polysaccharide from green algae, activates plant immunity through the jasmonic acid signaling pathway. J. Biomed. Biotechnol. 2010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- De Freitas, M.B.; Ferreira, L.G.; Hawerroth, C.; Duarte, M.E.R.; Noseda, M.D.; Stadnik, M.J. Ulvans induce resistance against plant pathogenic fungi independently of their sulfation degree. Carbohydr. Polym. 2015, 133, 384–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alves, A.; Sousa, R.; Reis, R.L. A practical perspective on ulvan extracted from green algae. Environ. Boil. Fishes 2012, 25, 407–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pangestuti, R.; Kurnianto, D. Green seaweeds-derived polysaccharides ulvan: Occurrence, medicinal value and potential applications. In Seaweed Polysaccharides; Elsevier BV: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2017; pp. 205–221. [Google Scholar]
- Tziveleka, L.-A.; Ioannou, E.; Roussis, V. Ulvan, a bioactive marine sulphated polysaccharide as a key constituent of hybrid biomaterials: A review. Carbohydr. Polym. 2019, 218, 355–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guriec, N.; Bussy, F.; Gouin, C.; Mathiaud, O.; Quero, B.; Le Goff, M.; Collén, P.N. Ulvan activates chicken heterophils and monocytes through toll-like receptor 2 and toll-like receptor 4. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 2725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chi, Y.; Zhang, M.; Wang, X.; Fu, X.; Guan, H.; Wang, P. Ulvan lyase assisted structural characterization of ulvan from Ulva pertusa and its antiviral activity against vesicular stomatitis virus. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 157, 75–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lopes, N.; Ray, S.; Espada, S.F.; Bomfim, W.A.; Ray, B.; Faccin-Galhardi, L.C.; Linhares, R.E.C.; Nozawa, C. Green seaweed Enteromorpha compressa (Chlorophyta, Ulvaceae) derived sulphated polysaccharides inhibit herpes simplex virus. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2017, 102, 605–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Briseño, J.A.A.; Cruz-Suarez, L.E.; Sassi, J.-F.; Ricque-Marie, D.; Zapata-Benavides, P.; Mendoza-Gamboa, E.; Rodríguez-Padilla, C.; Trejo-Avila, L.M. Sulphated polysaccharides from Ulva clathrata and Cladosiphon okamuranus seaweeds both inhibit viral attachment/entry and cell-cell fusion, in NDV infection. Mar. Drugs 2015, 13, 697–712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiu, Y.-H.; Chan, Y.-L.; Li, T.-L.; Wu, C.-J. Inhibition of Japanese Encephalitis Virus infection by the sulfated polysaccharide extracts from Ulva lactuca. Mar. Biotechnol. 2011, 14, 468–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kadam, S.; Tiwari, B.K.; O’Donnell, C. Extraction, structure and biofunctional activities of laminarin from brown algae. Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2014, 50, 24–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rioux, L.-E.; Turgeon, S.; Beaulieu, M. Characterization of polysaccharides extracted from brown seaweeds. Carbohydr. Polym. 2007, 69, 530–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Majee, S.B.; Avlani, D.; Biswas, G.R. Pharmacological, pharmaceutical, cosmetic and diagnostic applications of sulfated poly-saccharides from marine algae and bacteria. Afr. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 2017, 11, 68–77. [Google Scholar]
- Devillé, C.; Damas, J.; Forget, P.; Dandrifosse, G.; Peulen, O. Laminarin in the dietary fibre concept. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2004, 84, 1030–1038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neyrinck, A.; Mouson, A.; Delzenne, N. Dietary supplementation with laminarin, a fermentable marine β (1–3) glucan, protects against hepatotoxicity induced by LPS in rat by modulating immune response in the hepatic tissue. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2007, 7, 1497–1506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, A.G.; O’Doherty, J.V.; Reilly, P.; Ryan, M.; Bahar, B.; Sweeney, T. The effects of laminarin derived from Laminaria digitata on measurements of gut health: Selected bacterial populations, intestinal fermentation, mucin gene expression and cytokine gene expression in the pig. Br. J. Nutr. 2011, 105, 669–677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Deville, C.; Gharbi, M.; Dandrifosse, G.; Peulen, O. Study on the effects of laminarin, a polysaccharide from seaweed, on gut characteristics. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2007, 87, 1717–1725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moroney, N.; O’Grady, M.; O’Doherty, J.; Kerry, J. Addition of seaweed (Laminaria digitata) extracts containing laminarin and fucoidan to porcine diets: Influence on the quality and shelf-life of fresh pork. Meat Sci. 2012, 92, 423–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moroney, N.; O’Grady, M.; O’Doherty, J.; Kerry, J. Effect of a brown seaweed (Laminaria digitata) extract containing laminarin and fucoidan on the quality and shelf-life of fresh and cooked minced pork patties. Meat Sci. 2013, 94, 304–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moroney, N.C.; O’Grady, M.N.; Lordan, S.; Stanton, C.; Kerry, J.P. Seaweed polysaccharides (laminarin and fucoidan) as functional ingredients in pork meat: An evaluation of anti-oxidative potential, thermal stability and bioaccessibility. Mar. Drugs 2015, 13, 2447–2464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cui, D.; Ma, J.; Liang, T.; Sun, L.; Meng, L.; Liang, T.; Li, Q. Selenium nanoparticles fabricated in laminarin polysaccharides solutions exert their cytotoxicities in HepG2 cells by inhibiting autophagy and promoting apoptosis. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 137, 829–835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sellimi, S.; Maalej, H.; Rekik, D.M.; Benslima, A.; Ksouda, G.; Hamdi, M.; Sahnoun, Z.; Li, S.; Nasri, M.; Hajji, M. Antioxidant, antibacterial and in vivo wound healing properties of laminaran purified from Cystoseira barbata seaweed. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2018, 119, 633–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, A.J.; Graves, B.; Child, R.; Rice, P.J.; Ma, Z.; Lowman, D.W.; Ensley, H.E.; Ryter, K.T.; Evans, J.T.; Williams, D.L. Immunoregulatory activity of the natural product laminarin varies widely as a result of its physical properties. J. Immunol. 2018, 200, 788–799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zargarzadeh, M.; Amaral, A.J.; Custódio, C.A.; Mano, J.F. Biomedical applications of laminarin. Carbohydr. Polym. 2020, 232, 115774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozanne, H.; Toumi, H.; Roubinet, B.; Landemarre, L.; Lespessailles, E.; Daniellou, R.; Cesaro, A. Laminarin effects, a β-(1,3)-glucan, on skin cell inflammation and oxidation. Cosmetics 2020, 7, 66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, C.-F.; Ji, Y.-B.; Meng, D.-Y. Sulfated modification and anti-tumor activity of laminarin. Exp. Ther. Med. 2013, 6, 1259–1264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ren, X.; Liu, L.; Zhou, Y.; Zhu, Y.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, Z.; Li, H. Nanoparticle siRNA against BMI-1 with a Polyethylenimine–laminarin conjugate for gene therapy in human breast cancer. Bioconjugate Chem. 2015, 27, 66–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amaral, A.J.R.; Gaspar, V.; Mano, J.F. Responsive laminarin-boronic acid self-healing hydrogels for biomedical applications. Polym. J. 2020, 52, 997–1006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shang, H.-S.; Shih, Y.-L.; Chen, C.-P.; Lee, M.-H.; Lu, H.-F.; Chou, P.-Y.; Liao, N.-C.; Chen, Y.-L.; Hsueh, S.-C.; Chung, J.-G. Laminarin promotes immune responses and normalizes glutamic oxaloacetic transaminase and glutamic pyruvic transaminase levels in leukemic mice in vivo. In Vivo 2018, 32, 783–790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, D.; Dang, C.; Bai, J. Inhibiting effect of laminarin sulfate in hamster model of liver metastasis of pancreatic cancer. Chi-Nese J. Hepatobiliary Surg. 2004, 12, 15. [Google Scholar]
- Liang, G.; Xie, L.; Lian, Z.F.; Hu, S.F.; Wang, X. The effect of laminarin on SOD and MDA in irritated mice brain tissues. J. Youjiang Med. Coll. Natl. 2006, 28, 333–334. [Google Scholar]
- Park, H.-K.; Kim, I.-H.; Kim, J.; Nam, T.-J. Induction of apoptosis by laminarin, regulating the insulin-like growth factor-IR signaling pathways in HT-29 human colon cells. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2012, 30, 734–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lee, J.Y.; Kim, Y.-J.; Kim, H.J.; Kim, Y.-S.; Park, W. Immunostimulatory effect of laminarin on RAW 264.7 mouse macrophages. Molecules 2012, 17, 5404–5411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Aziz, A.; Poinssot, B.; Daire, X.; Adrian, M.; Bezier, A.; Lambert, B.; Joubert, J.-M.; Pugin, A. Laminarin elicits defense responses in grapevine and induces protection against botrytis cinerea and plasmopara viticola. Mol. Plant. Microbe Interact. 2003, 16, 1118–1128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, J.; Wang, K.; Zhang, Q.; Zhu, Y.; Jiang, L. Inhibition of laminarin against TMV and effect on protective enzymes in to-bacco. Acta Phytophylacica Sin. 2011, 38, 532–538. [Google Scholar]
- Ana, P.; Nathalie, B.; Gilles, B.; Daniel, R.; Tomás, M.-S.; Yolanda, F.-P. Anti-Herpes simplex virus (HSV-1) activity and antioxidant capacity of carrageenan-rich enzymatic extracts from Solieria filiformis (Gigartinales, Rhodophyta). Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2021, 168, 322–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jang, Y.; Shin, H.; Lee, M.K.; Kwon, O.S.; Shin, J.S.; Kim, Y.-i.; Kim, C.W.; Lee, H.-R.; Kim, M. Antiviral activity of lambda-carrageenan against influenza viruses and severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jyotsna; Vijayakumar, P.; Dhas, T.S.; Mani, R.; Raguraman, V. Antiviral activity of sulfated polysaccharides from Sargassum ilicifolium against fish Betanodavirus infection. Aquac. Int. 2021, 29, 1049–1067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Chen, X.; Zhang, L.; Liu, H.; Liu, S.; Yu, H.; Wang, X.; Qin, Y.; Li, P. The antiviral property of Sargassum fusiforme polysaccharide for avian leukosis virus subgroup J in vitro and in vivo. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 138, 70–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Wang, W.; Hou, L.; Qin, L.; He, M.; Li, W.; Mao, W. A sulfated glucuronorhamnan from the green seaweed Monostroma nitidum: Characteristics of its structure and antiviral activity. Carbohydr. Polym. 2020, 227, 115280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, Q.-L.; Li, Y.; Ni, L.-Q.; Cui, Y.-S.; Jiang, S.-L.; Xie, E.-Y.; Du, J.; Deng, F.; Dong, C.-X. Structural characterization and antiviral activity of two fucoidans from the brown algae Sargassum henslowianum. Carbohydr. Polym. 2020, 229, 115487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rashid, N.N.; Yusof, R.; Rothan, H.A. Antiviral and virucidal activities of sulphated polysaccharides against Japanese encephalitis virus. Trop. Biomed. 2020, 37, 713–721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Cui, B.; Liu, X.; Wang, L.; Xian, Q.; Lu, Z.; Liu, S.; Cao, Y.; Zhao, Y. Virucidal activity and the antiviral mechanism of acidic polysaccharides against Enterovirus 71 infection in vitro. Microbiol. Immunol. 2020, 64, 189–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morán-Santibañez, K.; Peña-Hernández, M.A.; Cruz-Suárez, L.E.; Ricque-Marie, D.; Skouta, R.; Vasquez, A.H.; Rodríguez-Padilla, C.; Trejo-Avila, L.M. Virucidal and synergistic activity of polyphenol-rich extracts of seaweeds against measles virus. Viruses 2018, 10, 465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cantelli, L.; Goncalves, P.; Guertler, C.; Kayser, M.; Pilotto, M.R.; Barracco, M.A.; Perazzolo, L.M. Dietary supplementation with sulfated polysaccharides from Gracilaria birdiae promotes a delayed immunostimulation in marine shrimp challenged by the white spot syndrome virus. Aquac. Int. 2018, 27, 349–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Chen, X.; Cheng, Z.; Liu, S.; Yu, H.; Wang, X.; Li, P. Degradation of polysaccharides from Grateloupia filicina and their antiviral activity to avian leucosis virus subgroup. J. Mar. Drugs 2017, 15, 345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Klongklaew, N.; Praiboon, J.; Tamtin, M.; Srisapoome, P. Chemical composition of a hot water crude extract (HWCE) from Ulva intestinalis and its potential effects on growth performance, immune responses, and resistance to white spot syndrome virus and yellowhead virus in Pacific white shrimp (Litopenaeus vannamei). Fish. Shellfish. Immunol. 2021, 112, 8–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terasawa, M.; Hayashi, K.; Lee, J.-B.; Nishiura, K.; Matsuda, K.; Hayashi, T.; Kawahara, T. Anti-Influenza A virus activity of rhamnan sulfate from green algae Monostroma nitidum in mice with normal and compromised immunity. Mar. Drugs 2020, 18, 254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castillo, E.; Duarte, L.F.; Corrales, N.; Álvarez, D.M.; Farías, M.A.; Henríquez, A.; Smith, P.C.; Agurto-Muñoz, C.; González, P.A. Anti-herpetic activity of Macrocystis pyrifera and Durvillaea antarctica algae extracts against HSV-1 and HSV-2. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]







| Seaweed Name (Source) | Polysaccharide Name | Activity (Targets) | References |
|---|---|---|---|
| Solieria filiformis | carrageenan | in vitro cytotoxicity and antiviral activity against HSV-1 | [165] |
| Not mentioned | lambda-carrageenan | in vitro and in vivo antiviral activity influenza A and B viruses and SARS-CoV-2 | [166] |
| Sargassum ilicifolium | sulfated polysaccharides | in vitro and in vivo antiviral activity against fish betanodavirus | [167] |
| Sargassum fusiforme | sargassum fusiforme polysaccharide (SFP-1, SFP-2, SFP-3, SFP-4 and SFP-5) | in vivo and in vitro antiviral activity-avian leukosis virus, Subgroup J | [168] |
| Monostroma nitidum | homogeneous polysaccharide (MWS) | antiviral activity against influenza virus, HSV and EV71 | [169] |
| Sargassum henslowianum | fucoidans SHAP-1 and SHAP-2 | in vitro antiviral activity against HSV-1 | [170] |
| red seaweed | carrageenan | in vitro and in vivo antiviral activity against Japanese encephalitis virus (JEV) | [171] |
| Ulva pertusa | ulvan | antiviral activity against vesicular stomatitis virus | [136] |
| Laminaria japonica | fucose, galactose, and mannose | in vitro inhibition of enterovirus EV71 and 3C protein activity | [172] |
| Solieria filiformis | polyphenol-rich extracts | antiviral activity against measles virus (MeV) | [173] |
| Gracilaria birdiae | sulfated polysaccharides | white spot syndrome virus (WSSV) | [174] |
| Grateloupia filicinia | polysaccharides | Antiviral activity towards avian leucosis virus (ALV-J) | [175] |
| Ulva intestinalis | crude extract | antiviral activity against white spot syndrome virus (WSSV) and yellowhead virus (YHV) | [176] |
| Monostroma nitidum | rhamnan sulfate | anti-influenza A virus activity | [177] |
| Macrocystis pyrifera Durvillaea antarctica | extract | anti-herpetic activity against HSV-1 and HSV-2 | [178] |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Geetha Bai, R.; Tuvikene, R. Potential Antiviral Properties of Industrially Important Marine Algal Polysaccharides and Their Significance in Fighting a Future Viral Pandemic. Viruses 2021, 13, 1817. https://doi.org/10.3390/v13091817
Geetha Bai R, Tuvikene R. Potential Antiviral Properties of Industrially Important Marine Algal Polysaccharides and Their Significance in Fighting a Future Viral Pandemic. Viruses. 2021; 13(9):1817. https://doi.org/10.3390/v13091817
Chicago/Turabian StyleGeetha Bai, Renu, and Rando Tuvikene. 2021. "Potential Antiviral Properties of Industrially Important Marine Algal Polysaccharides and Their Significance in Fighting a Future Viral Pandemic" Viruses 13, no. 9: 1817. https://doi.org/10.3390/v13091817







