1. Introduction
At present, deep learning has become a popular trend in the field of machine learning. Deep learning references the mode that the brain deals with images and speech and has achieved great success in the field of vision and speech processing [
1,
2,
3]. For natural language processing, people also proposed some topic models based on the deep learning to model documents, such as Replicated Softmax Model (RSM) [
4] and Deep Boltzmann Machine (DBM) [
5]. The basic assumption of topic model, followed by RSM and DBM, is that documents are represented as random mixtures over latent topics, where each topic is characterized by a distribution over words [
6]. In RSM and DBM, words and latent topics are respectively visible units and hidden units of Restricted Boltzmann Machine. However, compared with Latent Dirichlet Allocation (LDA), the document retrieval accuracy of deep topic models merely improves about 10% on a training dataset of 20-newsgroups. Although deep learning is suitable for visual and speech processing, it may not be suitable for the topic model. A recent study [
7] demonstrated some limiting factors of the topic model, such as number of documents, average document length and number of topics, without thinking whether the basic assumption of the topic model is valid or not. The assumption of topic model is not on the basis of biology [
8]. We explore a way that the brain processes languages according to neurolinguistics and use the way to model documents, which is different from topic models.
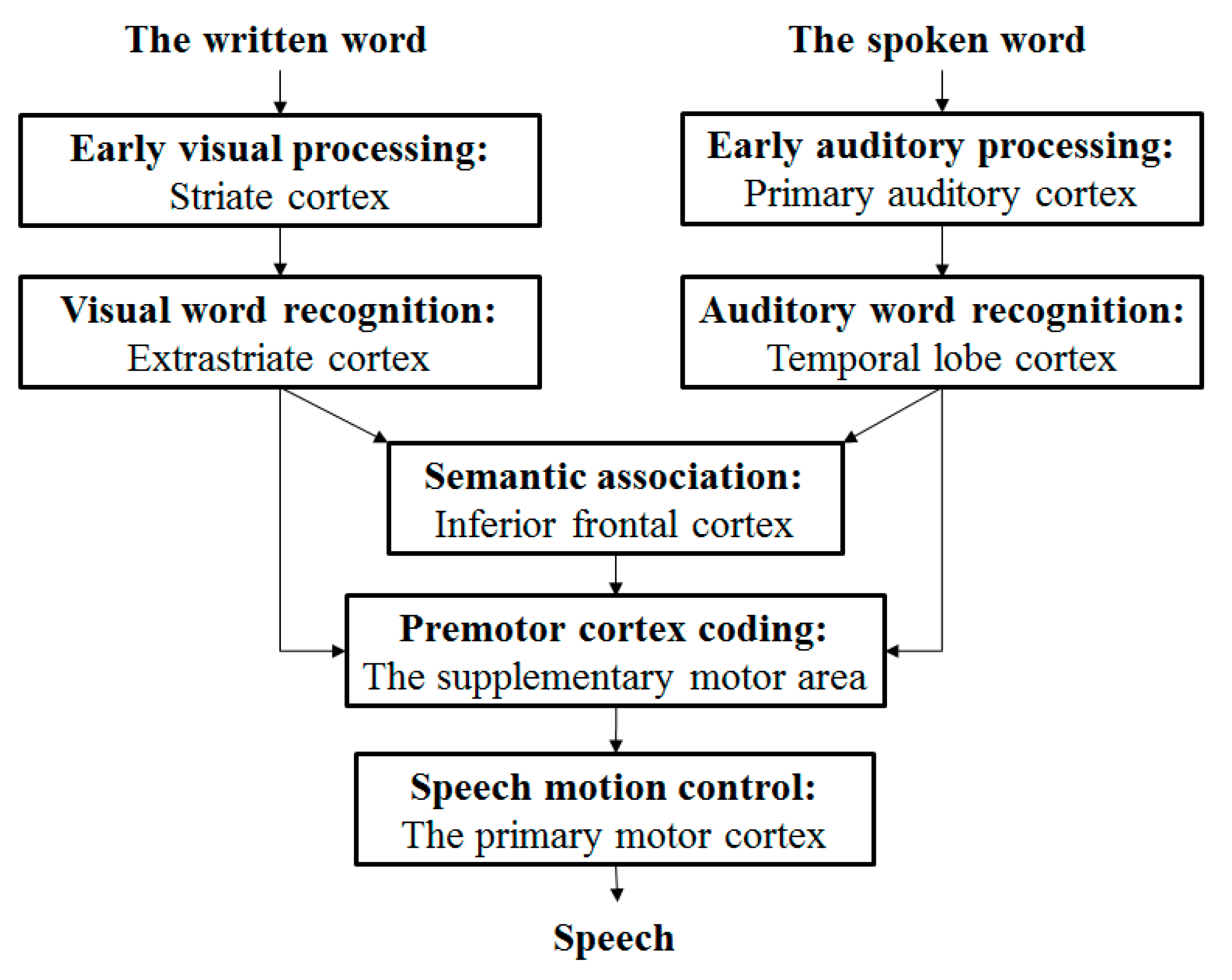
Figure 1.
A language processing in neurolinguistics. This picture marks various processing stages of written and spoken word retelling tasks. The cortical regions associated with above tasks and observed by PET imaging are shown under every stage. When people recognize words by sight or hearing, next there are two processing approaches. One is directly outputting. In addition to the written word and the spoken word, the brain can transform the input signals from vision, audition, et al. to words directly. This is the “WYSIWYG” way. Another approach is to use semantic association to find semantically similar words in the brain first and output.
Figure 1.
A language processing in neurolinguistics. This picture marks various processing stages of written and spoken word retelling tasks. The cortical regions associated with above tasks and observed by PET imaging are shown under every stage. When people recognize words by sight or hearing, next there are two processing approaches. One is directly outputting. In addition to the written word and the spoken word, the brain can transform the input signals from vision, audition, et al. to words directly. This is the “WYSIWYG” way. Another approach is to use semantic association to find semantically similar words in the brain first and output.
Figure 1 demonstrates that how the brain processes languages [
9]. In neurolinguistics, the language function of the brain is closely related to vision, audition, and other sensations. Recently researchers proposed many multimodal neural language models [
10,
11,
12,
13] for transforming images to texts. These models first recognize objects in the images and their corresponding words, then use a language model to generate texts. Brain and multimodal neural language models can process language using the “WYSIWYG” way, while it is not necessary to consider topics. We treat language as the description of events, such as an image, voice, behavior, or psychological activity rather than topics. A document, regardless of its length, can be viewed as an event. The following sentence is an example of an event.
A man is embracing a woman
It is difficult for us to find the relevance between the words (man, woman, embrace) and some specific topics. However, our brains can clearly imagine the scene described by this sentence, because man, woman, embrace, are very clear in the semantics and related with entity concepts.
In topic model, words are the input features and independent with each other. While semantic association between words is one of the language processing stages shown in
Figure 1, which should not be ignored. Furthermore, the premise of the semantic association is that the brain knows the semantics of words. That means before reading words, you must learn them first. For example, the condition of associating “blue” with “green” is that brain knows the two words represent colors.
For document modeling, we propose Event Model (EM). Event Model has two stages. The first stage is word learning and the second stage is dimensionality reduction. Word learning is to learn semantics of words by using context and distributed representations [
14,
15] of words. Dimensionality reduction is the process that representing documents as low dimensional vectors based on a linear document generating mechanism. We also proposed topic model based on word learning to further compare the document generating mechanisms of Event Model and topic model. Finally we report experimental results on document retrieval tasks.
2. Word Learning
The main task of word learning is finding the semantics of words. Humans’ ability with image and sound perception is innate, while words have to be learnt one by one. Words are high-level cognitive abstract entities of objects in nature and semantics of words are the attributes of objects.
In neurolinguistics, there are correlations between words and
Figure 2 illustrates these relations. The connections between words are generated from their context and distances between words represent their semantic similarities.
Figure 2.
Vector space. For Event Model, we do not deny the existence of topics, but they are only some specific words, such as science, computer and sport in the figure. People perceive topics by semantic association. We use a same way to deal with topics and other words.
Figure 2.
Vector space. For Event Model, we do not deny the existence of topics, but they are only some specific words, such as science, computer and sport in the figure. People perceive topics by semantic association. We use a same way to deal with topics and other words.
A word in the vector space can be expressed as a vector. Then its semantics can be obtained through its context using a statistical language model. CBOW is a statistical language model using distributed representations of words. The objective function is a log-likelihood function as
where
w is
word,
C is corpus and
Context is the context of
w. Every input word is mapped to a vector. We can get both language model and word vector by training a neural network. The network consists of three layers: input layer, projection layer, and output layer. The input layer contains 2c word vectors of
Context(
w) and
v(
Context(
w)
1),
v(
Context(
w)
2), ...
v(
Context(
w)
2c)
.
m is the length of the word vector. The projection layer sums the 2c word vectors, as
The output layer is a Huffman tree. Its leaf nodes are the words in dictionary and weights are frequencies of words in corpus. For the word
w in dictionary, there must be a path
pw from the root node to the corresponding leaf node of
w and
lw is equal the number of nodes in
pw.
pw consists
lw-1 branches. Each branch is a binary classification and presents a probability. Multiply all probabilities together to get
p(
w|
Context(
w)) and
where
denotes the Huffman code of w and
denotes the corresponding vectors of
j-1 non leaf nodes. Then use a stochastic gradient ascent algorithm to obtain the word vectors. The word vector generating process is word learning.
3. Dimensionality Reduction
We have already assumed that a document is the description of an event. Next we split an event (a document) into following layers:
A
scene is a fragment or picture of an event, whether concrete or abstract. Scenes correspond to the sentences in the document.
Figure 3 shows two specific scenes. The left one can be described by using the sentence “A grey cat is sitting in a house”. The right one is “An orange cat is walking in a house”.
An object is a basic element which constitutes the scene, such as character, time, place, behavior, emotion, and so on. Objects are commensurate with words in the document.
The event (document) generating process is object-scene-event (word-sentence-document), in which event (document) is the linear superposition of the scenes (sentences). For example, we can merge the two scenes in
Figure 3 to generate an event. After filtering out stop words, the dictionary is (grey, orange, cat, sit, lie, house). Let
S1 denote the left scene and
S2 denote the right scene.
S1 = (1, 0, 1, 1, 0, 1) and
S2 = (0, 1, 1, 0, 1, 1). Let
E be the event and
E =
S1 +
S2 = (1, 1, 2, 1, 1, 2). Furthermore, scene (sentence) is the linear combination of objects (words).
Figure 3.
Scenes and objects.
Figure 3.
Scenes and objects.
In topic model, words are simply regarded as input features and isolated from each other. However, for Event Model, words denote natural objects and there are associations between the basic properties of objects. It means that one word is linked with others in semantics. When we replace the words in a sentence with other semantically similar words to generate a new sentence, the scenes described by these two sentences are similar, as shown in
Figure 4.
Figure 4.
Similar scenes. In the word learning stage, we have already got the semantics of words based on deep learning. The dimensionality reducing mode of topic model is representing a document as an approximate posterior over the latent topics. Event Model uses the semantic similarities to reduce dimensionality.
Figure 4.
Similar scenes. In the word learning stage, we have already got the semantics of words based on deep learning. The dimensionality reducing mode of topic model is representing a document as an approximate posterior over the latent topics. Event Model uses the semantic similarities to reduce dimensionality.
A word class consists of several semantic similar words. For example, in
Figure 4, (grey, white, orange, black) compose the word class “color” and (cat, dog) compose the word class “pet”. Obviously, different word classes can compose sentences, so we let a word class become the intermediate layer between word and sentence. Without considering the order of words, the sentence layer can be removed. As the number of word classes is far less than the number of words, Event Model generates a low dimensional vector representing the document by the process shown in
Figure 5.
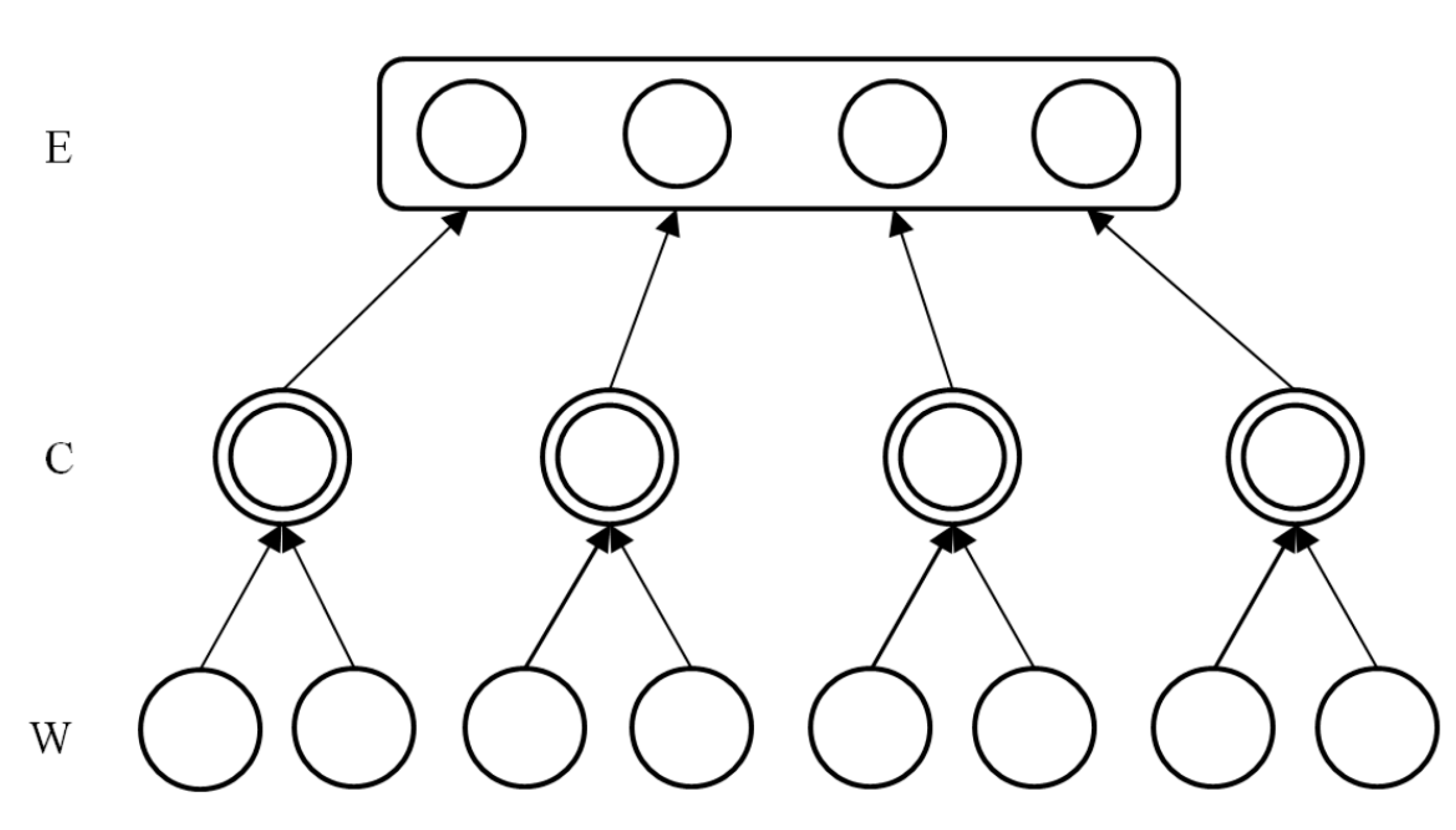
Figure 5.
The dimensionality reducing process of Event Model.
Figure 5.
The dimensionality reducing process of Event Model.
W is the word layer,
C is the word class layer and
E is the document (event) layer in
Figure 5. Let
K denote the dictionary size and
w be word.
ri are the distributed representations of
wi, then the network
R = {
r1,
….,rK}. Using K-means algorithm to cluster vectors in
R, the number of clustering is
N and record every word’s category.
c is a word class, and
ci= {
wm,…,
wn},
where i = 1 to
N and
m,
n ∈ (1,…,
K). Let
C be an
N dimensional vector, representing the word class that a word belongs to. If the number of words of a document is
D, then the number of
C is also
D. The value of
C is
where
i = 1 to
D and j ∈ (1,
N). It is the process that words are mapped to word classes. Only one dimension in
C is 1 and others are 0.
We have already introduced that an event is a linear combination of the words, thus the relationship between document and word classes is also linear. Let
E be an
N dimensional vector, then we have
Normalizing
E, then each document can be represented with an
N dimensional vector
En, computed as
All along, language model and topic model play important roles in different NLP areas. Now we apply the language model to document modeling. The language model is very different with document modeling of course, so we split Event Model into two stages. It is a daily experience of learning first then reading. The main difference between word learning and semantic perception is whether to consider the word order. Order is necessary for word learning. If there are two sentences written as following
room is running happily in the cat
dog is running happily in the house
Then the grammar and semantics of room and dog are same, which means that room and dog belong to a same word class, so do cat and house. That is obviously unreasonable. For semantic perception (used for document retrieval and classification), the word order is not important, such as
room is running happily in the cat
house is running happily in the dog
They convey the same meaning and we do not need to consider their true meanings.
4. Topic Models Based on Word Learning
The document generating mechanisms of topic model and Event Model are completely different. In order to further compare the two mechanisms, we propose a topic model based on word learning.
After obtaining word vectors and clustering them, words can be mapped to word class vector space. Word classes usually have specific concepts as shown in
Table 1, so we can explore the relationship between word classes and continue to reduce dimensionality in linear or nonlinear ways.
Table 1.
Word classes and their corresponding words.
Table 1.
Word classes and their corresponding words.
| Word Class | Word | Word Class | Word | Word Class | Word | Word Class | Word |
|---|
| Football | Ronaldo | Basketball | James | Brand | Google | Language | C |
| Messi | Kobe | Facebook | C++ |
| Neuer | Howard | Microsoft | Java |
| Dempsey | Duncan | Alibaba | Python |
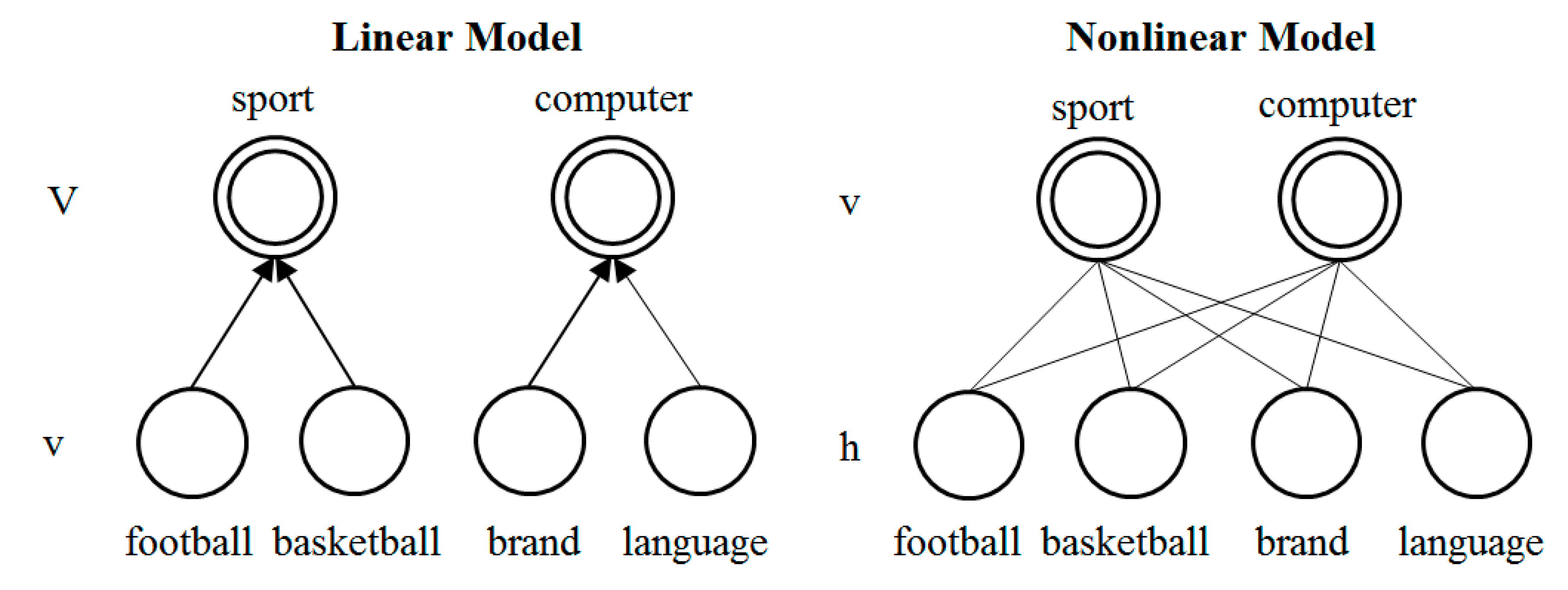
We use the following three ways to further reduce dimensionality: Event Model, WC-LDA, WC-RBM, as shown in
Figure 6. WC-LDA and WC-RBM are topic models based on word learning. The dimensionality reduction process of Event Model is same as word-word class and we merge word classes with similar semantics into a bigger word class. For this process, we do not need to analyze the semantics of word classes and just let
N be a value which is less than the number of word classes. Then generate the document according to the linear mode. The generative model of WC-LDA and WC-RBM is word class-topic-document, which replaces word in bag-of-words model with word class.
Figure 6.
Left: The Relationship of V and v is linear. V(1) = v(1) + v(2), etc. Right: For WC-LDA, The Relationship of v and h is nonlinear, as shown in Equations 9–12.
Figure 6.
Left: The Relationship of V and v is linear. V(1) = v(1) + v(2), etc. Right: For WC-LDA, The Relationship of v and h is nonlinear, as shown in Equations 9–12.
For WC-LDA, calculate the model parameters by
where
wc is word class, t is topic and
d is document. For WC-RBM, firstly change the dimensions which are not equal to 0 in the vector to 1. The energy function of word classes (
v) and latent topics (
h) is defined as
where
ai are bias weights for
v and
bj for
h. The joint probability distribution over
v and
h is
The partition function is