Hinokitiol-Loaded Mesoporous Calcium Silicate Nanoparticles Induce Apoptotic Cell Death through Regulation of the Function of MDR1 in Lung Adenocarcinoma Cells
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Synthesis and Characterization of Mesoporous Calcium Silicate Nanoparticles
2.2. Hinokitiol Loading and Release from MCS Nanoparticles
2.3. Ion Concentration
2.4. Cell Biocompatibility
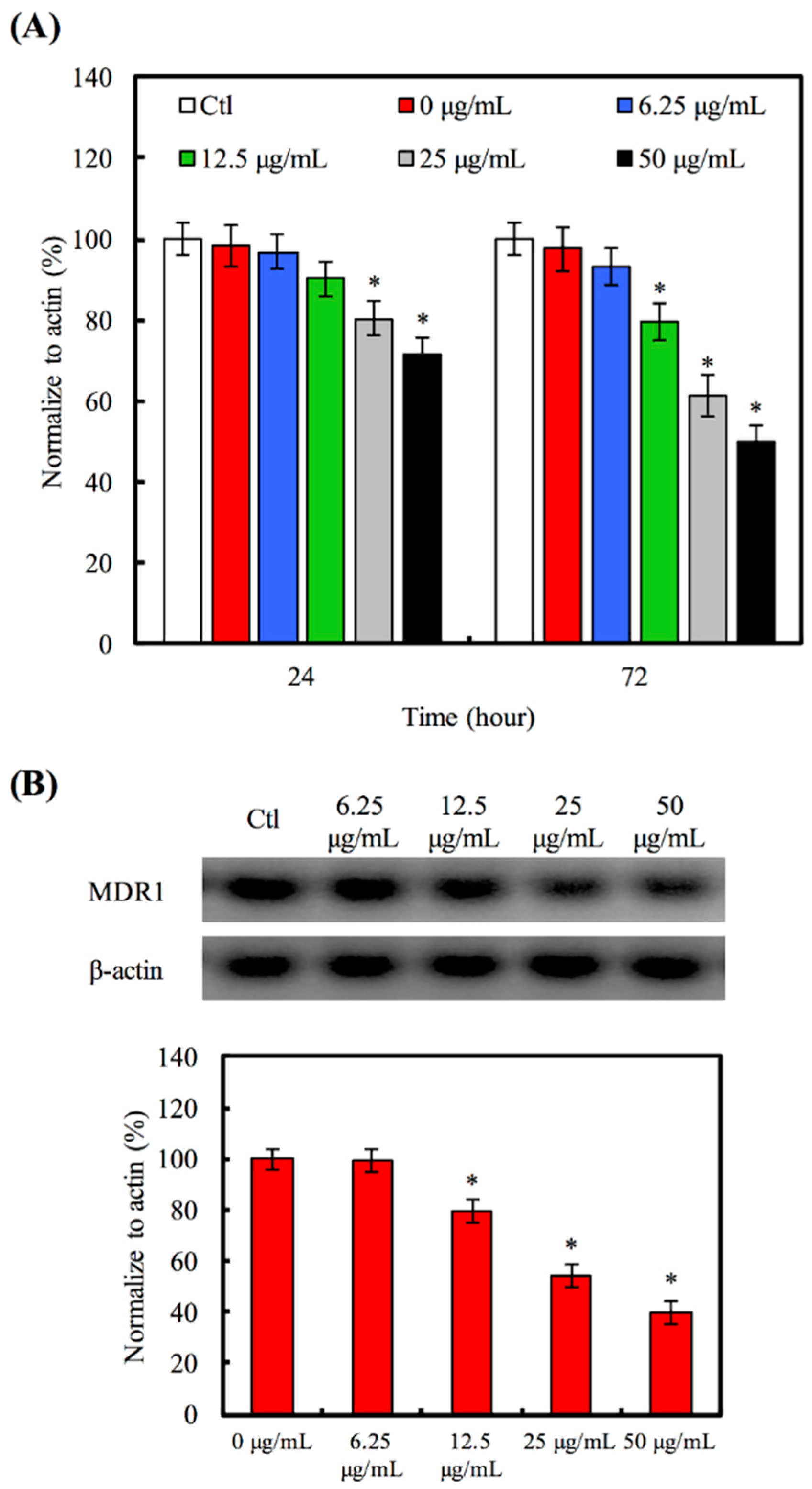
2.5. Multiple Drug Resistance Protein 1 (MDR1) Gene and Protein Expression
2.6. Assays for Caspase-3 and Caspase-9 Activities
2.7. Effects of the Reactive Oxygen Species (ROS) Scavenger on Cell Viability
2.8. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
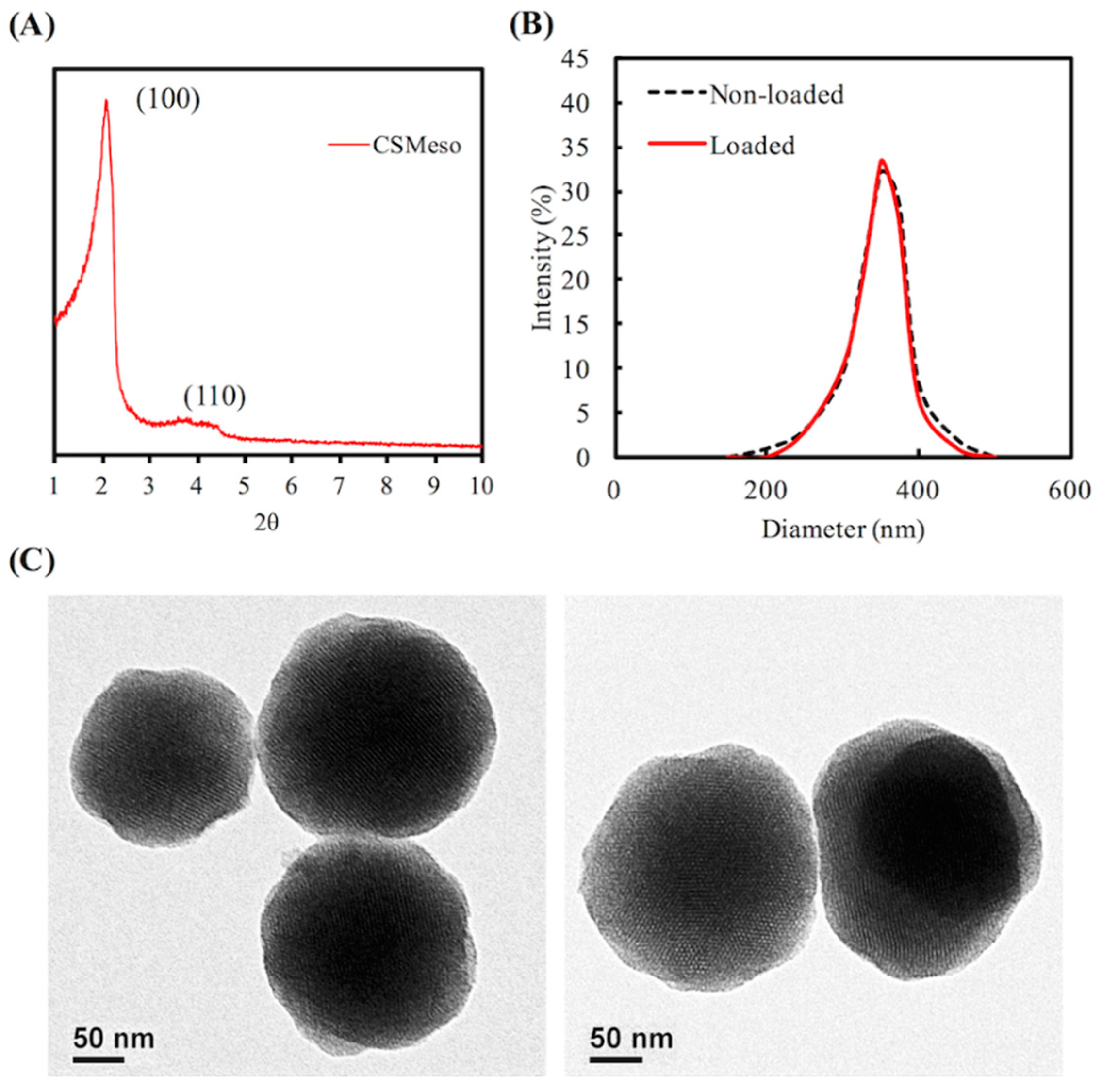
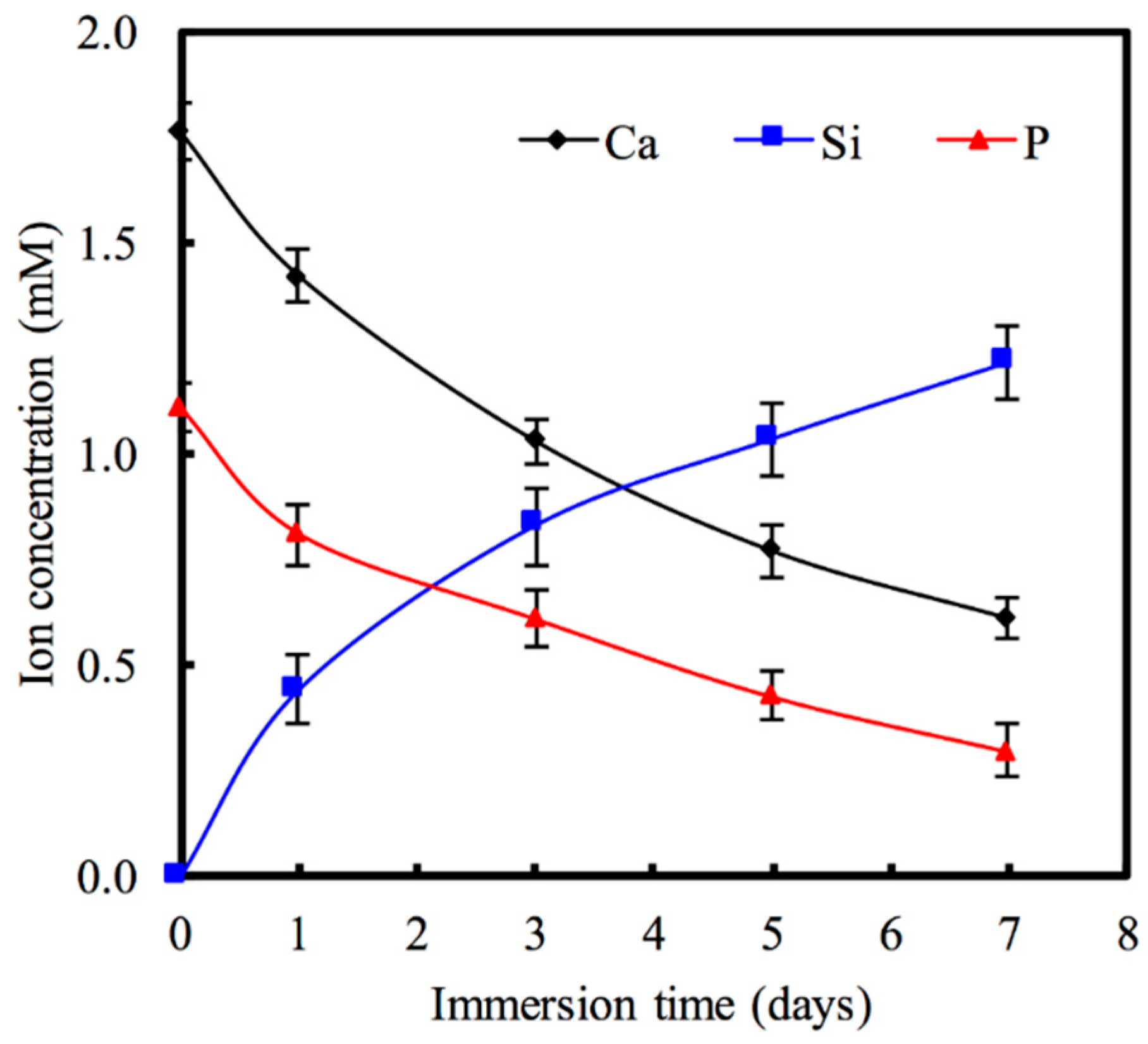
3.1. Characterization of MSC Nanoparticles
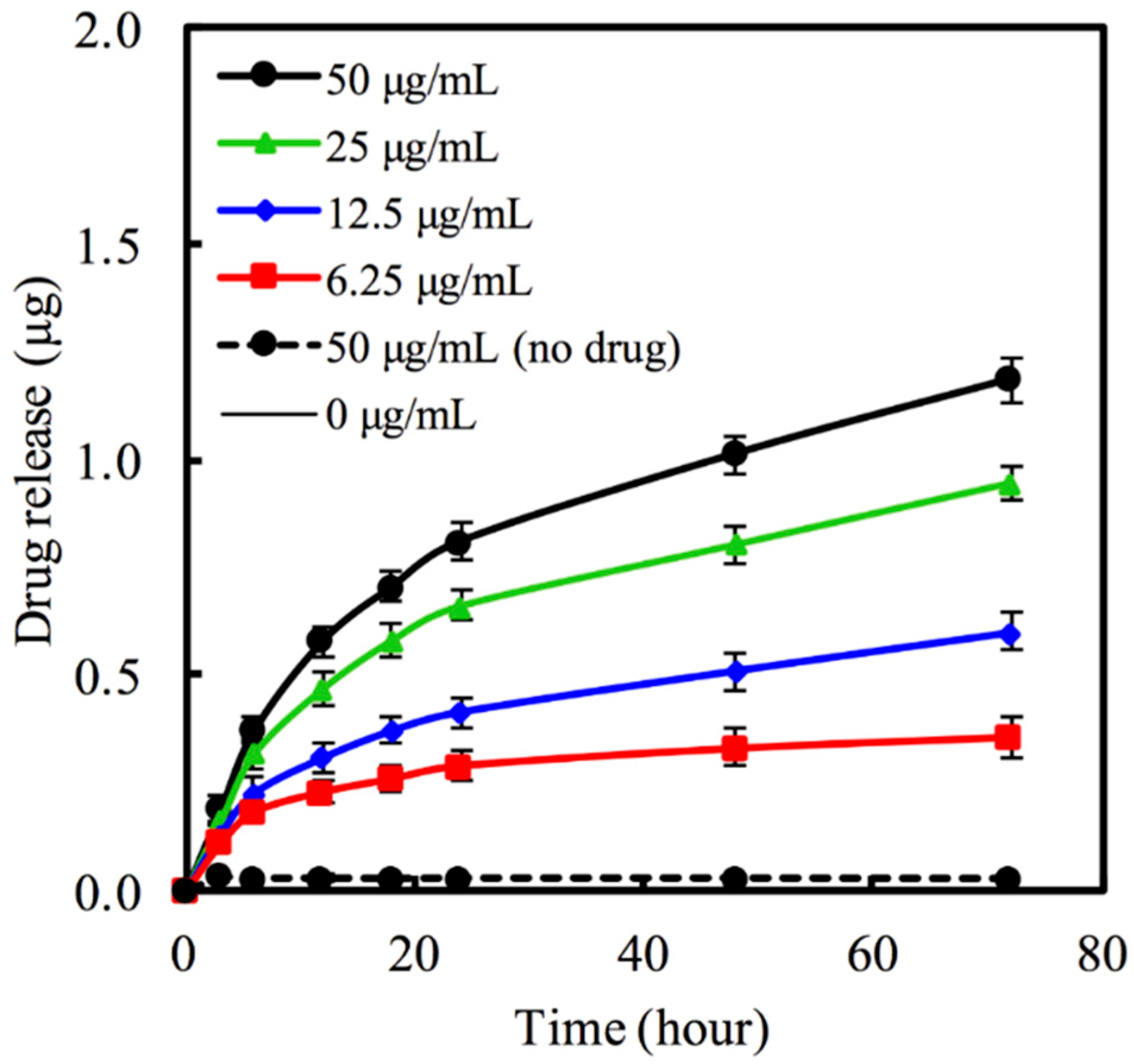
3.2. Hinokitiol Delivery from MBG Nanoparticles
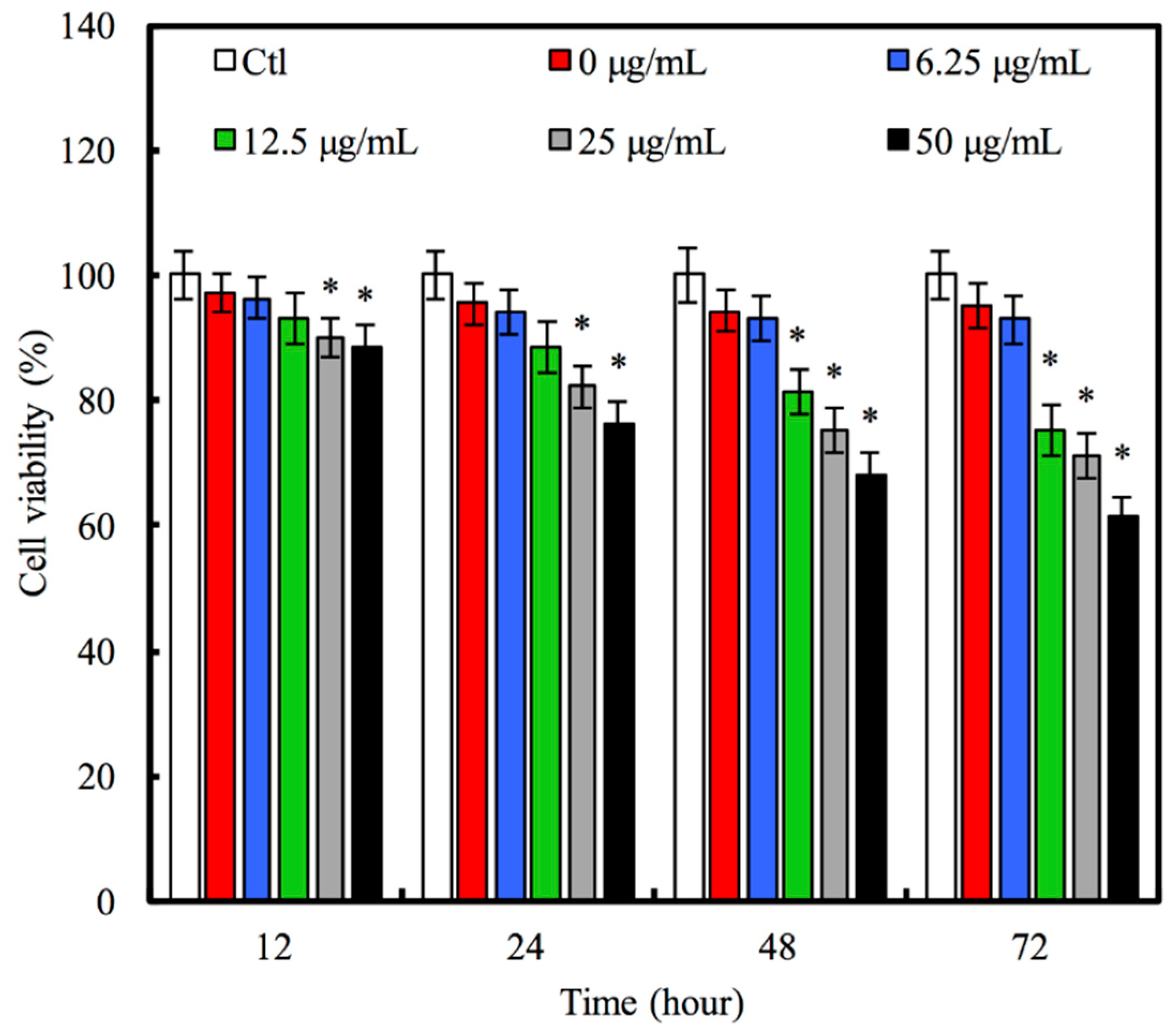
3.3. The Effect of Hinokitiol Delivery on A549 Viability
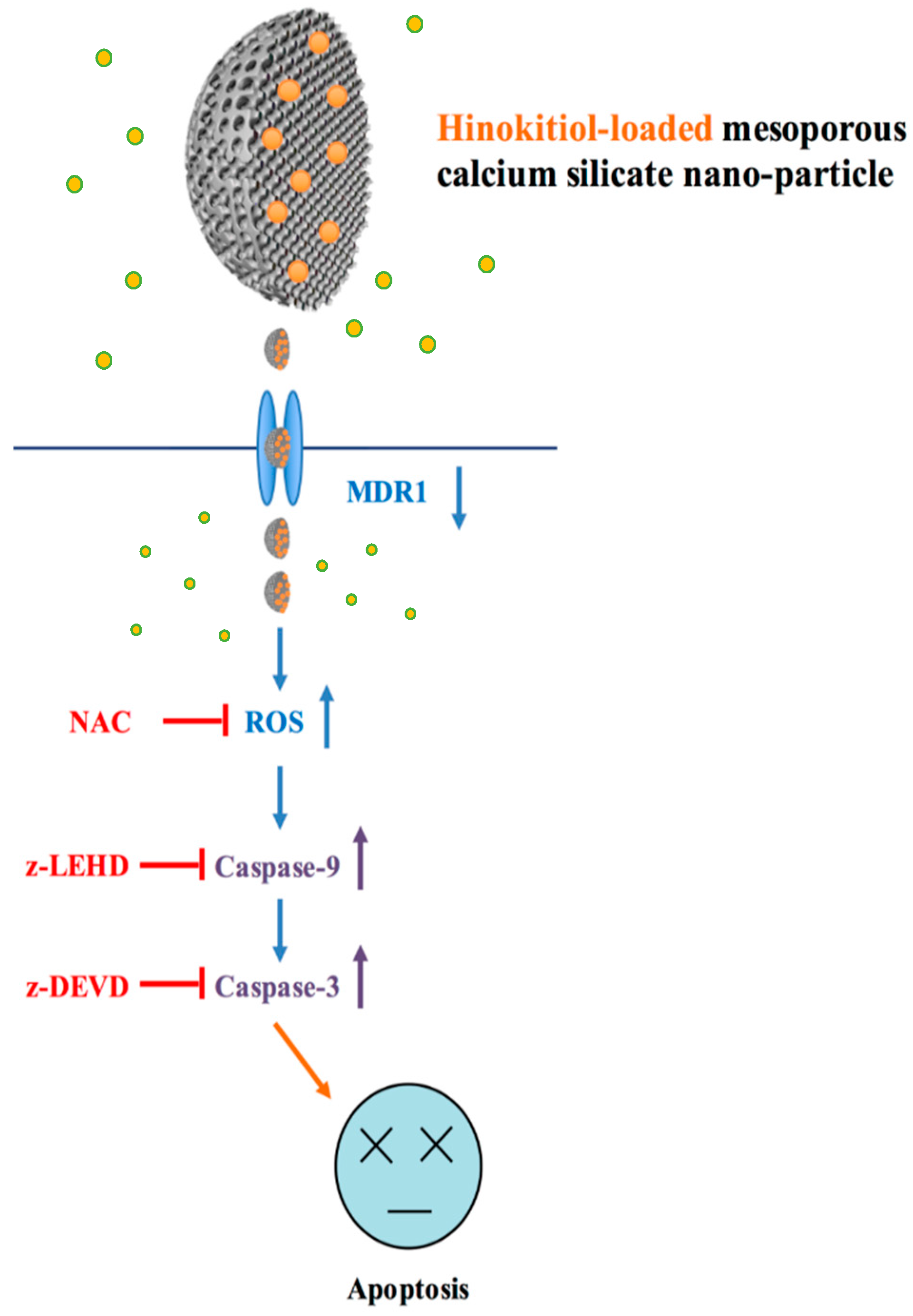
3.4. Hino-MCS Nanoparticles Induce Apoptosis and Suppress MDR1 in A549 Cells
3.5. Hino-MCS Nanoparticles Trigger Intrinsic Apoptotic Cell Death in A549 Cells
3.6. Hino-MCS Nanoparticles Enhance ROS-Generation-Dependent A549 Cell Apoptosis
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Su, C.C.; Kao, C.T.; Hung, C.J.; Chen, Y.J.; Huang, T.H.; Shie, M.Y. Regulation of physicochemical properties, osteogenesis activity, and fibroblast growth factor-2 release ability of β-tricalcium phosphate for bone cement by calcium silicate. Mater. Sci. Eng. C Mater. Biol. Appl. 2014, 37, 156–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ho, C.C.; Ding, S.J. The pH-controlled nanoparticles size of polydopamine for anti-cancer drug delivery. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Med. 2013, 24, 2381–2390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shadjou, N.; Hasanzadeh, M. Bone tissue engineering using silica-based mesoporous nanobiomaterials: Recent progress. Mater. Sci. Eng. C Mater. Biol. Appl. 2015, 55, 401–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hsu, F.Y.; Lu, M.R.; Weng, R.C.; Lin, H.M. Hierarchically biomimetic scaffold of a collagen-mesoporous bioactive glass nanofiber composite for bone tissue engineering. Biomed. Mater. 2015, 10, 025007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, C.; Yan, K.; Hu, C.; Zhao, Y.; Chen, Z.; Zhu, X.; Möller, M. Encapsulation of enzymes in silica nanocapsules formed by an amphiphilic precursor polymer in water. J. Mater. Chem. B 2015, 3, 1261–1267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gan, Q.; Zhu, J.; Yuan, Y.; Liu, H.; Qian, J.; Li, Y.; Liu, C. A dual-delivery system of pH-responsive chitosan-functionalized mesoporous silica nanoparticles bearing BMP-2 and dexamethasone for enhanced bone regeneration. J. Mater. Chem. B 2014, 3, 2056–2066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, M.S.; Choi, H.N.; Choi, W.S.; Lee, H.J. Polyelectrolyte-mediated hierarchical mesoporous calcium silicates: A platform for drug delivery carrier with ultrahigh loading capacity and controlle release behavior. J. Mater. Chem. B 2015, 3, 1001–1009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mendes, L.S.; Saska, S.; Martines, M.A.U.; Marchetto, R. Nanostructured materials based on mesoporous silica and mesoporous silica/apatite as osteogenic growth peptide carriers. Mater. Sci. Eng. C Mater. Biol. Appl. 2013, 33, 4427–4434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, F.; Wang, J.; Huang, P.; Zhang, Q.; Deng, J.; Cao, Q.; Jia, J.; Cheng, J.; Fang, Y.; Deng, D.Y.B.; et al. Outside-in stepwise functionalization of mesoporous silica nanocarriers for matrix type sustained release of fluoroquinolone drugs. J. Mater. Chem. B 2015, 3, 2206–2214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, N.; Jiang, C.; Zhang, X.; Gu, X.; Zhang, J.; Yuan, Y.; Liu, C.; Shi, J.; Wang, J.; Li, Y. Preparation of an rhBMP-2 loaded mesoporous bioactive glass/calcium phosphate cement porous composite scaffold for rapid bone tissue regeneration. J. Mater. Chem. B 2015, 3, 8558–8566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Q.; Zhang, X.; Lu, C.; Lan, X.; Hou, G.; Xu, Z. In vivo behaviors of Ca(OH)2 activated nano SiO2 (nCa/nSi=3) cement in rabbit model. Mater. Sci. Eng. C Mater. Biol. Appl. 2016, 58, 774–781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, H.J.; Kim, Y.B.; Kim, S.H.; Kim, G.H. Mineralized biomimetic collagen/alginate/silica composite scaffolds fabricated by a low-temperature bio-plotting process for hard tissue regeneration: Fabrication, characterisation and in vitro cellular activities. J. Mater. Chem. B 2014, 2, 5785–5798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.S.; Abadeer, N.; Haynes, C.L. Stability of small mesoporous silica nanoparticles in biological media. Chem. Commun. 2011, 47, 532–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, Y.S.; Haynes, C.L. Impacts of mesoporous silica nanoparticle size, pore ordering, and pore integrity on hemolytic activity. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2010, 132, 4834–4842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, J.; Wei, J.; Gan, Q.; Lu, X.; Hou, J.; Song, W.; Yan, Y.; Ma, J.; Guo, H.; Xiao, T.; et al. Preparation, bioactivity, degradability and primary cell responses to an ordered mesoporous magnesium–calcium silicate. Micropor. Mesopor. Mater. 2012, 163, 221–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, C.; Chen, X.; Miao, G.; Lin, C. Angiogenesis stimulated by novel nanoscale bioactive glasses. Biomed. Mater. 2015, 10, 025005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tu, M.G.; Chen, Y.W.; Shie, M.Y. Macrophage-mediated osteogenesis activation in co-culture with osteoblast on calcium silicate cement. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Med. 2015, 26, 276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, M.H.; Kao, C.T.; Chen, Y.W.; Hsu, T.T.; Shieh, D.E.; Huang, T.H.; Shie, M.Y. The synergistic effects of chinese herb and injectable calcium silicate/b-tricalcium phosphate composite on an osteogenic accelerator in vitro. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Med. 2015, 26, 161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, C.; Chang, J.; Fan, W. Bioactive mesoporous calcium–silicate nanoparticles with excellent mineralization ability, osteostimulation, drug-delivery and antibacterial properties for filling apex roots of teeth. J. Mater. Chem. 2012, 22, 16801–16809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.; Fan, W.; Chang, J. Functional mesoporous bioactive glass nanospheres: Synthesis, high loading efficiency, controllable delivery of doxorubicin and inhibitory effect on bone cancer cells. J. Mater. Chem. B 2013, 1, 2710–2718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, N.J.; Chen, Y.W.; Shieh, D.E.; Fang, H.Y.; Shie, M.Y. The effects of injectable calcium silicate-based composites with the Chinese herb on an osteogenic accelerator in vitro. Biomed. Mater. 2015, 10, 055004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.W.; Yeh, C.H.; Shie, M.Y. Stimulatory effects of the fast setting and degradable Ca–Si–Mg cement on both cementogenesis and angiogenesis differentiation of human periodontal ligament cells. J. Mater. Chem. B 2015, 3, 7099–7108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.W.; Hsu, T.T.; Wang, K.; Shie, M.Y. Preparation of the fast setting and degrading Ca-Si-Mg cement with both odontogenesis and angiogenesis differentiation of human periodontal ligament cells. Mater. Sci. Eng. C Mater. Biol. Appl. 2016, 60, 374–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, L.H.; Wu, P.; Lee, J.Y.; Li, P.R.; Hsieh, W.Y.; Ho, C.C.; Ho, C.L.; Chen, W.J.; Wang, C.C.; Yen, M.Y.; et al. Hinokitiol induces DNA damage and autophagy followed by cell cycle arrest and senescence in gefitinib-resistant lung adenocarcinoma cells. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e104203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baba, T.; Nakano, H.; Tamai, K.; Sawamura, D.; Hanada, K.; Hashimoto, I.; Arima, Y. Inhibitory effect of beta-thujaplicin on ultraviolet B-induced apoptosis in mouse keratinocytes. J. Investig. Dermatol. 1998, 110, 24–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shih, Y.H.; Lin, D.J.; Chang, K.H.; Hsia, S.M.; Ko, S.Y.; Lee, S.Y.; Hsue, S.S.; Wang, T.H.; Chen, Y.L.; Shieh, T.M. Evaluation physical characteristics and comparison antimicrobial and anti-inflammation potentials of dental root canal sealers containing hinokitiol in vitro. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e94941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Canitrot, Y.; Bichat, F.; Cole, S.P.C.; Deeley, R.G.; Gerlach, J.H.; Bastian, G.; Arvelo, F.; Poupon, M.-F. Multidrug resistance genes (MRP) and MDR1 expression in small cell lung cancer xenografts: Relationship with response to chemotherapy. Cancer Lett. 1998, 130, 133–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gan, Q.; Dai, D.; Yuan, Y.; Qian, J.; Sha, S.; Shi, J.; Liu, C. Effect of size on the cellular endocytosis and controlled release of mesoporous silica nanoparticles for intracellular delivery. Biomed. Microdevices 2011, 14, 259–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiong, L.; Du, X.; Shi, B.; Bi, J.; Kleitz, F.; Qiao, S.Z. Tunable stellate mesoporous silica nanoparticles for intracellular drug delivery. J. Mater. Chem. B 2015, 3, 1712–1721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, M.H.; Shen, Y.F.; Hsu, T.T.; Huang, T.H.; Shie, M.Y. Physical characteristics, antimicrobial and odontogenesis potentials of calcium silicate cement containing hinokitiol. Mater. Sci. Eng. C Mater. Biol. Appl. 2016, 65, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, T.T.; Yeh, C.H.; Kao, C.T.; Chen, Y.W.; Huang, T.H.; Yang, J.J.; Shie, M.Y. Antibacterial and odontogenesis efficacy of mineral trioxide aggregate combined with CO2 laser treatment. J. Endod. 2015, 41, 1073–1080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lai, W.Y.; Chen, Y.W.; Kao, C.T.; Hsu, T.T.; Huang, T.H.; Shie, M.Y. Human dental pulp cells responses to apatite precipitation from dicalcium silicates. Materials 2015, 8, 4491–4504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valerio, P.; Pereira, M.M.; Goes, A.M.; Leite, M.F. The effect of ionic products from bioactive glass dissolution on osteoblast proliferation and collagen production. Biomaterials 2004, 25, 2941–2948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shie, M.Y.; Ding, S.J.; Chang, H.C. The role of silicon in osteoblast-like cell proliferation and apoptosis. Acta Biomater. 2011, 7, 2604–2614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ye, J.; Xu, Y.F.; Lou, L.X.; Jin, K.; Miao, Q.; Ye, X.; Xi, Y. Anti-inflammatory effects of hinokitiol on human corneal epithelial cells: An in vitro study. Eye 2015, 29, 964–971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, W.K.; Lin, S.T.; Chang, W.W.; Liu, L.W.; Li, T.Y.T.; Kuo, C.Y.; Hsieh, J.L.; Lee, C.H. Hinokitiol induces autophagy in murine breast and colorectal cancer cells. Environ. Toxicol. 2016, 31, 77–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shih, Y.H.; Chang, K.W.; Hsia, S.M.; Yu, C.C.; Fuh, L.J.; Chi, T.Y.; Shieh, T.M. In vitro antimicrobial and anticancer potential of hinokitiol against oral pathogens and oral cancer cell lines. Microbiol. Res. 2013, 168, 254–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, P.Y.; Peng, S.F.; Lee, C.Y.; Lu, C.C.; Tsai, S.C.; Shieh, T.M.; Wu, T.S.; Tu, M.G.; Chen, Y.C.; Yang, J.S. Curcumin-loaded nanoparticles induce apoptotic cell death through regulation of the function of MDR1 and reactive oxygen species in cisplatin-resistant CAR human oral cancer cells. Int. J. Oncol. 2013, 43, 1141–1150. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ye, M.X.; Zhao, Y.L.; Li, Y.; Miao, Q.; Li, Z.K.; Ren, X.L.; Song, L.Q.; Yin, H.; Zhang, J. Curcumin reverses cis-platin resistance and promotes human lung adenocarcinoma A549/DDP cell apoptosis through HIF-1α and caspase-3 mechanisms. Phytomedicine 2012, 19, 779–787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Green, D.R.; Reed, J.C. Mitochondria and apoptosis. Science 1998, 281, 1309–1312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jayakumar, T.; Hsu, W.H.; Yen, T.L.; Luo, J.Y.; Kuo, Y.C.; Fong, T.H.; Sheu, J.R. Hinokitiol, a natural tropolone derivative, offers neuroprotection from thromboembolic stroke in vivo. Evid. Based Complement. Alternat. Med. 2013, 2013, 840487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, P.S.; Wang, M.J.; Jayakumar, T.; Chou, D.S.; Ko, C.Y.; Hsu, M.J.; Hsieh, C.Y. Antiproliferative activity of hinokitiol, a tropolone derivative, is mediated via the inductions of p-JNK and p-PLCγ1 signaling in PDGF-BB-stimulated vascular smooth muscle cells. Molecules 2015, 20, 8198–8212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


© 2016 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Shen, Y.-F.; Ho, C.-C.; Shie, M.-Y.; Wang, K.; Fang, H.-Y. Hinokitiol-Loaded Mesoporous Calcium Silicate Nanoparticles Induce Apoptotic Cell Death through Regulation of the Function of MDR1 in Lung Adenocarcinoma Cells. Materials 2016, 9, 306. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma9050306
Shen Y-F, Ho C-C, Shie M-Y, Wang K, Fang H-Y. Hinokitiol-Loaded Mesoporous Calcium Silicate Nanoparticles Induce Apoptotic Cell Death through Regulation of the Function of MDR1 in Lung Adenocarcinoma Cells. Materials. 2016; 9(5):306. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma9050306
Chicago/Turabian StyleShen, Yu-Fang, Chia-Che Ho, Ming-You Shie, Kan Wang, and Hsin-Yuan Fang. 2016. "Hinokitiol-Loaded Mesoporous Calcium Silicate Nanoparticles Induce Apoptotic Cell Death through Regulation of the Function of MDR1 in Lung Adenocarcinoma Cells" Materials 9, no. 5: 306. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma9050306
APA StyleShen, Y.-F., Ho, C.-C., Shie, M.-Y., Wang, K., & Fang, H.-Y. (2016). Hinokitiol-Loaded Mesoporous Calcium Silicate Nanoparticles Induce Apoptotic Cell Death through Regulation of the Function of MDR1 in Lung Adenocarcinoma Cells. Materials, 9(5), 306. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma9050306






