Preparation of Al/Fe-Pillared Clays: Effect of the Starting Mineral
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
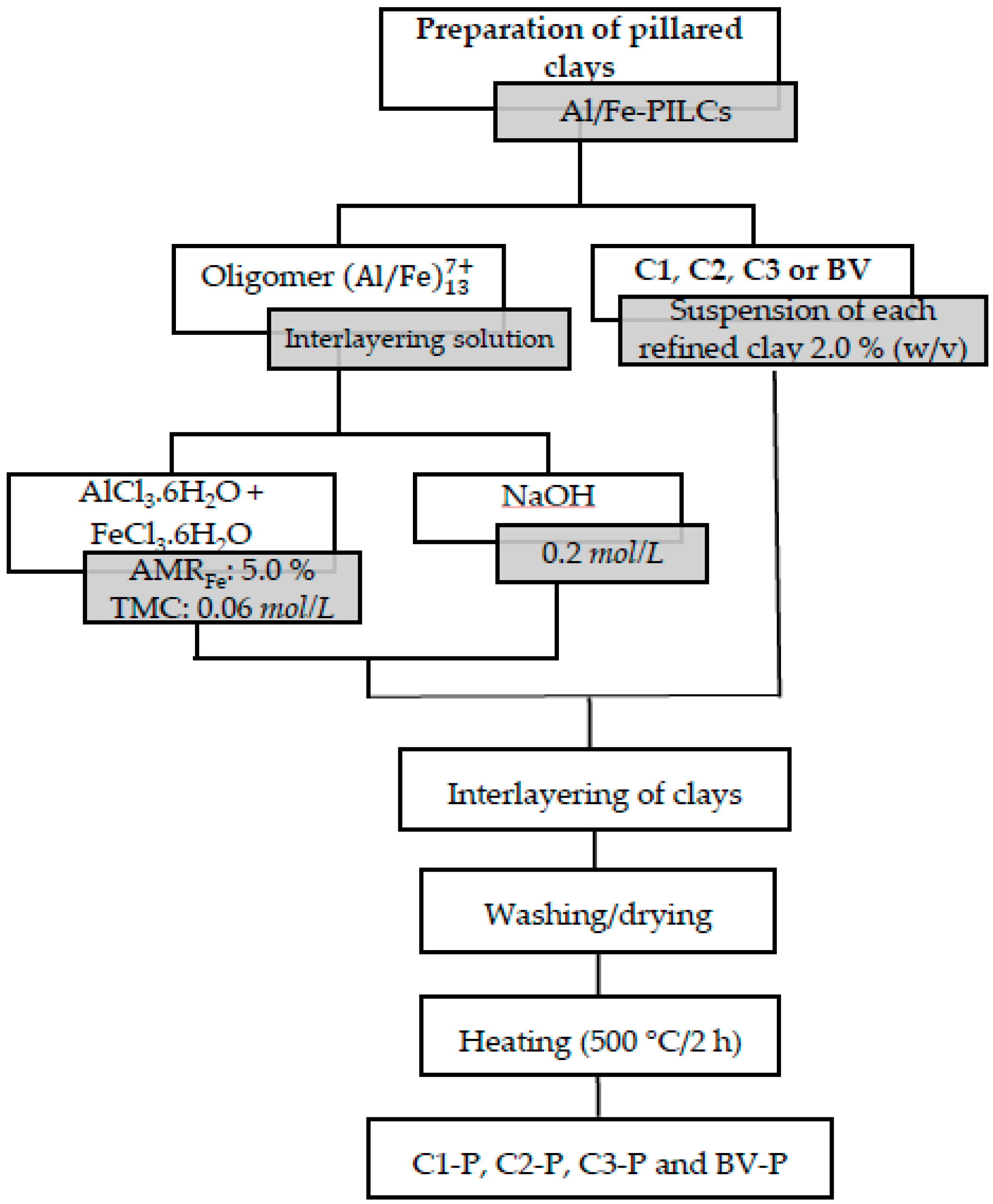
2.2. Preparation of Pillared Clays
2.3. Physicochemical Characterization
2.4. Catalytic Experiments
3. Results and Discussion
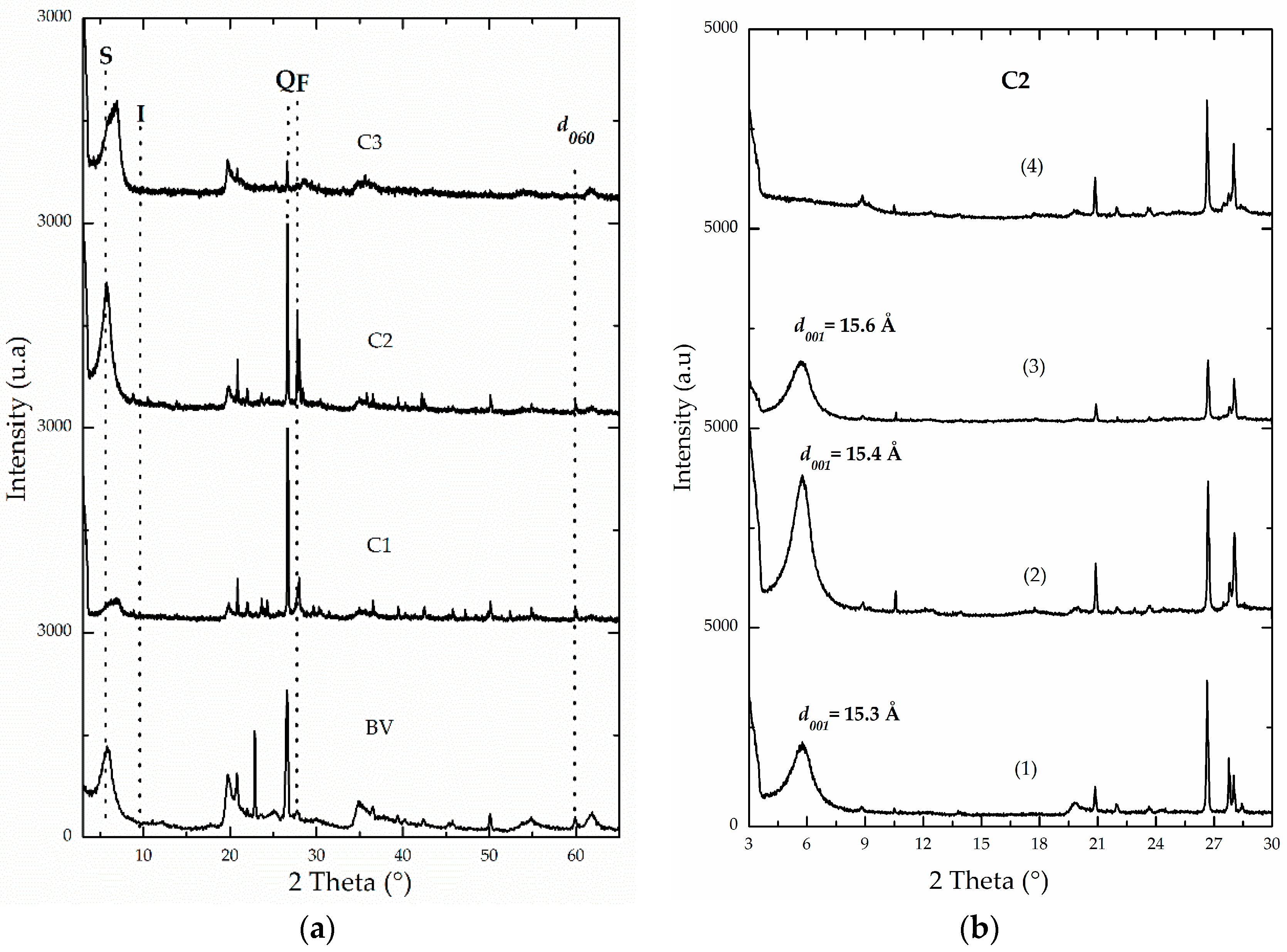
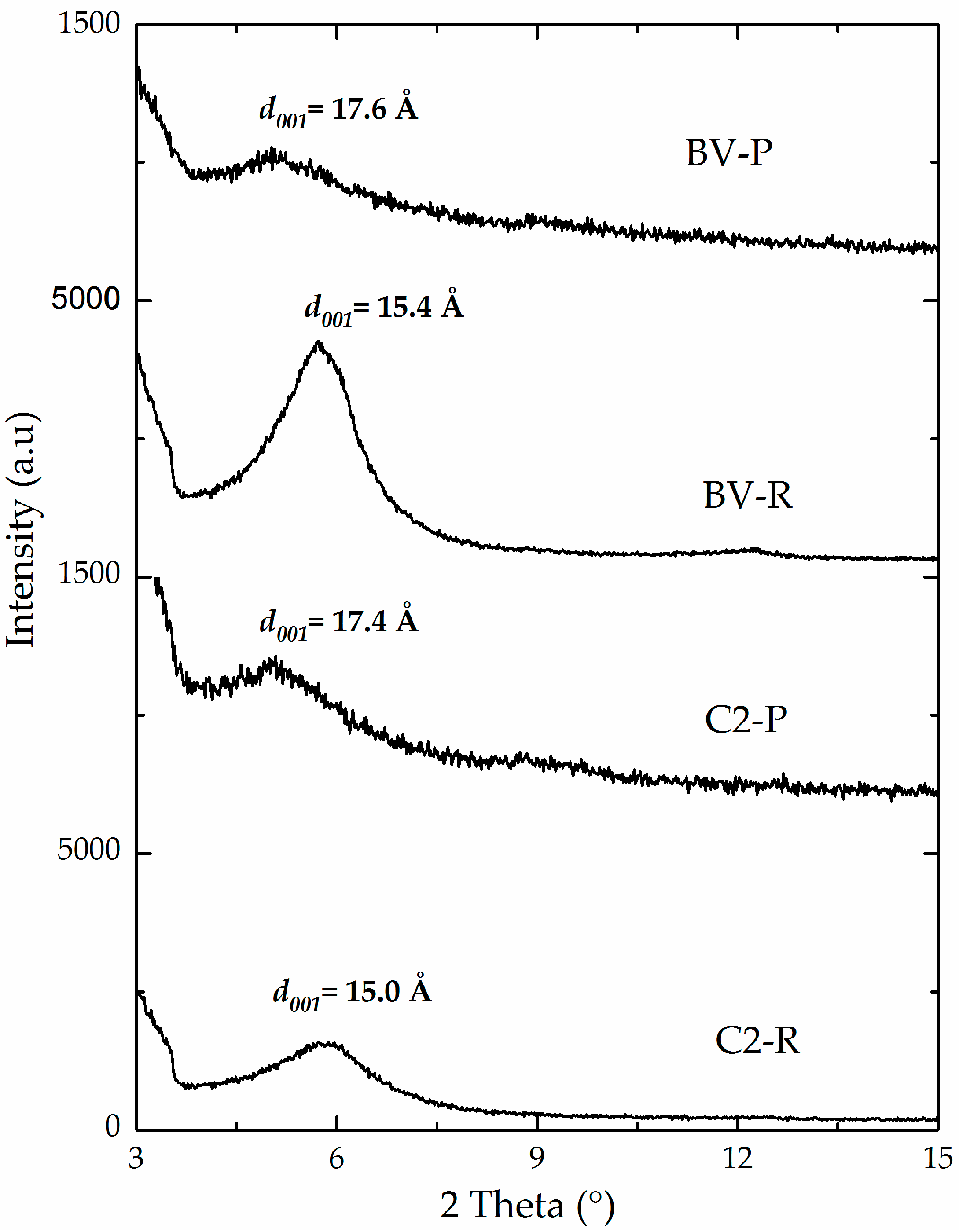
3.1. Physicochemical Characterization
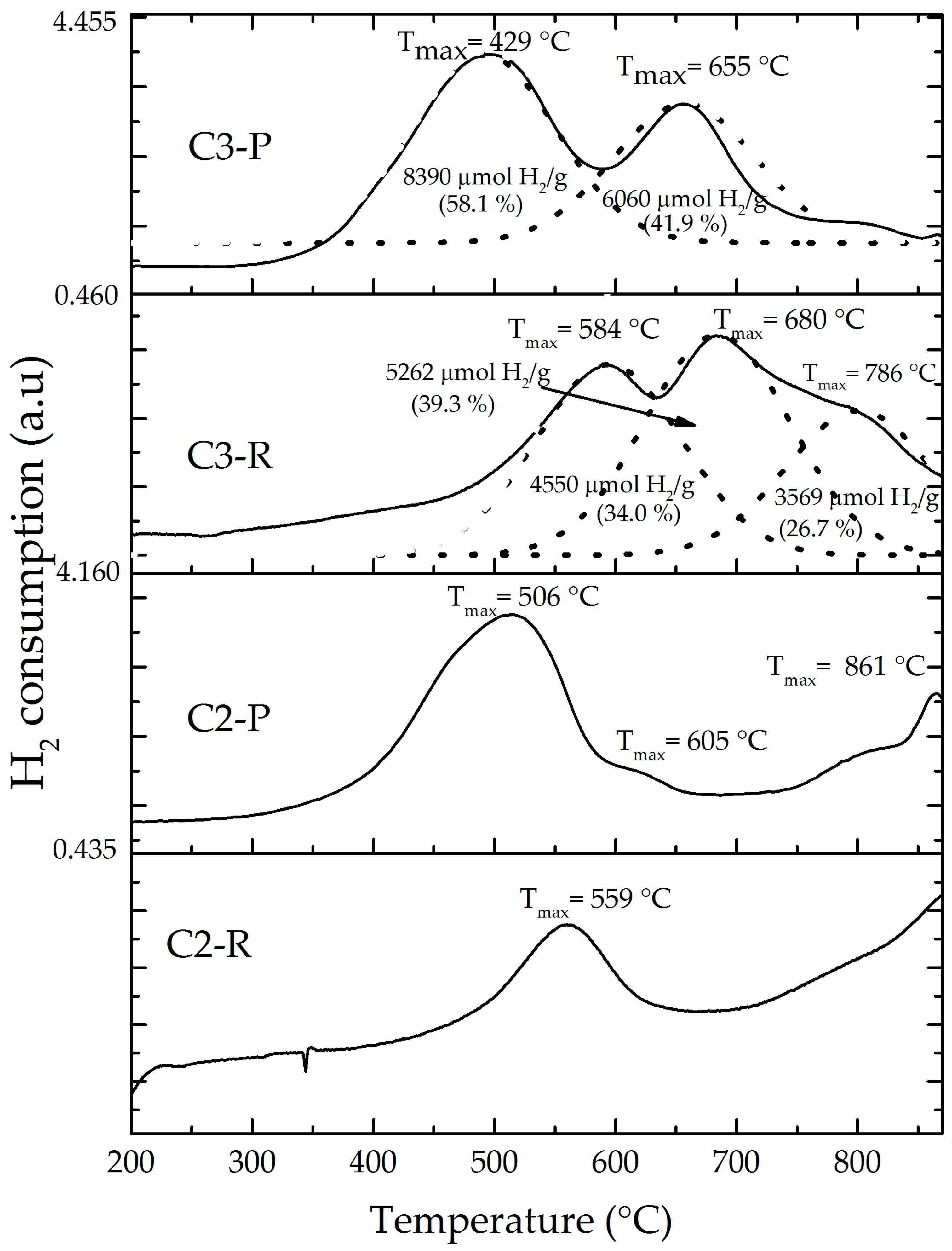
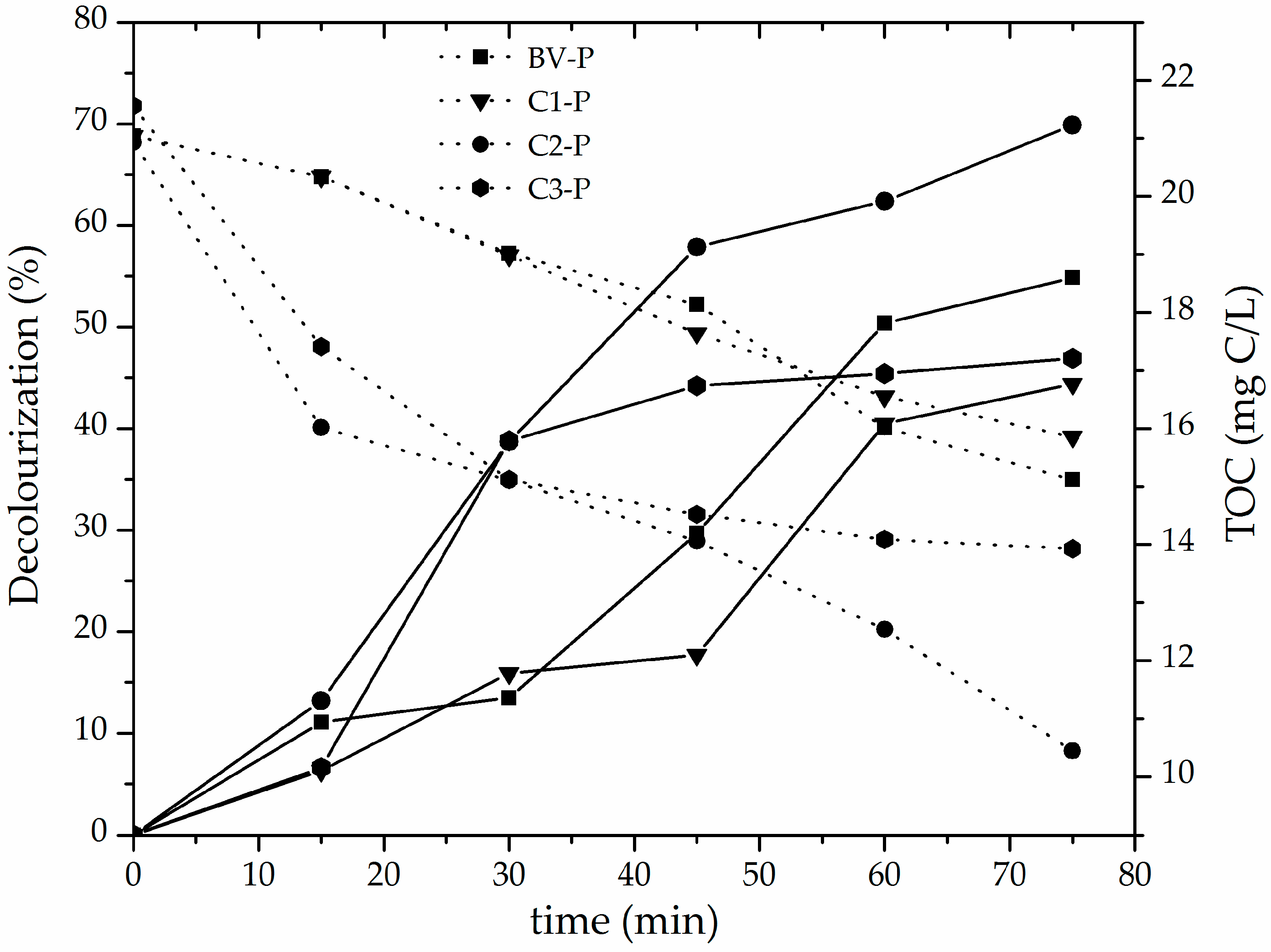
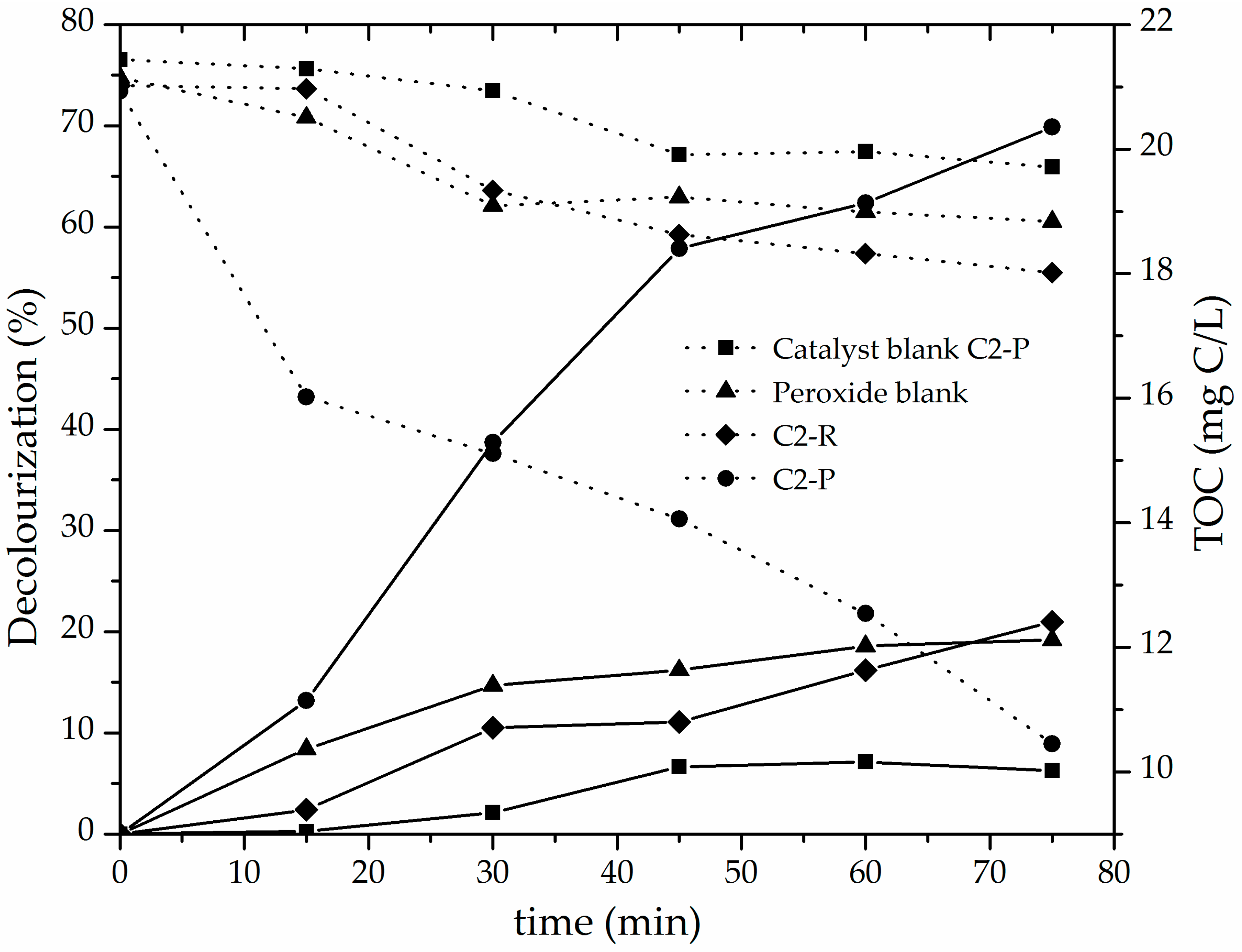
3.2. Catalytic Performance of the Al/Fe-PILCs
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Rouquerol, J.; Llewellyn, P.; Sing, K. Adsorption by Clays, Pillared Clays, Zeolites and Aluminophosphates; Springer: Oxford, UK, 2014; pp. 467–527. [Google Scholar]
- Vicente, M.A.; Gil, A.; Bergaya, F. Pillared clays and clay minerals. In Developments in Clay Science; Bergaya, F., Lagaly, G., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2013; Volume 5, pp. 523–557. [Google Scholar]
- Lagaly, G. Colloid Clay Science; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2006; Volume 1, pp. 141–245. [Google Scholar]
- Banković, P.; Milutinović-Nikolić, A.; Mojović, Z.; Jović-Jovičić, N.; Perović, M.; Spasojević, V.; Jovanović, D. Synthesis and characterization of bentonites rich in beidellite with incorporated Al or Al–Fe oxide pillars. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2013, 165, 247–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schoonheydt, R.A.; Pinnavaia, T.; Lagaly, G.; Gangas, N. Pillared clays and pillared layered solids. Pure Appl. Chem. 1999, 71, 2367–2371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khankhasaeva, S.; Dambueva, D.V.; Dashinamzhilova, E.; Gil, A.; Vicente, M.A.; Timofeeva, M.N. Fenton degradation of sulfanilamide in the presence of Al,Fe-pillared clay: Catalytic behavior and identification of the intermediates. J. Hazard. Mater. 2015, 293, 21–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Katdare, S.P.; Ramaswamy, V.; Ramaswamy, A.V. Factors affecting the preparation of alumina pillared montmorillonite employing ultrasonics. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2000, 37, 329–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Catrinescu, C.; Arsene, D.; Teodosiu, C. Catalytic wet hydrogen peroxide oxidation of para-chlorophenol over Al/Fe pillared clays (AlFePILCs) prepared from different host clays. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2011, 101, 451–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cool, P.; Vansant, E.F. Pillared clays: Preparation, characterization and applications. In Synthesis; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1998; pp. 265–288. [Google Scholar]
- Gil, A.; Korili, S.; Trujillano, R.; Vicente, M.A. Pillared Clays and Related Catalysts; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Christidis, G.E. Assessment of industrial clays. In Developments in Clay Science; Bergaya, F., Lagaly, G., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2013; Volume 5, pp. 425–449. [Google Scholar]
- Galeano, L.-A.; Vicente, M.Á.; Gil, A. Catalytic degradation of organic pollutants in aqueous streams by mixed Al/M-pillared clays (M = Fe, Cu, Mn). Catal. Rev. 2014, 56, 239–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galeano, L.A.; Gil, A.; Vicente, M.A. Effect of the atomic active metal ratio in Al/Fe-, Al/Cu- and Al/(Fe–Cu)-intercalating solutions on the physicochemical properties and catalytic activity of pillared clays in the cwpo of methyl orange. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2010, 100, 271–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirzaei, A.; Chen, Z.; Haghighat, F.; Yerushalmi, L. Removal of pharmaceuticals from water by homo/heterogonous fenton-type processes—A review. Chemosphere 2017, 174, 665–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Najjar, W.; Azabou, S.; Sayadi, S.; Ghorbel, A. Catalytic wet peroxide photo-oxidation of phenolic olive oil mill wastewater contaminants. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2007, 74, 11–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanabria, N.; Álvarez, A.; Molina, R.; Moreno, S. Synthesis of pillared bentonite starting from the Al–Fe polymeric precursor in solid state, and its catalytic evaluation in the phenol oxidation reaction. Catal. Today 2008, 133–135, 530–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molina, C.B.; Zazo, J.A.; Casas, J.A.; Rodriguez, J.J. CWPO of 4-Cp and industrial wastewater with Al-Fe pillared clays. Water Sci. Technol. 2010, 61, 2161–2168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Galeano, L.A.; Bravo, P.F.; Luna, C.D.; Vicente, M.Á.; Gil, A. Removal of natural organic matter for drinking water production by Al/Fe-PILC-catalyzed wet peroxide oxidation: Effect of the catalyst preparation from concentrated precursors. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2012, 111–112, 527–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banković, P.; Milutinović-Nikolić, A.; Mojović, Z.; Jović-Jovičić, N.; Žunić, M.; Dondur, V.; Jovanović, D. Al,Fe-pillared clays in catalytic decolorization of aqueous tartrazine solutions. Appl. Clay Sci. 2012, 58, 73–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Li, W.; Sun, H.; Zheng, Z.; Cui, X.; Wang, H.; Meng, F. A facile in situ pillaring method—The synthesis of Al-pillared montmorillonite. Appl. Clay Sci. 2014, 88–89, 228–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, L.; Ling, C.Y.; Lavikainen, L.P.; Hirvi, J.T.; Kasa, S.; Pakkanen, T.A. Influence of layer charge and charge location on the swelling pressure of dioctahedral smectites. Chem. Phys. 2016, 473, 40–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCabe, R.W.; Adams, J.M. Clay minerals as catalysts. In Developments in Clay Science; Bergaya, F., Lagaly, G., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2013; Volume 5, pp. 491–538. [Google Scholar]
- Zeng, L.; Wang, S.; Peng, X.; Geng, J.; Chen, C.; Li, M. Al–Fe PILC preparation, characterization and its potential adsorption capacity for aflatoxin B1. Appl. Clay Sci. 2013, 83–84, 231–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Catrinescu, C.; Arsene, D.; Apopei, P.; Teodosiu, C. Degradation of 4-chlorophenol from wastewater through heterogeneous fenton and photo-fenton process, catalyzed by Al–Fe PILC. Appl. Clay Sci. 2012, 58, 96–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, K.; Lei, J.; Yuan, G.; Weerachanchai, P.; Wang, J.-Y.; Zhao, J.; Yang, Y. Fe-, Ti-, Zr- and Al-pillared clays for efficient catalytic pyrolysis of mixed plastics. Chem. Eng. J. 2017, 317, 800–809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia, A.M.; Moreno, V.; Delgado, S.X.; Ramírez, A.E.; Vargas, L.A.; Vicente, M.Á.; Gil, A.; Galeano, L.A. Encapsulation of SALEN- and SALHD-Mn(III) complexes in an Al-pillared clay for bicarbonate-assisted catalytic epoxidation of cyclohexene. J. Mol. Catal. A Chem. 2016, 416, 10–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanabria, N.R.; Ávila, P.; Yates, M.; Rasmussen, S.B.; Molina, R.; Moreno, S. Mechanical and textural properties of extruded materials manufactured with AlFe and AlCeFe pillared bentonites. Appl. Clay Sci. 2010, 47, 283–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Urruchurto, C.M.; Carriazo, J.G.; Osorio, C.; Moreno, S.; Molina, R.A. Spray-drying for the preparation of Al–Co–Cu pillared clays: A comparison with the conventional hot-drying method. Powder Technol. 2013, 239, 451–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barrault, J.; Abdellaoui, M.; Bouchoule, C.; Majesté, A.; Tatibouët, J.M.; Louloudi, A.; Papayannakos, N.; Gangas, N.H. Catalytic wet peroxide oxidation over mixed (Al–Fe) pillared clays. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2000, 27, L225–L230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bergaya, F.; Hassoun, N.; Barrault, J.; Gatineau, L. Pillaring of synthetic hectorite by mixed [Al13-Xfex] pillars. Clay Miner. 1999, 28, 109–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thorez, J. Practical Identification of Clay Minerals: A Handbook for Teachers and Students in Clay Mineralogy, 1st ed.; Lelotte: Berkeley, CA, USA, 1976. [Google Scholar]
- Moore, D.; Reynolds, R., Jr. X-ray Diffraction and the Identification and Analysis of Clay Minerals, 2nd ed.; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 1997; p. 373. [Google Scholar]
- Tsozué, D.; Nzeugang, A.N.; Mache, J.R.; Loweh, S.; Fagel, N. Mineralogical, physico-chemical and technological characterization of clays from maroua (Far-North, Cameroon) for use in ceramic bricks production. J. Build. Eng. 2017, 11, 17–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguetnkam, J.P.; Kamga, R.; Villiéras, F.; Ekodeck, G.E.; Yvon, J. Altération différentielle du granite en zone tropicale. Exemple de deux séquences étudiées au cameroun (Afrique centrale). C. R. Geosci. 2008, 340, 451–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franco, F.; Pozo, M.; Cecilia, J.A.; Benítez-Guerrero, M.; Lorente, M. Effectiveness of microwave assisted acid treatment on dioctahedral and trioctahedral smectites. The influence of octahedral composition. Appl. Clay Sci. 2016, 120, 70–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chin, C.L.; Ahmad, Z.A.; Sow, S.S. Relationship between the thermal behaviour of the clays and their mineralogical and chemical composition: Example of Ipoh, Kuala Rompin and Mersing (Malaysia). Appl. Clay Sci. 2017, 143, 327–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, G.; Newman, A.C.D.; Rayner, J.H.; Weir, A.H. The structures and chemistry of soil clay minerals. In The Chemistry of Soil Constituents; Greenland, D.J., Hayes, M.H.B., Eds.; John Wiley & Sons: New York, NY, USA, 1978; pp. 29–178. [Google Scholar]
- Eusterhues, K.; Rumpel, C.; Kogel-Knabner, I. Organo-mineral associations in sandy acid forest soils: Importance of specific surface area, iron oxides and micropores. Eur. J. Soil Sci. 2005, 56, 753–763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galeano, L.A.; Gil, A.; Vicente, M.A. Strategies for immobilization of manganese on expanded natural clays: Catalytic activity in the cwpo of methyl orange. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2011, 104, 252–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, R.; Chen, Q.; Zhou, Q.; Xi, Y.; Zhu, J.; He, H. Adsorbents based on montmorillonite for contaminant removal from water: A review. Appl. Clay Sci. 2016, 123, 239–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonzalez, B.; Perez, A.H.; Trujillano, R.; Gil, A.; Vicente, M.A. Microwave-assisted pillaring of a montmorillonite with Al-polycations in concentrated media. Materials 2017, 10, 886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thommes, M.; Kaneko, K.; Neimark, A.V.; Olivier, J.P.; Rodriguez-Reinoso, F.; Rouquerol, J.; Sing, K.S.W. Physisorption of gases, with special reference to the evaluation of surface area and pore size distribution (IUPAC technical report). Pure Appl. Chem. 2015, 87, 1051–1069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kooli, F. Pillared montmorillontes from unusual antiperspirant aqueous solutions: Characterization and catalytic tests. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2013, 167, 228–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sing, K.S.W.; Everett, D.H.; Haul, R.A.W.; Moscou, L.; Pierotti, R.A.; Rouquérol, J.; Siemieniewska, T. Reporting physisorption data for gas/solid systems with special reference to the determination of surface area and porosity. Pure Appl. Chem. 1985, 57, 603–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carriazo, J.G. Influence of iron removal on the synthesis of pillared clays: A surface study by nitrogen adsorption, XRD and EPR. Appl. Clay Sci. 2012, 67–68, 99–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herney-Ramirez, J.; Lampinen, M.; Vicente, M.A.; Costa, C.A.; Madeira, L.M. Experimental design to optimize the oxidation of orange II dye solution using a clay-based fenton-like catalyst. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2008, 47, 284–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munoz, M.; Domínguez, P.; de Pedro, Z.M.; Casas, J.A.; Rodriguez, J.J. Naturally-occurring iron minerals as inexpensive catalysts for CWPO. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2017, 203, 166–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Sample | SiO2 | Al2O3 | Fe2O3 | MgO | TiO2 | CaO | K2O | Na2O | SiO2/Al2O3 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| C1 | 62.94 | 17.25 | 7.86 | 2.23 | 0.85 | 3.00 | 2.03 | 3.28 | 3.65 |
| C2 | 63.30 | 19.67 | 8.17 | 2.64 | 0.99 | 2.19 | 0.99 | 1.55 | 3.22 |
| C3 | 50.77 | 17.35 | 19.94 | 3.08 | 1.70 | 2.61 | 0.17 | 3.65 | 2.93 |
| BV | 60.25 | 23.20 | 9.37 | 3.16 | 1.17 | 0.93 | 0.80 | 0.74 | 2.60 |
| C1-R | 55.09 | 19.33 | 13.85 | 2.87 | 0.68 | 1.90 | 1.13 | 3.25 | 2.89 |
| C2-R | 60.31 | 21.82 | 11.02 | 2.74 | 1.09 | 1.05 | 1.09 | 0.54 | 2.76 |
| C3-R | 52.04 | 17.41 | 17.96 | 3.25 | 1.59 | 2.33 | 0.20 | 3.95 | 2.99 |
| BV-R | 57.57 | 22.02 | 10.98 | 2.60 | 1.24 | 1.34 | 0.90 | 2.88 | 2.61 |
| C1-P | 54.31 | 27.52 | 14.65 | 2.04 | 0.67 | 0.14 | 0.97 | 0.35 | 1.97 |
| C2-P | 55.33 | 30.71 | 13.39 | 2.07 | 1.05 | 0.09 | 0.83 | 0.27 | 1.80 |
| C3-P | 49.53 | 28.03 | 19.53 | 2.60 | 1.54 | 0.35 | 0.14 | 0.17 | 1.77 |
| BV-P | 53.37 | 33.26 | 12.58 | 2.15 | 1.11 | 0.08 | 0.64 | 0.19 | 1.60 |
| Mineral | Clay Phase | |
|---|---|---|
| Smectite (%) | Illite (%) | |
| BV | 60 | 40 |
| C1 | 34 | 66 |
| C2 | 46 | 54 |
| C3 | 54 | 46 |
| Sample | Feincorporated a (Fe2O3 w/w %) | CEC b (meq/100 g) | % CC c | d001 d (Å) | SBET (m2/g) | SExt (m2/g) | Sµp (m2/g) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| C1 | NA | 109 | NA | 12.8 | 45 | 30 | 15 |
| C2 | NA | 118 | NA | 15.3 | 62 | 47 | 15 |
| C3 | NA | 185 | NA | 12.7 | 113 | 75 | 37 |
| BV | NA | 124 | NA | 14.7 | 85 | 49 | 37 |
| C1-R | NA | 149 | NA | 16.3 | 105 | 78 | 27 |
| C2-R | NA | 192 | NA | 15.0 | 105 | 67 | 38 |
| C3-R | NA | 175 | NA | 12.6 | 95 | 67 | 28 |
| BV-R | NA | 137 | NA | 15.4 | 97 | 64 | 33 |
| C1-P | 0.80 | 82 | 45 | 16.9 | 144 | 25 | 119 |
| C2-P | 2.37 | 78 | 59 | 17.4 | 194 | 29 | 165 |
| C3-P | 1.57 | 81 | 54 | 17.7 | 185 | 48 | 136 |
| BV-P | 1.61 | 91 | 50 | 17.6 | 139 | 25 | 114 |
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Muñoz, H.-J.; Blanco, C.; Gil, A.; Vicente, M.-Á.; Galeano, L.-A. Preparation of Al/Fe-Pillared Clays: Effect of the Starting Mineral. Materials 2017, 10, 1364. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma10121364
Muñoz H-J, Blanco C, Gil A, Vicente M-Á, Galeano L-A. Preparation of Al/Fe-Pillared Clays: Effect of the Starting Mineral. Materials. 2017; 10(12):1364. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma10121364
Chicago/Turabian StyleMuñoz, Helir-Joseph, Carolina Blanco, Antonio Gil, Miguel-Ángel Vicente, and Luis-Alejandro Galeano. 2017. "Preparation of Al/Fe-Pillared Clays: Effect of the Starting Mineral" Materials 10, no. 12: 1364. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma10121364
APA StyleMuñoz, H.-J., Blanco, C., Gil, A., Vicente, M.-Á., & Galeano, L.-A. (2017). Preparation of Al/Fe-Pillared Clays: Effect of the Starting Mineral. Materials, 10(12), 1364. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma10121364








