1. Introduction
With the accelerated melting of two polar glaciers and rising sea levels in recent decades, global warming has become a major concern of the international community. To reduce greenhouse gases emissions and curb further global climate warming has turned into the common challenge faced by human society in this century. As the harm caused by climate warming continues to emerge, as well as the deepening awareness of the international community, a binding “Paris Agreement” was adopted in 2015. Of all the greenhouse gases, CO
2 emissions from human activity contribute most of the warming effect, and it has become the focus of emission reduction. China overtook the United States as the world’s largest carbon emitters in 2007. As of 2013, China contributed 27.1% of the world’s total carbon emissions [
1]. China is facing increasing international pressure in terms of carbon emissions. Some research results supported that there was an environmental Kuznets curve between economic development and carbon emissions in China. That is to say, with the development of the economy, China’s carbon emissions will increase first and then decrease; however, the inflection point of carbon emissions cannot be reached in a short time [
2,
3]. As awareness of environmental protection has constantly been enhanced and carbon emissions reduction is gradually seen as an opportunity to transform the mode of economic growth, the attitude of China towards carbon reduction is shifting from passive response to a positive response. In 2009, China promised that carbon intensity would be reduced by 40%–45% by 2020 based on the 2005 level. Moreover, this target has been embedded in the mid-and-long plan of national economic and social development as a rigid constraint index [
4]. The overall reduction goal is set at the national level, but there are significant differences in resource endowment, stage of economic development and technical level in the provinces, so it is impossible to require all provinces to take 40%–45% as the target of emission reduction. Therefore, the emission reduction potential of the provinces should be fully taken into account in the allocation and formulation of carbon emissions reduction targets [
5]. The energy of Beijing mainly relies on external input, which makes the energy security system vulnerable to external interference. In addition, as one of the most developed provinces in China, it has more capital and technology to achieve low-carbon development. Therefore, in this paper, carbon mitigation potential in Beijing is studied to provide reference for the policy departments and other provinces.
Carbon intensity has been extensively studied in recent years; however, study mainly focused on the influence factors of carbon intensity. Fan et al. [
6] analyzed the influencing factors of the carbon intensity of China’s energy consumption from 1980 to 2003 using Divisia index decomposition method. They found that the reduction of energy intensity was of decisive significance for the carbon intensity reduction, and the proportion of coal in primary energy should be further cut in the future. Based on the panel data of 48 states in the United States, Davidsdottir and Fisher [
7] studied the correlation between carbon intensity and economic development during 1980–2000. They concluded that there was a clear bi-directional relation between carbon intensity and economic development; that is to say, maintaining rapid economic growth and reducing carbon intensity can occur simultaneously. This conclusion was consistent with the empirical study on the influence factors of carbon intensity in China, namely economic development was conducive to the reduction of carbon intensity [
8]. The empirical study also indicated that the decline in the proportion of secondary industries was conducive to lower the carbon intensity. Zhang et al. [
9] explored the driving factors of carbon intensity of China’s 29 provinces from 1995 to 2012 employing the Logarithmic Mean Divisia Index (LMDI) method, and revealed that energy utilization technology progress and energy structure optimization were the two major driving forces for the decline of carbon intensity in the second and tertiary industries. In addition, Yi [
10] adopted fixed-effect panel regressions to test the impacts of clean-energy policies on carbon emissions of electricity sector in the U.S. states, and found that supply-side energy policy was conducive to the reduction of carbon intensity and more aggressive policies on the demand side were needed to reduce total carbon emissions in the U.S. electricity sector. Compared with the analysis of the influencing factors of carbon intensity, only a few studies have been conducted to calculate carbon intensity reduction potential. These studies tend to focus on the national level, whereas there is less research on the calculation of carbon intensity reduction potential of provinces. Wang et al. [
11] employed Markov chain model to predict China’s carbon intensity trend in 2011–2020, and then the contribution of optimizing energy structure on carbon intensity reduction was evaluated. Their finding showed that optimization of energy structure would promote the achievement of carbon intensity target under various scenarios. From the perspective of the development of thermal power, Liu et al. [
12] predicted China’s carbon intensity by 2020, and demonstrated that China could not reach their carbon intensity reduction target according to the current development trends of thermal power. However, the total amount of carbon emissions were calculated by carbon emissions of thermal power, there is a certain error in prediction results. Aim to explore carbon intensity in the context of economic growth and energy structure adjustment, Zhu et al. [
13] analyzed the quantitative relationship between economic growth and energy consumption using cointegration theory. Their finding suggested that China could achieve reduction targets by 2020 under different scenarios. Long et al. [
14] estimated the reduction potential of carbon intensity of Jiangsu Province in 48 scenarios using improved Human Impact Population Affluence Technology (IPAT) model, and the results indicated that only the northern and southern parts of Jiangsu province would accomplish the 40%–45% reduction target for carbon intensity in 2020 in all scenarios. In light of the Chinese government’s latest estimates, the average annual economic growth rate is expected to be 6.5% in 2015–2020. However, most of the literature generally considered the average annual growth rate for the period to remain at about 7% in the calculation of carbon intensity reduction potential. This overly optimistic forecast will result in larger errors in the future scenario settings. Therefore, new literature is needed to compensate for this deficiency.
Carbon intensity is equal to the ratio of carbon dioxide emissions to GDP in a country or region during a certain period; therefore, the existing studies mainly focus on the prediction of carbon emissions. The prediction method of carbon emissions mainly comprises the scenario analysis method, the Stochastic Impacts by Regression on Population, Affluence and Technology (STIRPAT) method and time series prediction method. Hao et al. [
15] employed scenario analysis method to predict the greenhouse gases emissions of China’s passenger vehicles during 2014–2020, and demonstrated that the current implementation of carbon mitigation and energy consumption policies played a positive role in preventing the growth of emissions. Taking population, per capita GDP, energy intensity and the level of urbanization as the influencing factors, Wang et al. [
11] constructed the STRIPAT model to predict the carbon emissions of Minhang District in 2015. Their finding indicated that Minhang District would reach the minimum emission in this circumstance where per capita GDP maintained a high growth rate and energy intensity decreased at a high speed and population growth rate and urbanization rate remained moderate. With an improved mixed nonlinear grey prediction model, Wang et al. [
16] predicted carbon intensity in Chinese provinces and various sectors of the economy in 2020, and allocated abatement tasks in various provinces and departments according to the principle of minimizing the cost of emission reduction.
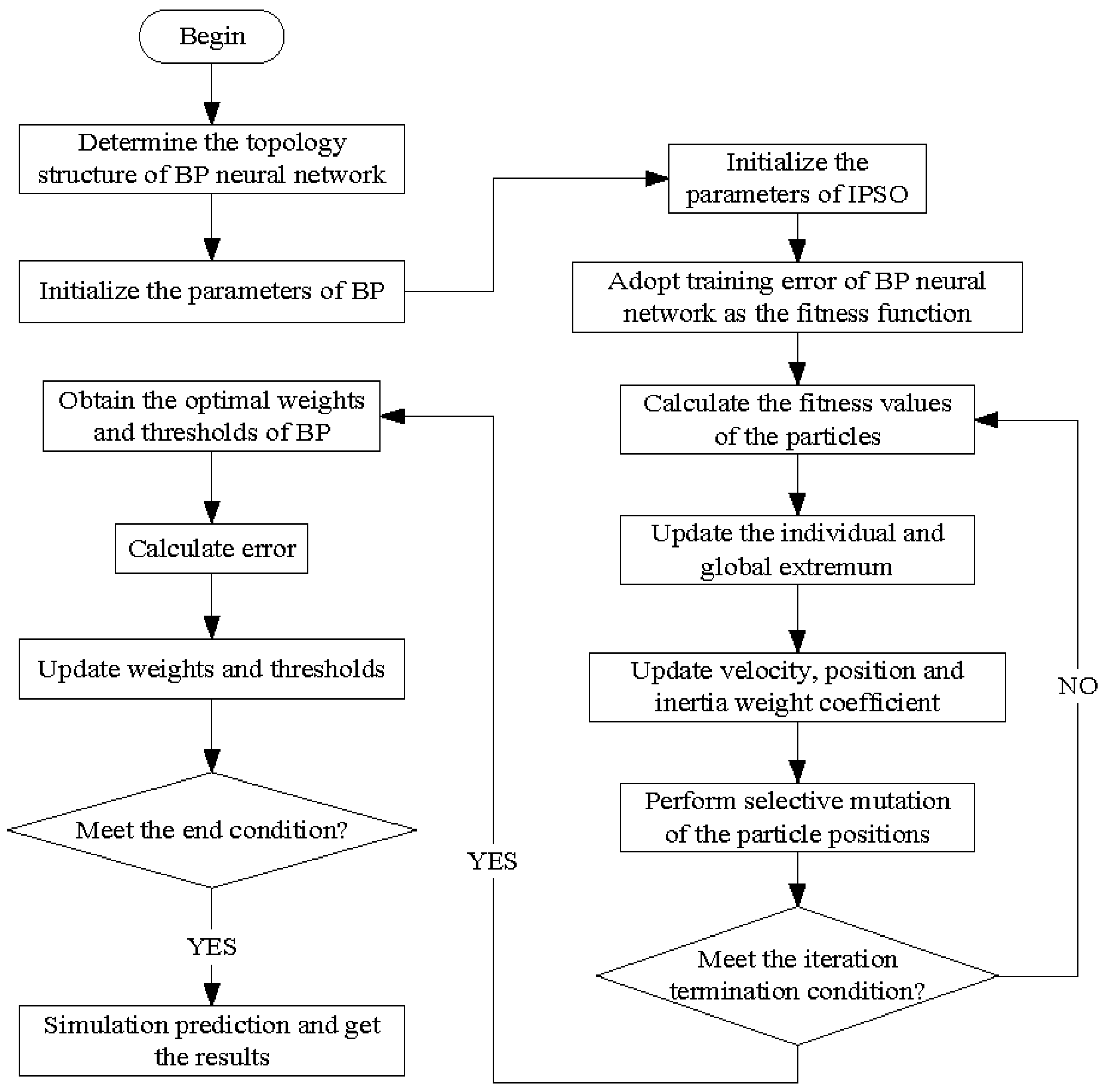
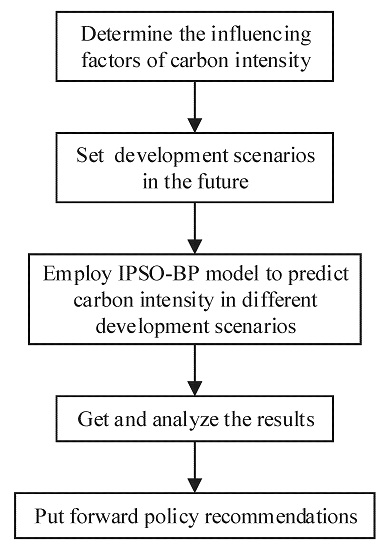
Scenario analysis is a kind of method to forecast probable events that can occur in the future. It can be used to compare the carbon emissions under different scenarios, however, large errors exist in the prediction results of the method. In the STIRPAT model, the effects of population, economy and technology on carbon emissions are taken into consideration. However, the prediction error caused by the multicollinearity of influencing factors cannot be avoided. Time series prediction method ignores the causal relationship between things and assumes that the development trend of things will continue in the future, therefore it only applies to the relatively short-term prediction. Aiming at the problems existing in the above methods, the back propagation (BP) neural network optimized by improved particle swarm optimization algorithm (IPSO) combined with scenario analysis method are proposed to forecast the carbon emissions and carbon intensity in Beijing in this paper. Because of the favorable self-organization and nonlinear mapping ability, BP neural network is suitable to predict carbon emissions of nonlinear systems affected by many factors. In order to enhance the global search ability and convergence ability of BP neural networks, IPSO is introduced to optimize the initial connection weights and thresholds of BP neural network, hereafter referred to as IPSO-BP. The IPSO-BP model not only makes full use of the global search ability of IPSO and local optimization capability of BP neural network, but also overcomes the intrinsic defects of BP neural network. In order to present the details of the measurement of carbon emissions reduction potential in Beijing, the rest of this paper will be deployed as follows. Firstly, based on the analysis of the influence factors of carbon emissions in Beijing using the grey relational analysis method (GRA), this paper takes GDP, resident population size, energy structure, industrial structure, technical level as the indicators to set the development scenarios of Beijing in the years 2015–2020. Secondly, the IPSO-BP model is adopted to calculate the carbon intensity reduction potential under different development scenarios. Finally, according to the results of the calculation, the policy recommendations are provided to exploit the potential of carbon emissions reduction in Beijing.
3. Description of Scenarios
According to the results of grey relational analysis, this study set scenarios for economic growth, resident population growth, energy structure adjustment, industrial structure adjustment, and technical progress based on different economic growth rates, resident population growth rates, energy structure adjustment rates, industrial structure adjustment rates and technical progress rates. Based on diverse economic growth rate, this study set three series: a low economic growth rate, a medium economic growth rate, and a high economic growth. Moreover, this study set medium and low rates of resident population growth, high and medium rates of energy structure adjustment, medium and low rates of industrial structure adjustment, and medium and low rates of technical progress. The details of scenario settings are described as follows.
3.1. Economic Growth
With economic expansion having moderated to a “new normal” pace, economic growth of Beijing showed a downward trend year by year during the Twelfth Five-Year Plan, and economic growth is expected to continue to decline in the future [
35]. However, because of the driving effect of innovation to economic growth and the implementation of Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei regional integration and The Belt and Road Initiative, Beijing still has the potential to maintain medium-to-high growth of economy. In the government work report of 2016, the GDP annual average growth rate for Beijing was set at 6.5% in the Thirteenth Five-Year Plan [
36]. Taking into account the actual situation of economic development and the economic plan of the government, the economic growth rate of Beijing is set to high, medium and low categories from 2015 to 2020 (
Table 1).
3.2. Resident Population Growth
In light of the statistical yearbook of Beijing, the average annual growth rate of the resident population in Beijing was 2% during the Twelfth Five-Year Plan, and the rate decreased year by year. Moreover, the government announced that the number of resident population would be controlled within 23 million during the Thirteenth Five-Year Plan. However, due to the obvious location advantages and resource advantages, the future population of Beijing will continue to maintain a rigid growth. Therefore, the population growth rate in Beijing is set to the medium and low categories from 2015 to 2020 (
Table 2).
3.3. Energy Structure
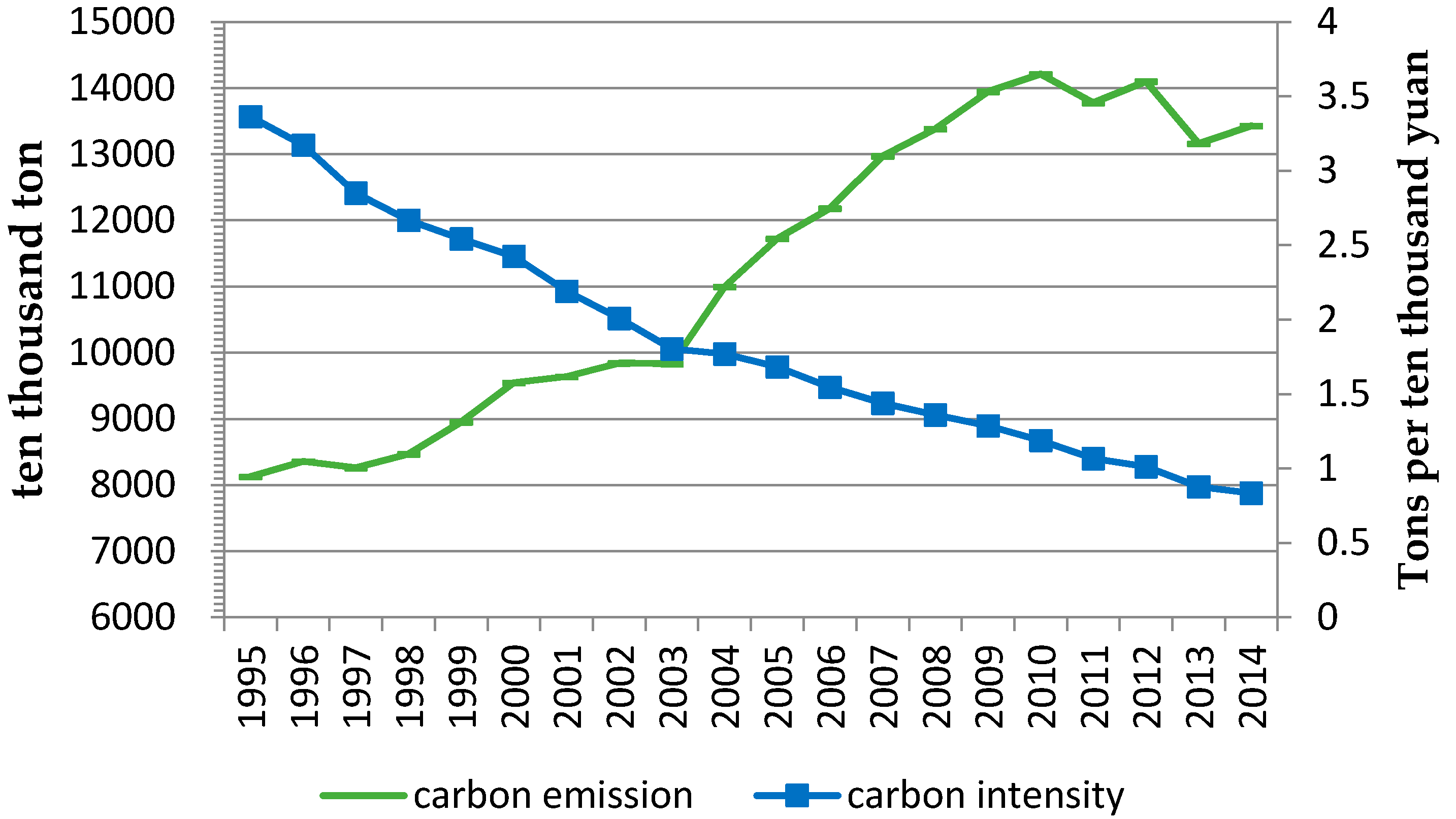
According to the statistical yearbook of Beijing, coal consumption of Beijing accounted for the proportion of total primary energy consumption is 18.16% in 2014, and the ratio decreased by 66.63% compared to 1995. Because coal not only has a higher carbon emission coefficient but also causes haze easily, the government of Beijing plans to control the amount of coal consumption below nine million tons in 2020. Furthermore, the government of Beijing plans to make the total amount of energy consumption less than 88 million tons of standard coal in 2020 and make the proportion of high-quality energy increased to about 92% [
37]. Therefore, the energy structure adjustment rate in Beijing is set to the high and medium categories from 2015 to 2020 (
Table 3).
3.4. Industrial Structure
The tertiary industry output value of Beijing accounted for 77.9% of the GDP by 2014. With the promotion of Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei regional integration, the government more actively promotes the transition from industrial economy to the service economy and transfer of the secondary industry to the surrounding areas. Therefore, this study expects the proportion of tertiary industry will continue to ascend. Given the proportion of tertiary industry is already at the high level, its future growth will gradually slow down. Therefore, the industrial structure adjustment rate in Beijing is set to the medium and low categories from 2015 to 2020 (
Table 4).
3.5. Technical Progress
Beijing achieved an average annual economic growth of 8.6% in context of an average annual energy consumption growth of 2.5% from 2008 to 2014. The energy intensity fell by 23.66% during the Twelfth Five-Year Plan, which exceeded the energy intensity reduction targets of 17%. The energy intensity reduction target is set to 15% by government during the Thirteenth Five-Year Plan. Moreover, with the upgrade of the industrial structure, the optimization of energy structure and growing pressure on energy-saving and emission reduction, energy intensity will continue to decline in the future. Therefore, the technical progress rate in Beijing is set to the medium and low categories from 2015 to 2020 (
Table 5).
As shown in
Table 6, based on the varying economic growth rates, this study sets three main scenarios for Beijing: the base development scenario (BD), the optimized development scenario (OD), and the strengthened development scenario (SD). By combining the three main scenarios with each change rate of the five indexes set out above, 48 series are contained in this paper.
4. Results and Discussion
The combination of scenarios was taken as the predictive inputs of the IPSO-BP neural network to forecast carbon emissions in different scenarios in Beijing, and then the carbon emissions were divided by the corresponding GDP to get the carbon intensity. The carbon intensity of Beijing in different scenarios was as follows.
4.1. Calculation of Carbon Intensity in Based Development Scenarios
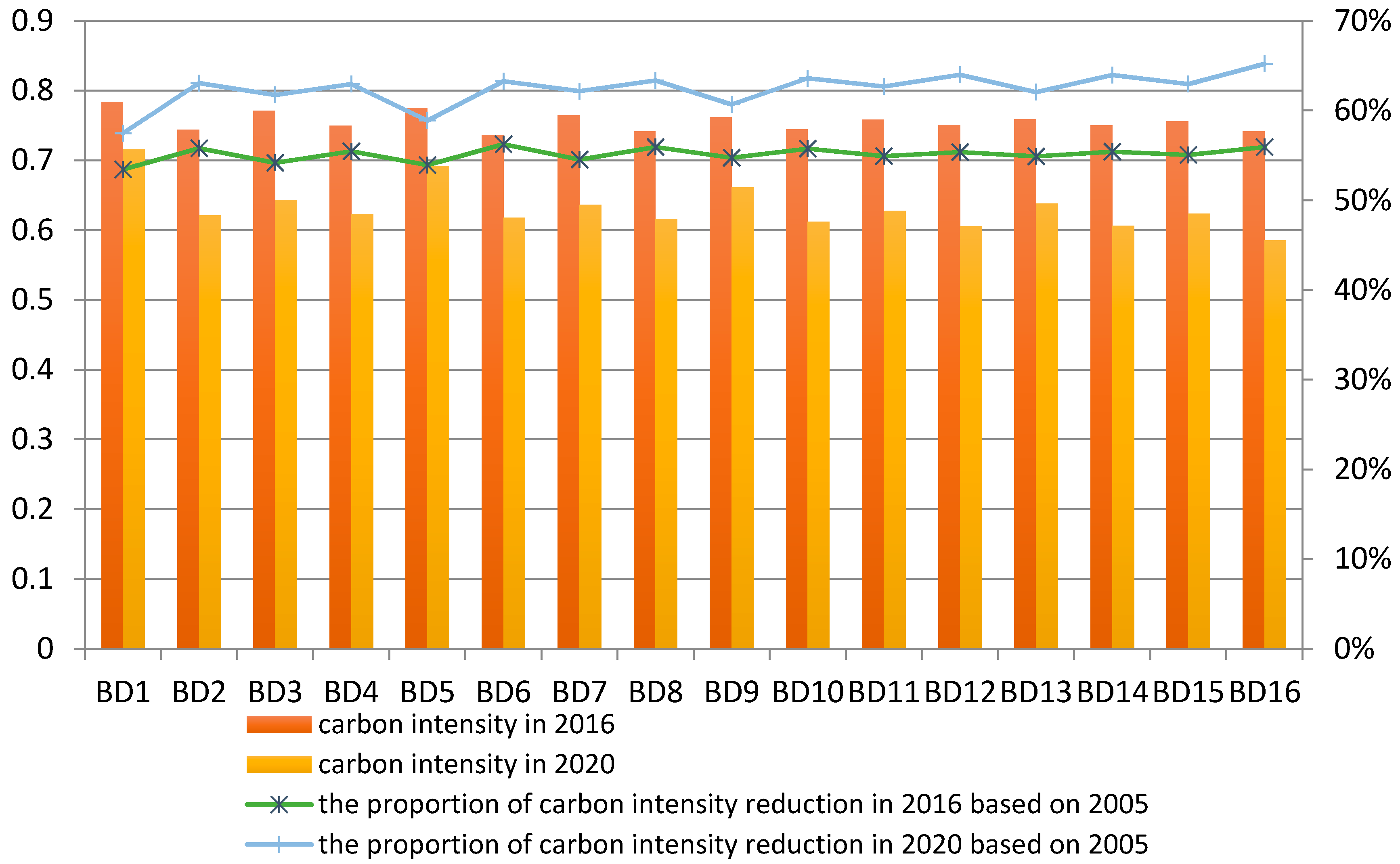
The base development scenarios comprised 16 kinds of series, and the economic development of these series was set at the low rate. The predicted values of carbon intensity and the proportion of carbon intensity reduction of Beijing in 2016 and 2020 are shown in
Figure 4.
The prediction results revealed that the potential of carbon intensity reduction was above 53% in 2016 and above 55% in 2020 in the based development scenarios. The potential of carbon intensity reduction can exceed the 40%–45% reduction target of carbon intensity in 2020 in all series. For the prediction values of 2016 and 2020, carbon intensity would reach the peak in scenarios BD1, and the potential of carbon intensity reduction would achieve the minimum value in scenarios BD1, in which the resident population growth rate was at the medium level and the change rate of energy structure, industrial structure and technical progress were at the low level. In addition, carbon intensity would reach the minimum value in scenarios BD16, and the potential of carbon intensity reduction would be at the peak in scenarios BD16, in which the resident population growth rate was at the low level and the change rate of energy structure, industrial structure and technical progress were at the high level, medium level and medium level, respectively. The prediction results showed that the lower population growth rate, the higher energy structure adjustment rate, the higher industrial structure adjustment rate and the higher technical progress rate were conducive to the decline of carbon intensity, but the contribution of these influencing factors to carbon intensity was different. Through the comparison of BD2 and BD3, BD6 and BD7, BD11 and BD10, BD15 and BD14, the contribution of technical progress on carbon intensity reduction was 2.2 times higher than that of industrial structure adjustment. Through the comparison of BD3 and BD5, and BD11 and BD13, the contribution of energy structure adjustment on the carbon intensity reduction was 21% higher than that of the industrial structure adjustment. Although the rate of energy structure adjustment was greater than that of technical progress, the comparison of BD1 and BD6, and BD9 and BD14 showed that the contribution of technical progress on carbon intensity reduction was 1.4 times higher than that of energy structure adjustment. The growth of resident population went against the reduction of carbon intensity, the comparison of BD1 and BD9 indicated that if the resident population growth rate increased by 0.1%, the carbon intensity in 2020 would increase by 0.8%.
4.2. Calculation of Carbon Intensity in Optimized Development Scenarios
The optimized development scenarios contained 16 kinds of series, and the economic development of these series was set at the medium rate. The predicted values of carbon intensity and the proportion of carbon intensity reduction of Beijing in 2016 and 2020 are shown in
Figure 5.
The prediction results indicated that the potential of carbon intensity reduction was above 53% in 2016 and above 57% in 2020 in the optimized development scenarios. The potential of carbon intensity reduction can exceed the reduction target of China in 2020 in 16 kinds of series. For the prediction values of 2016 and 2020, carbon intensity would reach the peak in scenarios OD1, and the potential of carbon intensity reduction would achieve the minimum value in scenarios OD1, in which the resident population growth rate was at the medium level and the change rate of energy structure, industrial structure and technical progress were at the low level. Furthermore, carbon intensity would reach the minimum value in scenarios OD16, and the potential of carbon intensity reduction would reach the peak in scenarios BD16, in which the resident population growth rate was at the low level and the change rate of energy structure, industrial structure and technical progress were at the high level, medium level and medium level respectively. Although the forecast results showed that the lower population growth rate, the higher energy structure adjustment rate, the higher industrial structure adjustment rate as well as the higher technical progress rate were conducive to the decline of carbon intensity, the contribution of these influencing factors to carbon intensity was different. Through the comparison of OD2 and OD3, OD6 and OD7, OD11 and OD10, and OD15 and OD14, the contribution of technical progress on carbon intensity reduction was 2.1 times higher than that of industrial structure adjustment. Through the comparison of OD3 and OD5, and OD11 and OD13, the contribution of energy structure adjustment on the carbon intensity reduction was 23% higher than that of the industrial structure adjustment. Although the rate of energy structure adjustment was greater than that of technical progress, the comparison of OD1 and OD6, and OD9 and OD14 revealed that the contribution of technical progress on carbon intensity reduction was 1.7 times higher than that of energy structure adjustment. Similar to the based development scenario, the growth of resident population was not conducive to the reduction of carbon intensity, and the comparison of BD1 and BD9 indicated that if the resident population growth rate increased by 0.1%, the carbon intensity in 2020 would increase by 0.7%.
4.3. Calculation of Carbon Intensity in Strengthened Development Scenarios
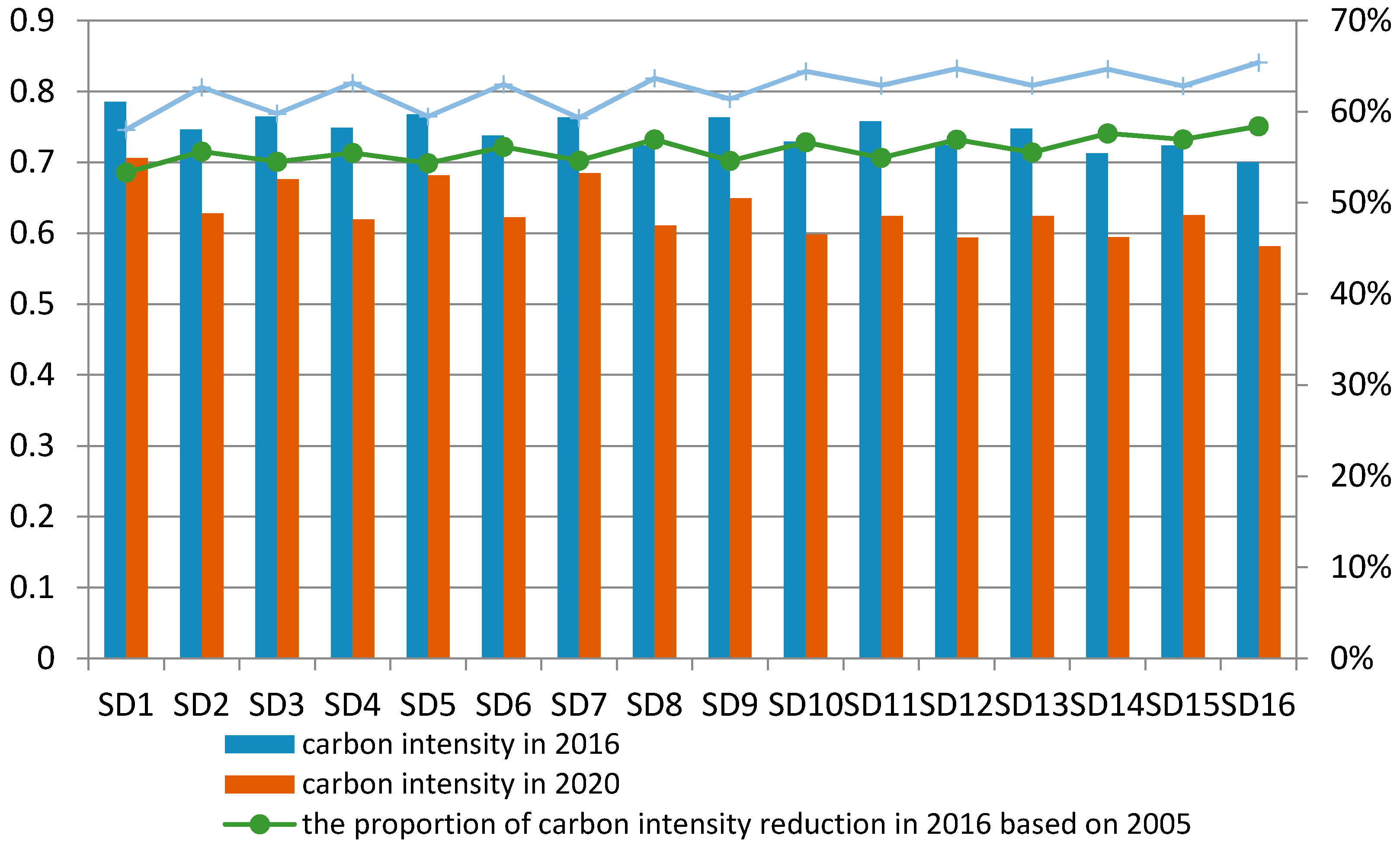
The strengthened development scenarios were comprised by 16 kinds of series, and the economic development of these series was set at the high rate. The predicted values of carbon intensity and the proportion of carbon intensity reduction of Beijing in 2016 and 2020 are shown in
Figure 6.
The prediction results showed that the potential of carbon intensity reduction was more than 53% in 2016 and more than 55% in 2020 in the strengthened development scenarios. The potential of carbon intensity reduction can exceed the 40%–45% reduction target of carbon intensity in 2020 in all series. As far as the prediction values of 2016 and 2020 were concerned, carbon intensity would reach the peak in scenarios SD1, and the potential of carbon intensity reduction will achieve the minimum in scenarios SD1, in which the resident population growth rate was at the medium level and the change rate of energy structure, industrial structure and technical progress were at the low level. In addition, carbon intensity would reach the minimum value in scenarios SD16, and the potential of carbon intensity reduction would be at the peak in scenarios SD16, in which the resident population growth rate was at the low level and the change rate of energy structure, industrial structure and technical progress were at the high level, medium level and medium level respectively. The prediction results demonstrated that the lower population growth rate, the higher energy structure adjustment rate, the higher industrial structure adjustment rate and the higher technical progress rate contributed to lower carbon intensity. Nevertheless, the contribution of these influencing factors to carbon intensity was diverse. Through the comparison of SD2 and SD3, SD6 and SD7, SD11 and SD10, and SD15 and SD14, the contribution of technical progress on carbon intensity reduction was 2.2 times higher than that of industrial structure adjustment. Through the comparison of BD3 and SD5, and SD11 and SD13, the contribution of energy structure adjustment on the carbon intensity reduction was 15% higher than that of the industrial structure adjustment. Although the rate of energy structure adjustment was greater than that of technical progress, the comparison of SD1 and SD6, and SD9 and BD14 revealed that the contribution of technical progress on carbon intensity reduction was 1.6 times higher than that of energy structure adjustment. The growth of resident population went against the reduction of carbon intensity: the comparison of SD1 and SD9 indicated that if the resident population growth rate increased by 0.1%, the carbon intensity in 2020 would increase by 0.9%.
4.4. Comparison of Scenarios
Through comparison of the three development scenarios, we found that if the economic growth rate increased by 0.1%, the carbon emissions in 2020 would increase by 0.24%. However, there was no consistent relationship between carbon intensity and economic growth, and higher economic growth did not necessarily lead to higher carbon intensity. All three main scenarios demonstrated that the higher resident population growth meant the higher carbon intensity and the smaller potential of carbon intensity reduction. The contribution of technical progress to carbon intensity reduction was higher than the contribution of industrial structure adjustment in all of the scenarios. This might be attributed to the fact that the average annual change rate of technical progress and industrial structure adjustment were 3.65% and 0.65%, respectively. The contribution of energy structure adjustment to carbon intensity reduction was higher than that of industrial structure adjustment in three main scenarios. This might be attributed to the fact that the average annual adjustment rates of industrial structure and energy structure were 0.65% and 8%, respectively. The adjustment rate of industrial structure was less than energy structure. Although the energy structure adjustment rate was greater than the technical progress rate in three main scenarios, the contribution of energy structure adjustment to carbon intensity reduction was less than that of technical progress, which could be explained as follow: technical progress represents a decline in overall energy intensity; but the proportion of coal in primary energy consumption was only 18.16% in 2014; compared with the technical progress, the larger adjustment rate of energy structure cannot bring about the greater contribution to carbon intensity reduction. In conclusion, the energy structure adjustment and the technical progress made the greatest contribution to carbon intensity reduction, and they were the key factors of carbon intensity reduction for Beijing.
5. Conclusions and Policy Implications
5.1. Conclusions
In this study, IPSO-BP model was employed to calculate the carbon intensity of Beijing in 2016 and 2020. Based on different economic growth rates, resident population growth rates, energy structure adjustment rates, industrial structure adjustment rates and technical progress rates, this study set 48 development scenarios to explore the key influencing factors to the potential of carbon intensity reduction in 2016 and 2020.
From the analysis above, it can be concluded that Beijing can exceed the national target that carbon intensity will be reduced by 40%–45% by 2020 based on the 2005 level. The minimum carbon intensity reduction potential is 57.46%, which appears in the scenario OD1. The maximum carbon intensity reduction potential is 65.43%, which appears in the scenario SD16. In the three main scenarios, the lower resident population growth rate, the higher energy structure adjustment rate, the higher industrial structure adjustment rate and the higher technical progress rate will bring about the greater carbon intensity reduction potential, and energy structure adjustment and technical progress are the two major driving factors to carbon intensity decline.
5.2. Policy Implications
Based on the above conclusions, the following policy recommendations can be given to Beijing.
First of all, energy intensity should be kept falling, and comprehensive utilization efficiency of energy should be kept improving. Beijing should continue to promote energy conservation and emission reduction and further improve energy efficiency standards for different industries. Considering that the proportion of the tertiary industry in Beijing in 2014 has reached 77.9%, more attention should be given to energy efficiency in the tertiary industry, and the higher standards of energy efficiency should be formulated for key fields such as buildings, appliances and vehicles. In addition, Beijing should make full use of its rich resources of Higher Learning Institutions and further improve the level of cooperation between universities and enterprises to speed up the conversion efficiency of technology. Given that the developed countries have accumulated rich experience in energy-saving and emission-reduction, it is wise to learn experience and technologies from forerunners [
38].
Secondly, energy structure should be kept optimizing. Effective measures are needed to further reduce the proportion of coal in primary energy and increase the consumption ratio of clean energy at the same time. The widely application of gas in households, industry and transport should be accelerated, as well as replacing coal with natural gas for heating in winter. Moreover, the proportion of coal-fired power generation should be lowered, and the vigorous development of non-coal power including gas, nuclear, wind, solar and waste incineration should be encouraged. The government should continue to provide tax incentives and financial subsidies to promote the development of renewable energy represented by wind energy and solar energy. The government should cooperate with the China State Grid Corp to accelerate the development of smart grid and distributed generation system to solve the difficult problem faced by renewable energy, such as hard to access the grid and high electric price level.
Thirdly, Beijing should continue to raise residents’ awareness of low-carbon and maintain a moderate speed of economic development to prevent the further growth of carbon emissions. Considering that the Chinese government pledged to reach the carbon emissions peak no later than 2030 at the climate conference in Paris, it is better for Beijing to convert the focus of carbon emissions reduction from carbon intensity to carbon emissions and promote carbon emissions reduction by means of market mechanism and administrative means.