Laminar Flame Characteristics of C1–C5 Primary Alcohol-Isooctane Blends at Elevated Temperature
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Experimental Apparatus and Data Derivation
3. Results and Discussion
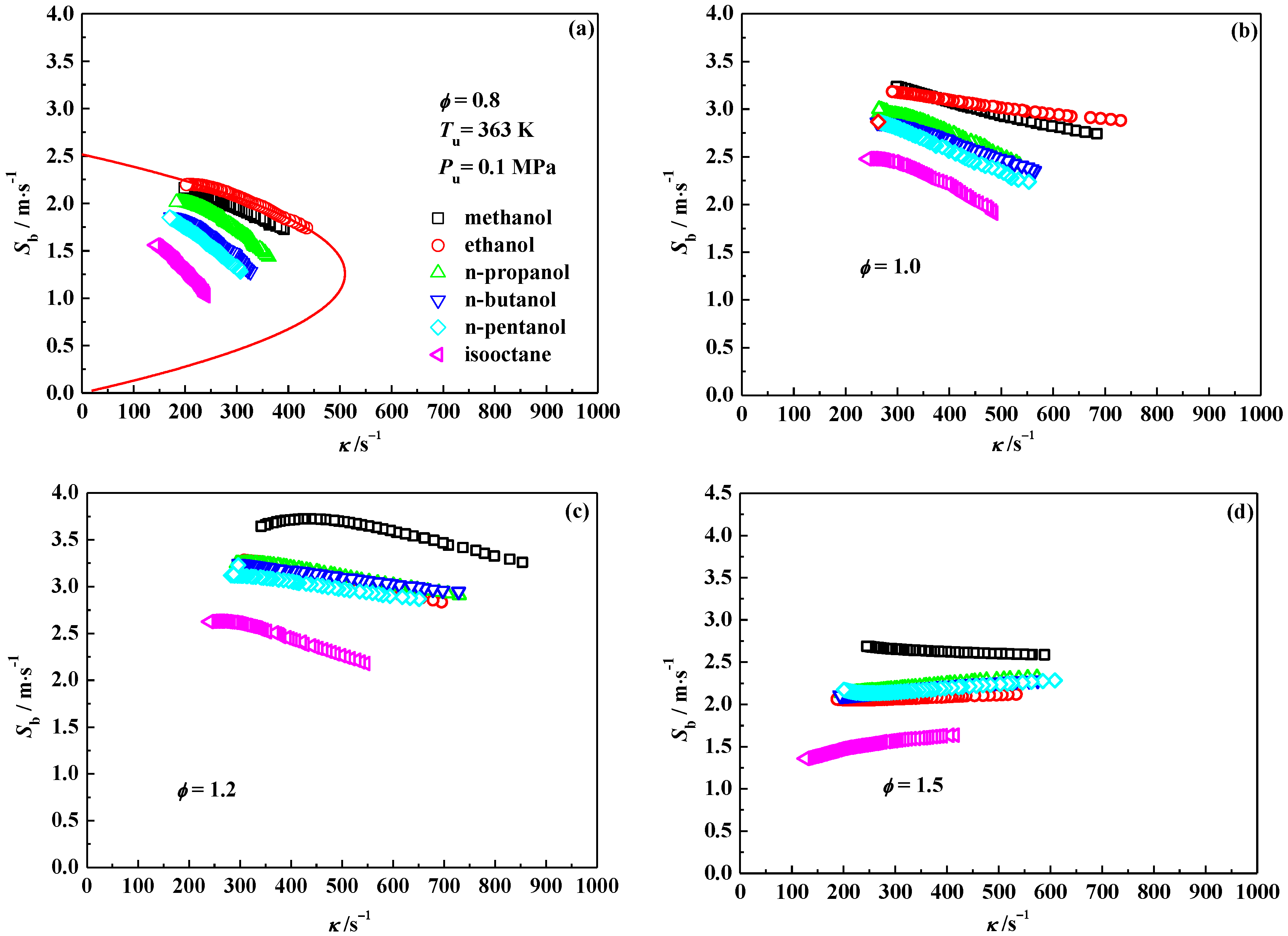
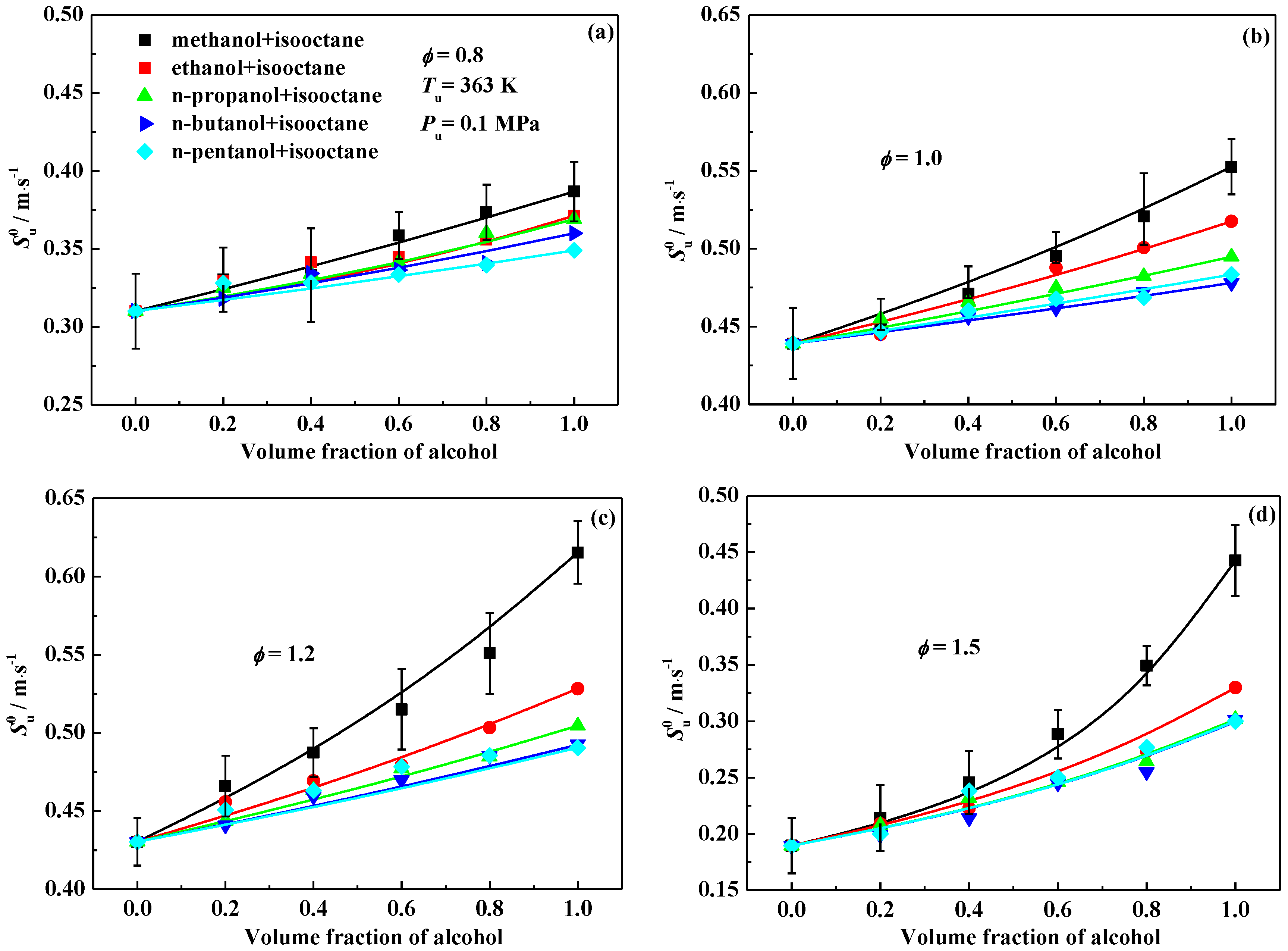
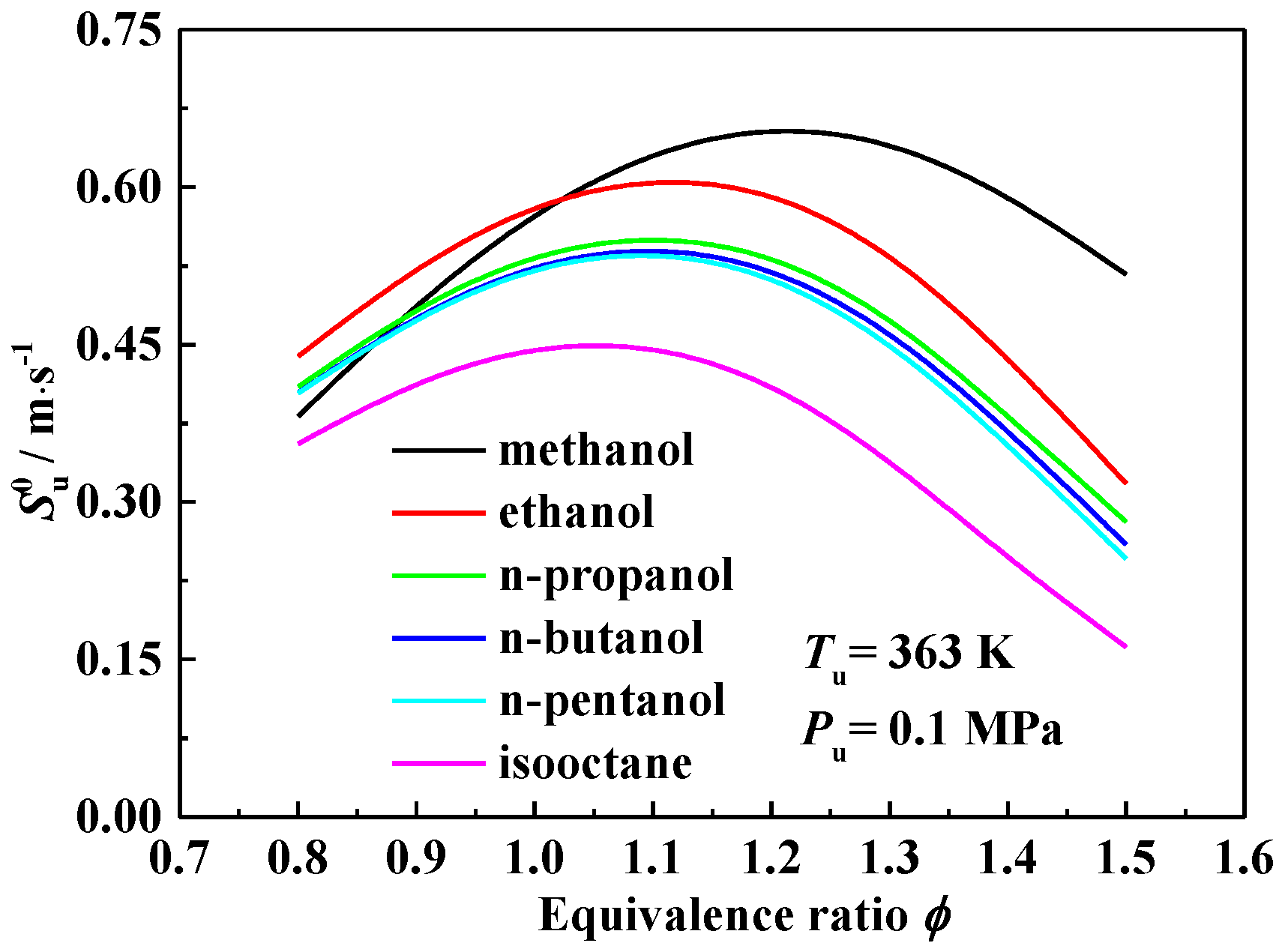
3.1. Laminar Flame Speed
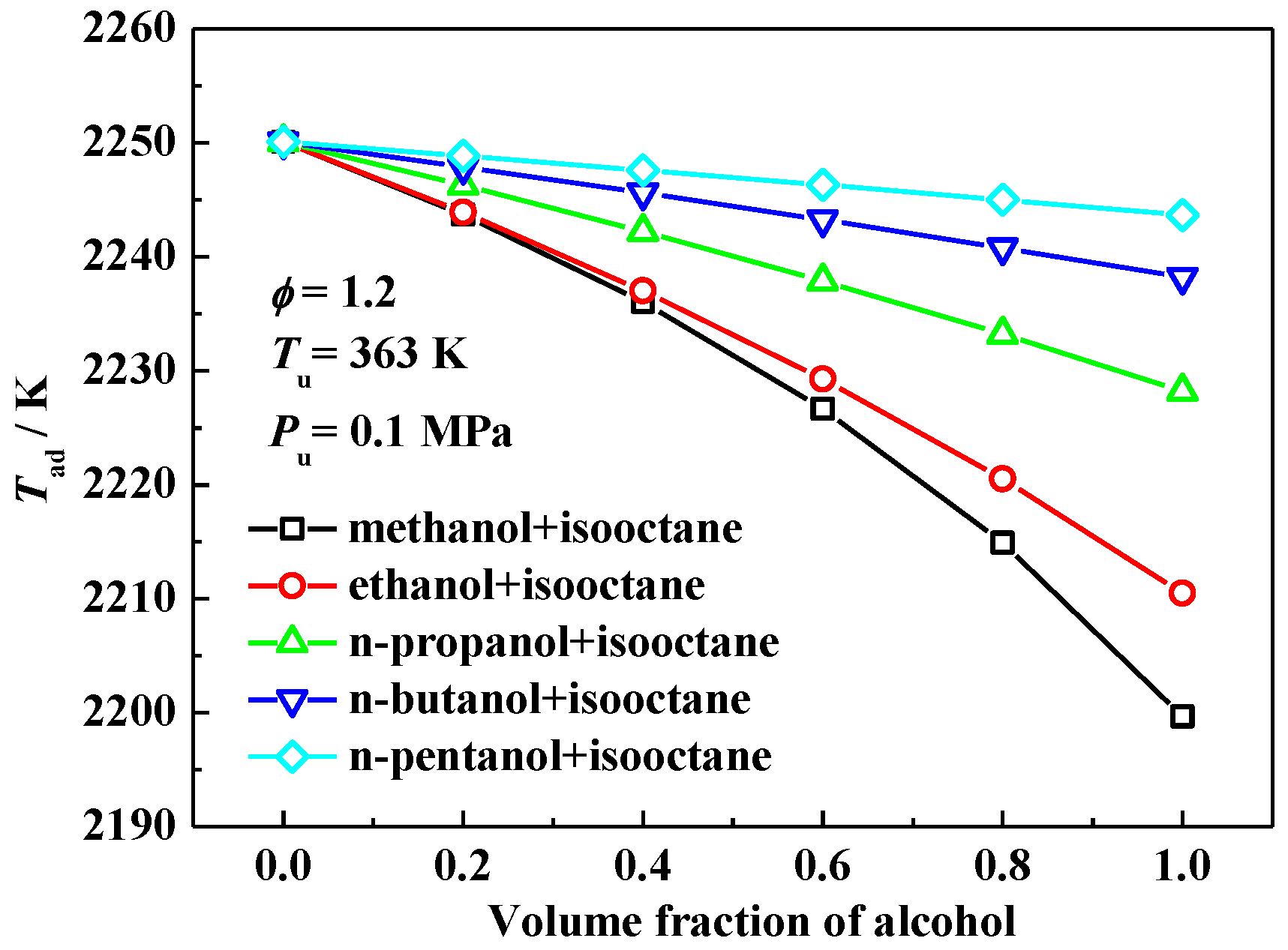
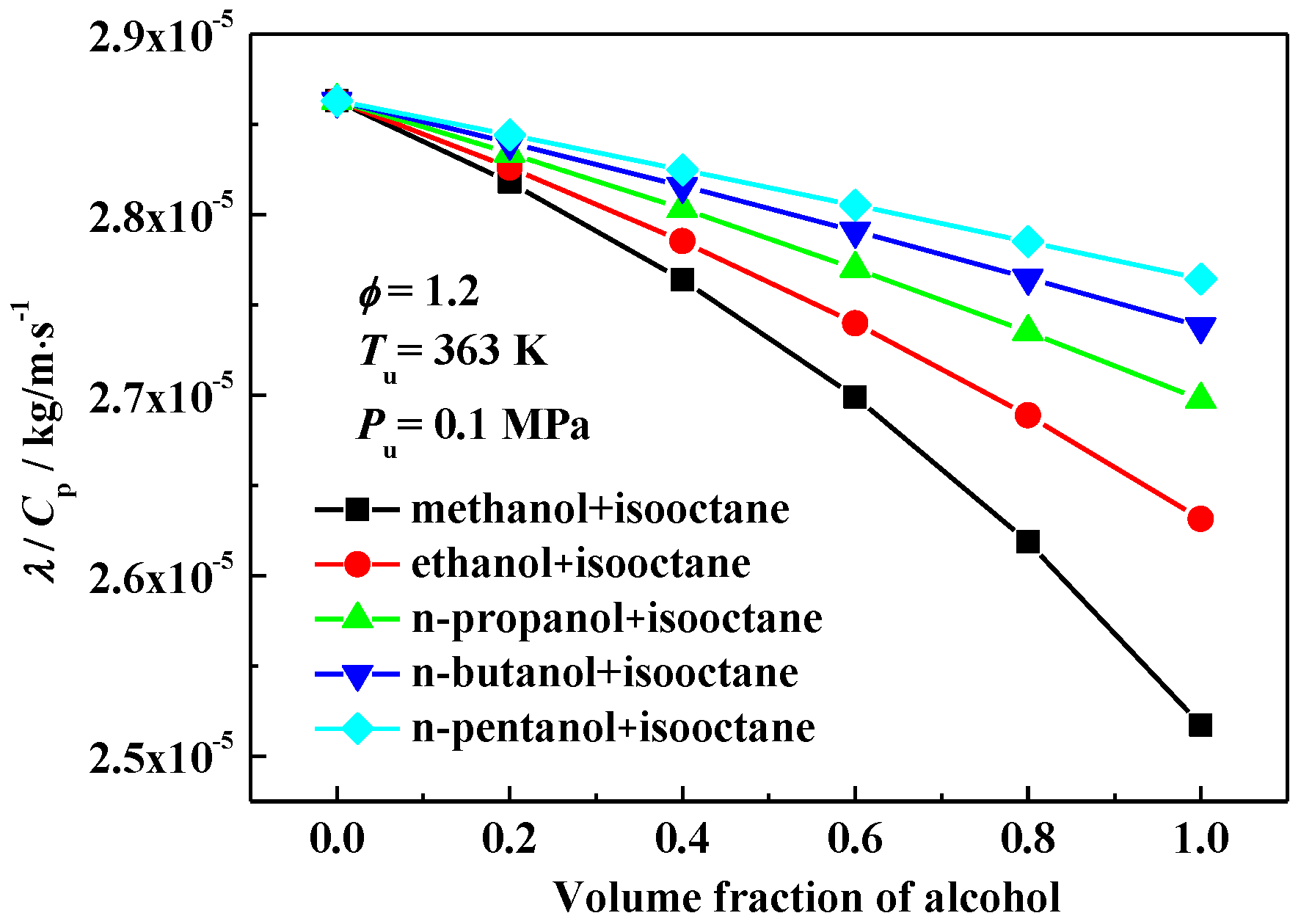
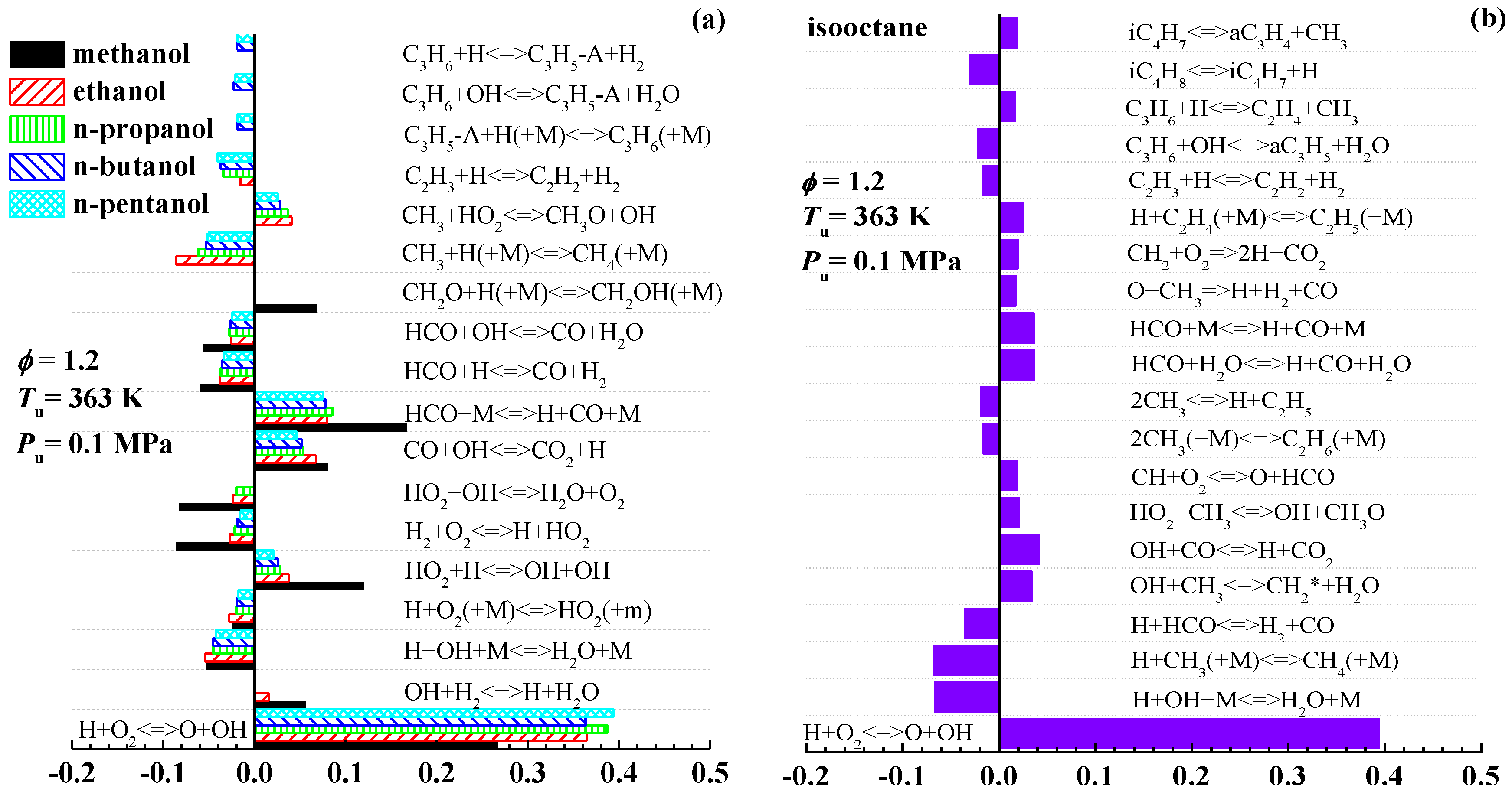
3.2. Interpretation on the Variation of Laminar Flame Speeds
3.3. The Effect of Oxygen Content
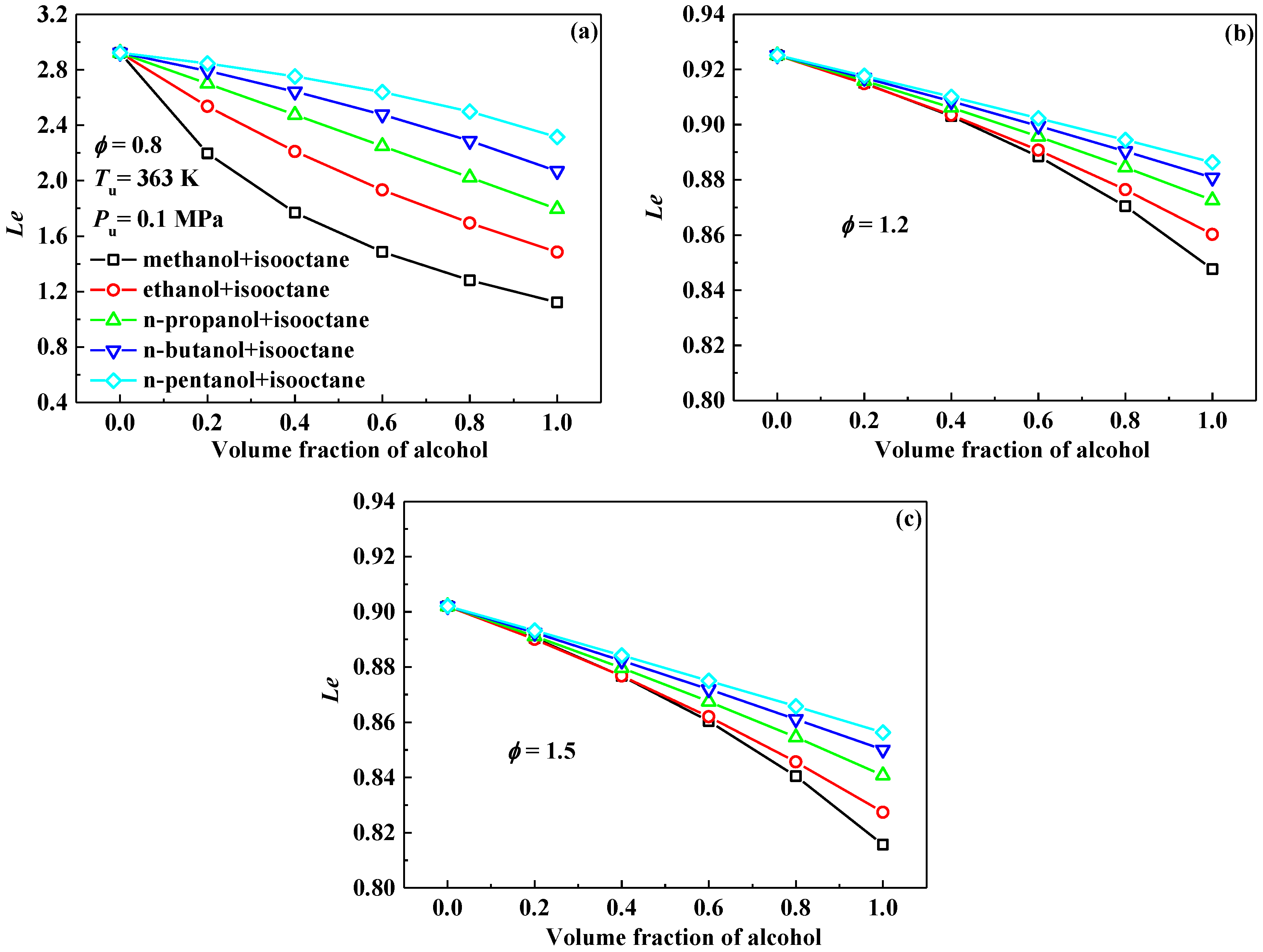
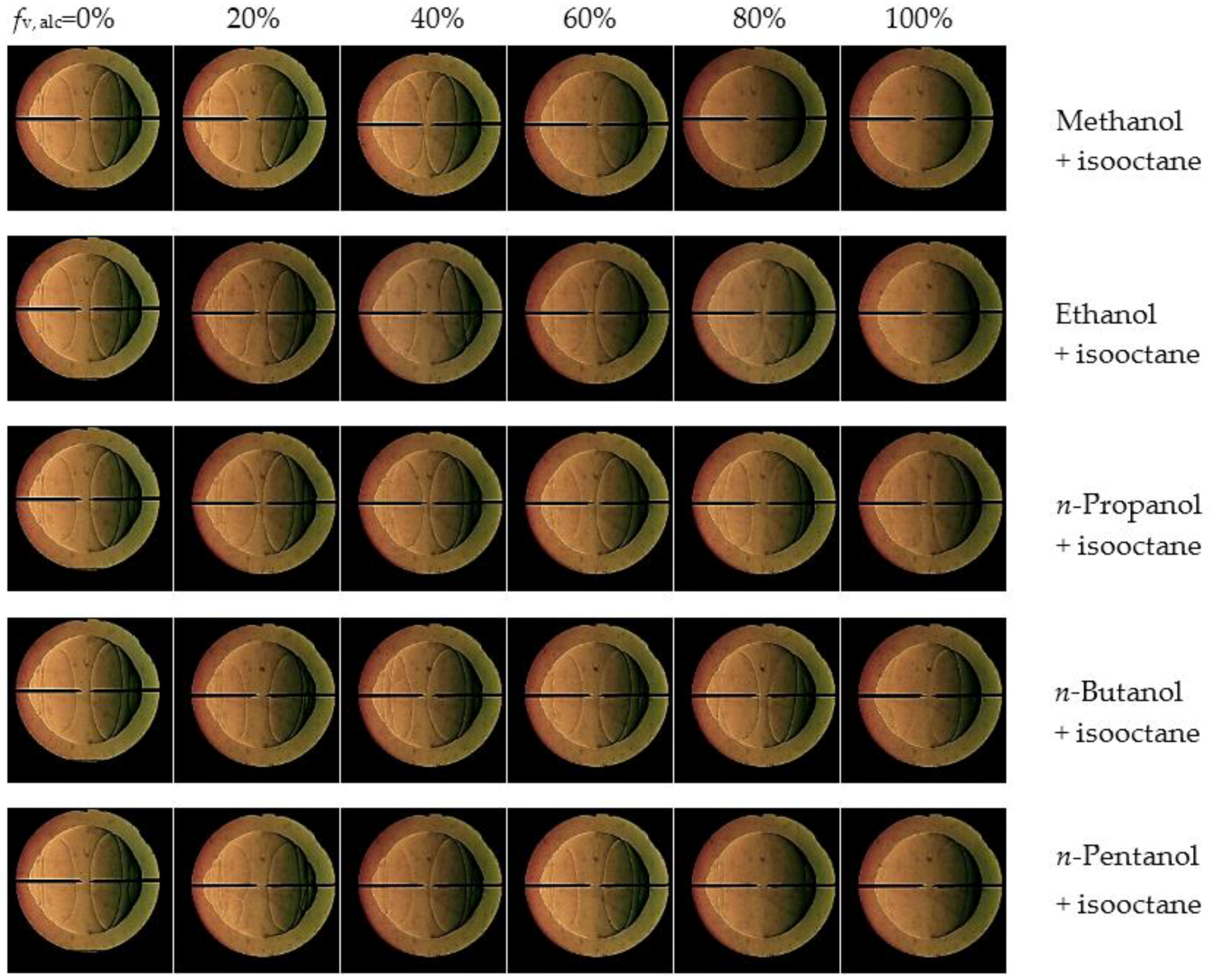
3.4. Markstein Length and Flame Instability
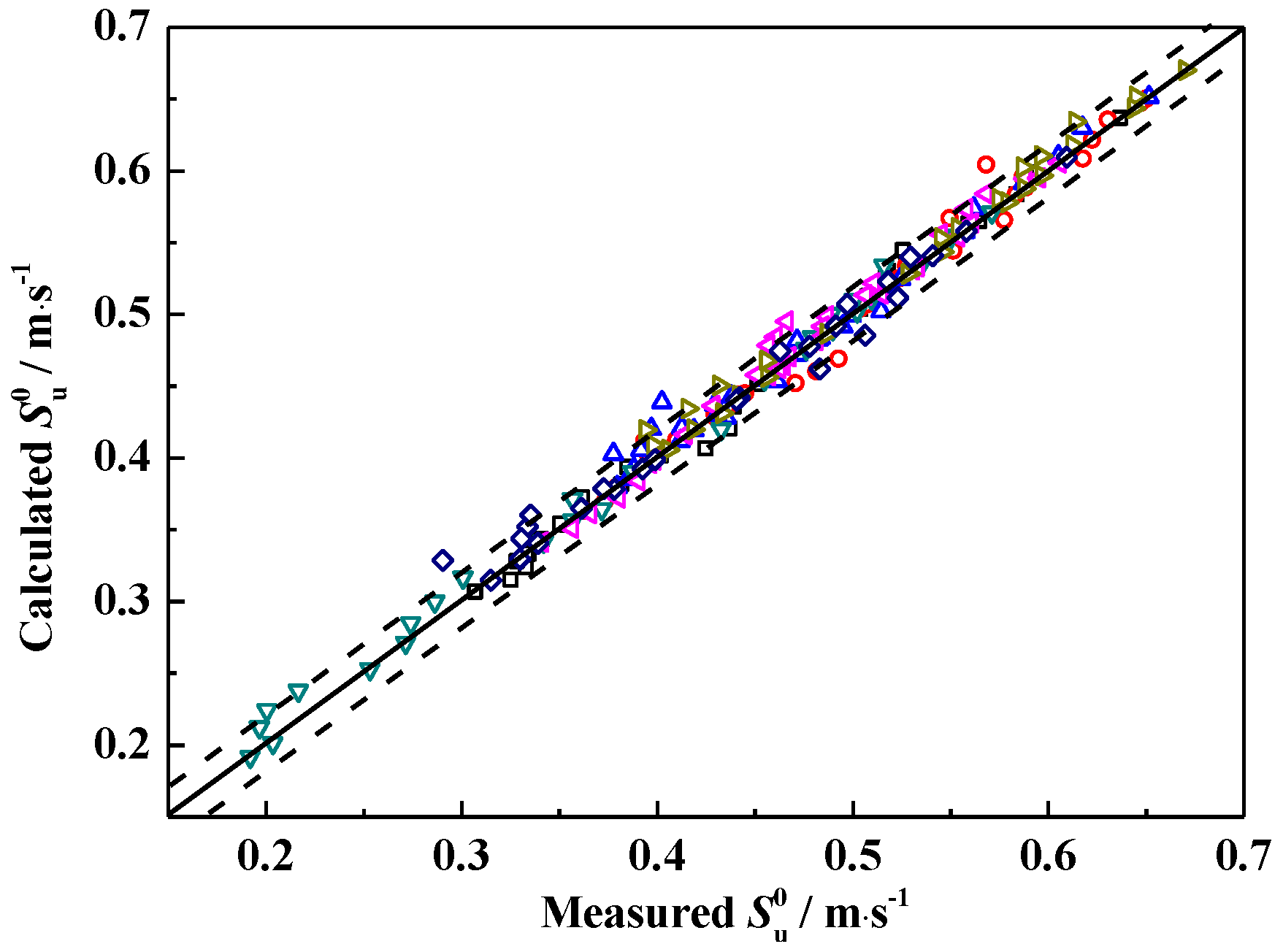
3.5. Laminar Flame Speed Correlation
4. Conclusions
- (1)
- The laminar flame speeds of alcohol-isooctane blends increase monotonously with the addition of alcohol into isooctane. At a fixed alcohol blending ratio, methanol-isooctane blends present the highest values due to the chemical kinetic effect. Ethanol addition yields a comparable laminar flame speed enhancement as the additions of n-propanol, n-butanol and n-pentanol do at 0.8 and 1.5, but stronger enhancement at 1.0 and 1.2.
- (2)
- The laminar flame speeds of the alcohol-isooctane blends increase significantly with the increasing oxygen content in the blends. At the fixed oxygen content and equivalence ratio of 0.8, the alcohol-isooctane blends exhibit similar values. At higher equivalence ratios, the addition of heavier alcohol tends to exhibit higher laminar flame speeds.
- (3)
- Markstein length displays a decreasing tendency with the addition of alcohol into isooctane at the equivalence ratios of 0.8, 1.0 and 1.2, however, it increases at 1.5. Therefore, the Lb–φ curve of the isooctane flame crosses with those of the pure C1–C5 primary alcohol flames. The equivalence ratios corresponding to the crosses are approximately 1.2–1.3.
- (4)
- An empirical correlation was provided between the laminar flame speed and the volume fraction of alcohol based on the experimental data.
Supplementary Materials
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Al-lwayzy, S.; Yusaf, T. Combustion of microalgae oil and ethanol blended with diesel fuel. Energies 2015, 8, 13985–13995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gautam, M.; Martin, D.W. Combustion characteristics of higher-alcohol/gasoline blends. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part A J. Power Energy 2000, 214, 497–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gautam, M.; Martin, D.W.; Carder, D. Emissions characteristics of higher alcohol/gasoline blends. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part A J. Power Energy 2000, 214, 165–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karavalakis, G.; Durbin, T.D.; Shrivastava, M.; Zheng, Z.; Villela, M.; Jung, H. Impacts of ethanol fuel level on emissions of regulated and unregulated pollutants from a fleet of gasoline light-duty vehicles. Fuel 2012, 93, 549–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozsezen, A.N.; Canakci, M. Performance and combustion characteristics of alcohol-gasoline blends at wide-open throttle. Energy 2011, 36, 2747–2752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Surisetty, V.R.; Dalai, A.K.; Kozinski, J. Alcohols as alternative fuels: An overview. Appl. Catal. A Gen. 2011, 404, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szwaja, S.; Naber, J.D. Combustion of n-butanol in a spark-ignition IC engine. Fuel 2010, 89, 1573–1582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yucesu, H.S.; Topgul, T.; Cinar, C.; Okur, M. Effect of ethanol-gasoline blends on engine performance and exhaust emissions in different compression ratios. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2006, 26, 2272–2278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Sung, C.J.; Eng, J.A. Laminar flame speeds of primary reference fuels and reformer gas mixtures. Combust. Flame 2004, 139, 239–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sileghem, L.; Alekseev, V.A.; Vancoillie, J.; Van Geem, K.M.; Nilsson, E.J.K.; Verhelst, S.; Konnov, A.A. Laminar burning velocity of gasoline and the gasoline surrogate components iso-octane, n-heptane and toluene. Fuel 2013, 112, 355–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foong, T.M.; Morganti, K.J.; Brear, M.J.; da Silva, G.; Yang, Y.; Dryer, F.L. The octane numbers of ethanol blended with gasoline and its surrogates. Fuel 2014, 115, 727–739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bradley, D.; Hicks, R.A.; Lawes, M.; Sheppard, C.G.W.; Woolley, R. The measurement of laminar burning velocities and markstein numbers for iso-octane–air and iso-octane–n-heptane–air mixtures at elevated temperatures and pressures in an explosion bomb. Combust. Flame 1998, 115, 126–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, S.G.; Law, C.K. Laminar flame speeds and oxidation kinetics of iso-octane-air and n-heptane-air flames. Symp. Int. Combust. 1998, 27, 521–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, C.S.; Sarathy, S.M.; Veloo, P.S.; Westbrook, C.K.; Egolfopoulos, F.N. Effects of fuel branching on the propagation of octane isomers flames. Combust. Flame 2012, 159, 1426–1436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, K.; Freeh, J.E.; Sung, C.J.; Huang, Y. Laminar flame speeds of preheated iso-octane/O2/N2 and n-heptane/O2/N2 mixtures. J. Propuls. Power 2007, 23, 428–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Fu, J.; Wu, X.; Tang, C.; Huang, Z. Laminar flame speeds of DMF/iso-octane-air-N2/CO2 mixtures. Energy Fuels 2012, 26, 917–925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Metghalchi, M.; Keck, J.C. Burning velocities of mixtures of air with methanol, isooctane, and indolene at high-pressure and temperature. Combust. Flame 1982, 48, 191–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryan, T.W.; Lestz, S.S. The laminar burning velocity of isooctane, n-heptane, methanol, methane, and propane at elevated temperature and pressures in the presence of a diluent. SAE Tech. Pap. 1980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saeed, K.; Stone, C.R. Measurements of the laminar burning velocity for mixtures of methanol and air from a constant-volume vessel using a multizone model. Combust. Flame 2004, 139, 152–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, Z.Y.; Huang, Z.H.; Wang, X.G.; Xiang, J.; Wang, X.B.; Miao, H.Y. Measurements of laminar burning velocities and markstein lengths for methanol-air-nitrogen mixtures at elevated pressures and temperatures. Combust. Flame 2008, 155, 358–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Togbé, C.; Halter, F.; Foucher, F.; Mounaim-Rousselle, C.; Dagaut, P. Experimental and detailed kinetic modeling study of 1-pentanol oxidation in a JSR and combustion in a bomb. Proc. Combust. Inst. 2011, 33, 367–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veloo, P.S.; Wang, Y.L.; Egolfopoulos, F.N.; Westbrook, C.K. A comparative experimental and computational study of methanol, ethanol, and n-butanol flames. Combust. Flame 2010, 157, 1989–2004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veloo, P.S.; Egolfopoulos, F.N. Studies of n-propanol, iso-propanol, and propane flames. Combust. Flame 2011, 158, 501–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beeckmann, J.; Cai, L.; Pitsch, H. Experimental investigation of the laminar burning velocities of methanol, ethanol, n-propanol, and n-butanol at high pressure. Fuel 2014, 117, 340–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarathy, S.M.; Oßwald, P.; Hansen, N.; Kohse-Höinghaus, K. Alcohol combustion chemistry. Prog. Energy Combust. Sci. 2014, 44, 40–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Tang, C.; Yu, H.; Huang, Z. Flame-front instabilities of outwardly expanding isooctane/n-butanol blend–air flames at elevated pressures. Energy Fuels 2014, 28, 2258–2266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Tang, C.; Yu, H.; Li, Q.; Gong, J.; Huang, Z. Laminar flame characteristics of iso-octane/n-butanol blend–air mixtures at elevated temperatures. Energy Fuels 2013, 27, 2327–2335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Broustail, G.; Halter, F.; Seers, P.; Moréac, G.; Mounaïm-Rousselle, C. Experimental determination of laminar burning velocity for butanol/iso-octane and ethanol/iso-octane blends for different initial pressures. Fuel 2013, 106, 310–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Broustail, G.; Seers, P.; Halter, F.; Moreac, G.; Mounaim-Rousselle, C. Experimental determination of laminar burning velocity for butanol and ethanol iso-octane blends. Fuel 2011, 90, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gulder, Ö.L. Laminar burning velocities of methanol, isooctane and isooctane/methanol blends. Combust. Sci. Technol. 1983, 33, 179–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gülder, O.L. Burning velocities of ethanol isooctane blends. Combust. Flame 1984, 56, 261–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, H.; Quinton, K.; Peng, Z.; Zhao, H.; Ladommatos, N. Effects of oxygen content of fuels on combustion and emissions of diesel engines. Energies 2016, 9, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sathiyagnanam, A.P.; Saravanan, C.G.; Gopalakrishnan, M. Hexanol-Ethanol Diesel Blends on DI-Diesel Engine to Study the Combustion and Emission. In Proceedings of the World Congress on Engineering (WCE 2010), London, UK, 30 June–2 July 2010; pp. 1–5.
- Farkade, H.S.; Pathre, A.P. Experimental investigation of methanol, ethanol and butanol blends with gasoline on SI engine. Int. J. Emerg. Technol. Adv. Eng. 2012, 2, 2250–2459. [Google Scholar]
- Tang, C.L.; Huang, Z.H.; Wang, J.H.; Zheng, J.J. Effects of hydrogen addition on cellular instabilities of the spherically expanding propane flames. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 2009, 34, 2483–2487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, X.L.; Huang, Z.H.; Wu, S.; Li, Q.Q. Laminar burning velocities and flame instabilities of butanol isomers-air mixtures. Combust. Flame 2010, 157, 2318–2325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, X.; Li, Q.; Huang, Z.; Zhang, N. Measurement of laminar flame speeds and flame stability analysis of tert-butanol-air mixtures at elevated pressures. Energy Convers. Manag. 2011, 52, 3137–3146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lapuerta, M.N.; García-Contreras, R.; Campos-Fernández, J.; Dorado, M.P. Stability, lubricity, viscosity, and cold-flow properties of alcohol−diesel blends. Energy Fuels 2010, 24, 4497–4502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z. On the extraction of laminar flame speed and Markstein length from outwardly propagating spherical flames. Combust. Flame 2011, 158, 291–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frankel, M.L.; Sivashinsky, G.I. On effects due to thermal expansion and Lewis number in spherical flame propagation. Combust. Sci. Technol. 1983, 31, 131–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moffat, R.J. Describing the uncertainties in experimental results. Exp. Therm. Fluid Sci. 1988, 1, 3–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Shen, W.; Fan, M.; Zhang, H.; Li, S. Laminar flame speed studies of lean premixed H2/CO/air flames. Combust. Flame 2014, 161, 2492–2495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krejci, M.C.; Mathieu, O.; Vissotski, A.J.; Ravi, S.; Sikes, T.G.; Petersen, E.L.; Kérmonès, A.; Metcalfe, W.; Curran, H.J. Laminar flame speed and ignition delay time data for the kinetic modeling of hydrogen and syngas fuel blends. J. Eng. Gas Turbines Power 2013, 135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lowry, W.; de Vries, J.; Krejci, M.; Petersen, E.; Serinyel, Z.; Metcalfe, W.; Curran, H.; Bourque, G. Laminar flame speed measurements and modeling of pure alkanes and alkane blends at elevated pressures. J. Eng. Gas Turbines Power 2011, 133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Tang, C.; Cheng, Y.; Guan, L.; Huang, Z. Laminar flame speeds and kinetic modeling of n-pentanol and its isomers. Energy Fuels 2015, 29, 5334–5348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, S.Y.; Jiang, D.M.; Huang, Z.H.; Zeng, K.; Cheng, Q. Determination of the laminar burning velocities for mixtures of ethanol and air at elevated temperatures. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2007, 27, 374–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Egolfopoulos, F.N.; Du, D.X.; Law, C.K. A study on ethanol oxidation kinetics in laminar premixed flames, flow reactors, and shock tubes. Symp. Int. Combust. 1992, 24, 833–841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gülder, Ö.L. Laminar burning velocities of methanol, ethanol and isooctane-air mixtures. Symp. Int. Combust. 1982, 19, 275–281. [Google Scholar]
- Baloo, M.; Dariani, B.M.; Akhlaghi, M.; Chitsaz, I. Effect of iso-octane/methane blend on laminar burning velocity and flame instability. Fuel 2015, 144, 264–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dirrenberger, P.; Glaude, P.A.; Bounaceur, R.; le Gall, H.; da Cruz, A.P.; Konnov, A.A.; Battin-Leclerc, F. Laminar burning velocity of gasolines with addition of ethanol. Fuel 2014, 115, 162–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rau, F.; Hartl, S.; Voss, S.; Still, M.; Hasse, C.; Trimis, D. Laminar burning velocity measurements using the heat flux method and numerical predictions of iso-octane/ethanol blends for different preheat temperatures. Fuel 2015, 140, 10–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, F.; Law, C.K. An experimental and mechanistic study on the laminar flame speed, Markstein length and flame chemistry of the butanol isomers. Combust. Flame 2013, 160, 2744–2756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, C.L.; Huang, Z.H.; Law, C.K. Determination, correlation, and mechanistic interpretation of effects of hydrogen addition on laminar flame speeds of hydrocarbon–air mixtures. Proc. Combust. Inst. 2011, 33, 921–928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Law, C.K. Combustion Physics, 1st ed.; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Kee, R.J.; Grcar, J.F.; Smooke, M.D.; Miller, J.A. PRMIX: A Fortran Program for Modeling Steady Laminar One-Dimensional Premixed Flames; SAND Report 85-8240; Sandia National Laboratory: Livermore, CA, USA, 1985.
- Kee, R.J.; Dixon-Lewis, G.; Warnatz, J.; Coltrin, M.E.; Miller, J.A. A Fortran Computer Code Package for the Evaluation of Gas-Phase, Multicomponent Transport Properties; SAND-86-8246; Sandia National Laboratory: Livermore, CA, USA, 1986.
- Kee, R.J.; Miller, J.A. Computational modeling of flame structure. Phys. D 1984, 12, 198–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kee, R.J.; Rupley, F.M.; Miller, J.A. Chemkin-II: A Fortran Chemical Kinetics Package for the Analysis of Gas-Phase Chemical Kinetics; Technical Report SAND89-8009; Sandia National Laboratory: Livermore, CA, USA, 1989.
- Chaos, M.; Kazakov, A.; Zhao, Z.; Dryer, F.L. A high-temperature chemical kinetic model for primary reference fuels. Int. J. Chem. Kinet. 2007, 39, 399–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Sarli, V.; Benedetto, A.D. Laminar burning velocity of hydrogen–methane/air premixed flames. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 2007, 32, 637–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| Property | Isooctane | Methanol | Ethanol | n-Propanol | n-Butanol | n-Pentanol |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Chemical formula | C8H18 | CH4O | C2H6O | C3H8O | C4H10O | C5H12O |
| Molecular weight (g·mol−1) | 114.23 | 32.04 | 46.07 | 60.1 | 74.12 | 88.15 |
| Oxygen content (wt%) | 0 | 49.93 | 34.73 | 26.62 | 21.59 | 18.15 |
| Density (g·cm−3) | 691.9 | 792 | 789 | 804 | 810 | 811 |
| Boiling point (°C) | 99.3 | 64.7 | 78.37 | 97 | 117.7 | 137–139 |
| Vapor pressure at 20 °C (kPa) | 5.5 | 13.02 | 5.95 | 1.99 | 0.82 | 0.2 |
| Flash point (°C) | −12 | 11 | 13 | 22 | 35 | 49 |
| Lower heating value (MJ·kg−1) | 44.4 | 19.58 | 26.83 | 30.63 | 33.09 | 34.65 |
| Solubility in water | Insoluble | Soluble | Soluble | Soluble | Slight soluble | Slight soluble |
© 2016 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, Q.; Jin, W.; Huang, Z. Laminar Flame Characteristics of C1–C5 Primary Alcohol-Isooctane Blends at Elevated Temperature. Energies 2016, 9, 511. https://doi.org/10.3390/en9070511
Li Q, Jin W, Huang Z. Laminar Flame Characteristics of C1–C5 Primary Alcohol-Isooctane Blends at Elevated Temperature. Energies. 2016; 9(7):511. https://doi.org/10.3390/en9070511
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Qianqian, Wu Jin, and Zuohua Huang. 2016. "Laminar Flame Characteristics of C1–C5 Primary Alcohol-Isooctane Blends at Elevated Temperature" Energies 9, no. 7: 511. https://doi.org/10.3390/en9070511
APA StyleLi, Q., Jin, W., & Huang, Z. (2016). Laminar Flame Characteristics of C1–C5 Primary Alcohol-Isooctane Blends at Elevated Temperature. Energies, 9(7), 511. https://doi.org/10.3390/en9070511







