Risk Assessment of Failure of Outdoor High Voltage Polluted Insulators under Combined Stresses Near Shoreline
Abstract
:1. Introduction
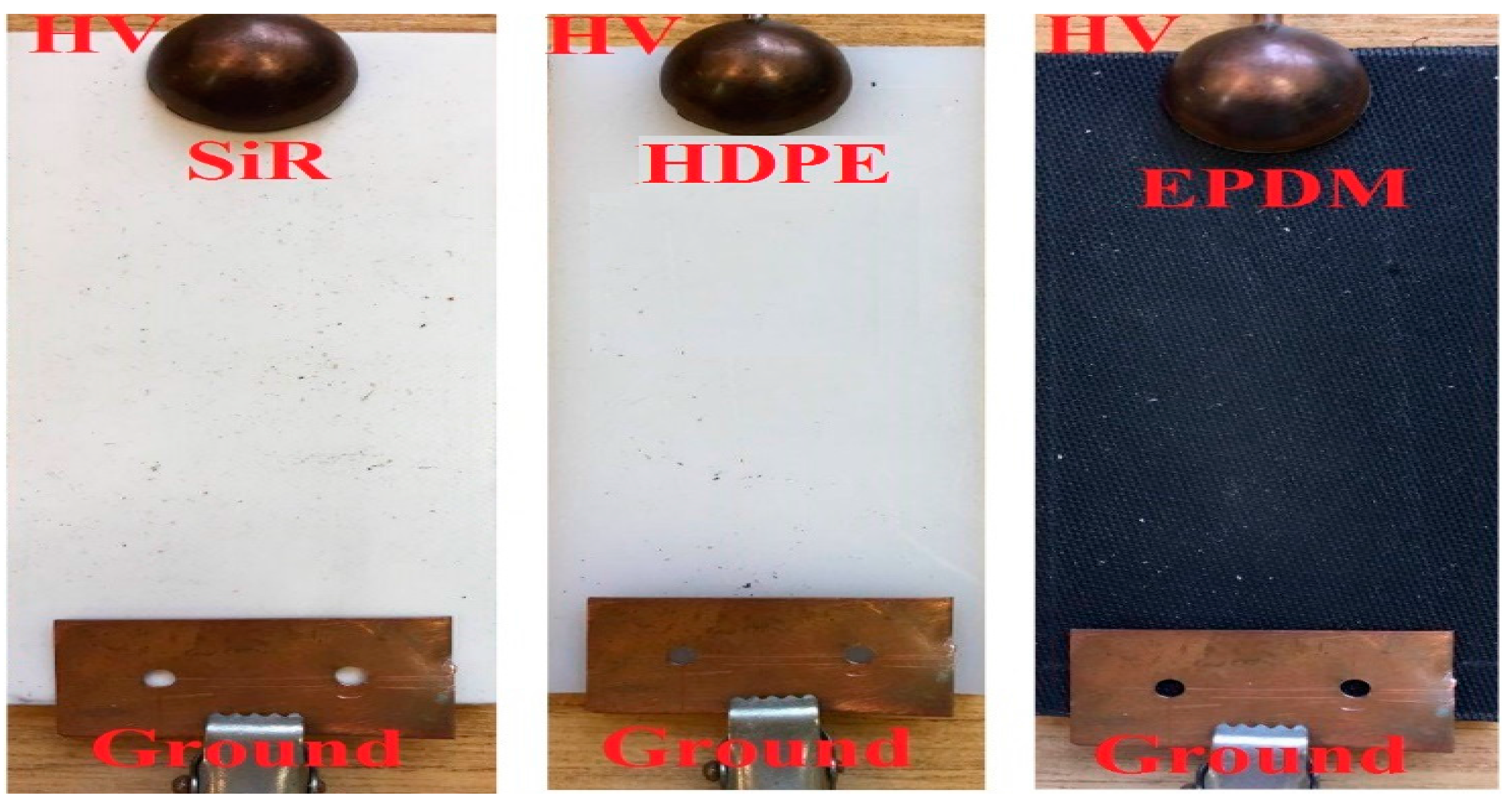
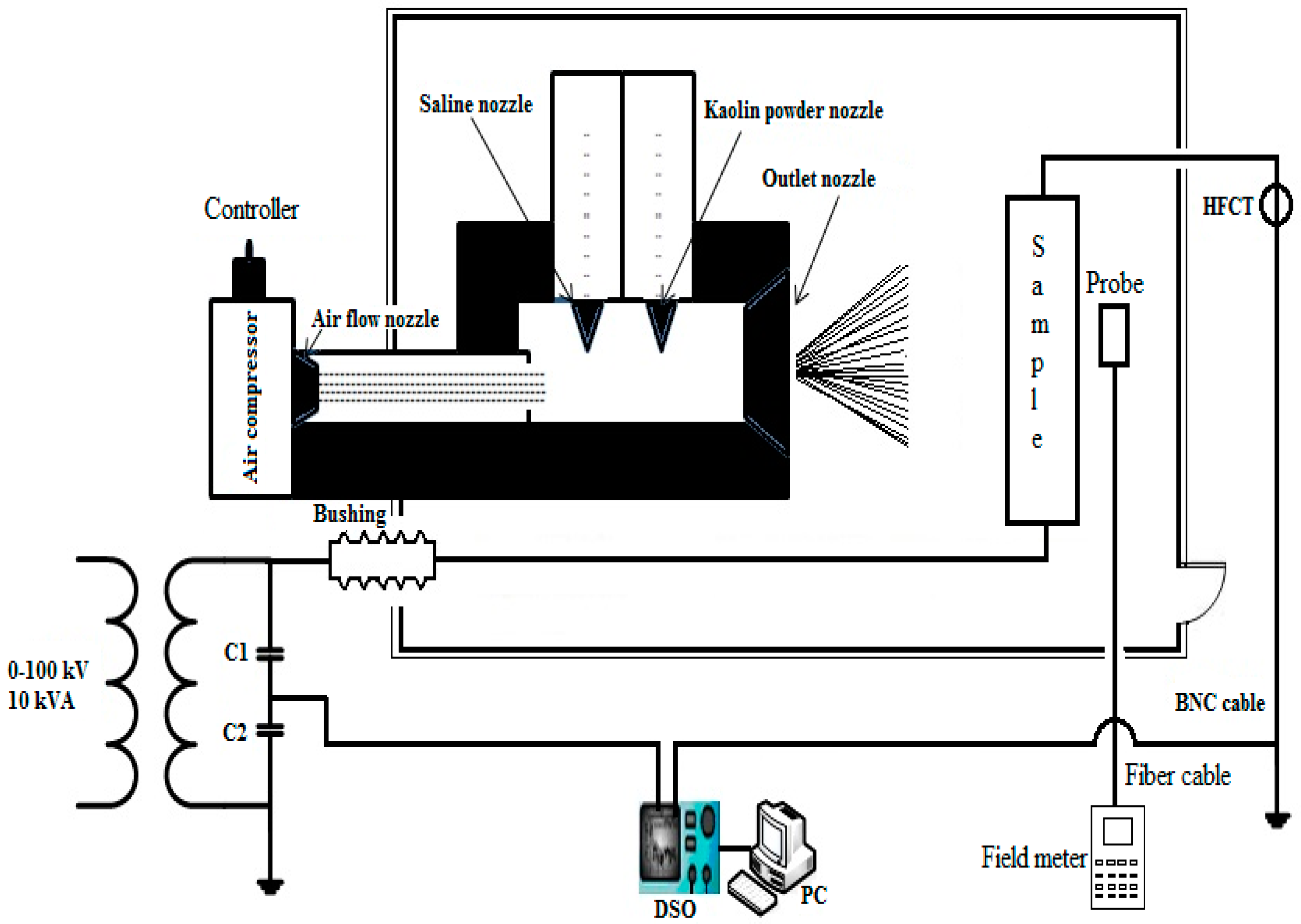
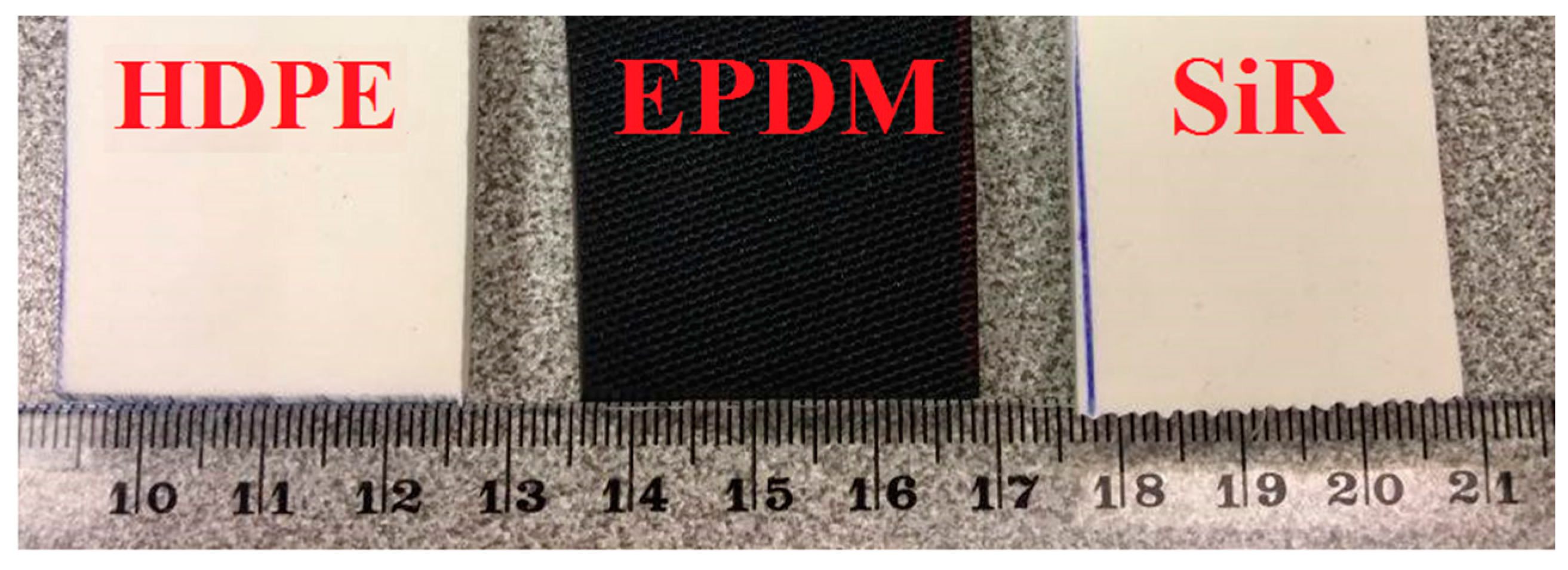
2. Test Arrangement
3. Results and Discussions
3.1. Electrical Properties
3.1.1. Effect of Acidic and Clean Cold Fog on Discharge Current
3.1.2. Effect of Acidic and Clean Cold Fog on E-Field Distribution
3.2. Physico-Chemical Properties
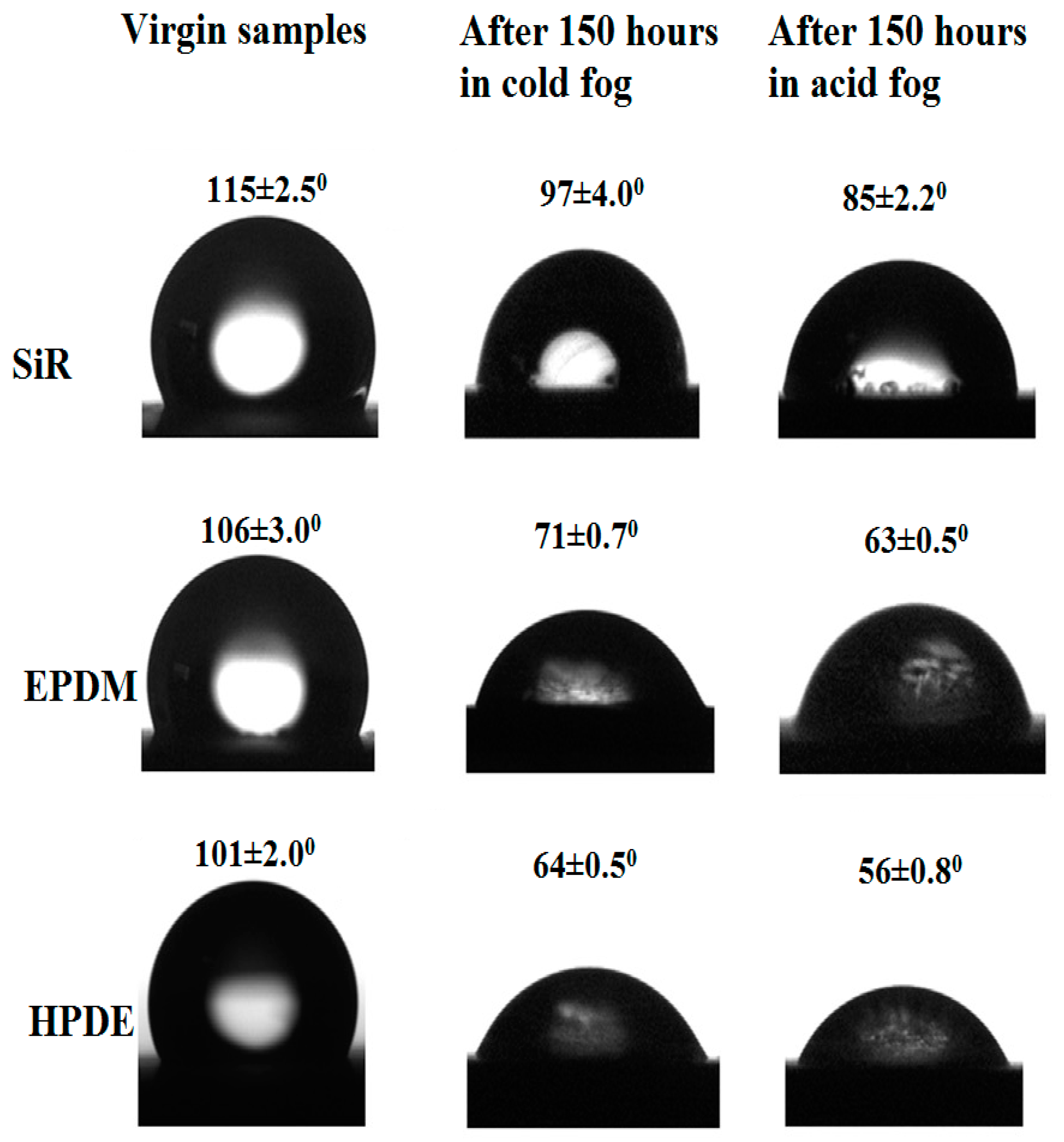
3.2.1. Contact Angle and Hydrophobicity Measurement
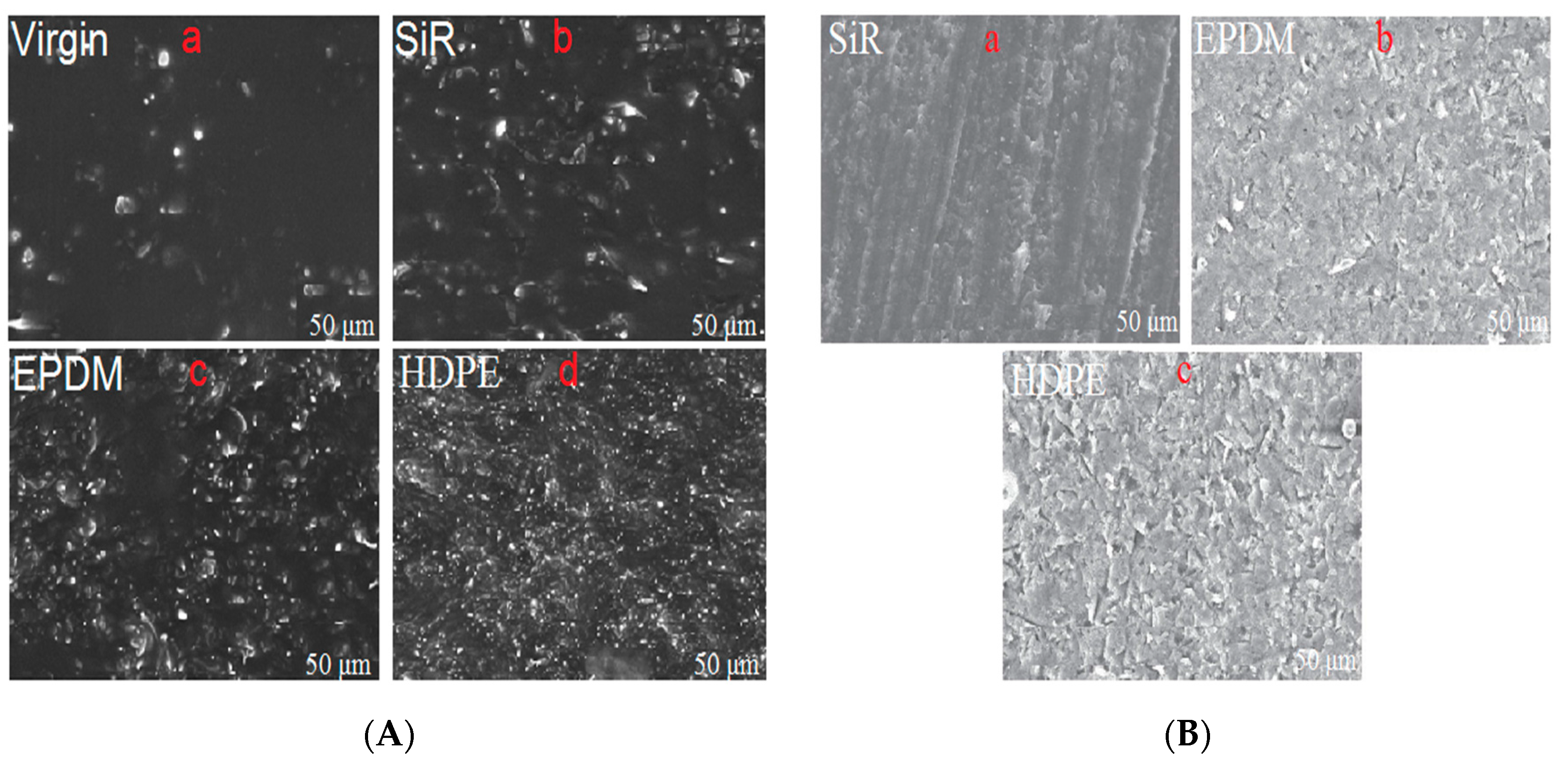
3.2.2. Scanning Electron Microscopic (SEM) Analysis
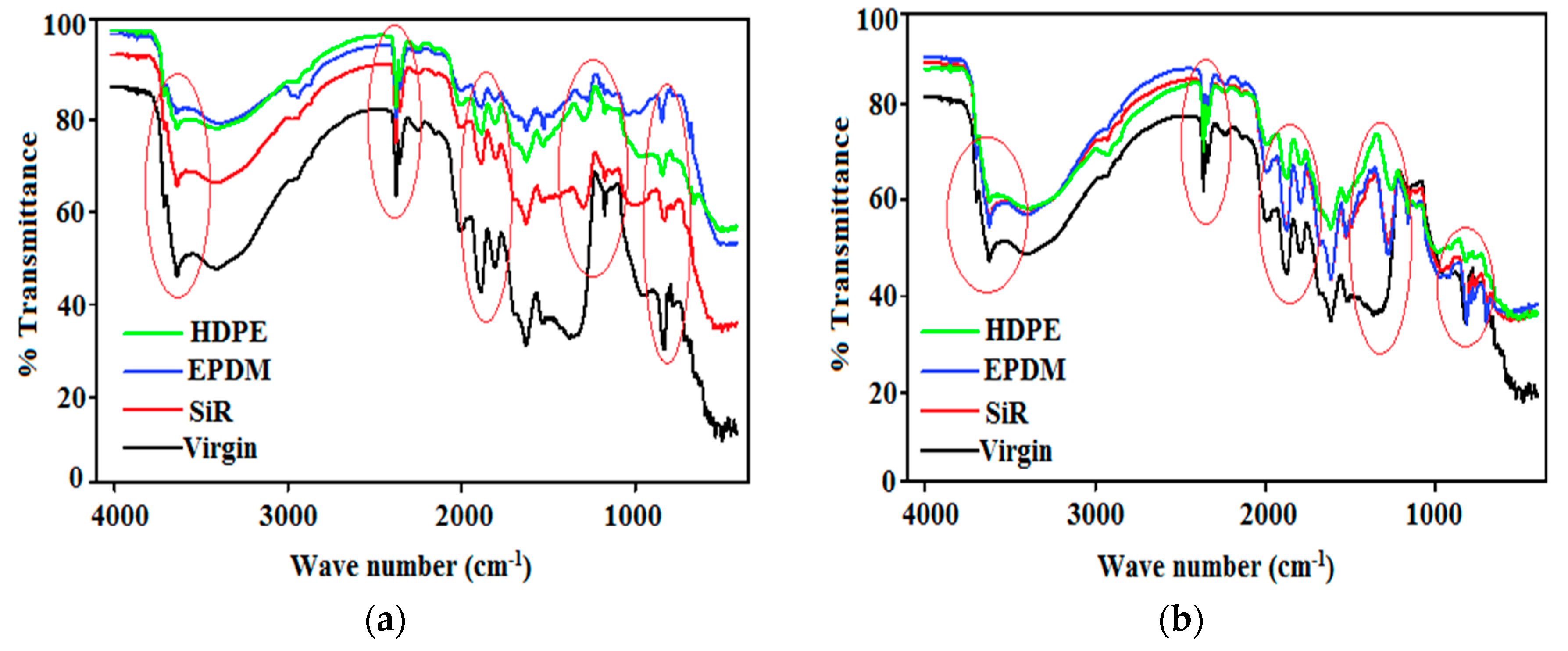
3.2.3. Fourier Transform Infrared (FTIR) Analysis
3.2.4. Surface Roughness
3.2.5. Dielectric and Physical Changes
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wang, C.; Li, T.; Tu, Y.; Yuan, Z.; Li, R.; Zhang, F.; Gong, B. Heating phenomenon in unclean composite insulators. J. Eng. Fail. Anal. 2016, 50, 48–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, J.W.; Gorur, R.S. Surface recovery of silicone rubber used for HV outdoor insulator. IEEE Trans. Dielectr. Electr. Insul. 1994, 2, 1039–1046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, H.; Hackam, R.; Cherney, E.A. Influence of thickness, substrate type, amount of silicone fluid and solvent type on electrical performance of RTV silicone rubber coatings. IEEE Trans. Power Deliv. 1996, 11, 431–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.H.; Cherney, E.A.; Hackam, R.; Rutherford, K.G. Chemical changes at the surface of RTV silicone rubber coatings on insulators during dry-band arcing. IEEE Trans. Dielectr. Electr. Insul. 1996, 1, 106–123. [Google Scholar]
- Houlgate, G. Field Experience and Laboratory Research on Composite Insulators for Overhead Lines. In Proceedings of the CIGRE Session Papers and Proceedings, Paris, France, 26–31 August 1986. [Google Scholar]
- Schneider, H.M.; Guidi, W.W.; Burnham, J.T.; Gorur, R.S.; Hall, J.F. Accelerated aging and flashover tests on 138 kV nonceramic line post insulators. IEEE Trans. Power Derliv. 1993, 8, 325–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.H.; Cherney, E.A.; Hackam, R. The loss and recovery of hydrophobicity of RTV silicone rubber insulator coatings. IEEE Trans. Power Deliv. 1990, 5, 1491–1500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghunem, R.A. Using the inclined-plane test to evaluate the resistance of outdoor polymer insulating materials to electrical tracking and erosion. IEEE Electr. Insul. Mag. 2015, 31, 16–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selection and Dimensioning of High-Voltage Insulators Intended for Use in Polluted Conditions; Technical Report IEC TS 60815-1; International Electrotechnical Commission: Geneva, Switzerland, October 2008.
- Montesinos, J.; Gorur, R.S.; Mobasher, B. Mechanical performance of GRP rods used innonceramic insulators after exposure to acid attack. In Proceedings of the 11th Internatioal Conference on High Voltage Engineering, London, UK, 27–23 August 1999; Volume 4. [Google Scholar]
- Claudia, O.; Philip, T.; Ignacio, M.; Raji, S. Influence of acid rain + multistress conditions on the long term performance of 28 kV polymeric insulators. In Proceedings of the 2005 Annual Report Conference on Electrical Insulation and Dielectric Phenomena, Nashville, TN, USA, 16–19 October 2005; pp. 341–344. [Google Scholar]
- Vet, R.; Artz, R.S.; Carou, S.; Shaw, M.; Ro, C.-U.; Aas, W.; Baker, A.; Bowersox, V.C.; Dentener, F.; Galy-Lacaux, C.; et al. A global assessment of precipitation chemistry and deposition of sulfur, nitrogen, sea salt, base cation, organic acids, acidity and pH and phosphorus. Atmos. Environ. 2014, 93, 3–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chrzan, K.L.; Andino, J.M.; Twarowski, R. Effects of acid rain on outdoor insulators. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Advances in Processing, Testing and Application of Dielectric Materials, Wroclaw, Poland, 17–19 September 2001; pp. 212–216. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, X.; Kumagai, S.; Yoshimura, N. Contamination performance of silicone rubber insulator subjected to acid rain. IEEE Trans. Dielectr. Electr. Insul. 1998, 5, 909–916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calva, P.A.; Ruiz, E.P.; Marquez, M.G.; Cabrera, G.P. Measuring and analysis of the effect of acid rain in polluted polymer insulators at high altitude. In Proceedings of the Conference on Electrical Insulation and Dielectric Phenomena, Albuquerque, NM, USA, 19–22 October 2003; pp. 410–413. [Google Scholar]
- Sundararajan, R.; Godinez, V.; Amin, M. Performance of thermoplastic elastomeric and thermoset insulators under accelerated acid rain multistress conditions. In Proceedings of the 15th National Power Systems Conference, Bombay, India, 16–18 December 2008; pp. 356–360. [Google Scholar]
- Yoshimura, N.; Shikimura, A.; Hasegawa, S. The Effect of acid rain on the tracking resistance of organic insulating materials. IEEJ Trans. Fundam. Mater. 1995, 115, 890–895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreno, V.M.; Gorur, R.S. Effect of long-term corona on nonceramic outdoor insulator housing materials. IEEE Trans. Dielectr. Electr. Insul. 2001, 8, 117–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreno, V.M.; Gorur, R.S. Impact of corona on the long-term performance of nonceramic insulators. IEEE Trans. Dielectr. Electr. Insul. 2003, 10, 80–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Otsubo, M.; Honda, C.; Hashimoto, Y.; Ohno, A. Mechanism for change in leakage current waveform on a wet silicone rubber surface—A study using a dynamic 3-D model. IEEE Trans. Dielectr. Electrl. Insul. 2005, 12, 556–565. [Google Scholar]
- Ali, M.; Hackam, R. Recovery of hydrophobicity of HTV silicone rubber after accelerated aging in saline solutions. IEEE Trans. Dielectr. Electr. Insul. 2009, 16, 842–852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Standard Test Methods for Liquid-Contaminant, Inclined-Plane Tracking and Erosion of Insulating Materials; Active Standard ASTM D2303-13; ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 1997.
- Meyer, L.; Jayaram, S.H.; Cherney, E.A. Thermal conductivity of filled silicone rubber and its relationship to erosion resistance in the inclined plane test. IEEE Trans. Dielectr. Electr. Insul. 2004, 11, 620–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The European Monitoring and Evaluation Programme. Available online: http://www.emep.int (accessed on 24 August 2016).
- Gene, E.L.; Richard, F.W.; James, N.G.; Thomas, J.B. Acid Rain: In recent decades the acidity of rain and snow has increased sharply over wide areas. The principal cause is the release of sulfur and nitrogen oxides by the of fossil fuels. Sci. Am. 1979, 241, 43–51. [Google Scholar]
- Tzimas, A.; Zachariades, C.; Rowland, S.M. Electric field analysis of 132kV EPDM insulator and correlation with ageing features. In Proceedings of the 2013 IEEE Electrical Insulation Conference, Ottawa, ON, Canada, 2–5 June 2013; pp. 210–214. [Google Scholar]
- Aras, F.; Alekperov, V.; Can, N.; Kirkici, H. Aging of 154 kV underground power cable insulation under combines thermal and electrical stresses. IEEE Electr. Insul. Mag. 2007, 23, 25–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crine, J.P. On the interpretation of some electrical aging and relaxation phenomena in solid dielectrics. IEEE Trans. Dielectr. Electr. Insul., 2005, 12, 1089–1101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guidance on the Measurement of Wettabilityof Insulator Surfaces (IEC TS 62073); Technical Report; International Electrotechnical Commission: Geneva, Switzerland, June 2003.
- Papailiou, K.O.; Schmuck, F.M. Silicone Composite Insulators Materials, Design, Applications; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Deng, H.; Hackam, R. Electrical performance of RTV silicone rubber coating of different thickness on porcelain. IEEE Trans. Power Deliv. 1997, 12, 857–866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Ingredients | Compositions (mg/L) |
|---|---|
| NH4Cl | 235 |
| KCl | 5.9 |
| HNO3 | 25 |
| MgSO4 | 35.2 |
| CaSO4·2H2O | 29.5 |
| NaCl | 170 |
| ON State | ON/OFF State |
|---|---|
| Saline contamination and acidic cold fog are deposited continuously from the start of the test at a constant voltage of 33 kV. | Saline contamination and acidic cold fog injections are periodically set to turn the setup on and off at constant voltage of 33 kV. |
| Types of Materials | Total SR (µm) | Root Mean sq. (SR) (µm) | Avg. SR (µm) |
|---|---|---|---|
| SiR | 4.78 ± 0.02 | 2.19 ± 0.02 | 1.01 ± 0.02 |
| 11.09 ± 0.02 | 3.330.02 | 3.29 ± 0.02 | |
| EPDM | 6.03 ± 0.02 | 2.46 ± 0.02 | 1.71 ± 0.02 |
| 16.51 ± 0.02 | 4.060.02 | 2.82 ± 0.02 | |
| HDPE | 7.93 ± 0.02 | 2.82 ± 0.02 | 1.99 ± 0.02 |
| 19.37 ± 0.02 | 4.40 ± 0.02 | 4.06 ± 0.02 |
| Insulation Materials | Discharge Current (mA) | Tangent Loss % | Permittivity % |
|---|---|---|---|
| SiR | 77.1 | 54 | 1.1 |
| EPDM | 89.0 | 67 | 6.1 |
| HDPE | 99.1 | 285 | −5.2 |
| Insulation Materials | Weight Loss % | Corrosion Speed (mg/h) |
|---|---|---|
| SiR | 0.05 | 0.016 |
| EPDM | 0.17 | 0.029 |
| HDPE | 0.19 | 0.95 |
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hussain, M.M.; Farokhi, S.; McMeekin, S.G.; Farzaneh, M. Risk Assessment of Failure of Outdoor High Voltage Polluted Insulators under Combined Stresses Near Shoreline. Energies 2017, 10, 1661. https://doi.org/10.3390/en10101661
Hussain MM, Farokhi S, McMeekin SG, Farzaneh M. Risk Assessment of Failure of Outdoor High Voltage Polluted Insulators under Combined Stresses Near Shoreline. Energies. 2017; 10(10):1661. https://doi.org/10.3390/en10101661
Chicago/Turabian StyleHussain, Muhammad Majid, Shahab Farokhi, Scott G. McMeekin, and Masoud Farzaneh. 2017. "Risk Assessment of Failure of Outdoor High Voltage Polluted Insulators under Combined Stresses Near Shoreline" Energies 10, no. 10: 1661. https://doi.org/10.3390/en10101661





