Impact of Diabetes Mellitus on Human Erythrocytes: Atomic Force Microscopy and Spectral Investigations
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
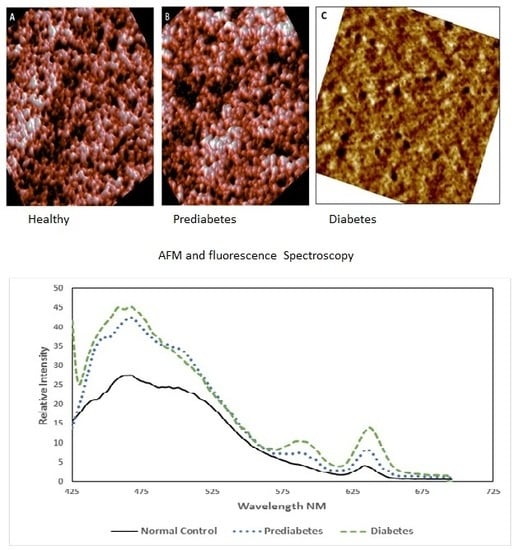
3.1. Morphological Analysis by AFM
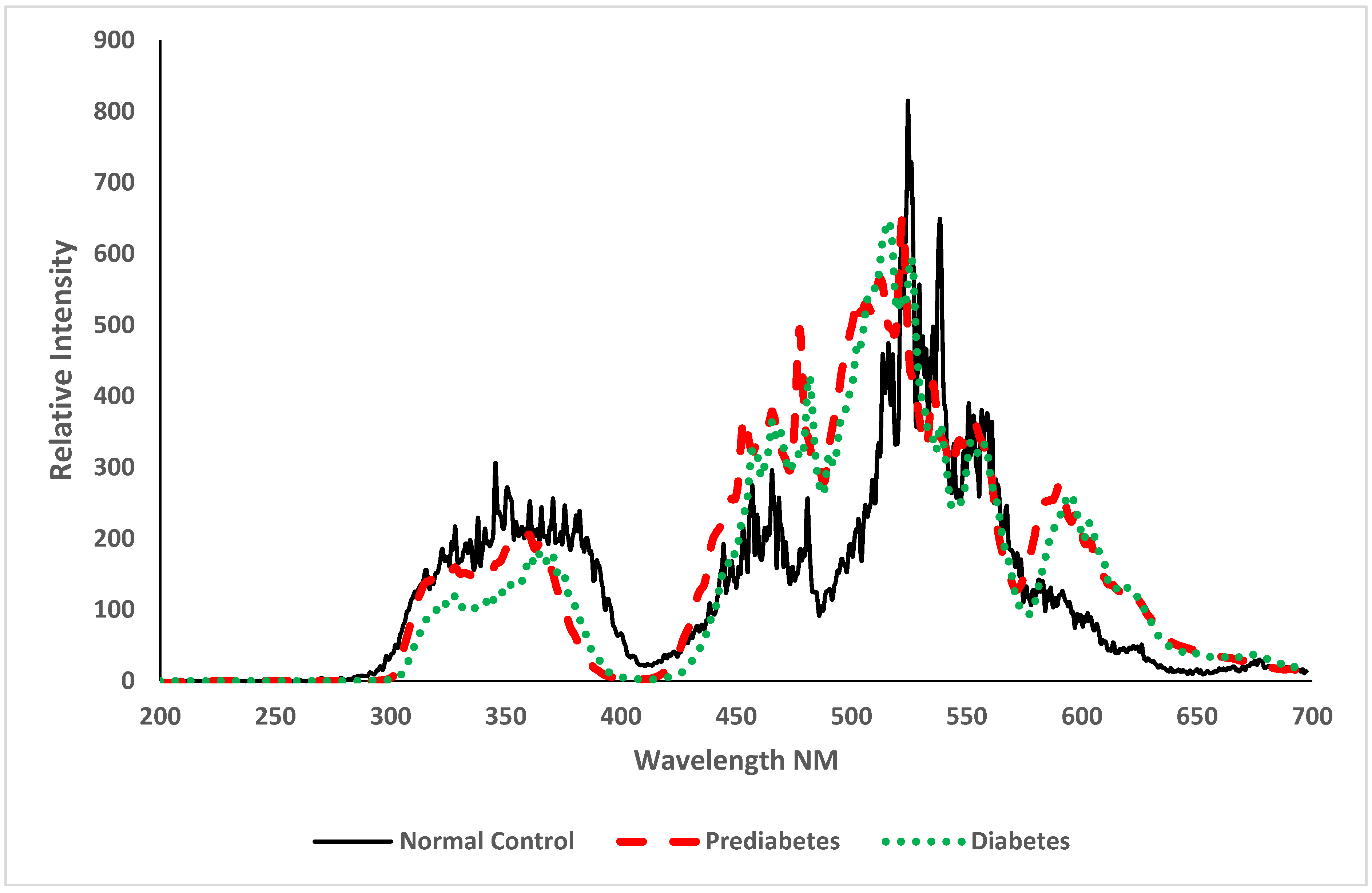
3.2. Spectroscopic Analysis
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- American Diabetes Association. Diagnosis and classification of diabetes mellitus. Diabetes Care 2010, 33, S62–S69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, D. Prevalence, predisposition and prevention of type II diabetes. Nutr. Metab. 2005, 2, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mittal, K.; Mani, R.J.; Katare, D.P. Type 3 Diabetes: Cross Talk between Differentially Regulated Proteins of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus and Alzheimer’s Disease. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 25589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pretorius, E.; du Plooy, J.N.; Soma, P.; Keyser, I.; Buys, A.V. Smoking and fluidity of erythrocyte membranes: A high resolution scanning electron and atomic force microscopy investigation. Nitric Oxide 2013, 35, 42–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, J.; Jiang, C.; Xiao, X.; Fang, Z.; Li, L.; Han, L.; Mei, A.; Feng, Y.; Guo, Y.; Li, H.; et al. Changes in red blood cell membrane structure in G6PD deficiency: An atomic force microscopy study. Clin. Chim. Acta 2015, 444, 264–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.; Li, J. Detection of erythrocytes in patients with Waldenström macro globulinemia using atomic force microscopy. Acta Biochim. Biophys. Sin. 2014, 46, 420–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nirmala, R. Fluorescence spectroscopy of neoplastic and non-neoplastic tissues. Neoplasia 2000, 2, 89–117. [Google Scholar]
- Alfano, R.R.; Yang, Y. Stokes shift emission spectroscopy of human tissue and key biomolecules. IEEE J. Quant. Electron. 2003, 9, 148–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masilamani, V.; Trinka, V.; Al-Salhi, M.; Elangovan, M.; Raghavan, V.; Al Diab, A.R.; Hajjar, W.; Ainia, M.; Al-Mustafa, A.; Al-Nachawati, H.A. New Lung Cancer Biomarker—A Preliminary Report. Photomed. Laser Surg. 2011, 29, 161–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- AlSalhi, M.S.; AlMehmadi, A.M.; Abdo, A.A.; Prasad, S.; Masilamani, V. Diagnosis of liver cancer and cirrhosis by the fluorescence spectra of blood and urine. Technol. Cancer Res. Treat. 2012, 11, 345–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Masilamani, V.; AlSalhi, M.S.; Devanesan, S.; Algahtani, F.H.; Abu-Salah, K.M.; Ahamad, I.; Agastian, P. Spectral detection of sickle cell anemia and thalassemia. Photodiagn. Photodyn. Ther. 2013, 10, 429–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Masilamani, V.; Vijmasi, T.; AlSalhi, M.S.; Govindaraj, K.; Vijaya-Raghavan, A.P.; Antonisamy, B. Cancer Detection by Native Fluorescence of Urine. J. Biomed. Opt. 2010, 15, 057003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Masilamani, V.; AlZahrani, K.; Devanesan, S.; AlQahtani, H.; AlSalhi, M.S. Smoking Induced Hemolysis: Spectral and microscopic investigations. Sci. Rep. 2016, 19, 21095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mangialardi, G.; Katare, R.; Oikawa, A.; Meloni, M.; Reni, C.; Emanueli, C.; Madeddu, P. Diabetes Causes Bone Marrow Endothelial Barrier Dysfunction by Activation of the RhoA–Rho-Associated Kinase Signaling Pathway. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2013, 33, 555–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cho, Y.I.; Mooney, M.P.; Cho, D.J. Hemorheological Disorders in Diabetes Mellitus. J. Diabetes Sci. Technol. 2008, 2, 1130–1138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, H.; Xing, X.; Zhao, H.; Chen, Y.; Huang, X.; Ma, S.; Ye, H.; Cai, J. Detection of erythrocytes influenced by aging and type 2 diabetes using atomic force microscope. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2010, 391, 1698–1702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buys, A.V.; Van Rooy, M.J.; Soma, P.; Van Papendorp, D.; Lipinski, B.; Pretorius, E. Changes in red blood cell membrane structure in type 2 diabetes: A scanning electron and atomic force microscopy study. Cardiovasc. Diabetol. 2013, 12, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mishra, N.; Singh, N. Blood viscosity, lipid profile, and lipid peroxidation in type-1 diabetic patients with good and poor glycemic control. N. Am. J. Med. Sci. 2013, 5, 562–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, D.; Tan, K.S.; Zhang, X.; Sun, A.Y.; Sun, G.Y.; Lee, J.C.M. Hydrogen peroxide alters membrane and cytoskeleton properties and increases intercellular connections in astrocytes. J. Cell Sci. 2005, 118, 3695–3703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muliyil, S.; Narasimha, M. Mitochondrial ROS Regulates Cytoskeletal and Mitochondrial Remodeling to Tune Cell and Tissue Dynamics in a Model for Wound Healing. Dev. Cell 2014, 28, 239–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kurtzhals, J.A.L.; Addae, M.M.; Akanmori, B.D.; Dunyo, S.; Koram, K.A.; Appawu, M.A.; Nkrumah, F.K.; Hviid, L. Anaemia caused by asymptomatic Plasmodium falciparum infection in semi-immune African schoolchildren. Trans. R. Soc. Trop. Med. Hyg. 1999, 93, 623–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asgary, S.; Naderi, G.H.; Ghannady, A. Effects of cigarette smoke, nicotine and cotinine on red blood cell hemolysis and their –SH capacity. Exp. Clin. Cardiol. 2005, 10, 116–119. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Muhammad Ibrahim, K.; Mulazim Hussain, B.; Mhammad saleem, A.; Sharmaine, B. Effect of smoking on red blood cells count, hemoglobin concentration and red cell indices. Pak. J. Med. Health Sci. 2014, 8, 361–364. [Google Scholar]
- Malenica, M.; Prnjavorac, B.; Bego, T.; Dujic, T.; Semiz, S.; Skrbo, S.; Gusic, A.; Hadzic, A.; Causevic, A. Effect of Cigarette Smoking on Haematological Parameters in Healthy Population. Med. Arch. 2017, 71, 132–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sari, M.I.; Sari, N.; Darlan, D.M.; Prasetya, R.J. Cigarette Smoking and Hyperglycaemia in Diabetic Patients. Open Access Maced. J. Med. Sci. 2018, 6, 634–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Swihart, A.; Mikrut, J.; Ketterson, J.; Macdonald, R. Atomic force microscopy of the erythrocyte membrane skeleton. J. Microsc. 2001, 204, 212–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaczmarska, M.; Fornal, M.; Messerli, F.H.; Korecki, J.; Grodzicki, T.; Burda, K. Erythrocyte membrane properties in patients with essential hypertension. Cell Biochem. Biophys. 2013, 67, 1089–1102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takeuchi, M.; Miyamoto, H.; Sako, Y.; Komizu, H.; Kusumi, A. Structure of the Erythrocyte Membrane Skeleton as Observed by Atomic Force Microscopy. Biophys. J. 1998, 74, 2171–2183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruggeri, F.S.; Marcott, C.; Dinarelli, S.; Longo, G.; Girasole, M.; Dietler, G.; Knowles, T.P.J. Identification of Oxidative Stress in Red Blood Cells with Nanoscale Chemical Resolution by Infrared Nanospectroscopy. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 2582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pérez-Belmonte, L.M.; Moreno-Santos, I.; Cabrera-Bueno, F.; Sánchez-Espín, G.; Castellano, D.; Such, M.; Crespo-Leiro, M.G.; Carrasco-Chinchilla, F.; Alonso-Pulpón, L.; López-Garrido, M.; et al. Expression of Sterol Regulatory Element-Binding Proteins in epi-cardial adipose tissue in patients with coronary artery disease and diabetes mellitus: Preliminary study. Int. J. Med. Sci. 2017, 14, 268–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Catalano, C.; Muscelli, E.; Natali, A.; Mazzoni, A.; Masoni, A.; Bernardini, B.; Seghieri, G.; Ferrannini, E. Reciprocal association between insulin sensitivity and the haematocrit in man. Eur. J. Clin. Investig. 1997, 27, 634–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez-Martin, A.; Dumortier, M.; Pierrisnard, E.; Raynaud, E.; Mercier, J.; Brun, J. Multivariate analysis of relationships between insulin sensitivity and blood rheology: Is plasma viscosity a marker of insulin resistance? Clin. Hemorheol. Microcirc. 2001, 25, 91–103. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ghosh, S.; Chakraborty, I.; Chakraborty, M.; Mukhopadhyay, A.; Mishra, R.; Sarkar, D. Evaluating the morphology of erythrocyte population: An approach based on atomic force microscopy and flow cytometry. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2016, 1858, 671–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kannel, W.B.; McGee, D.L. Diabetes and cardiovascular disease. The Framingham study. JAMA 1979, 241, 2035–2038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gu, K.; Cowie, C.C.; Harris, M.I. Mortality in adults with and without diabetes in a national cohort of the U.S. population, 1971–1993. Diabetes Care 1998, 21, 1138–1145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Colwell, J.A. Vascular thrombosis in type II diabetes mellitus. Diabetes 1993, 42, 8–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valavanidis, A.; Vlachogianni, T.; Fiotakis, K. Tobacco smoke: Involvement of reactive oxygen species and stable free radicals in mechanisms of oxidative damage, carcinogenesis and synergistic effects with other respirable particles. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2009, 6, 445–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

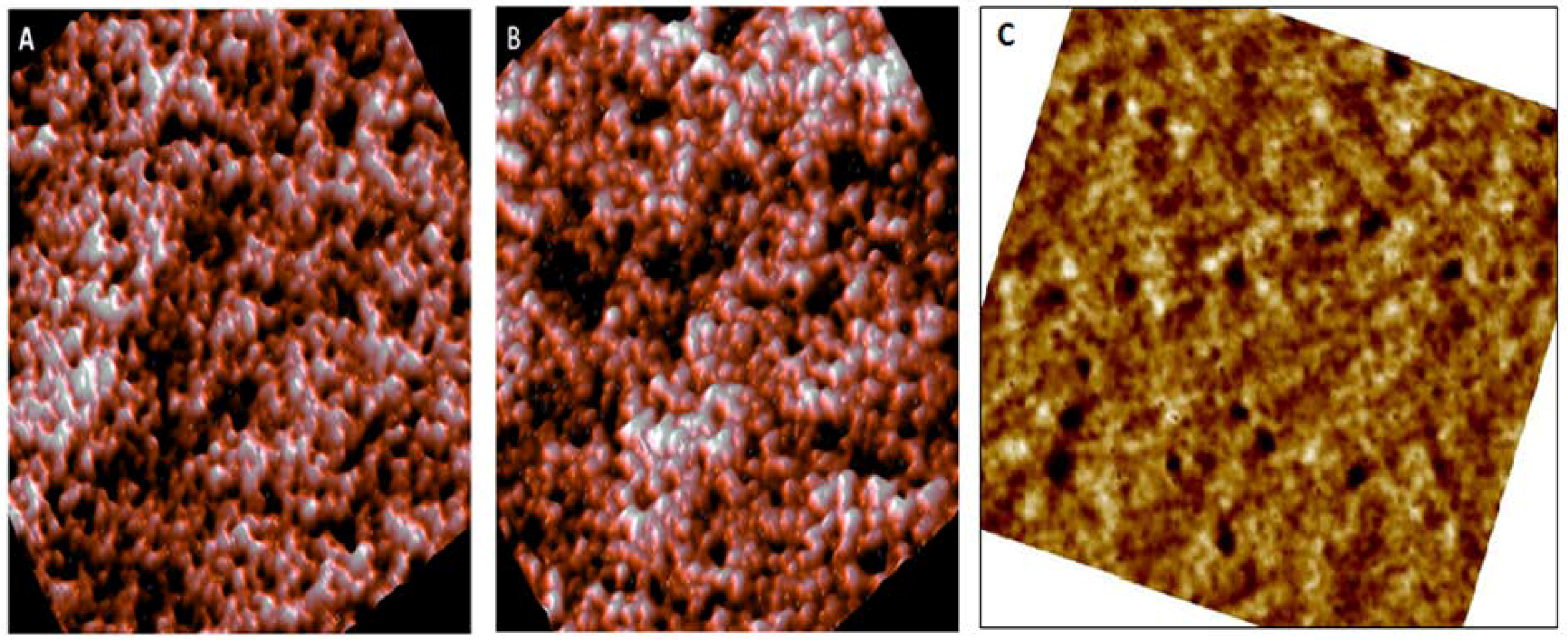

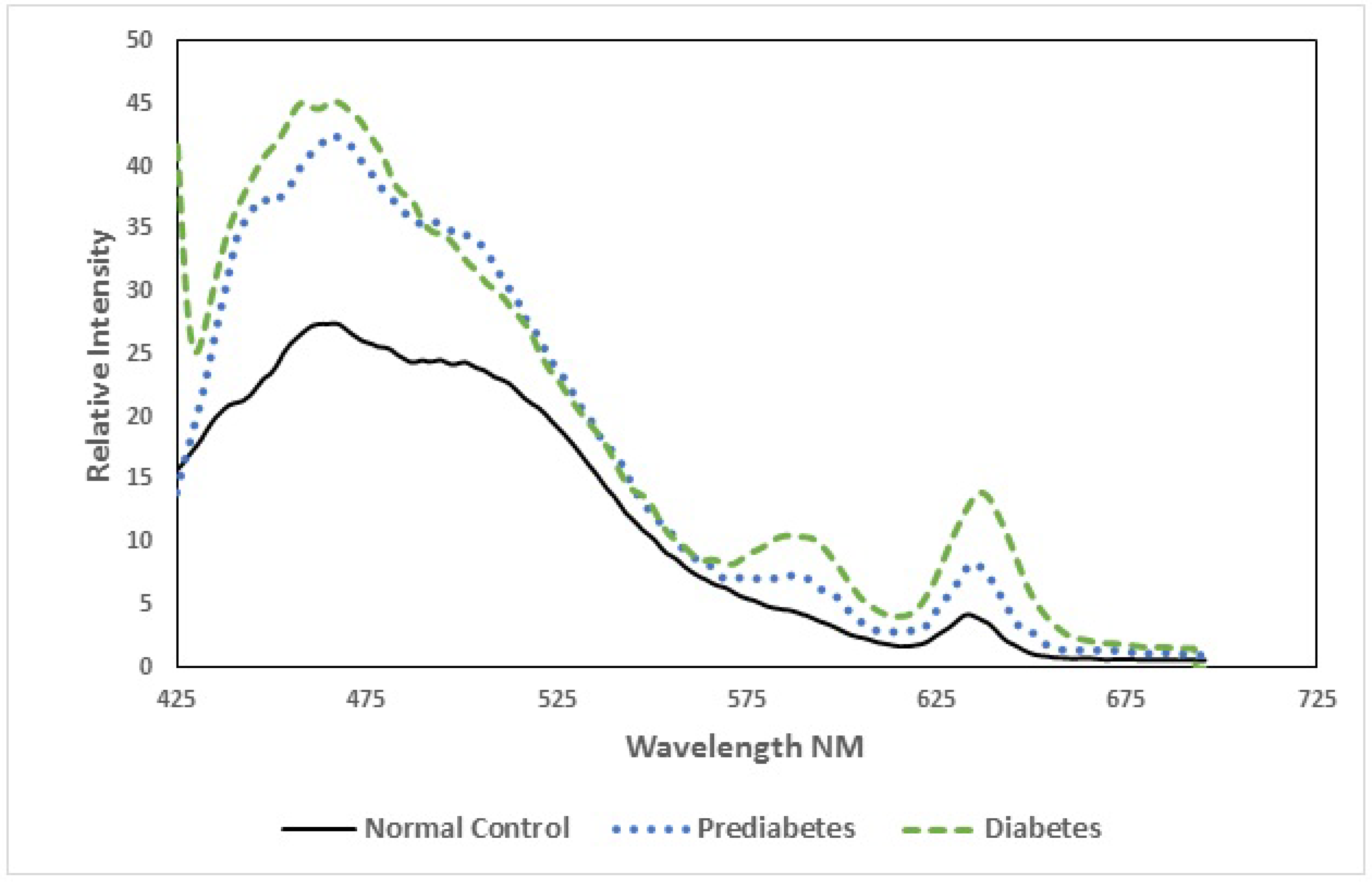


| Parameter | Normal (Control) | Pre-Diabetic | Diabetic |
|---|---|---|---|
| Diameter (µm) | 8.13 ± 0.81 | 6.87 ± 0.56 | 9.11 ± 0.81 |
| Concave depth (nm) | 267.1 ± 66 | 113 ± 46 | convex |
| Roughness (nm) | 1.07 ± 0.45 | 1.05 ± 0.31 | 1.18 ± 0.60 |
| Hematological Parameters | Normal Control (n = 31) | Smokers (Male) (n = 21) | Smokers (Female) (n = 10) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Hemoglobin (g/L) | 165 ± 0.95 (normal range male 130–180) 139 ± 1.15 (normal range female 120–160) | 171.13 ± 1.09 | 143.18 ± 1.38 |
| Hematocrit (%) | 41 ± 0.59 (normal range male 42–52); (normal range female 37–47) | 43.25 ± 2.01 | 39.47 ± 0.98 |
| Red blood cell (RBC, ×1012/L) | 4.9 ± 0.45 (normal range male 4.7–6.1) 4.4 ± 0.31 (normal range female 4.2–5.5) | 5.02 ± 1.12 | 4.71 ± 1.18 |
| Mean corpuscular volume (MCV) (fL) | 85 ± 1.12 (normal range 80–94) | 89.12 ± 1.52 | 86.4 ± 1.45 |
| Parameter | Normal (Control) | Moderate Smokers | Heavy Smokers | Pre-Diabetic | Diabetic |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Diameter (µm) | 8.13 ± 0.81 | 10.3 ± 1.06 | Irregular shape | 6.87 ± 0.56 | 9.11 ± 0.81 |
| Concave depth (nm) | 267.1 ± 66 | 296 ± 33 | 80 ± 41 | 113 ± 46 | convex |
| Roughness (nm) | 1.07 ± 0.45 | 1.30 ± 0.3 | 5.5 ± 3.0 | 1.05 ± 0.31 | 1.18 ± 0.60 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
S. AlSalhi, M.; Devanesan, S.; E. AlZahrani, K.; AlShebly, M.; Al-Qahtani, F.; Farhat, K.; Masilamani, V. Impact of Diabetes Mellitus on Human Erythrocytes: Atomic Force Microscopy and Spectral Investigations. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2018, 15, 2368. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph15112368
S. AlSalhi M, Devanesan S, E. AlZahrani K, AlShebly M, Al-Qahtani F, Farhat K, Masilamani V. Impact of Diabetes Mellitus on Human Erythrocytes: Atomic Force Microscopy and Spectral Investigations. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2018; 15(11):2368. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph15112368
Chicago/Turabian StyleS. AlSalhi, Mohamad, Sandhanasamy Devanesan, Khalid E. AlZahrani, Mashael AlShebly, Fatima Al-Qahtani, Karim Farhat, and Vadivel Masilamani. 2018. "Impact of Diabetes Mellitus on Human Erythrocytes: Atomic Force Microscopy and Spectral Investigations" International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 15, no. 11: 2368. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph15112368
APA StyleS. AlSalhi, M., Devanesan, S., E. AlZahrani, K., AlShebly, M., Al-Qahtani, F., Farhat, K., & Masilamani, V. (2018). Impact of Diabetes Mellitus on Human Erythrocytes: Atomic Force Microscopy and Spectral Investigations. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 15(11), 2368. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph15112368