Coverage and Influencing Determinants of Influenza Vaccination in Elderly Patients in a Country with a Poor Vaccination Implementation
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Objective
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Design and Setting
3.2. Study Population and Sampling
3.3. Study Instrument
3.4. Statistical Analysis
4. Results
4.1. Demographic
4.2. Vaccination Status
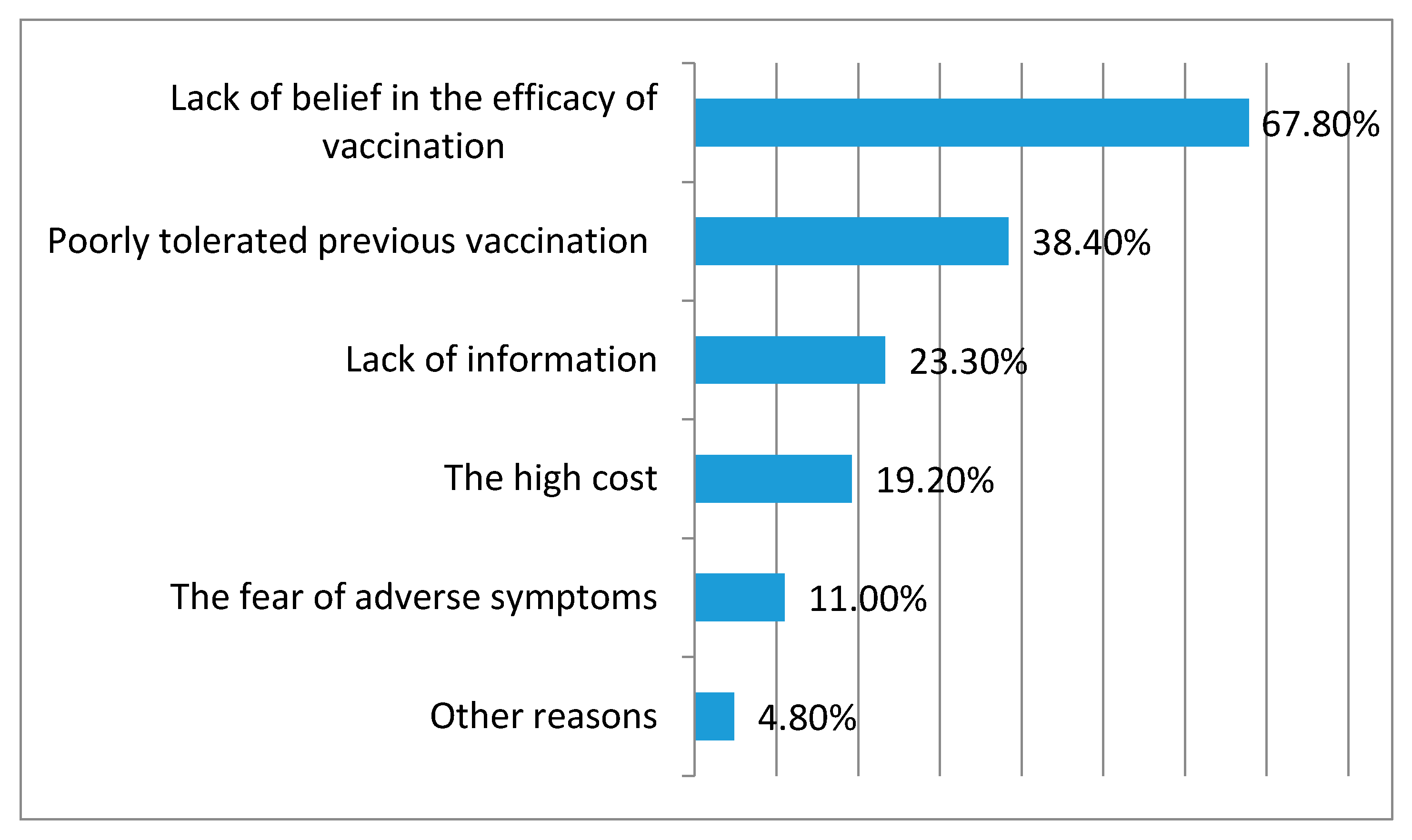
4.3. Sources of Information and Reasons for Influenza Vaccination
4.4. Beliefs about Influenza Vaccination
4.5. Determinants Related to Vaccination
5. Discussion
5.1. Overview of Results
5.2. Vaccination Uptake
5.3. Factors Related to Vaccination
5.4. Structural Patient-Related Determinants
5.5. Implications for Immunization Policy
6. Limitations
7. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Brydak, L.B.; Kosek, A.W.; Nitsch-Osuch, A. Influenza vaccines and vaccinations in Poland—Past, present and future. Med. Sci. Monit. 2012, 11, RA166–RA171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Centre for Disease Prevention and Control: Seasonal Influenza. Factsheet for Health Professionals. Available online: http://ecdc.europa.eu/en/healthtopics/seasonal_influenza/basic_facts/ Pages/factsheet_professionals_seasonal_influenza.aspx (accessed on 15 February 2017).
- Kondratiuk, K.; Czarkowski, M.P.; Hallmann-Szelińska, E.; Staszewska, E.; Bednarska, K.; Cielebąk, E.; Brydak, L.B. Influenza in Poland in 2013 and 2013/2014 epidemic season. Przegl. Epidemiol. 2016, 3, 407–419. [Google Scholar]
- Thompson, W.W.; Weintraub, E.; Dhankhar, P.; Cheng, P.Y.; Brammer, L.; Meltzer, M.I.; Bresee, J.S.; Shay, D.K. Estimates of US influenza-associated deaths made using four different methods. Influenza Other Respir. Viruses 2009, 3, 37–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jefferson, T.; Di Pietrantonj, C.; Al-Ansary, L.A.; Ferroni, E.; Thorning, S.; Thomas, R.E. Vaccines for Preventing Influenza in the Elderly. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2010, 2, CD004876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jefferson, T.; Di Pietrantonj, C.; Debalini, M.G.; Rivetti, A.; Demicheli, V. Inactivated influenza vaccines: Methods, policies, and politics. J. Clin. Epidemiol. 2009, 7, 677–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kramarz, P.; Ciancio, B.; Nicoll, A. Seasonal and pandemic influenza vaccines for the elderly and other risk groups: A review of available data. Pol. Arch. Med. Wewn. 2009, 10, 654–659. [Google Scholar]
- Grohskopf, L.A.; Olsen, S.J.; Sokolow, L.Z.; Bresee, J.S.; Cox, N.J.; Broder, K.R.; Karron, R.A.; Walter, E.B.; Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Prevention and control of seasonal influenza with vaccines: Recommendations of the Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices (ACIP)—United States, 2014–2015 influenza season. Morb. Mort. Wkly. Rep. 2014, 2, 691–697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Polish Mandatory Immunization Program for 2017. Available online: http://gis.gov.pl/images/ ep/so/pso_2017_-_nowelizacja.pdf (accessed on 16 June 2017).
- Blank, P.R.; Schwenkglenks, M.; Szucs, T.D. Vaccination coverage rates in eleven European countries during two consecutive influenza seasons. J. Infect. 2009, 6, 446–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- European Centre for Disease Prevention and Control. Seasonal Influenza Vaccination in Europe. Available online: http://ecdc.europa.eu/en/publications/Publications/Seasonal-influenza-vaccination-Europe-2012-2013.pdf (accessed on 15 February 2017).
- European Centre for Disease Prevention and Control. Seasonal Influenza Vaccination Programme Country Profile: Poland 2012–2013 Season. Available online: http://ecdc.europa.eu/en/publications/report%20Assets/seasonal-vaccination-coverage-in-europe-2012-2013/Seasonal-Influenza-Vaccination-Programme-Country-Profile-Poland.pdf (accessed on 15 February 2017).
- Kardas, P.; Zasowska, A.; Dec, J.; Stachurska, M. Reasons for low influenza vaccination coverage: Cross-sectional survey in Poland. Croat. Med. J. 2011, 2, 126–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagata, J.M.; Hernández-Ramos, I.; Kurup, A.S.; Albrecht, D.; Vivas-Torrealba, C.; Franco-Paredes, C. Social determinants of health and seasonal influenza vaccination in adults ≥65 years: A systematic review of qualitative and quantitative data. BMC Public Health 2013, 13, 388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmid, P.; Rauber, D.; Betsch, C.; Lidolt, G.; Denker, M.L. Barriers of Influenza Vaccination Intention and Behavior—A Systematic Review of Influenza Vaccine Hesitancy, 2005–2016. PLoS ONE 2017, 1, e0170550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nessler, K.; Krztoń-Królewiecka, A.; Chmielowiec, T.; Jarczewska, D.; Windak, A. Determinants of influenza vaccination coverage rates among primary care patients in Krakow, Poland and the surrounding region. Vaccine 2014, 52, 7122–7127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Łukomska, A. Factors behind the elderly’s decision to accept or reject vaccination against influenza. Gerontol. Pol. 2009, 17, 114. [Google Scholar]
- Nowalk, M.P.; Zimmerman, R.K.; Shen, S.; Jewell, I.K.; Raymund, M. Barriers to Pneumococcal and Influenza Vaccination in Older Community-Dwelling Adults (2000–2001). J. Am. Geriatr. Soc. 2004, 1, 25–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shemesh, A.A.; Rasooly, I.; Horowitz, P.; Lemberger, J.; Ben-Moshe, Y.; Kachal, J.; Danziger, J.; Clarfield, A.M.; Rosenberg, E. Health behaviors and their determinants in multiethnic, active Israeli seniors. Arch. Gerontol. Geriatr. 2008, 1, 63–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- R Development Core Team. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing; R Foundation for Statistical Computing: Vienna, Austria, 2008; ISBN 3-900051-07-0. [Google Scholar]
- Hosmer, D.W.; Lemeshow, S. Applied Logistic Regression, 2nd ed.; John Wiley & Sons Inc.: New York, NY, USA; Chichester, UK; Weinheim, Germany; Brisbane, Australia; Singapore; Toronto, ON, Canada, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Venables, W.N.; Ripley, B.D. Modern Applied Statistics with S, 4th ed.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Kwong, E.W.; Lam, I.O. Chinese older people in Hong Kong: Health beliefs about influenza vaccination. Nurs. Older People 2008, 7, 29–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fedson, D.S.; Hannoun, C.; Leese, J.; Sprenger, M.J.; Hampson, A.W.; Bro-Jørgensen, K.; Ahlbom, A.M.; Nøkelby, H.; Valle, M.; Olafsson, O.; et al. Influenza vaccination in 18 developed countries, 1980–1992. Vaccine 1995, 7, 623–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The State Sanitary Inspection. The Need for Vaccination. Available online: http://szczepienia.gis.gov.pl/index.php/akcja_informacyjna/samorzadowe_programy_zdrowotne/zachodniopomorskie (accessed on 5 February 2017).
- Ward, L.; Draper, J. A review of the factors involved in older people’s decision making with regard to influenza vaccination: A literature review. J. Clin. Nurs. 2008, 1, 5–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sarría-Santamera, A.; Timoner, J. Influenza vaccination in old adults in Spain. Eur. J. Public Health 2003, 2, 133–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Damiani, G.; Federico, B.; Visca, M.; Agostini, F.; Ricciardi, W. The impact of socio-economic level on influenza vaccination among Italian adults and elderly: A cross-sectional study. Prev. Med. 2007, 5, 373–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Andres, A.L.; Garrido, P.C.; Hernández-Barrera, V.; Del Pozo, S.V.; De Miguel, A.G.; Jiménez-García, R. Influenza vaccination among the elderly Spanish population: Trend from 1993 to 2003 and vaccination-related factors. Eur. J. Public Health 2007, 17, 272–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ryu, S.Y.; Kim, S.H.; Park, H.S.; Park, J. Influenza Vaccination among Adults 65 Years or Older: A 2009–2010 Community Health Survey in the Honam Region of Korea. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2011, 8, 4197–4206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chiatti, C.; Di Rosa, M.; Barbadoro, P.; Lamura, G.; Di Stanislao, F.; Prospero, E. Socio-economic determinants of influenza vaccination among older adults in Italy. Prev. Med. 2010, 51, 332–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Malley, A.S.; Forrest, C.B. Immunization Disparities in Older Americans: Determinants and Future Research Needs. Am. J. Prev. Med. 2006, 2, 150–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, P.; Tao, G.; Irwin, K.L. Utilization of preventive medical services in the United States: A comparison between rural and urban populations. J. Rural Health 2000, 16, 349–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lau, J.T.; Yang, X.; Tsui, H.Y.; Kim, J.H. Prevalence of influenza vaccination and associated factors among community-dwelling Hong Kong residents of age 65 or above. Vaccine 2006, 24, 5526–5534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zimmerman, R.K.; Santibanez, T.A.; Janosky, J.E.; Fine, M.J.; Raymund, M.; Wilson, S.A.; Bardella, I.J.; Medsger, A.R.; Nowalk, M.P. What affects influenza vaccination rates among older patients? An analysis from inner-city, suburban, rural, and veterans affairs practices. Am. J. Med. 2003, 114, 31–38. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Giese, C.; Mereckiene, J.; Danis, K.; O’Donnell, J.; O’Flanagan, D.; Cotter, S. Low vaccination coverage for seasonal influenza and pneumococcal disease among adults at-risk and health care workers in Ireland, 2013: The key role of GPs in recommending vaccination. Vaccine 2016, 34, 3657–3662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brydak, L.; Roiz, J.; Faivre, P.; Reygrobellet, C. Implementing an influenza vaccination programme for adults aged ≥65 years in Poland: A cost-effectiveness analysis. Clin. Drug Investig. 2012, 2, 73–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blanton, L.; Mustaquim, D.; Alabi, N.; Kniss, K.; Kramer, N.; Budd, A.; Garg, S.; Cummings, C.N.; Fry, A.M.; Bresee, J.; et al. Update: Influenza Activity—United States, 2 October 2016–4 February 2017. Morb. Mort. Wkly. Rep. 2017, 66, 159–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thommes, E.W.; Ismaila, A.; Chit, A.; Meier, G.; Bauch, C.T. Cost-effectiveness evaluation of quadrivalent influenza vaccines for seasonal influenza prevention: A dynamic modeling study of Canada and the United Kingdom. BMC Infect. Dis. 2015, 15, 465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kristiansen, C.M.; Harding, C.M. The social desirability of preventive health behavior. Public Health Rep. 1984, 99, 384–388. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]

| Variable | Number of Respondents n (%) | Vaccinated n (%) | Unvaccinated n (%) | p |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gender | ||||
| women | 183 (79.6) | 61 (76.2) | 122 (81.3) | 0.39 |
| men | 47 (20.4) | 19 (23.8) | 28 (18.7) | |
| Age (Years) | ||||
| 65–70 | 125 (54.3) | 51 (63.7) | 74 (49.3) | 0.04 |
| 71–80 | 66 (28.7) | 14 (17.5) | 52 (34.7) | |
| >80 | 39 (17.0) | 15 (18.8) | 24 (16.0) | |
| Residency | ||||
| town with <50,000 inhabitants | 22 (9.6) | 6 (7.5) | 16 (10.7) | 0.04 |
| town with 50,000–150,000 inhabitants | 46 (20.0) | 24 (30.0) | 22 (14.6) | |
| town with >150,000 inhabitants | 144 (62.6) | 48 (60.0) | 96 (64.0) | |
| rural area | 18 (7.8) | 2 (2.5) | 16 (10.7) | |
| Education Level | ||||
| primary | 16 (7.0) | 4 (5.0) | 12 (8.0) | 0.55 |
| vocational | 73 (31.7) | 26 (32.5) | 47 (31.3) | |
| secondary | 109 (47.4) | 37 (46.25) | 72 (48.0) | |
| university | 32 (13.9) | 13 (16.25) | 19 (12.7) | |
| Economic Status (Self-Assessed) | ||||
| high | 19 (8.2) | 8 (10.0) | 11 (7.3) | 1.00 |
| satisfactory | 126 (54.8) | 42 (52.5) | 84 (56.0) | |
| low | 85 (37.0) | 30 (37.5) | 55 (36.7) | |
| Accommodation | ||||
| living alone | 79 (34.4) | 34 (42.5) | 45 (30.0) | 0.06 |
| with family | 144 (62.6) | 42 (52.5) | 102 (68.0) | |
| private nursing/social welfare home | 7 (3.0) | 4 (5.0) | 3 (2.0) | |
| Source of Income | ||||
| pension | 136 (59.1) | 40 (50.0) | 96 (64.0) | 0.12 |
| employment | 47 (20.4) | 21 (26.3) | 26 (17.3) | |
| disability benefit | 42 (18.4) | 18 (22.5) | 24 (16.0) | |
| dependent (no income) | 4 (1.7) | 0 (0.0) | 4 (2.7) | |
| other | 1 (0.4) | 1 (1.2) | 0 (0.0) | |
| Chronic Disease | ||||
| present | 193 (83.9) | 73 (91.2) | 120 (80.0) | 0.04 |
| absent | 37 (16.1) | 7 (8.8) | 30 (20.0) | |
| Health Status (Self-Assessed) | ||||
| very good/good | 140 (60.9) | 40 (50.0) | 100 (66.7) | 0.02 |
| poor/very poor | 90 (39.1) | 40 (50.0) | 50 (33.3) | |
| Vaccinated Family Member | ||||
| yes | 54 (23.5) | 23 (28.8) | 29 (19.3) | 0.14 |
| no/cannot recall | 176 (76.5) | 57 (71.2) | 121 (80.7) | |
| Previous Information about Vaccination | ||||
| yes | 186 (80.9) | 80 (100.0) | 106 (70.7) | <0.0001 |
| no/cannot recall | 44 (19.1) | 0 (0.0) | 44 (29.3) | |
| Total | 230 | 80 | 150 | - |
| Variable | OR | 95% CI |
|---|---|---|
| Age: <70 years | 7.69 | 2.94–25.00 |
| Urban area: yes | 7.69 | 1.18–100.00 |
| Comorbidities: yes | 2.70 | 1.05–7.69 |
| Received information on influenza vaccination: yes | 5.00 | 1.23–33.89 |
| Vaccinated family member: yes | 3.57 | 1.29–11.13 |
| Willingness to be vaccinated the next year: yes | 8.59 | 3.27–26.50 |
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ganczak, M.; Gil, K.; Korzeń, M.; Bażydło, M. Coverage and Influencing Determinants of Influenza Vaccination in Elderly Patients in a Country with a Poor Vaccination Implementation. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2017, 14, 665. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph14060665
Ganczak M, Gil K, Korzeń M, Bażydło M. Coverage and Influencing Determinants of Influenza Vaccination in Elderly Patients in a Country with a Poor Vaccination Implementation. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2017; 14(6):665. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph14060665
Chicago/Turabian StyleGanczak, Maria, Karolina Gil, Marcin Korzeń, and Marta Bażydło. 2017. "Coverage and Influencing Determinants of Influenza Vaccination in Elderly Patients in a Country with a Poor Vaccination Implementation" International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 14, no. 6: 665. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph14060665
APA StyleGanczak, M., Gil, K., Korzeń, M., & Bażydło, M. (2017). Coverage and Influencing Determinants of Influenza Vaccination in Elderly Patients in a Country with a Poor Vaccination Implementation. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 14(6), 665. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph14060665





