Spatial Distribution of Underweight, Overweight and Obesity among Women and Children: Results from the 2011 Uganda Demographic and Health Survey
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Experimental Section
2.1. Data Source
2.2. Anthropometric Measures
2.3. Explanatory Variables
2.4. Statistical Analysis
2.5. Spatial Analysis
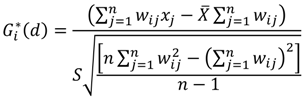
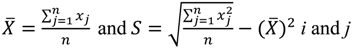 are geographical locations (coordinates) and xi and xj are values of the variables under study (BMI for adults and BMI percentile for children) at the coordinates i and j. The variable wi j stands for the association weights for coordinates i and j at distance d.
are geographical locations (coordinates) and xi and xj are values of the variables under study (BMI for adults and BMI percentile for children) at the coordinates i and j. The variable wi j stands for the association weights for coordinates i and j at distance d.3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Risk Analysis
| Variables | Normal/Underweight | % | Overweight/Obese | % |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sample population | 1,951 | 81 | 469 | 19 |
| Residence | ||||
| Urban | 522 | 68 | 248 | 32 |
| Rural | 1,429 | 87 | 221 | 13 |
| Wealth class * | ||||
| Low | 780 | 94 | 53 | 6 |
| Medium | 335 | 87 | 51 | 13 |
| High | 836 | 70 | 365 | 30 |
| Education * | ||||
| None | 291 | 87 | 45 | 13 |
| Primary | 1,131 | 84 | 217 | 16 |
| Secondary | 435 | 75 | 141 | 25 |
| Above secondary | 94 | 59 | 66 | 41 |
| Children’s BMI percentile category | 951 | 86 | 148 | 13 |
| Variables | Coefficients | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mothers (N = 2,420) | SE | Children (N = 1,099) | SE | |
| Maternal BMI | 0.015 *** | 0.004 | ||
| Age | 0.044 *** | 0.010 | 0.038 ** | 0.012 |
| Marital status: ever married | 1.002 *** | 0.21 | ||
| Residence: urban | 1.079 *** | 0.19 | ||
| Maternal education level | 0.054 *** | 0.022 | −0.003 | 0.003 |
| Wealth class: medium | 0.75 *** | 0.24 | ||
| Wealth class: high | 1.61 *** | 0.23 | ||
| Cash crop producing region: yes | 0.75 | 0.18 | ||
| Conflict prone region: yes | −0.81 | 0.23 | ||
| Intercept | 18.61 *** | 0.31 | −0.003 | 0.003 |
| R2 | 18.17% | 4.52% | ||
| Variables | Underweight | Overweight and obese | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Log odds ratio (SE) | Odds ratio [95% CI] | Log odds ratio (SE) | Odds ratio [95% CI] | |
| Age | 0.022 (0.011) | 1.022 [1.000,1.045] | 0.044 *** (0.0075) | 1.045 *** [1.030,1.052] |
| Marital status: evermarried | −0.66 ** (0.25) | 0.512 ** [0.32, 0.84] | 0.36 * (0.17) | 1.43 * [1.034, 1.98] |
| Residence: urban | 0.0029 (0.27) | 1.003 [0.59,1.69] | 0.56 *** (0.14) | 1.76 *** [1.34, 2.29] |
| Education level | −0.028 (0.028) | 0.97 [0.92, 1.027] | 0.031 * (0.016) | 1.032 * [1.001, 1.063] |
| Wealth class: medium | −0.89 ** (0.27) | 0.41 ** [0.24, 0.69] | 0.34 (0.23) | 1.41 [0.89, 2.19] |
| Wealth class: high | −0.92 *** (0.26) | 0.39 *** [0.24,0.66] | 1.079 *** (0.19) | 2.94 *** [1.99,4.35] |
| Cash crop producing region: yes | −0.32 (0.22) | 0.72 [0.47, 1.11] | 0.23 (0.13) | 1.26 [0.97, 1.62] |
| Conflict prone region: yes | 0.17 (0.22) | 1.19 [0.78, 1.81] | −0.73 ** (0.24) | 0.48 ** [0.29, 0.78] |
| Intercept | −1.72 *** (0.35) | −3.98 *** (0.28) | ||
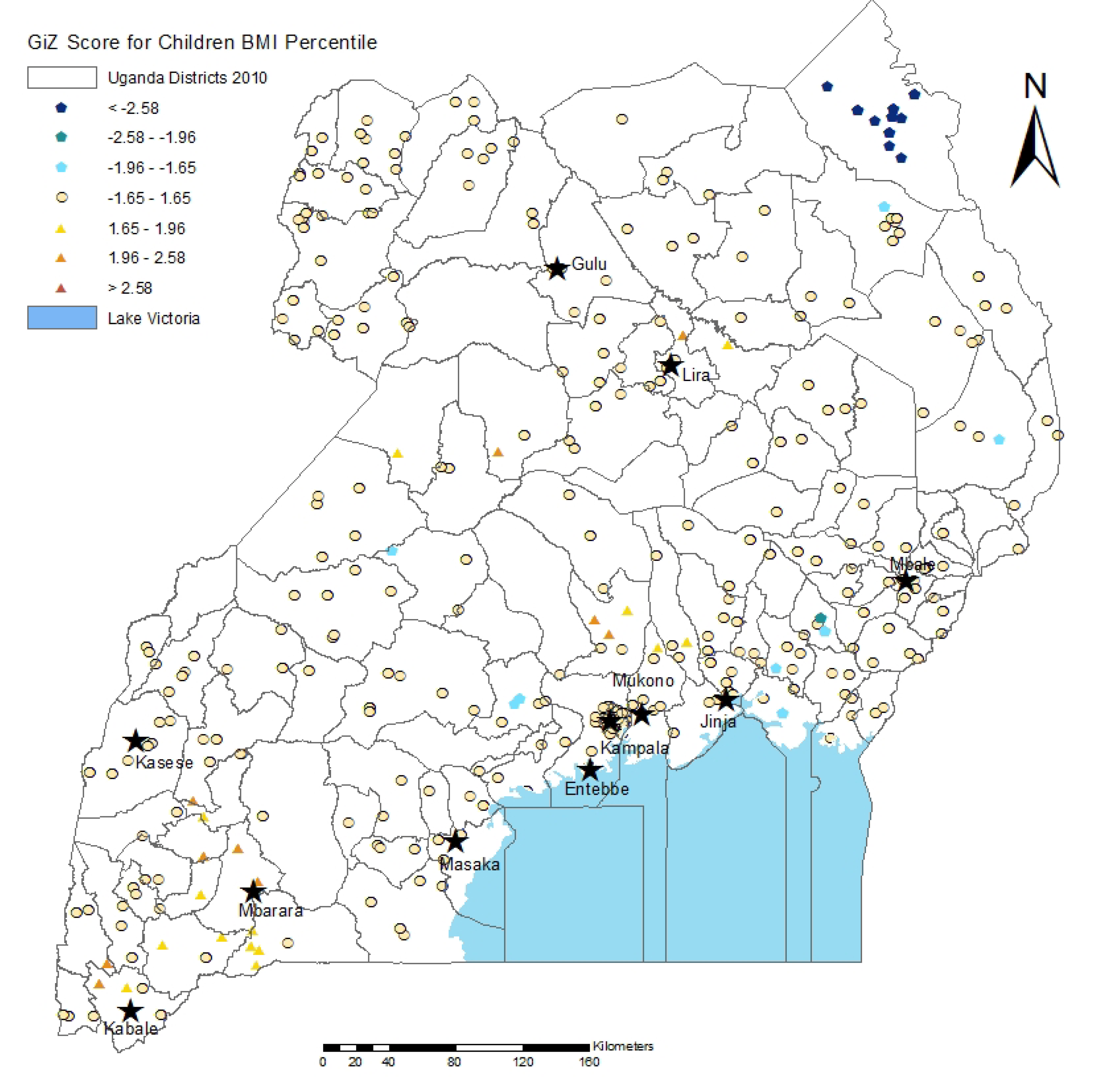
3.2. Spatial Analysis Results
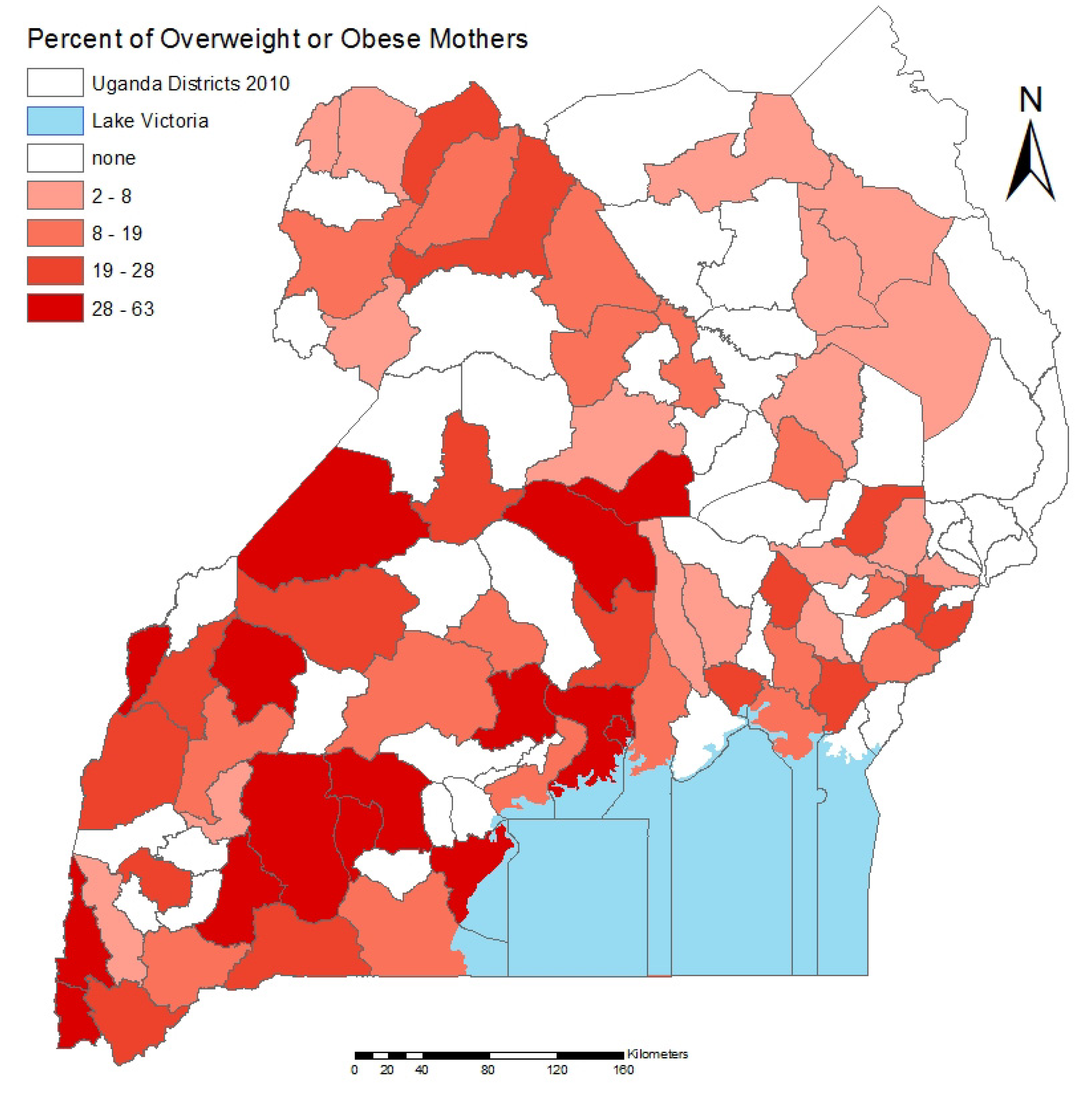
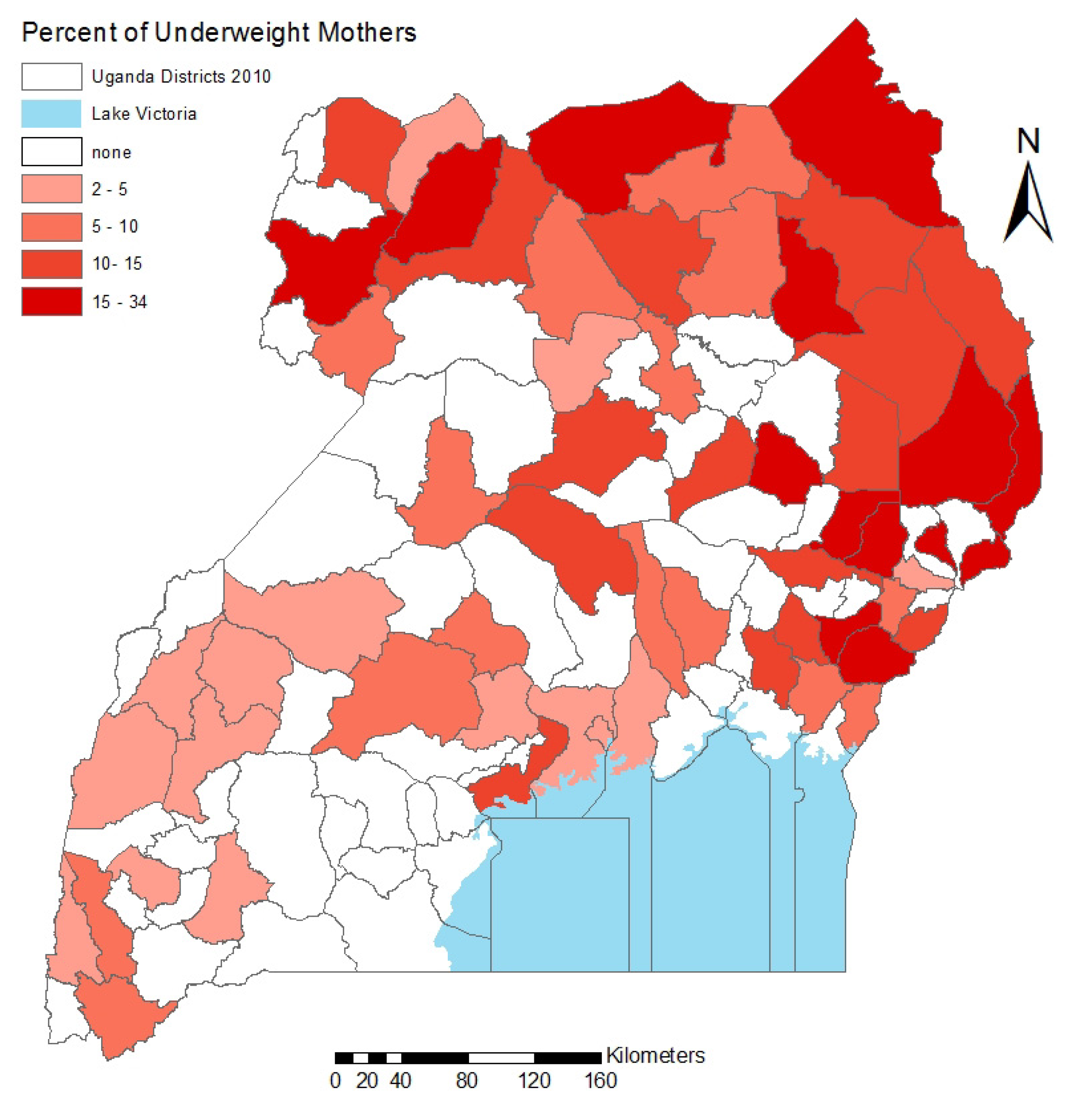
3.3. Discussion

3.4. Strengths and Limitations
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Tanumihardjo, S.A.; Anderson, C.; Kaufer-Horwitz, M.; Bode, L.; Emenaker, N.J.; Haqq, A.M.; Satia, J.A.; Silver, H.J.; Stadler, D.D. Poverty, obesity, and malnutrition: An international perspective recognizing the paradox. J. Am. Diet. Assoc. 2007, 107, 1966–1972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Popkin, B.M.; Adair, L.S.; Ng, S.W. Global nutrition transition and the pandemic of obesity in developing countries. Nutr. Rev. 2012, 70, 3–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization, Global InfoBase. Available online: https://apps.who.int/infobase/ (accessed on 22 October 2012).
- Finucane, M.M.; Stevens, G.A.; Cowan, M.J.; Danaei, G.; Lin, J.K.; Paciorek, C.J.; Singh, G.M.; Gutierrez, H.R.; Lu, Y.; Bahalim, A.N.; et al. National, regional, and global trends in body-mass index since 1980: Systematic analysis of health examination surveys and epidemiological studies with 960 country-years and 9.1 million participants. Lancet 2011, 377, 557–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bloom, D.E.; Cafiero, E.T.; Jané-Llopis, E.; Abrahams-Gessel, S.; Bloom, L.R.; Fathima, S.; Feigl, A.B.; Gaziano, T.; Mowafi, M.; Pandya, A.; et al. The Global Economic Burden of Noncommunicable Diseases; World Economic Forum: Geneva, Switzerland, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- World Health Organization (WHO), Global Status Report on Noncommunicable Diseases 2010; WHO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2011.
- Dalal, S.; Beunza, J.J.; Volmink, J.; Adebamowo, C.; Bajunirwe, F.; Njelekela, M.; Mozaffarian, D.; Fawzi, W.; Willett, W.; Adami, H.O.; et al. Non-Communicable diseases in sub-Saharan Africa: What we know now. Int. J. Epidemiol. 2011, 40, 885–901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ziraba, A.K.; Fotso, J.C.; Ochako, R. Overweight and obesity in urban Africa: A problem of the rich or the poor? BMC Public Health 2009, 9, 465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Twagirumukiza, M.; de Bacquer, D.; Kips, J.G.; de Backer, G.; Stichele, R.V.; van Bortel, L.M. Current and projected prevalence of arterial hypertension in sub-Saharan Africa by sex, age and habitat: An estimate from population studies. J. Hypertens 2011, 29, 1243–1252. [Google Scholar]
- Hall, V.; Thomsen, R.W.; Henriksen, O.; Lohse, N. Diabetes in sub-Saharan Africa 1999–2011: Epidemiology and public health implications. A systematic review. BMC Public Health 2011, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cromley, E.K. GIS and disease. Annu. Rev. Publ. Health 2003, 24, 7–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rushton, G. Public health, GIS, and spatial analytic tools. Ann. Rev. Publ. Health 2003, 24, 43–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pearce, J.; Witten, K.; Bartie, P. Neighbourhoods and health: A GIS approach to measuring community resource accessibility. J. Epidemiol. Commun. Health 2006, 60, 389–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Hulst, A.; Gauvin, L.; Kestens, Y.; Barnett, T.A. Neighborhood built and social environment characteristics: A multilevel analysis of associations with obesity among children and their parents. Int. J. Obes. (Lond.) 2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lovasi, G.S.; Schwartz-Soicher, O.; Quinn, J.W.; Berger, D.K.; Neckerman, K.M.; Jaslow, R.; Lee, K.K.; Rundle, A. Neighborhood safety and green space as predictors of obesity among preschool children from low-income families in New York City. Prev. Med. 2013, 57, 189–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saelens, B.E.; Sallis, J.F.; Frank, L.D.; Couch, S.C.; Zhou, C.; Colburn, T.; Cain, K.L.; Chapman, J.; Glanz, K. Obesogenic neighborhood environments, child and parent obesity: The neighborhood impact on kids study. Am. J. Prev. Med. 2012, 42, e57–e64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grigsby-Toussaint, D.S.; Chi, S.H.; Fiese, B.H. Where they live, how they play: Neighborhood greenness and outdoor physical activity among preschoolers. Int. J. Health Geogr. 2011, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laxer, R.E.; Janssen, I. The proportion of youths’ physical inactivity attributable to neighbourhood built environment features. Int. J. Health Geogr. 2013, 12, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pawloski, L.R.; Curtin, K.M.; Gewa, C.; Attaway, D. Maternal-child overweight/obesity and undernutrition in Kenya: A geographic analysis. Public Health Nutr. 2012, 15, 2140–2147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, C.Y.; Cheng, T.O. Prevalence and geographic distribution of childhood obesity in China in 2005. Int. J. Cardiol. 2008, 131, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lasky, D.; Becerra, E.; Boto, W.; Otim, M.; Ntambi, J. Obesity and gender differences in the risk of type 2 diabetes mellitus in Uganda. Nutrition 2002, 18, 417–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mayega, R.W.; Makumbi, F.; Rutebemberwa, E.; Peterson, S.; Ostenson, C.G.; Tomson, G.; Guwatudde, D. Modifiable socio-behavioural factors associated with overweight and hypertension among persons aged 35 to 60 years in eastern Uganda. PLoS One 2012, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maher, D.; Waswa, L.; Baisley, K.; Karabarinde, A.; Unwin, N.; Grosskurth, H. Distribution of hyperglycaemia and related cardiovascular disease risk factors in low-income countries: A cross-sectional population-based survey in rural Uganda. Int. J. Epidemiol. 2011, 40, 160–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uganda Bureau of Statistics (UBOS), ICF International Inc. In Uganda Demographic and Health Survey 2011; UBOS: Kampala, Uganda, and ICF International Inc.: Calverton, MD, USA, 2012; pp. 143–162.
- Food and Agriculture Organization, FAOSTAT: Country Profiles: Uganda. Available online: http://faostat.fao.org/site/666/default.aspx (accessed on 30 May 2013).
- Uganda PROFILES, Nutrition Advocacy Technical Working Group PROFILES Meeting Report; Ministry of Health: Kampala, Uganda, 2010.
- Swinburn, B.; Egger, G.; Raza, F. Dissecting obesogenic environments: The development and application of a framework for identifying and prioritizing environmental interventions for obesity. Prev. Med. 1999, 29, 563–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- FANTA-2, The Analysis of the Nutrition Situation in Uganda; Food and Nutrition Technical Assistance II Project (FANTA-2); FHI 360: Washington, DC, USA, 2010.
- Wilson, A.C.; Forsyth, J.S.; Greene, S.A.; Irvine, L.; Hau, C.; Howie, P.W. Relation of infant diet to childhood health: Seven year follow up of cohort of children in Dundee infant feeding study. Brit. Med. J. 1998, 316, 21–25. [Google Scholar]
- Kikafunda, J.K.; Walker, A.F.; Tumwine, J.K. Weaning foods and practices in central Uganda: A cross-sectional study. Afr. J. Food Agr. Nutr. Dev. 2003, 3. Available online: http://www.bioline.org.br/request?nd03012#kikafunda (accessed on 30 July 2013).
- Who Child Growth Standards: Length/Height-for-Age, Weight-for-Age, Weight-for-Length, Weight-for-Height and Body Mass Index-for-Age: Methods and Development; WHO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2006.
- Uganda Bureau of Statistics, The 2002 Uganda Population and Housing Census: Analytical Report; UBOS: Kampala, Uganda, 2006. Available online: http://www.ubos.org/onlinefiles/uploads/ubos/pdf documents/2002CensusPopnSizeGrowthAnalyticalReport.pdf (accessed on 1 July 2013).
- Humanitarian Response Common Operational Datasets (COD)-Fundamental Operational Datasets (FODs) registry. Uganda: Admin Level 3 Boundaries and Settlements. Available online: http://cod.humanitarianresponse.info/fr/search/field_country_region/187?search_api_views_fulltext (accessed on 3 September 2013).
- Geographic Information Support Team (GIST). Repository at the University of Georgia. Uganda Cash Crop Production. Available online: https://gistdata.itos.uga.edu/ (accessed on 3 September 2013).
- Ord, J.K.; Getis, A. Local spatial autocorrelation statistics: Distributional issues and an application. Geogr. Anal. 1995, 27, 286–306. [Google Scholar]
- Mitchell, A. The ESRI Guide to GIS Analysis; ESRI Press: Redlands, CA, USA, 2005; Volume 2. [Google Scholar]
- Grieve, J. A Comparison of Statistical Methods for the Aggregation of Regional Linguistic Variation. In Aggregating Dialectology and Typology: Linguistic Variation in Text and Speech, Within and Across Languages; Szmrecsanyi, B., Walchli, B., Eds.; Walter de Gruyter: Berlin, Germany, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Getis, A.; Ord, J.K. The analysis of spatial association by use of distance statistics. Geogr. Anal. 1992, 24, 189–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Behrend, H. Alice Lakwena and the Holy Spirits: War in Northern Uganda 1985–97; Fountain Publishers: Kampala, Uganda, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Finnström, S. Living with Bad Surroundings: War and Existential Uncertainty in Acholiland., Northern Uganda; Uppsala University Press: Uppsala, Sweden, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Branch, A. Neither peace nor justice: Political violence and the peasantry in northern Uganda, 1986–1998. Afr. Stud. Quart. 2005, 8. Available online: http://web.africa.ufl.edu/asq/v8/v8i2a1.htm (accessed on 30 August 2013).
- Van Wesenbeeck, C.F.; Keyzer, M.A.; Nube, M. Estimation of undernutrition and mean calorie intake in Africa: Methodology, findings and implications. Int. J. Health Geogr. 2009, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2013 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Turi, K.N.; Christoph, M.J.; Grigsby-Toussaint, D.S. Spatial Distribution of Underweight, Overweight and Obesity among Women and Children: Results from the 2011 Uganda Demographic and Health Survey. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2013, 10, 4967-4981. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph10104967
Turi KN, Christoph MJ, Grigsby-Toussaint DS. Spatial Distribution of Underweight, Overweight and Obesity among Women and Children: Results from the 2011 Uganda Demographic and Health Survey. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2013; 10(10):4967-4981. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph10104967
Chicago/Turabian StyleTuri, Kedir N., Mary J. Christoph, and Diana S. Grigsby-Toussaint. 2013. "Spatial Distribution of Underweight, Overweight and Obesity among Women and Children: Results from the 2011 Uganda Demographic and Health Survey" International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 10, no. 10: 4967-4981. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph10104967
APA StyleTuri, K. N., Christoph, M. J., & Grigsby-Toussaint, D. S. (2013). Spatial Distribution of Underweight, Overweight and Obesity among Women and Children: Results from the 2011 Uganda Demographic and Health Survey. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 10(10), 4967-4981. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph10104967




