Laminarin from Irish Brown Seaweeds Ascophyllum nodosum and Laminaria hyperborea: Ultrasound Assisted Extraction, Characterization and Bioactivity
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Laminarin and Phenolics Content
| Seaweed Species | Solvent Type | Extraction Method | Time (min) | Sample Code | Laminarin Assay (% db) | Total Phenolic Content (mg PGE/gdb) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Laminaria hyperborea | Water | Ultrasound | 15 | LHWU | 5.975 ± 0.467 | 0.365 ± 0.039 |
| Laminaria hyperborea | 0.1 M HCl | Ultrasound | 15 | LHAU | 6.240 ± 0.008 | 0.343 ± 0.003 |
| Laminaria hyperborea | Water | Solid liquid | 150 | LHWS | 4.362 ± 0.197 | 0.363 ± 0.057 |
| Laminaria hyperborea | 0.1 M HCl | Solid liquid | 150 | LHAS | 3.254 ± 0.235 | 0.352 ± 0.021 |
| Ascophyllum nodosum | Water | Ultrasound | 15 | ANWU | 5.290 ± 0.480 | 0.156 ± 0.014 |
| Ascophyllum nodosum | 0.1 M HCl | Ultrasound | 15 | ANAU | 5.822 ± 0.343 | 0.128 ± 0.008 |
| Ascophyllum nodosum | Water | Solid liquid | 150 | ANWS | 4.599 ± 0.030 | 0.166 ± 0.015 |
| Ascophyllum nodosum | 0.1 M HCl | Solid liquid | 150 | ANAS | 4.304 ± 0.165 | 0.110 ± 0.007 |
2.2. Characterization of Extracts
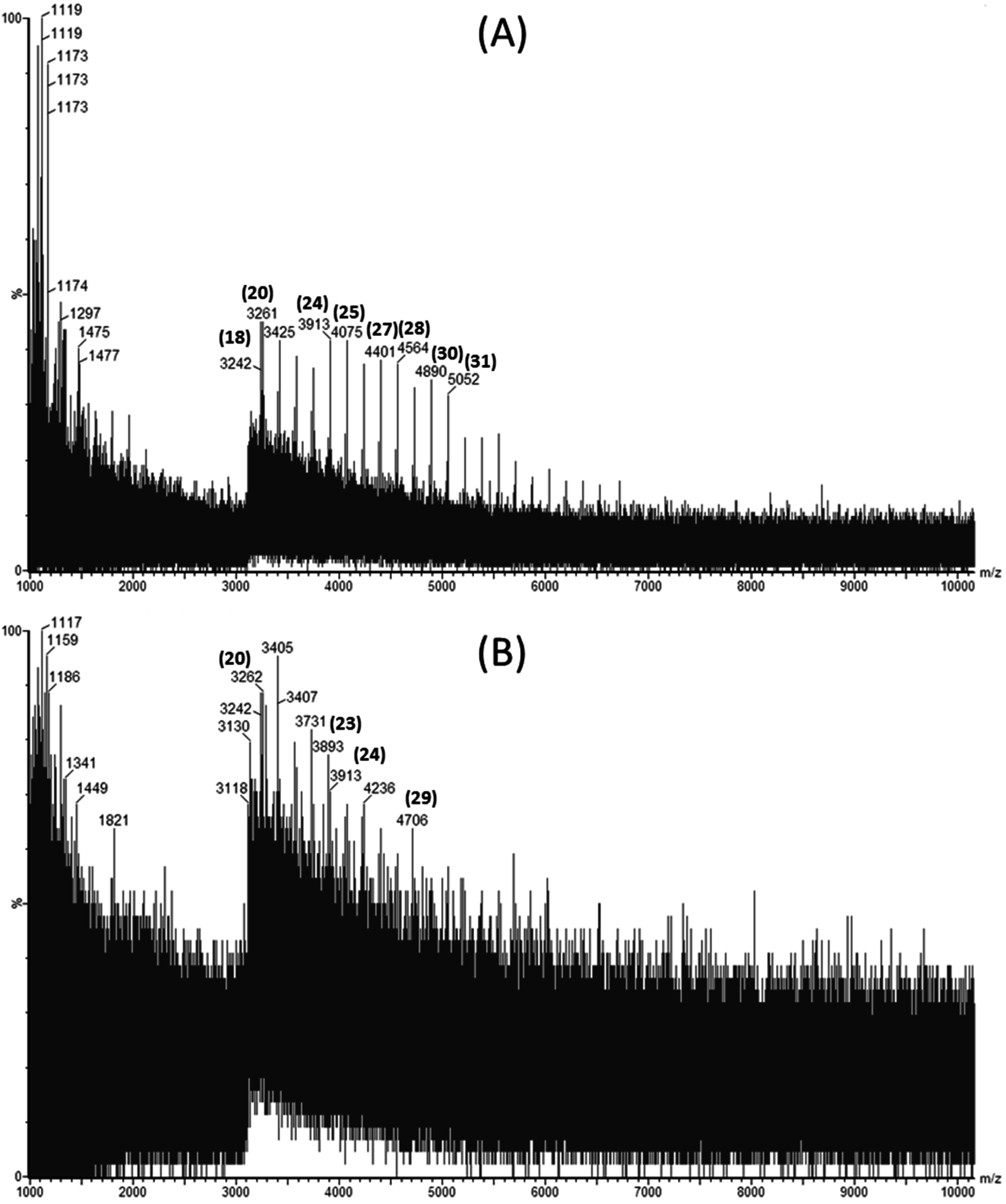
2.3. Bioactivities of Laminarin Rich Extract
| Sample | Antioxidant Activity (% DPPH Inhibition) | MIC (mg/mL) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| E. coli | S. typhimurium | S. aureus | L. monocytogenes | ||
| LHWU | 52.78 | 21.0 | 21.0 | 5.3 | 2.6 |
| LHAU | 87.58 | 13.1 | 13.1 | 6.6 | 3.3 |
| LHWS | 73.91 | 45.6 | 22.8 | 11.4 | 5.7 |
| LHAS | 86.04 | 28.2 | 28.2 | 7.0 | 7.0 |
| ANWU | 61.46 | 43.2 | 21.6 | NI * | NI |
| ANAU | 93.24 | 596.8 | 14.9 | 29.8 | 59.7 |
| ANWS | 15.13 | NI | 25.5 | NI | NI |
| ANAS | 87.82 | NI | 33.4 | 66.8 | 66.8 |
3. Experimental Section
3.1. Chemicals and Reagents
3.2. Seaweed Samples
3.3. Ultrasound Assisted Extraction
| Seaweed Species | Solvent Type | Extraction | Time (min) | Sample Code |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Laminaria hyperborea | Water | Ultrasound | 15 | LHWU |
| Laminaria hyperborea | 0.1 M HCl | Ultrasound | 15 | LHAU |
| Laminaria hyperborea | Water | Solid liquid | 150 | LHWS |
| Laminaria hyperborea | 0.1 M HCl | Solid liquid | 150 | LHAS |
| Ascophyllum nodosum | Water | Ultrasound | 15 | ANWU |
| Ascophyllum nodosum | 0.1 M HCl | Ultrasound | 15 | ANAU |
| Ascophyllum nodosum | Water | Solid liquid | 150 | ANWS |
| Ascophyllum nodosum | 0.1 M HCl | Solid liquid | 150 | ANAS |
3.4. Laminarin Assay
3.5. Total Phenolic Content
3.6. Matrix Assisted Laser Desorption Ionization Quadrupole Time-of-Flight Mass Spectrometry (MALDI-Q-TOF-MS)
3.7. Antioxidant Activity—DPPH Method
3.8. Antimicrobial Activity—Iodonitrotetrazolium Chloride (INT) Dye Method
3.8.1. Bacterial Strains and Culture Conditions
3.8.2. Minimum Inhibitory Concentration (MIC) Assay
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kadam, S.U.; Prabhasankar, P. Marine foods as functional ingredients in bakery and pasta products. Food Res. Int. 2010, 43, 1975–1980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, S.; Abu-Ghannam, N. Bioactive potential and possible health effects of edible brown seaweeds. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2011, 22, 315–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, S.; Abu-Ghannam, N. Recent developments in the application of seaweeds or seaweed extracts as a means for enhancing the safety and quality attributes of foods. Innov. Food Sci. Emerg. Technol. 2011, 12, 600–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Z.; Okimura, T.; Yokose, T.; Yamasaki, Y.; Yamaguchi, K.; Oda, T. Effects of sulfated fucan, ascophyllan, from the brown Alga Ascophyllum nodosum on various cell lines: A comparative study on ascophyllan and fucoidan. J. Biosci. Bioeng. 2010, 110, 113–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Werner, A.; Kraan, S. Review of the Potential Mechanisation of Kelp Harvesting in Ireland; National University of Ireland: Galway, Ireland, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Rioux, L.E.; Turgeon, S.L.; Beaulieu, M. Characterization of polysaccharides extracted from brown seaweeds. Carbohydr. Polym. 2007, 69, 530–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kadam, S.U.; Tiwari, B.K.; O’Donnell, C.P. Extraction, structure and biofunctional activities of laminarin from brown algae. Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2014, 50, 24–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miao, H.-Q.; Ishai-Michaeli, R.; Peretz, T.; Vlodavsky, I. Laminarin sulfate mimics the effects of heparin on smooth muscle cell proliferation and basic fibroblast growth factor-receptor binding and mitogenic activity. J. Cell. Physiol. 1995, 164, 482–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yvin, J.C.; LeVasseur, F.; Hud’Homme, F. Use of Laminarin and Oligosaccharides Derived Therefrom in Cosmetics and for Preparing a Skin Treatment Drug. U.S. Patent US5980916 A, 9 November 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Zha, X.-Q.; Xiao, J.-J.; Zhang, H.-N.; Wang, J.-H.; Pan, L.-H.; Yang, X.-F.; Luo, J.-P. Polysaccharides in Laminaria japonica (LP): Extraction, physicochemical properties and their hypolipidemic activities in diet-induced mouse model of atherosclerosis. Food Chem. 2012, 134, 244–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chizhov, A.O.; Dell, A.; Morris, H.R.; Reason, A.J.; Haslam, S.M.; McDowell, R.A.; Chizhov, O.S.; Usov, A.I. Structural analysis of laminarans by MALDI and FAB mass spectrometry. Carbohydr. Res. 1998, 310, 203–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Date, Y.; Sakata, K.; Kikuchi, J. Chemical profiling of complex biochemical mixtures from various seaweeds. Polym. J. 2012, 44, 888–894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vilkhu, K.; Mawson, R.; Simons, L.; Bates, D. Applications and opportunities for ultrasound assisted extraction in the food industry—A review. Innov. Food Sci. Emerg. Technol. 2008, 9, 161–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deville, C.; Damas, J.; Forget, P.; Dandrifosse, G.; Peulen, O. Laminarin in the dietary fibre concept. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2004, 84, 1030–1038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rinaudo, M. Seaweed polysaccharides. In Comprehensive Glycoscience; Johannis, P.K., Ed.; Elsevier: Oxford, UK, 2007; pp. 691–735. [Google Scholar]
- Kadam, S.U.; Tiwari, B.K.; O’Donnell, C.P. Application of novel extraction technologies for bioactives from marine algae. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2013, 61, 4667–4675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kadam, S.U.; Tiwari, B.K.; O’Connell, S.; O’Donnell, C.P. Effect of ultrasound pre-treatment on the extraction kinetics of bioactives from brown seaweed (Ascophyllum nodosum). Sep. Sci. Technol. 2014, 50, 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Kadam, S.U.; Tiwari, B.K.; Smyth, T.J.; O’Donnell, C.P. Optimization of ultrasound assisted extraction of bioactive components from brown seaweed Ascophyllum nodosum using response surface methodology. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2015, 23, 308–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Sullivan, A.M.; O’Callaghan, Y.C.; O’Grady, M.N.; Queguineur, B.; Hanniffy, D.; Troy, D.J.; Kerry, J.P.; O’Brien, N.M. In vitro and cellular antioxidant activities of seaweed extracts prepared from five brown seaweeds harvested in spring from the west coast of Ireland. Food Chem. 2011, 126, 1064–1070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balboa, E.M.; Conde, E.; Moure, A.; Falqué, E.; Domínguez, H. In vitro antioxidant properties of crude extracts and compounds from brown algae. Food Chem. 2013, 138, 1764–1785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kenny, O.; Smyth, T.J.; Walsh, D.; Kelleher, C.T.; Hewage, C.M.; Brunton, N.P. Investigating the potential of under-utilised plants from the Asteraceae family as a source of natural antimicrobial and antioxidant extracts. Food Chem. 2014, 161, 79–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jaswir, I.; Tawakalit Tope, A.-H.; Raus, R.A.; Ademola Monsur, H.; Ramli, N. Study on anti-bacterial potentials of some Malaysian brown seaweeds. Food Hydrocoll. 2014, 42, 275–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, S.P.; McLoughlin, P.; O’Sullivan, L.; Prieto, M.L.; Gardiner, G.E.; Lawlor, P.G.; Hughes, H. Development of a novel antimicrobial seaweed extract-based hydrogel wound dressing. Int. J. Pharm. 2013, 456, 10–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Black, W.A.P.; Cornhill, W.J.; Dewar, E.J.; Woodward, F.N. Manufacture of algal chemicals. III. Laboratory-scale isolation of laminarin from brown marine algae. J. Appl. Chem. 1951, 1, 505–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ermakova, S.; Men’shova, R.; Vishchuk, O.; Kim, S.-M.; Um, B.-H.; Isakov, V.; Zvyagintseva, T. Water-soluble polysaccharides from the brown alga Eisenia bicyclis: Structural characteristics and antitumor activity. Algal Res. 2013, 2, 51–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, W.; Zhang, W.; Wang, J.; Ren, S.; Song, N.; Duan, D.; Zhang, Q. Characterization of laminaran and a highly sulfated polysaccharide from Sargassum fusiforme. Carbohydr. Res. 2014, 385, 58–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Devillé, C.; Gharbi, M.; Dandrifosse, G.; Peulen, O. Study on the effects of laminarin, a polysaccharide from seaweed, on gut characteristics. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2007, 87, 1717–1725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Wu, Y.; Chen, G.; Yue, W.; Liang, Q.; Wu, Q. Optimisation of ultrasound assisted extraction of phenolic compounds from Sparganii rhizoma with response surface methodology. Ultrason. Sonochemistry 2013, 20, 846–854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shetty, K.; Curtis, O.F.; Levin, R.E.; Witkowsky, R.; Ang, W. Prevention of vitrification associated with in vitro shoot culture of oregano (Origanum vulgare) by Pseudomonas spp. J. Plant Physiol. 1995, 147, 447–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eloff, J.N. A sensitive and quick microplate method to determine the minimal inhibitory concentration of plant extracts for bacteria. Planta Med. 1998, 64, 711–713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
© 2015 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kadam, S.U.; O'Donnell, C.P.; Rai, D.K.; Hossain, M.B.; Burgess, C.M.; Walsh, D.; Tiwari, B.K. Laminarin from Irish Brown Seaweeds Ascophyllum nodosum and Laminaria hyperborea: Ultrasound Assisted Extraction, Characterization and Bioactivity. Mar. Drugs 2015, 13, 4270-4280. https://doi.org/10.3390/md13074270
Kadam SU, O'Donnell CP, Rai DK, Hossain MB, Burgess CM, Walsh D, Tiwari BK. Laminarin from Irish Brown Seaweeds Ascophyllum nodosum and Laminaria hyperborea: Ultrasound Assisted Extraction, Characterization and Bioactivity. Marine Drugs. 2015; 13(7):4270-4280. https://doi.org/10.3390/md13074270
Chicago/Turabian StyleKadam, Shekhar U., Colm P. O'Donnell, Dilip K. Rai, Mohammad B. Hossain, Catherine M. Burgess, Des Walsh, and Brijesh K. Tiwari. 2015. "Laminarin from Irish Brown Seaweeds Ascophyllum nodosum and Laminaria hyperborea: Ultrasound Assisted Extraction, Characterization and Bioactivity" Marine Drugs 13, no. 7: 4270-4280. https://doi.org/10.3390/md13074270









