Experimental Analysis of Bisbenzocyclobutene Bonded Capacitive Micromachined Ultrasonic Transducers
Abstract
:1. Introduction
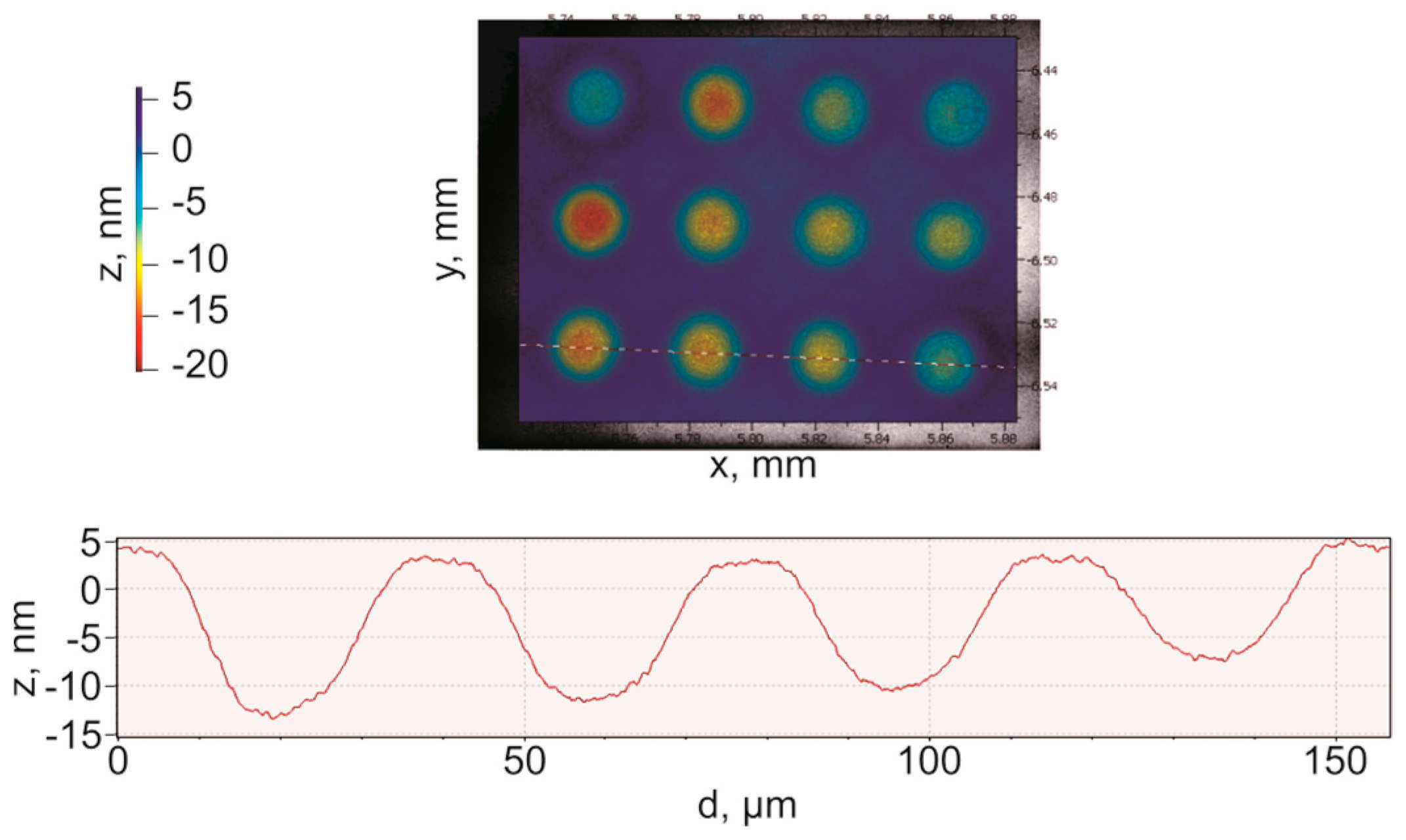
2. Fabrication Characterization of CMUT Array
3. Behavioral Characterization
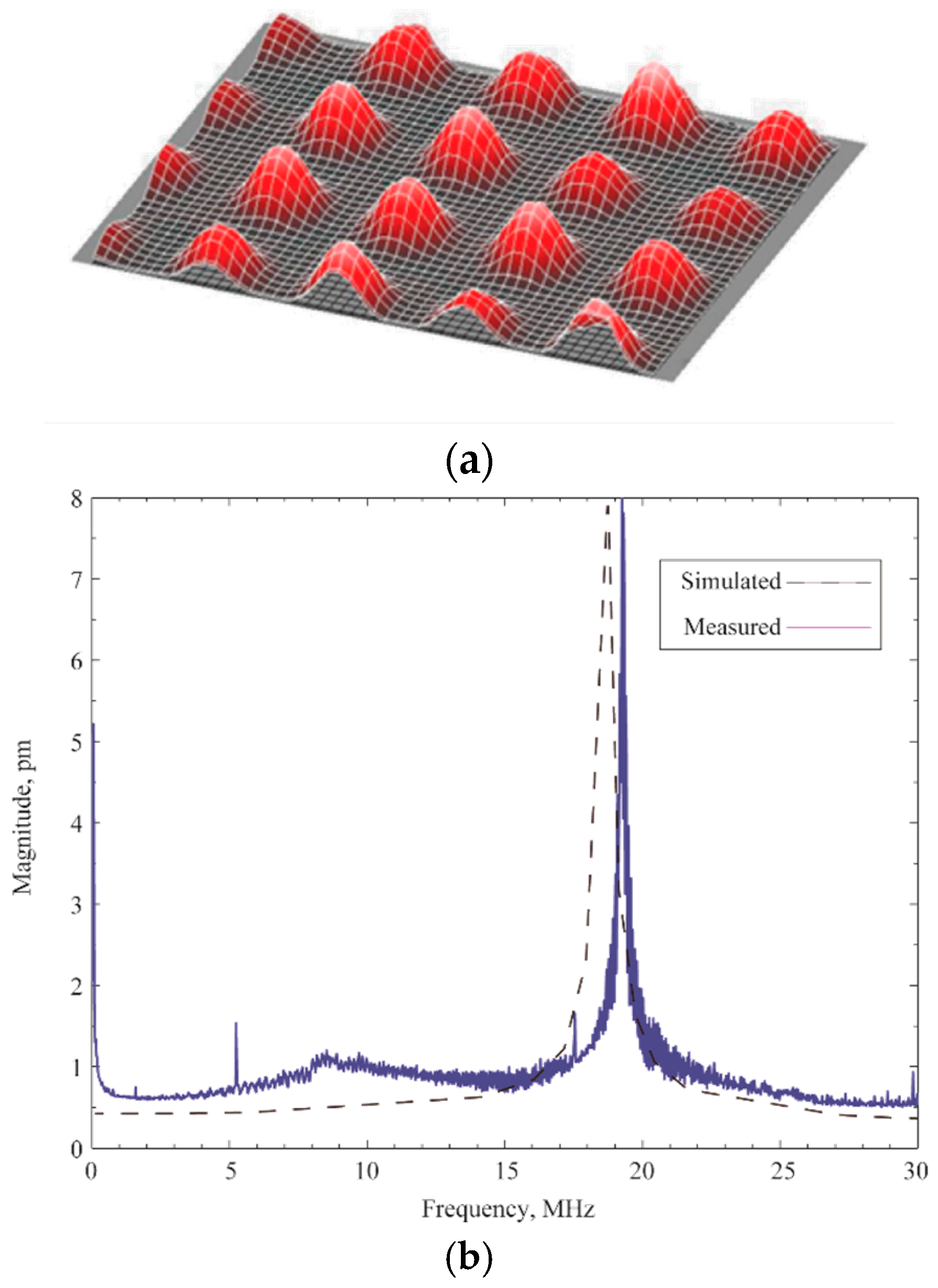
3.1. Capacitance and Imepdance Measurements
3.2. Coupling Coefficient
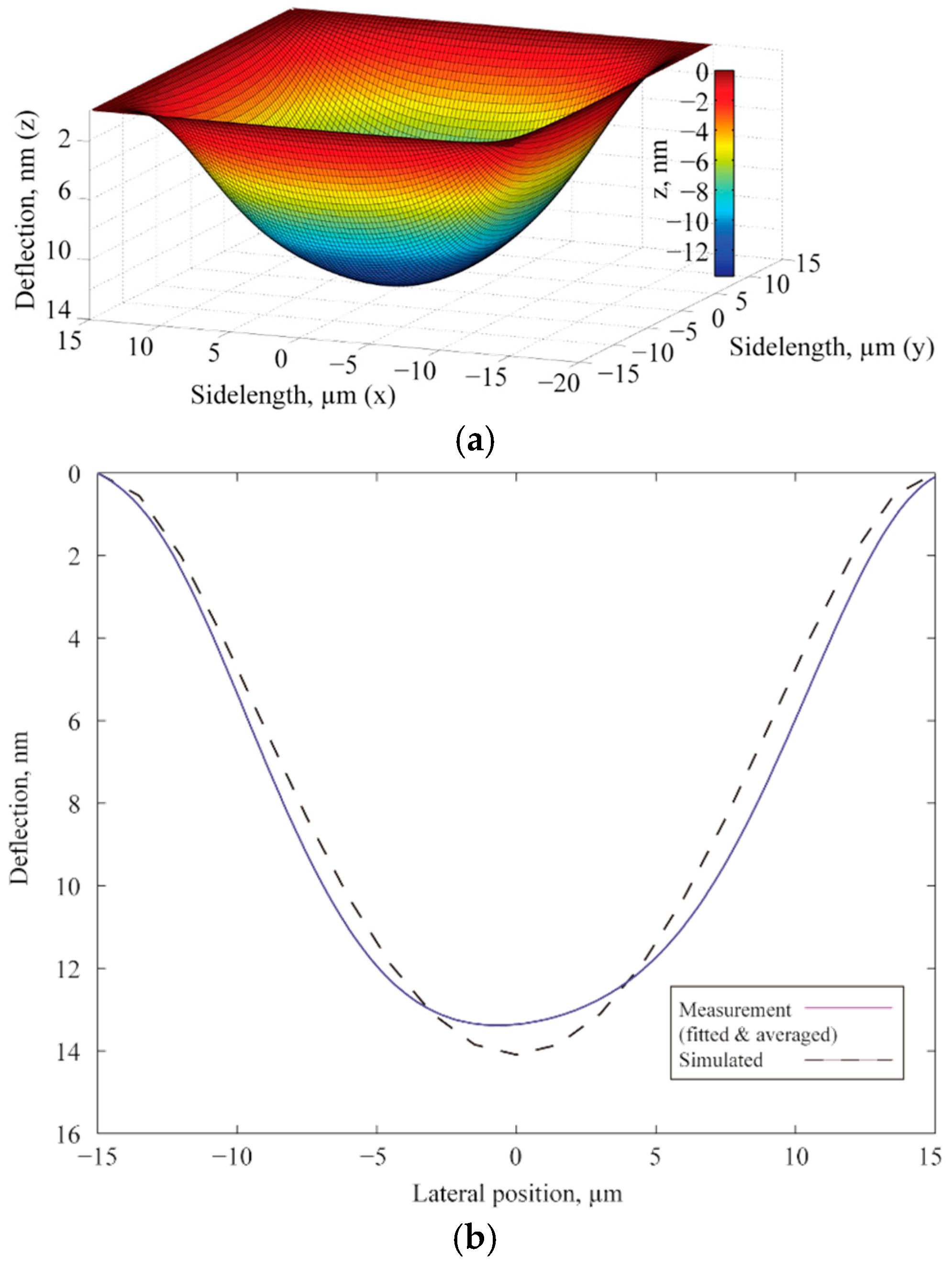
3.3. Deflection and Velocity Profile of CMUT Diaphragm
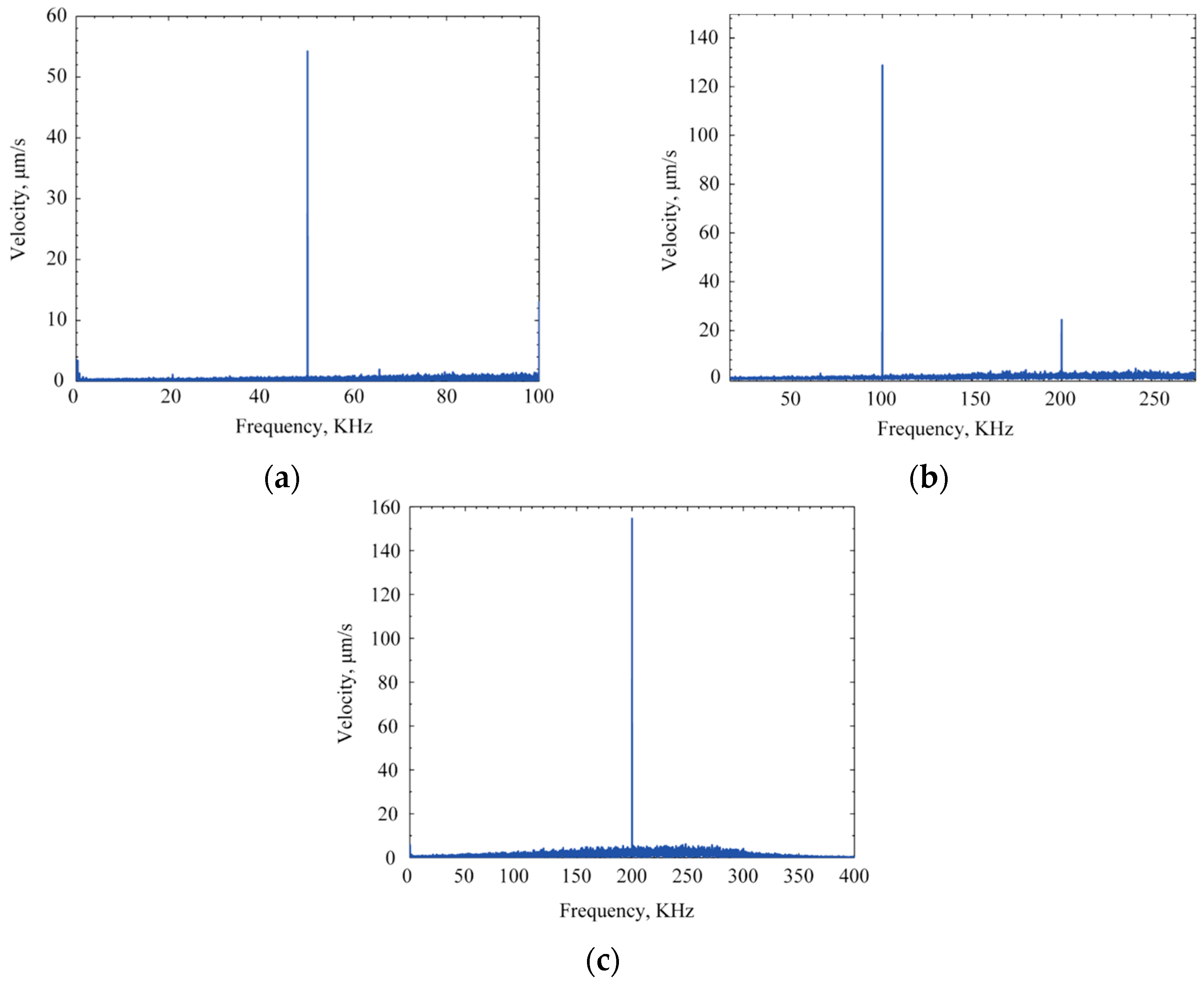
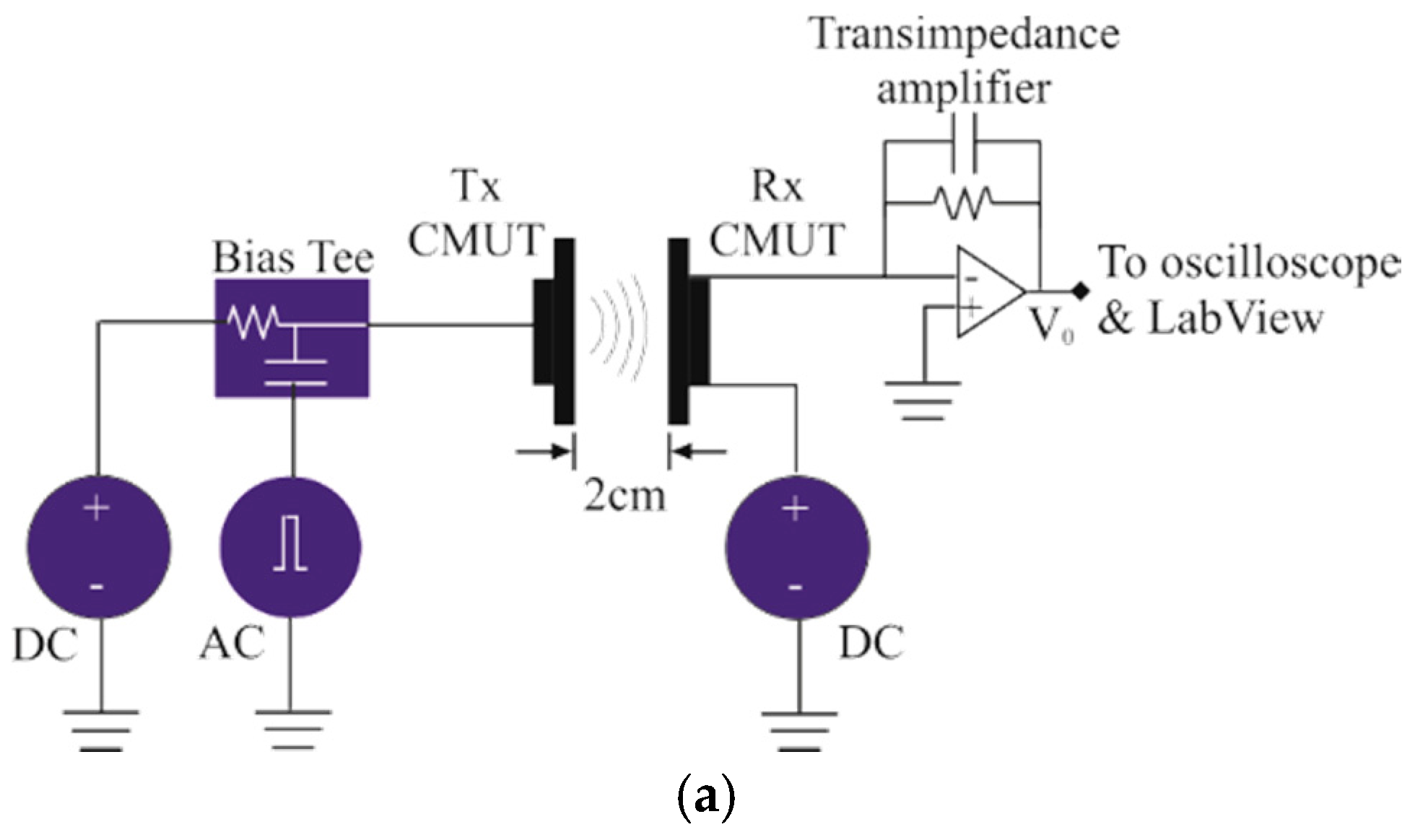
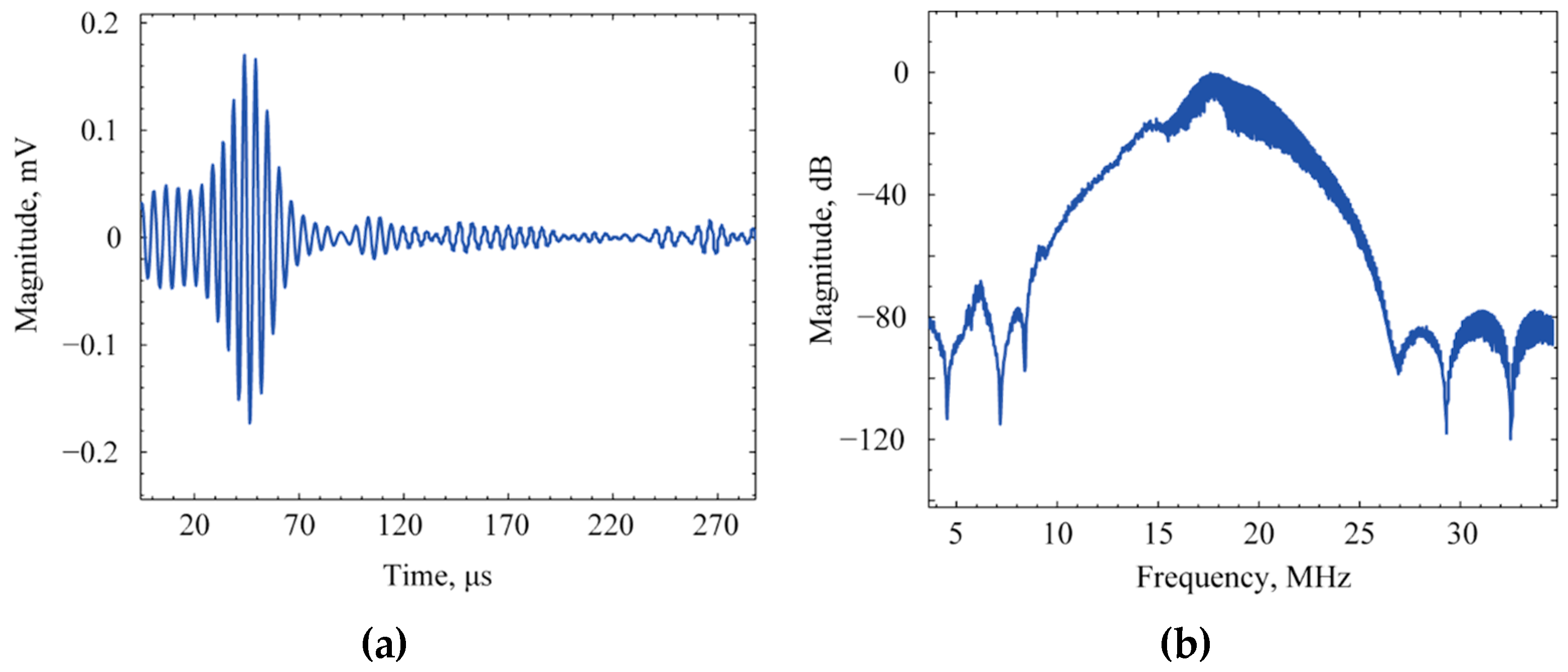
3.4. Pitch-Catch Mode
4. Discussion and Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ergun, A.S.; Yaralioglu, G.G.; Oralkan, O.; Khuri-Yakub, B.T. Chapter 7: Techniques & Applications of Capacitive Micromachined Ultrasonic Transducer. In MEMS/ NEMS Handbook Techniques and Applications; Leondes, C.T., Ed.; Springer Science + Business Media Inc.: Los Angeles, CA, USA, 2006; Volume 2, pp. 222–332. [Google Scholar]
- Song, J.; Xue, C.; He, C.; Zhang, R.; Mu, L.; Cui, J.; Miao, J.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, W. Capacitive Micromachined Ultrasonic Transducers (CMUTs) for Underwater Imaging Applications. Sensors 2015, 15, 23205–23217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oralkan, O.; Hansen, S.T.; Bayram, B.; Yaralioglu, G.G.; Ergun, A.S.; Khuri-Yakub, B.T. High-Frequency CMUT Arrays for High-Resolution Medical Imaging. IEEE Ultrason. Symp. Proc. 2004, 1, 399–402. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, Y.; Ergun, A.S.; Haeggström, E.; Badi, M.H.; Khuri-Yakub, B.T. Fabricating Capacitive Micromachined Ultrasonic Transducers with Wafer Bonding. IEEE/ASME J. Microelectromech. Syst. 2003, 12, 128–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinussen, H.; Aksnes, A.; Leirset, E.; Engan, H. CMUT Characterization by Interferometric and Electric Measurements. IEEE Trans. Ultrason. Ferroelectr. Freq. Control 2009, 56, 2711–2721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, R.; Zhang, W.; He, C.; Zhang, Y.; Song, J.; Xue, C. Underwater Imaging Using a 1 × 16 CMUT Linear Array. Sensors 2016, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.; Wang, X.; He, C.; Xue, C. Design and Performance Analysis of Capacitive Micromachined Ultrasonic Transducer Linear Array. Micromachines 2014, 5, 420–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oralkan, O.; Bayram, B.; Yaralioglu, G.G.; Ergun, A.S.; Kupnik, M.; Yeh, D.T.; Wygant, I.O.; Khuri-Yakub, B.T. Experimental Characterization of Collapse-Mode CMUT Operation. IEEE Trans. Ultrason. Ferroelectr. Freq. Control 2006, 53, 1513–1523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rahman, M.; Chowdhury, S. A New Deflection Shape Function for Square Diaphragm CMUT Design. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Symposium on Circuits and Systems (ISCAS), Paris, France, 30 May 2010; pp. 2019–2022.
- Zure, T.; Hernandez, J.; Chowdhury, S. Dynamic Analysis of an SOI based CMUT. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Industrial Technology (ICIT), Athens, Greece, 19–21 March 2012; pp. 539–544.
- Streetman, B.G.; Banerjee, K.S. Field-Effect Transistors. In Solid State Electronics Devices, 7th ed.; Horton, M.J., Ed.; Pearson Education, Inc.: Upper Saddle River, NJ, USA, 2015; pp. 289–299. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, X.G. Etching of Silicon. In Electrochemistry of Silicon and its Oxide; Kluwer Academic Publishers: New York, NY, USA, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Voorthuyzen, J.A.; Keskin, K.; Bergveld, P. Investigations of the Surface Conductivity of Silicon Dioxide and Methods to Reduce it. Surf. Sci. 1987, 187, 201–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, V. Study of Charges Present in Silicon Nitride Thin Films and Their Effect on Silicon Solar Cell Efficiencies. Ph.D. Thesis, Arizona State University, Tempe, AZ, USA, December 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Reid, J.R. Simulation and Measurement of Dielectric Charging in Electrostatically Actuated Capacitive Microwave Switches. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Modeling and Simulation of Microsystems, San Juan, Puerto Rico, 15 April 2002; pp. 250–253.
- CYCLOTENE Advanced Electronics Resins—Electrical Properties. The Dow Chemical Company. Available online: http://www.dow.com/cyclotene/solution/elecprop.htm (accessed on 18 April 2016).
- Manwar, R.; (University of Windsor, Windsor, ON, Canada); Mills, L.K.; (The DOW Chemical Company, Midland, MI, USA). Personal communication, 2016.
- Bakhtazad, A.; Manwar, R.; Chowdhury, S. Fabrication and Characterization of Sealed Cavities Realized by Adhesive Wafer Bonding with Dry Etched Cyclotene™. Microsyst. Technol. 2015, 21, 2435–2442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- So, Y.-H.; Garrou, P.E.; Im, J.-H.; Ohba, K. Benzocyclobutene-Based Polymers for Microelectronic Applications. Polym. Micromelectrion. Nanoelectrion. 2004, 874, 279–293. [Google Scholar]
- Dragoi, V.; Glinsner, T.; Mittendofer, G.; Wieder, B.; Lindner, P. Adhesive Wafer Bonding for MEMS Application. Proc. SPIE 2003, 5116, 160–167. [Google Scholar]
- Yaralioglu, G.; Ergun, A.; Bayram, B.; Haeggstrom, E.; Khuri Yakub, B.T. Calculation and Measurement of Electromechanical Coupling Coefficient of Capacitive Micromachined Ultrasonic Transducers. IEEE Trans. Ultrason. Ferroelectr. Freq. Control 2003, 50, 449–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hernandez, J. A 5 meter range non-planar CMUT array for Automotive Collision Avoidance. Master’s Thesis, University of Windsor, Windsor, ON, Canada, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Park, K.K.; Lee, H.J.; Kupnik, M.; Oralkan, O.; Khuri-Yakub, B.T. Fabricating Capacitive Micromachined Ultrasonic Transducrs with Direct Wafer Bonding and LOCOS Technology. In Proceedings of the IEEE 21st International Conference on Micro Electro Mechanical Systems, Wuhan, China, 13–17 January 2008; pp. 339–342.
- Cardarelli, F. Insulators and dielectrics. In Materials Handbook: A Concise Desktop Reference, 2nd ed.; Springer: London, UK, 2008; pp. 519–542. [Google Scholar]
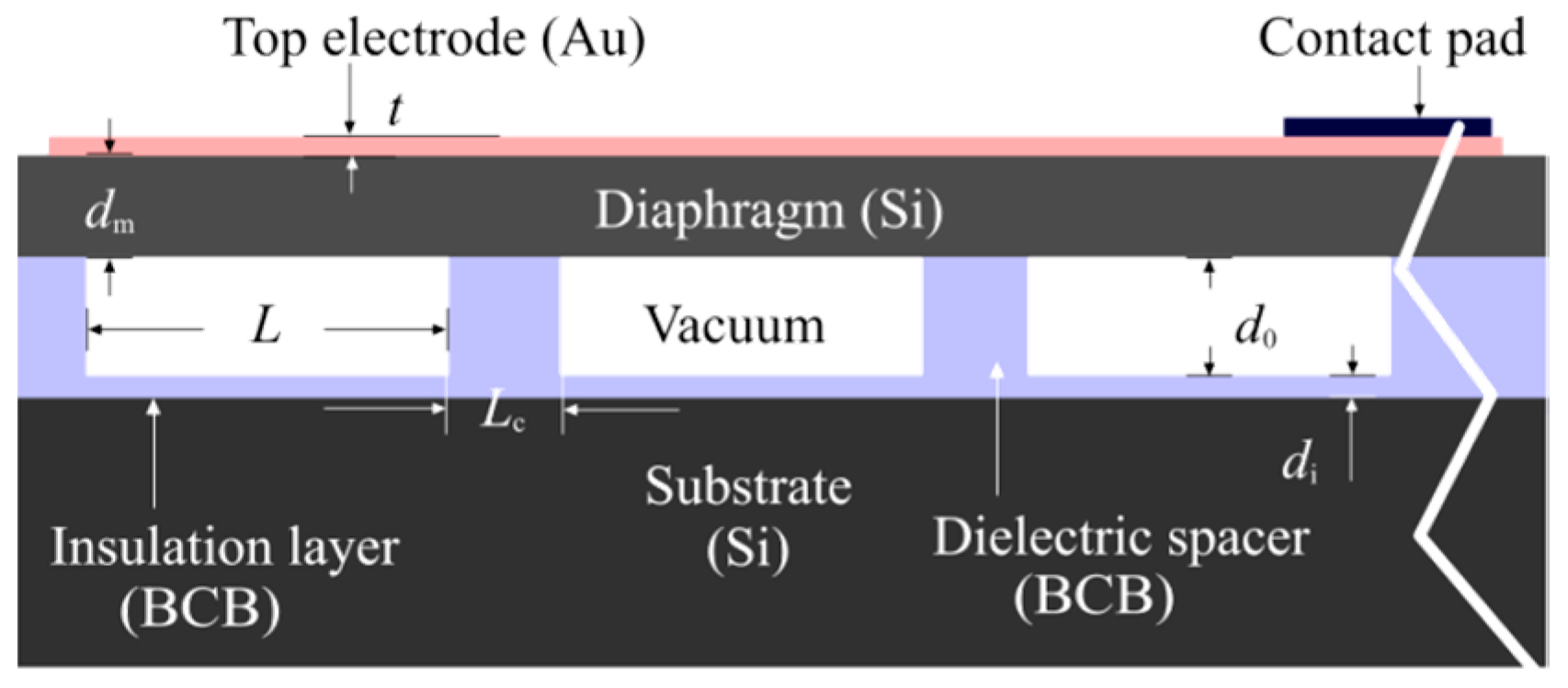
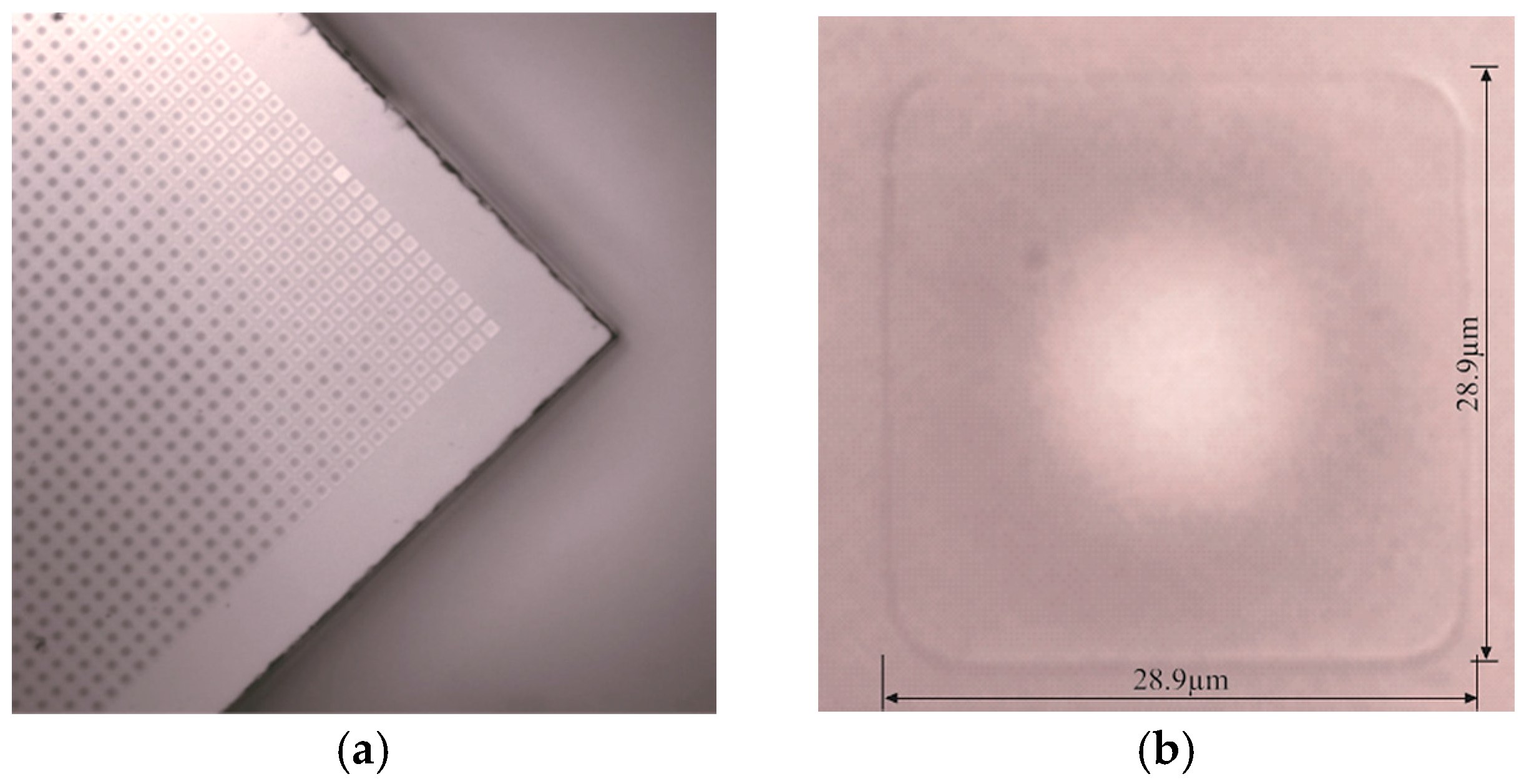



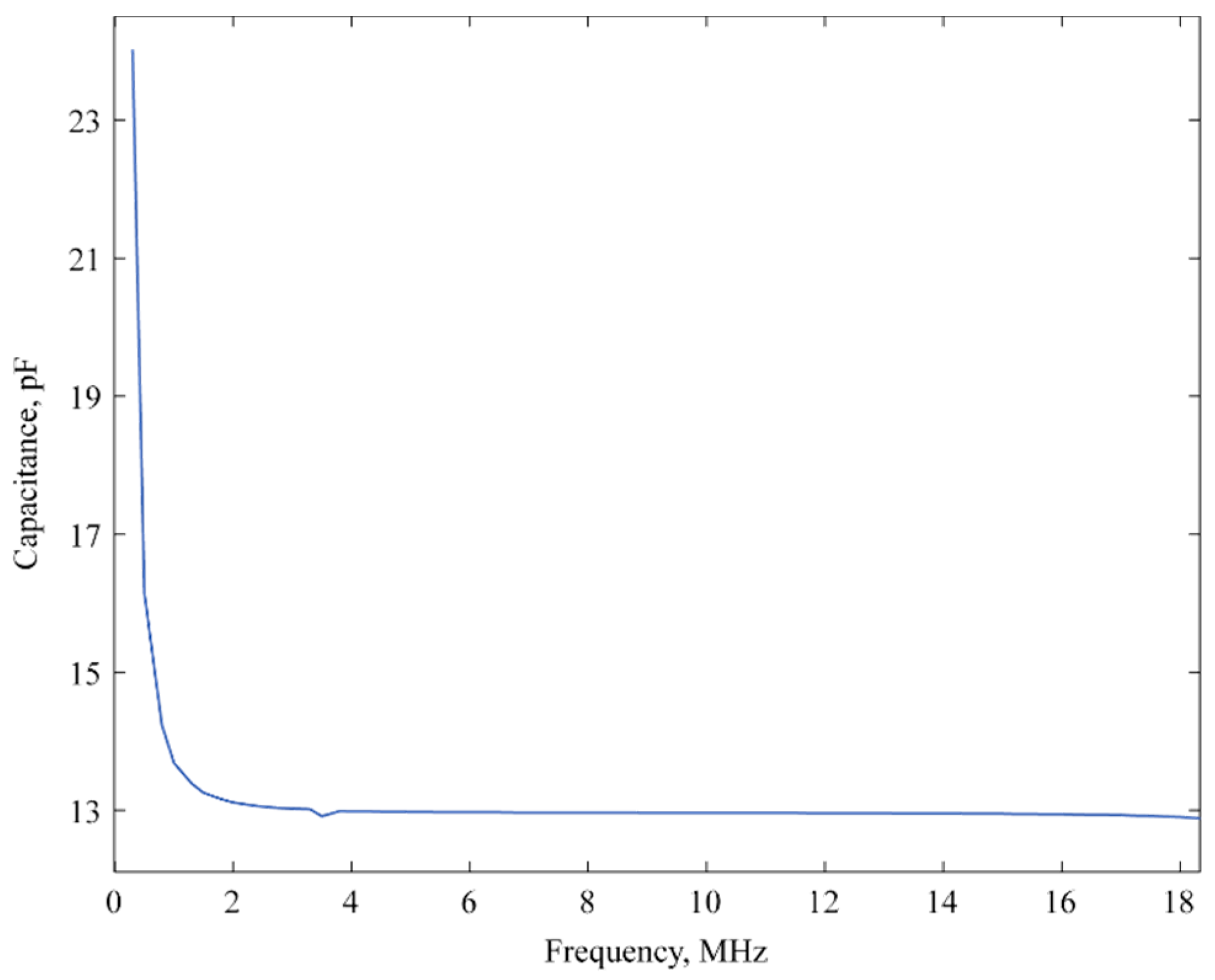
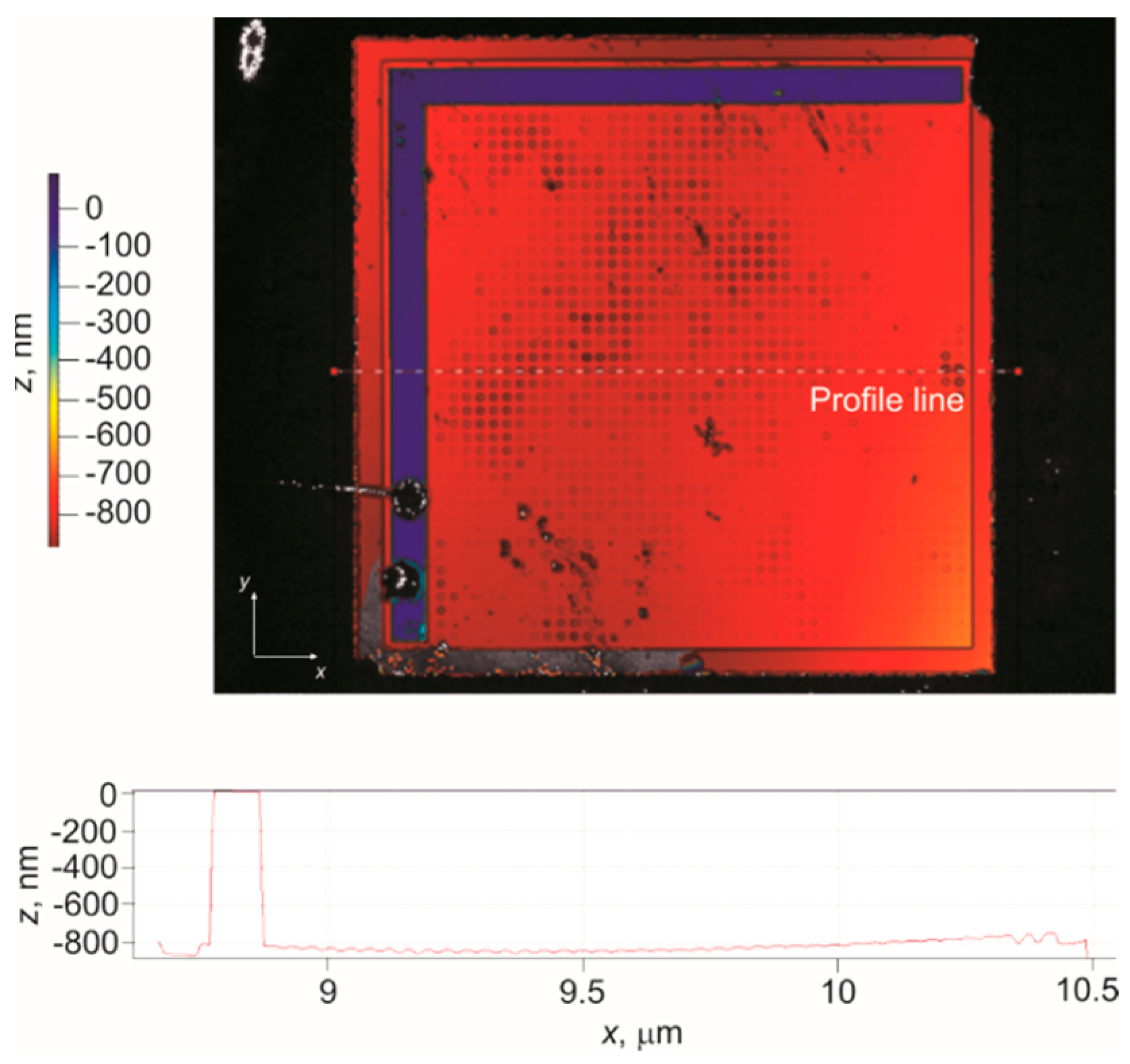


| Parameters | Values |
|---|---|
| No. of cells | 1600 (40 × 40) |
| Cell diameter/sidelength, L, (2a)/μm | 28 |
| Dielectric spacer width, Lc/μm | 10 |
| Diaphragm thickness, dm/nm | 800 |
| Cavity height, d0/ nm | 900 |
| Insulating layer thickness, di/nm | 200 |
| Top electrode thickness, t/nm | 100 |
| Contact strip (pad) width, wc/μm | 150 |
| Contac strip (pad) thickness, tc/μm | 1 |
| Parameters | Cyclotene™ (BCB) | Gold (Au) | Low Resistivity Silicon 100 (Si) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Young’s modulus, E/GPa | 2.9 | 70 | 165 |
| Poisson’s ratio, ν | 0.34 | 0.44 | 0.26 |
| Density, ρ/kgm−3 | 1050 | 19,300 | 2329 |
| Residual stress, σ/MPa | 28 | 106 | 55 |
| Relative permittivity, ε | 2.6 | 6.9 | 11.8 |
© 2016 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Manwar, R.; Chowdhury, S. Experimental Analysis of Bisbenzocyclobutene Bonded Capacitive Micromachined Ultrasonic Transducers. Sensors 2016, 16, 959. https://doi.org/10.3390/s16070959
Manwar R, Chowdhury S. Experimental Analysis of Bisbenzocyclobutene Bonded Capacitive Micromachined Ultrasonic Transducers. Sensors. 2016; 16(7):959. https://doi.org/10.3390/s16070959
Chicago/Turabian StyleManwar, Rayyan, and Sazzadur Chowdhury. 2016. "Experimental Analysis of Bisbenzocyclobutene Bonded Capacitive Micromachined Ultrasonic Transducers" Sensors 16, no. 7: 959. https://doi.org/10.3390/s16070959





